A sole proprietorship is the easiest and most common business structure in the United States. Because sole proprietorships are unincorporated and run by individuals or their families, there is no distinction between the entity and its founder (Dungan, 2017). Its formation does not require significant formal action other than obtaining necessary licenses and permits, which may vary from state to state and from one industry to another.
Accrual Accounting and Cash Basis
Accrual accounting means that the business recognizes and records revenues and expenses as they occur while cash basis accounting implies not documenting these details until there is an actual exchange of cash between the institution and the customer (van Helden & Reichard, 2018). Based on the type of business and the client’s system of accounting, the impact of revenue and expenses recognition is declaring profitability or losses and filing returns.
When Revenue Would Be Recognized on the Sale
The accrual accounting system recognizes revenues when orders are received while the cash basis does so when payments are made. Thus, the accrual system differs from the cash basis in that it focuses on anticipated (rather than actual) revenues and expenses.
Economic Impact
A sole proprietorship will have a positive economic impact on the client’s financial status if it is successful. Because the sole proprietor and the business they form are the same things, the business is not taxed separately. The businesses’ income or losses is treated as the owner’s and would be reported with a Schedule C and the standard Form 1040 filing.
Tax Consequences
Capital gains or losses are either long- or short-term assets depending on how long they have been held by the owner. Ordinary income rate taxes of up to 37 percent apply to short-term capital gains; taxes for long-term gains are lower (up to only 20 percent) (Reporting capital gains, n.d.). The tax rate will depend on the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act (TCJA) of 2017. Individuals report capital gains on Form 1040, Schedule D, Capital Gains, and Losses, and then transfer them to line 7 of Form 1040, U.S. Individual Income Tax Return. The amount is equivalent to the selling price minus expenses, broker fees, appraisal, and closing costs.
Limited Liability Protection
The client should consider a business with limited liability protection if they intend to perform extensive business operations with significant risks. Sole proprietorships have unlimited personal liability because no legal separation exists between the owner and the business. In this regard, in case the business has any debts (or liabilities due to employee actions), the owner will be held accountable and responsible.
Tax Effect
Taxes will take away some money from the business thereby reducing the operating capital or the profits. Filing returns on time reduces the accrual of penalties and interests, which further reduces the sole proprietor’s cash. All payments due to the government must be submitted with the tax returns by 15th April every year. The sole proprietorship is not taxed separately as the owner reports all earnings and losses on their “personal” income tax (pass-through taxation) because business profits pass through the owner paying personal taxes.
Economic impact on Client’s “Personal” Returns
A personal proprietorship is ideal because it is easy and inexpensive to form and run. Legal costs are limited to obtaining permits and licenses only. On the contrary, the other organizations require more complex processes legal fees, even though they may extend protection to the customer by limited persona liabilities. A sole proprietorship also has easy tax preparations. Since the business is not taxed separately, the operator files personal returns which are also the business returns.
Ownership Interest
The daughter has an interest in the business as the founder’s kin. Since this is a sole proprietorship, no ownership complexity exists. The daughter helps with the daily running of the business as the owner’s next of kin. Her share of the company’s profits comes in the form of cash transfers (rather than officially stipulated salaries).
Cash Basis and Accrual Accounting Summary
For a sole proprietorship, the cash basis accounting is more ideal. The business owner records and recognizes revenues and expenses when they occur. The owner can do this without employing accountants or complicated formulas. Since the business volume is low, the cash basis is appropriate. On the contrary, the accrual method is better utilized by larger corporations with extended coverage scope. The most important consideration in accrual accounting is recording revenues and expenses based on forecasts. Both accounting methods are appropriate given the Treasury regulations and Internal Revenue Code.
After-Tax Effects on the Client’s Cash Flow
The cash flow of the client will be impacted significantly after-tax owing to the minimal nature of the revenue receipts. As the business grows, the amount of taxes that the client must remit to the government will also increase. The small business costs are high because the client has to pay the federal and the local and state governments for business permits and licenses. Cutting on these costs is difficult because they represent mandatory payments that small businesses must make to continue operating in the United States. It is one of the disadvantages of establishing and running a sole proprietorship. Luckily, the owner has complete control over the business and can determine its operations and business focus. Creating and implementing strategies is easier among sole proprietorships because there are no rigid rules or bureaucracies that must be followed.
Salary or Cash Distribution
The client and his child should take a cash distribution rather than a salary. The cash distribution will depend on the performance of the business for that month. Giving the daughter and the business owner a fixed salary would be problematic in case the business makes losses (Hamel, n.d.). The only challenge with cash distribution is that it can consume all the business resources or profits per month. One way to avoid this problem is to specify the proportion of the profits that the client and the daughter can share each month. For example, they can take 50 percent of the profits and share it based on a predetermined ratio and use the other 50 percent as business savings or for reinvesting into the business.
Appendix
Schedules and Tax Forms
Schedule D shows the capital gains
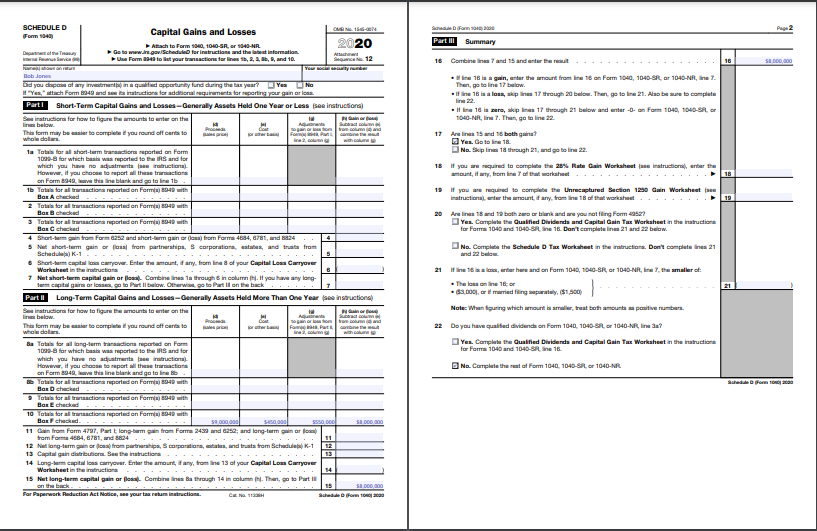
Appendix A: Schedule D
Form 1040 Pages
The applicable line for Form 1040 is line 7, which talks about capital gains. The completed form is based on the assumption that the customer made $1000 worth of capital gains in 2020.
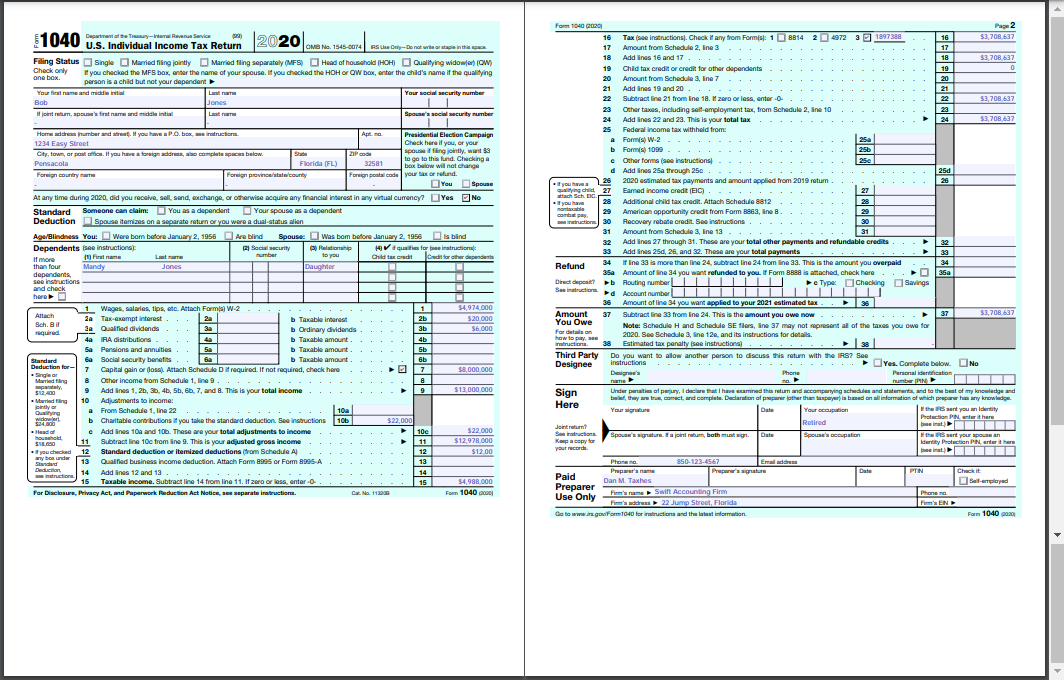
Appendix B: Form 1040
Professional Advice
Best pieces of advice emanate from an understanding of the subject area. One can do this by researching extensively and familiarizing themselves with content. Therefore, the client has gotten the best advice regarding business creation. The sole proprietorship is easy to run and maintain compared to S and C type corporations. Business individuals should only do the minimum when it comes to forming a company to minimize costs and associated complexities.
References
Dungan, A. (2017). Sole Proprietorship Returns, Tax Year 2015. Statistics of Income. SOI Bulletin, 37(2), 2-28.
Hamel, G. (n.d.). Do sole proprietors take a salary? Chron. Web.
Reporting capital gains (n.d.). IRS. Web.
van Helden, J., & Reichard, C. (2018). Cash or accruals for budgeting? Why some governments in Europe changed their budgeting mode and others not. OECD Journal on Budgeting, 18(1), 91-113.
