Introduction
Managerial accounting provides accounting information to managers of an organization to enable them perform planning and control functions within the firm. Managerial accountants are responsible for various reports in an organization. The reports address how a business unit has actually performed in comparison to the budgeted or planned activity and they give frequent and timely updates on key financial indicators Atkinson, Kaplan and Matsumura (2007).
Managers are responsible for the production of analytical reports, which help in investigating challenges facing the organization such as decline in profitability. The reports help identify opportunity that might arise and any other business situation. Managerial information includes budgets, which is a quantitative expression of a plan Horngren, Datar and Foster (2006).
Managerial accounting vs. financial accounting
The following essay is about the planning and control functions of a budget using the case study of a charter school. Planning function involves the determination of the program and organizational activities and then evaluates the alternative ways for their achievement.
Static budget
The budget for the charter school is a static budget. This is because the budget is prepared at the beginning of the year and it is usually valid for a period of one year, which means that it is a master budget. It is a static budget because the total numbers of students is known, the employees are known, and therefore, their salaries and benefits for the period can be calculated at the start of the year. All the assumptions can be made and conclusions drawn meaning that the adjustment of the budget cannot be done in the middle of the year. The total numbers of school days are known and all the number of teachers is known which makes it a static budget.
Total revenue per student
Total expenses per student
Necessity of expenses
Most of the expenses incurred by the charter schools are necessary. This is because they are necessary in the day-to-day running objective of the schools. Computer expenses used for purchasing equipment should be reduced since it reduces the revenue for the school. The payroll and salaries should be reduced when the enrollment of students is less so that these expenses are reduced. Building lease for the school is not necessary since it is consuming a lot of money and therefore, the school should find an alternative to leases. This expenses should be [aid on a pro-rata basis, that is, the total expenses paid should commensurate the number of students.
Viability of the school
The charter school is viable. This is because it has positive revenue when it enrolls 120 and 100 students.
Break even analysis
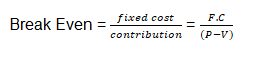
Assumptions of the break – even
- The change in costs and revenue incurred by the school is due to major changes in the number of students.
- The total expenses incurred by the school can be divided into variable and fixed component with respect to the various level of activity. Computer equipment, dues and subscriptions, general supplies, among others represent fixed costs, costs such as printing and copying, food service and field trips represent variable costs.
- It is assumed that the unit cost per student, that is, variable and fixed costs remain constant.
- The other assumption is that changes in the number of students are the only factor that affects other costs.
- The variable costs incurred by the firm will continue to be variable while the fixed costs of the school remain constant regardless of the level of activity (Drury, 2007).
Benefits of preparing this budget
- It enables the managers of the school to think far ahead and plan the school’s target and device a means of achieving the targets.
- It will enable managers to review past performances, thus evaluate any weaknesses by drawing up new action plans to rectify any weaknesses, and help to identify any opportunity for further growth.
- The budget compares the actual performance of the school against the budget performance.
- The budget will make the preparation of the next reporting period easier since the managers already have the figures Edmonds, Olds, and Schneider (2006).
Control function the budget
The budget performs the control function since it compels the management to set out plans for achieving the goals of the school. It requires the entire department and operating units to set targets that they must achieve thus, it gives direction and purpose to the school. The budget as a tool of control defines the responsibility of all people involved. The budget corrects any variance that may arise and it is used to motivate employees. The budget improves the allocation and distribution of scarce resources Harris and West (2007).
Variance analysis
Variance analysis refers to the evaluation of performance by the use of variances, whose timely reporting improves the opportunity for remedial action.
Advantages of variance analysis
- Performance measurement – managers use variance analysis to determine whether a variance is adverse or favorable. It will be used to asses the performance of the managers.
- Responsibility accounting – it enables the manager to be held accountable of what they do. Organizations are divided into divisions and department and each is held responsible for all its activities. Variance analysis is done on a departmental basis. This enables managers and division heads to be held accountable for any deviations in their area of work.
- Management by exception – where there is significant variance from the planned level, managers can take corrective action easily.
Disadvantages of variance analysis
- The market forces make the prices to fall.
- There is a tenderness to use wrong standard material prices
- It skews profitability since it determines revenue by subtracting expenses from revenues.
- Variance analysis may emphasis on the achievement of certain objectives at the expense of others.
Alternative performance measures
Benchmarking is an alternative measure of performance. The budgeted amounts are used as points of reference from where comparisons are made. Benchmarking is the continues process of measuring services and activities against the best industry level.
References
Atkinson, A., Kaplan, R., & Matsumura. (2007). Management Accounting. New York: Pearson/Prentice Hall.
Drury, C. (2007). Management and Cost Accounting. Chicago: Cengage Learning EMEA.
Edmonds, C., Olds, P., & Schneider, N. (2006). Fundamental Manaerial Accounting. New York: McGraw-Hill Irwin.
Harris, E., & West, C. (New York). Variance Analysis. 2007: Chartered Institute of Management Accountants.
Horngren, T., Datar, S., & Foster (2006). Cost accounting: a managerial emphasis. New York: Pearson Prentice Hall.
