Analysis of DS Smith PLC
Reflectively, this analytical paper employs financial data in the analysis of capital structure that will facilitate the making of decisions at Smith PLC. Specifically, various tools and techniques of capital structure analysis are explored in detail. This comparative data analysis paper used the financial statements of Smith Company. The scope of this analytical paper concentrates on investment decisions analysis based on ratio computation. Besides, the analysis comprises percentage change monitoring units that are necessary for interpreting the current, ideal, and eventual situation at Smith Company. The recommendations made in the paper are compared to financial theories of financial analysis.
About the Company
David Solomon Smith founded DS Smith PLC in 1940. It is a British-based public company trading in the London Stock Exchange. DS Smith PLC is a multinational company that deals with the production of packaging papers for consumer goods. Currently, it employs more than 20,000 people (DS Smith PLC Annual Report 2012). As a matter of fact, despite economic swings, the company has embraced properly researched policies to ensure survival. Among the policies include diversification, expansion, affordability, and quality in their chain of packaging papers. These policies are simultaneously applied by the company within its investment portfolio.
Major Investments
In the last five years, the company has experienced constant revenue growth of more than 10% due to its decision to expand the FMCG customer base in Eastern Europe and investment in recycling plants (DS Smith PLC Annual Report 2012). As a result, the operating profit margins increased to 5.5% as an increase in fleet improved efficiency. In addition, the acquisition of Otor improved the corrugated packaging line (DS Smith PLC Investors 2012). Reflectively, these investment decisions improved the working capital productivity by almost “£24 million ROACE up 260bps to 12.7%” (Newage International Publishers 2012). The businesses of DS Smith PLC Company fall in one industry, therefore, having a simple structure. The profitability of the organization has generally increased. The company has a brighter and more sustainable future based on statistical growth of the market, market expansion, production efficiency, and outsourcing, and still very competitive prices which cannot be offered by competitors. The company’s almost half the market price offer on its high-quality products will continue to lure the middle-class companies who make up almost 40% of the market (DS Smith PLC Annual Report 2012).
Financing and capital structure
Several approaches have been adopted by Smith PLC Company towards balancing equity, debt, and financial gearings in its operations. These factors are incorporated by the company in its endeavors to finance expansionary projects while maintaining a fair balance in a collision of equity and debt mix for minimizing the cost of capital for investments. Between the years 2007 and 2012, the company had stable financial capital leverage of between 2008 and 2011; DS Smith PLC Company recorded a 49.21 capital leverage that was channeled towards diversification of the expansionary investment policies. Besides, 42.52 percent income leverage was recorded within these years in form of paid loan interests (DS Smith Investors 2012). A portion of this income
leverage was directed towards balance securing for obligatory debt repayment. Repayment of obligatory debts was essential in the expansion decision.
From the table above, current ratio for DS Smith PLC Company ranges from 1.6 in 1998 to 1.54 in 2008. Similarly, quick ratio range from 1.65 in 1998 to 1.09 in 2008. Further, the liquidity ratios for all the years are greater than one. We can deduce that DS Smith PLC Company has good liquidity ratios and is able to meet its current obligations if compared with ideal rates. Ideal current ratio is 2:1 while quick ratio 1:1. However, this can change depending on the industry ratio. The table graph below capture behavior of these ratios.
According to trade off theory, it is essential to monitor minimum return expected as a precaution for keeping keep the company in a sustainable investment position in expansion and debt financing (Watson & Head 2010). Therefore, the mixture of debt and equity financing strategies form the basis for equity and debt financing in form of cost and benefits balancing (DS Smith PLC Investors 2012). As indicated in the pecking order theory, debt financing, agency costs and equity financing are essential tools for capital structure computation (Moorad, Joannas, Pereira & Pienaar 2003). Usually, when debt equity ratio rises, the resulting effect will be creation of an optimal capital structure that creates a trade off position for tax shield and insolvency (Moorad, Joannas, Pereira & Pienaar 2003). DS Smith PLC Company’s rate of risk 4.61% with market returns averaging at 14.36% (DS Smith PLC Investors 2012). Thus, DS Smith PLC Company’s pretax debt cost averages at 5.31% (DS Smith PLC Investors 2012). Despite series of criticism by theorists such as Myer, the most favorite financial gearing analysis theory remains to be the Trade off Theory since it accommodates capital structure variations and changes in the asset price (Watson & Head 2010).
Equity and Dividend
Equity
Appendix 1 shows the average monthly share prices of the company for the past five years. It also shows the company’s average and standard deviation of monthly total shareholder return (TSR) for the past five years. The chart shows historical share price for the past five years.
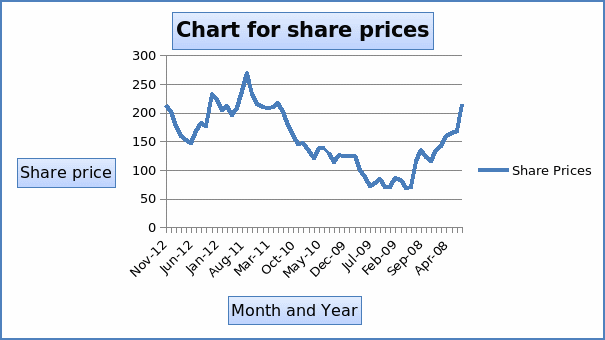
Dividends
Changes have not been made to the dividend policy of the company between 2010 and 2012. The table below shows dividends information of the company for the past three years.
Findings
This company is in stable position for expansionary investment opportunities despite swings in the main currency exchange rate (Moorad, Joannas, Pereira & Pienaar 2003). However, the company may not be in a position to balance its leverages at a constant low value since a good percentage of its income in the form of Euro which is frequently affected by volatility in the currency exchange rates (Watson & Head 2010). In addition, liquidity risks may not be fully balanced by equity and debt financing since its maturities on assets are minimal (Moorad, Joannas, Pereira & Pienaar 2003).
Recommendations
Reflectively, the company should explore bankruptcy costs, tax implications default costs, debt cost, and business risk in derivation of scientific capital structure control policies (Watson & Head 2010). When debt levels are lower than equity levels, investment equity will become more stable than its present state. In addition, political, technological, social and economic aspects should be factored in the balancing of long term debts and equity financing to manage a positive financial gearing necessary for growth (Siddiqui 2005).
Usually, price/earnings ratio is commonly used to evaluate performance of an entity (Ehrhardt & Houston 2009). However, this depends on financial solvency and market conditions that may influence profitability in a positive or negative way (Gibson 2010). Specifically, a high earnings ratio in DS Smith PLC Company suggests that it is expecting stable high earnings in all its major market niches.
Appendix 1
Reference List
DS Smith PLC 2012, Annual Report, Web.
DS Smith PLC 2012, Investors, Web.
Ehrhardt, B & Houston, J 2009, Fundamentals of financial management, South-Western Cengage Learning, USA
Gibson, C 2010, Financial reporting and analysis: using financial accounting information, South-Western Cengage Learning, United States of America.
Moorad, C, Joannas, D, Pereira, R & Pienaar, R 2003, Capital Market Instruments: Analysis and Valuation, Pearson Education Limited, London.
Newage International Publishers 2012, International financial markets, Web.
Siddiqui, A 2005, Managerial economics and financial analysis, New Age International (P) limited, New Delhi.
Watson, D & Head, A 2010, Corporate Finance: Principle and Practice, Financial Times Management, USA

