Executive Summary
Global entrepreneurship is a major sector in the world of business and economics. Entrepreneurship provides new markets, jobs, and new product and services to different societies. Entrepreneur go beyond geographical boundaries to pursue their strategies/plans like investing. The international business sector has however faced some issues that hinder the progress in diverse ways. Issues human resource sector, ethnicity, gender equality, and global leadership adversely affect global entrepreneurship.
Introduction
Global entrepreneurship refers to the act of creating new businesses across national borders. Global entrepreneurship has become common in the current globalized society, with entrepreneurs operating businesses in different states. Global entrepreneurship has opened doors for new products and services to appease different customers in different markets. The diversity is advantageous as it provides a competitive advantage, labor costs, new products, manufacturing abilities, and raw materials for the entrepreneur. Global entrepreneurs utilize their global awareness to determine trans-state prospects that will work in their favor (Light, 2021). Global entrepreneurs can focus on both profit and nonprofit business; others may have either of the two. The research paper analyzes the challenges and issues in the global business market that affect the running of operations (Budhwar et al., 2017). The main problems experienced by entrepreneurs in running global businesses include human resource management, global leadership, gender inequality, and ethnicity issues.
Literature Review
Human resource management
Human resources across ethnic and geographic borders hinder progress for managers and business owners. Evolving technology has pushed organizations to higher levels of human resource management (Brewster, Mayrhofer and Farndale, 2018). There is a difference in the way interactions, perceptions, and work run in the new economy. The new levels push business owners and managers to levels with better talents. Managing a global workforce is not that simple; organizations need to select the best resources and prices for the market (Morozova, Popkova and Litvinova, 2019). The main issues faced by the human resource sector include:
- lack of effective communication, an organization operating around the globe will need to use a virtual workforce to maintain communication with the managers and clients.
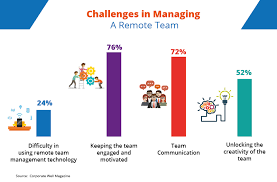
Secondly, managing the talent diversity available in a global environment is challenging for managers. However, the managers should implement practices that ensure the working team is efficient, creative, and productive. the third issue in human resources is the local laws that change from state to state. The laws incur huge costs and can harm the business if not followed. International entrepreneurs have to abide by the different laws in the different states for brand image retention. Lastly, international entrepreneurs face conflicts of interest (Verbeke, Coeurderoy and Matt, 2018). The need to integrate the adverse market available in each operating state is, to some extent, tedious.
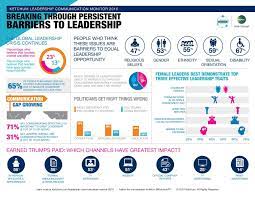
Global leadership
Global Leadership is complex; global leaders face a highly diverse complexity, unlike regional and domestic leaders. Firstly, a global team entails individuals of different cultural intelligence, and the leader of such a team has to overcome many challenges (Felix, Aparicio and Urbano, 2018). The procedures and protocols understood by one cultural group are different from those of other cultures, creating complexity for the leadership environment—the first issue created by global leadership complexity in handling multicultural conflicts. Conflicting values and priorities are hard to solve and even notice; the matters should be handled delicately. Secondly, cultural ways may influence the thoughts of the global leader. Therefore, global leaders should avoid adopting their cultural ways; instead, they should go beyond their thinking (Figueroa et al., 2019).
Thirdly, it is difficult to find ground when leading in a global situation. Global leaders should create and implement shared goals and work, respectively. The diversity in the team should be honored in the shared interests to enhance appreciation of other cultural perspectives. Fourthly is the duality created by the local and global management relationship. There is tension between local, regional, and global offices; leaders have to find a means to communicate to team members in different locations to enhance effectiveness (Pruthi, Mitra and Mitra, 2020). The final challenge is the barriers created in the leadership sector. These barriers can be duet language differences, legal differences, historical diversity, the ruling government, economic factors, and other external factors. A global leader should act and think in new ways to enhance effectiveness.
Gender Equality Issues
Gender equality is also a great issue in the global economy. Females are more affected by gender issues in business sectors than men. Firstly, gender equality is unfair to women through corporate governance (Boone et al., 2019). Most organizations lack the criteria to promote, develop, and encourage female workers. A female leadership channel should be a crucial tool for international business. Secondly, Leadership is also a gender equality issue in global business. A female professional is open to more scrutiny and challenges than a male professional.
Most organizations do not consider females for the top management roles; others lack a friendly corporate environment, while in others, the opportunities are not referred to as female applicants ((Dilli and Westerhuis, 2018). Leadership is not a gender-based profession, and international organizations should consider all genders. Thirdly, there is a lack of formal networking opportunities for women; more opportunities are in the informal area, and Venture Capital (VC) funding for women entrepreneurs is minimal (Nasiri and Hamelin, 2018). Lastly, there is a lack of innovation in the Intellectual property (IP) section. Women are underrepresented and face rejections when they request protection. Education on female protection, innovation, and commercialization is subtle to female entrepreneurs.
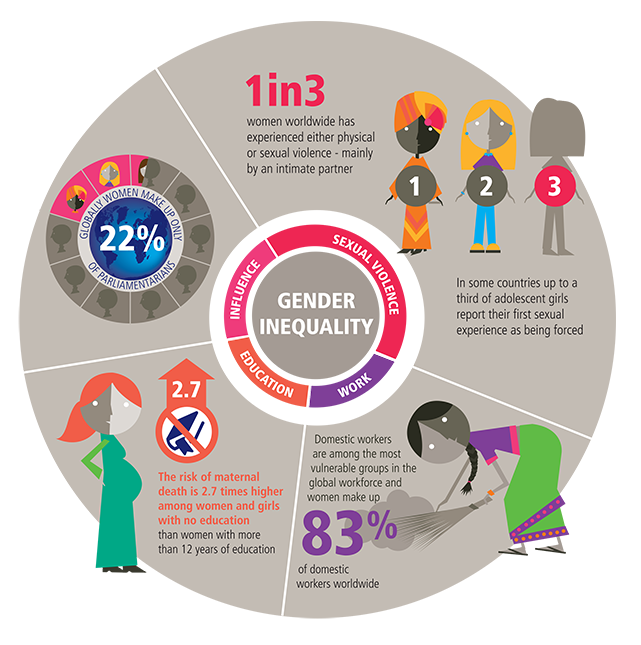
Women do not file for legal IP protection and/or receive greater scrutiny and more rejections when they do, and women drop out of the innovation cycle before patent application. Educate female innovators about IP protection systems (Markina et al., 2019). Facilitate networks for female innovators to share knowledge about innovation protection and commercialization. Encourage women to remain active in the entire innovation cycle, from conception to protection and commercialization.
Ethnicity
Ethnicity is also a great issue in the global market. Entrepreneurs should not ignore cultural diversity. Otherwise, it may lead to reputational damage, legal challenges, expatriate failure, low returns on investment, productivity loss, weak market share, premature termination, or missed opportunities (Aggarwal, Jindal and Seth, 2019). Cultural risks evident in global business include failure to adapt to the local market. Glocalization should be adopted to fit the market preferences, habits, and customs.
A global entrepreneur should restructure the price, product or service, and marketing of the business models in the different areas. Cultural diverse individuals face discrimination and social stigma in the workplace. The ethnicity problem mostly affects the minor ethnic groups; business perception varies from one ethnicity to another. Some values need to be adopted, even informal setups, and global entrepreneurs should consider the ethnic culture for success (Claire, Lefebvre and Ronteau, 2020.). However, ethnic difference creates diversity, a great wide market, and competitive advantage. Stereotypes, prejudice, behavior, and beliefs vary from one ethnic group to another.
Conclusion
The emergence of globalization has greatly affected the innovators and the people. New products have been introduced in the markets for the people, while entrepreneurs have taken advantage of the expanding market to generate more income. However, global entrepreneurship has been experiencing some difficulties in operation due to diversity and equality issues. Gender inequality and ethnic differences have challenged global managers and entrepreneurs in their operations. Other problems experienced in global entrepreneurship include leadership issues and human resource management issues. The global entrepreneurship community should mitigate these issues for a better working environment and greater success.
Reference List
Aggarwal, R., Jindal, V. and Seth, R. (2019). ‘Board diversity and firm performance: the role of business group affiliation’, International Business Review, 28(6), p.101600.
Ayob, A.H. (2018). ‘Diversity, trust and social entrepreneurship’, Journal of Social Entrepreneurship, 9(1), pp. 1-12.
Boone, C., Lokshin, B., Guenter, H. and Belderbos, R. (2019). ‘Top management team nationality diversity, corporate entrepreneurship, and innovation in multinational firms’, Strategic management journal, 40(2), pp. 277-302.
Brewster, C., Mayrhofer, W. and Farndale, E. eds. (2018). Handbook of research on comparative human resource management. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Budhwar, P., Tung, R.L., Varma, A. and Do, H. (2017). ‘Developments in human resource management in MNCs from BRICS nations: A review and future research agenda’, Journal of International Management, 23(2), pp. 111-123.
Claire, C., Lefebvre, V. and Ronteau, S. (2020). ‘Entrepreneurship as practice: Systematic literature review of a nascent field’, Entrepreneurship & Regional Development, 32(3-4), pp. 281-312.
Dilli, S. and Westerhuis, G. (2018). ‘How institutions and gender differences in education shape entrepreneurial activity: A cross-national perspective’, Small Business Economics, 51(2), pp.371-392.
Felix, C., Aparicio, S. and Urbano, D. (2018). ‘Leadership as a driver of entrepreneurship: An international exploratory study’, Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, 26(3), pp. 397-420.
Figueroa, C.A., Harrison, R., Chauhan, A. and Meyer, L.(2019). ‘Priorities and challenges for health leadership and workforce management globally: A rapid review’, BMC health services research, 19(1), pp. 1-11.
Light, IH. (2021). Global entrepreneurship and transnationalism. In World Encyclopedia of Entrepreneurship. Edward Elgar Publishing.
Markina, I., Safonov, Y., Zhylinska, O., Gaidai, T. and Kahanov, Y. (2019). ‘Entrepreneurship education management in the context of global changes in economy’, Journal of Entrepreneurship Education, 22(6), pp. 1-10.
Morozova, I.A., Popkova, E.G. and Litvinova, T.N. (2019). ‘Sustainable development of global entrepreneurship: infrastructure and perspectives’, International Entrepreneurship and Management Journal, 15(2), pp. 589-597.
Nasiri, N. and Hamelin, N. (2018). ‘Entrepreneurship driven by opportunity and necessity: effects of educations, gender and occupation in MENA’, Asian Journal of Business Research, 8(2), pp. 57-71.
Pruthi, S., Mitra, J. and Mitra, J., (2020). ‘Special Issue on ‘Migrant and Transnational Entrepreneurs: International Entrepreneurship and Emerging Economies’, Journal of Entrepreneurship and Innovation in Emerging Economies, 6(1), pp. 7-11.
Verbeke, A., Coeurderoy, R. and Matt, T. (2018). ‘The future of international business research on corporate globalization that never was…’, Journal of International Business Studies, 49(9), pp. 1101-1112.

