Introduction
Today we live in a highly globalized world so it is not uncommon for employees of different nationalities to work together in the same company or interact with people of different nationalities working for other companies. Developing an understanding of cultural differences and successfully using them to find better solutions for dilemmas inherent in international business relations, but also using these cultural differences to develop innovative concepts and businesses that reach a broad audience is today of capital importance for any company and especially for any company with international development claims. We will therefore in this document present to you the business idea that we have developed after analysis of our different cultures.
Basic Information and Cultural Idiosyncrasy
France
France is a transcontinental sovereign state whose metropolitan territory is located in Western Europe. France also has important maritime facades on the Atlantic and the Mediterranean. Its ultramarine territory spans the Indian, Atlantic and Pacific Oceans and South America.
France is a unitary constitutional republic with a semi-presidential regime. The motto of the Republic is since 1875 «Liberty, Equality, Fraternity». Its founding principle is democracy: the “government of the people, by the people and for the people”. Its capital is Paris and its official language is French since 1539.
The only country in the world to exercise its sovereignty over territories spread over four oceans and two continents, it plays an important geopolitical role at the global level, thanks to an extensive network of embassies and consulates, the second largest in the world after that of the United States, and has military bases on all continents and the world’s third-largest military nuclear power.
the French culture was profoundly marked by the Age of Enlightenment and the ideas conveyed by the philosophers of that era that led to the French revolution, a landmark event in its history.
Spain
Spain is the second largest EU country, sharing the Iberian Peninsula with Portugal. Spanish is the second most spoken language in the world, even though inside Spain, there are 4 different regions that have their own local idiom. Because it is bathed by the Mediterranean sea as well as by the Atlantic ocean, it has always been a commercial gem, focusing on many cultures and civilizations throughout history.
Nowadays, as a constitutional monarchy, we are a country based on tourism, seen by many people, a lot of European citizens looking for destiny with great weather. In 2018, Spain was the second most visited country in the world, with an amazing figure of 82.8 million visitors. Since we host 47 UNESCO World Heritage Sites, there is a great attraction for tourists to come and enjoy our weather and third sector focused economy.
Even before being known as such, Spain has been invaded and influenced by an astonishing number of different civilizations, being the most distinctive one, the Islamic dominium of almost all of Spain, from years 711-to 1492. Our deep routes on sharing our culture perdure until the present, being foreigners a 13% of the total Spanish population, 5.235.000. Headed by Romania and Morocco, and followed by Great Britain and Italy.
Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia is the largest country in the Middle East and is located in the southwest of Asia, its location is considered an ancient commercial center.
Saudi society has experienced tremendous development over the past several decades. The discovery of oil in Saudi Arabia 80 years ago affected the demographics of the society and raised the economic and welfare level of people.
It has become an attractive environment for foreigners who are looking for jobs, as they now became 35% of the total population in the country. Most people have left the countryside for big cities for doing more skilled jobs and low professions have become restricted to non-citizens.
Libya
Living or doing business in Libya requires understanding and adhering to its culture (key concepts and values). In Libya, most deals are based on good relationships. Though hard and time-consuming to establish and maintain, relationship networks form the basis of the business culture here. Interpersonal relations are essential in Libya as this can help in doing things faster and bending the rules in one’s favor. It is customary to reserve the initial part of the business meeting for general conversations, even in businesses. This facilitates the establishment of a great relationship with business associates. The concept of ‘Face’; personal values, social status and respect are key in business dealings. Consequently, Libyans take time to know you and the company you represent before they develop trust for business dealings.
Islam is the most practiced religion in Libya; hence Islamic rule pervades Libya’s customs and culture, thus providing a behavior framework for people in social and business contexts. Most Libyans are religiously conservative. Their cultures are therefore rooted in the Islamic religion. Islamic rules dominate Libya, thus making it an integral part of the Libyan people. One is therefore expected to pay attention and adhere to these cultures.
Libya is a strongly hierarchical society; social status, power distance and titles are important. Therefore, business success is dependent on one’s respect for social positions, profession and family name. Delegation is non-existence in most companies in Libya. One person has the authority to supervise all other people and is answerable for decisions within the organization.
Today Libya, despite Libya facing economic and political challenges, offers significant business opportunities (Omar, 2020). Doing business in Libya requires an in-depth understanding of the culture behind Libya’s social and business customs.
China
China, located in East Asia, is a country with a history of over five thousand years. China has a vast territory and a large population base, which makes its internal culture diverse and inclusive. China is made up of 56 ethnic groups, among which the Han is the dominant one. Buddhism flourished from the Tang Dynasty in China and continues into modern times, while Islam, the second largest religion that is widely distributed in most of China’s provinces and regions. As the most mainstream culture, Confucianism has greatly influenced the world outlook and values of Chinese people, such as forbearance, introversion, and observance of order.
The characteristics of Chinese traditional culture mainly refer to the material production is based on the individual agricultural economy, the social organization structure is based on the patriarchal system as the bond to maintain the social order, and the cultural level is based on the Confucian ethics and morality as the core and mainstream value orientation.
Comparison of the Five Countries Cultural Trait
Hofstede Framework
Hofstede’s Cultural Dimension Theory is a framework proposed by Geert Hofstede who divides cultural values into six fundamental dimensions, power distance, individualism versus collectivism, uncertainty avoidance, masculinity, long-term or short-term orientation, and indulgence to tell similarities and differences among countries. France, Spain, Saudi Arabia, Libya and China will be analyzed and compared under six dimensions to reveal cultural characteristics.
Power Distance
In summary, these five countries have relatively strong power distance, which fully shows that the division of power and social hierarchy in these countries are acceptable to a certain extent.
Individualism versus Collectivism
In summary, France scores the highest among the 5 countries as well as the obvious characteristics of individualism can be seen in French people, who tend to be more independent and obey their own will, while Spain is right in the middle between individualism and collectivism. Lower-scoring countries are Libya, Saudi Arabia and China. These countries tend to be more collectivistic and people can sacrifice personal interests in order to conform to family and organizational benefits.
Uncertainty Avoidance
In summary, France, Spain, Saudi Arabia and Libya have strong uncertainty avoidance, which indicates that the countries are more inclined to regulate society and people’s behavior by making rules. Compared with the other 4 countries, China’s social security is not entirely dependent on legal norms but on self-management and self-supervision, which can be regarded as the reason why China has the lowest score in uncertainty avoidance.
Masculinity vs. Femininity
In summary, China and Saudi Arabia tend to be Masculine societies. This means that competition awareness is high and the criteria of success are the achievements they make. Libya has an intermediate score, society is both masculine and feminine. France and Spain are more female societies. There are strong female qualities in their social culture, such as caring and sympathy, etc. In addition, women also have a certain social status in the social hierarchy.
Long-term orientation vs. Short-term orientation
In summary, China and France are in the long-term orientation. People tend to combine tradition with modernity and look at things from the perspective of sustainable development.
Spain is anyways a normative society, short-time oriented, and tend to respect tradition over change. While in comparison, Libya and Saudi Arabia are more close to short-term orientations which means that people are more willing to preserve their traditions and worry less about the future.
Indulgence versus Restraint
According to the analysis, most countries belong to Restraint, while Saudi Arabia is in the middle with no preference. It shows that in the social attributes of most countries, society has a relatively large constraint on people. They are encouraged to create value rather than enjoy life without restraints.
Critical Approach Toward Hofstede Framework
Culture has always been a process of dynamic development while Hofstede’s cultural dimension has certain limitations in the study of cultural dynamism. Although Hofstede’s model of cultural dimensions at the national level clarifies cultural differences among the countries, for a district’s culture, stereotypes should still be avoided and individual differences should be paid attention to in the practical application because there are always antagonistic values in the mainstream culture of a country to some extent.
Edward Hall framework
- Context: High/Low
- Space (Territoriality, Personal space, Proxemics, Multisensory)
- Time: Monochronic / Polychronic
- Critical Approach Toward Hall Framework
- Comparison among Five Countries
- Points of Synergy between the Five Countries
Diversity of cultural background can bring different views and create innovations. In addition, cultural characteristics (Islamic, Christian and Confucian), geographical advantages (Chinese and European markets) and resource advantages (Libyan and Arab oil resources, Chinese population resources) can also create many opportunities for business cooperation. - Points of Conflicts between the Five Countries
- Potential for religious conflict. Christianity in Europe, Islam in North Africa and the Middle East, and Buddhism in China differ greatly in terms of cultural etiquette and cognition, which may lead to stereotyped understandings of different cultures.
- Differences in living habits and working styles may lead to cultural clashes. Europeans have a clear definition of the dividing line between life and work, as well as interpersonal relationships, and pay more attention to the legal protection of individual rights. However, Chinese people are good at using and maintaining interpersonal relationships, and the line between life and work is very vague. When these different cultures interact together, it can lead to conflict.
- Points of Synergy between the Five Countries
Business Collaboration Plan
as an area for collaboration we choose E-Commerce our team will have a range of viewpoints together with the wide-ranging personal and professional experience, and we are going to be able to inspire one another to work out the workplace and therefore the world differently. Our team will have the local market knowledge and insight on all five countries and a stronger understanding of local laws, regulations, and customs, as the moreover the competitive landscape. Moreover, local connections, linguistic communication skills, and cultural understanding will boost business development exponentially. because of all the above-mentioned aspects, we will offer a large range of products or have the likelihood to quickly adapt to new product categories thanks to our diversity.
Business Introduction
Craft bazaar
- online portal that has come up with the idea of promoting and selling international traditional & Handmade Industries online.
- we obsess over customers and their desire for a trusted destination for handcrafted goods, which is what prompted us to start Handmade. Artisans from over the world are following their passion and selling their craft (craft bazaar). Together, we are growing craft communities and successful business.
Geographic location
For begging our team will cover the following market
- EU
- CHINA
- MENA MARKT & NORTH AFRICA
Operating plan
Who can sell on Handmade?
The Handmade store is available for artisans to sell their handcrafted products to craft bazaar customers all over the world.
Visitors to the site can browse our handmade collections, buy products online and have the ability to contact Creators directly with questions or requests.
The registration process ?
First, you will need to set up a Selling Account with Craft bazaar. You can get started by visiting How to start selling on craft bazaar. Once you have completed registration, you can apply to sell in bazaar Handmade, where we will request details about your products and business to ensure the integrity of the Handmade store. Once you are approved, resources are available to create your first Handmade listing, set up your Maker profile, and manage your business.
What categories are available on Handmade?
traditional Products and Suppliers From local market
Handmade is open to Artisans who make Accessories, Artwork, Baby, Beauty & Personal Care, Clothing, Shoes & Handbags, Home, Outdoor & Home Care, Jewelry & Watches, Kitchen & Dining, Pet Supplies, Sporting Goods, Stationery & Party
Business model. Subscription model
Joining Handmade, creating your shop, and listing products is free. When you make a sale, Handmade will deduct a 10% referral fee.
During registration, you will register with a Professional selling plan that provides you with Handmade-specific tools and support to grow your business. While the Professional selling plan costs $35 per month for craft bazaar Seller, this monthly fee is for Handmade artisans.
Profit-making method
- Subscription monthly fee
- commission
- Ads & promoting fees
What categories are available on Handmade?
Traditional Products and Suppliers From local market
Handmade is open to Artisans who make Accessories, Artwork, Baby, Beauty & Personal Care, Clothing, Shoes & Handbags, Home, Outdoor & Home Care, Jewelry & Watches, Kitchen & Dining, Pet Supplies, Sporting Goods, Stationery & Party Supplies and Toys & Games.
Payment – Model
- Direct payment
- Barter exchange
- Auction for unique items
Craft Fair & Sponsoring Program
Craft Fair
The idea Behind This Event is To increase Global Awareness To The Online Handmade Industry, for both, artisans and Potential customers.
Sponsorship Program
In This Program Will be Customised For Individual Investor, Startup Community and The Artisans To Show Them Talents, This Event Gives An Opportunity To The Artisans Who Seek For Fund Support To Develop their Works, In Exchange Of Interest.
Marketing activities
the following promotion options provide the company the best chance of product recognition, qualified leads, web traffic,
Media advertising (newspaper, magazine, television, radio)
Direct mail
Seminars or business conferences
Joint advertising with other companies
Digital marketing such as social media, email marketing, & SEO
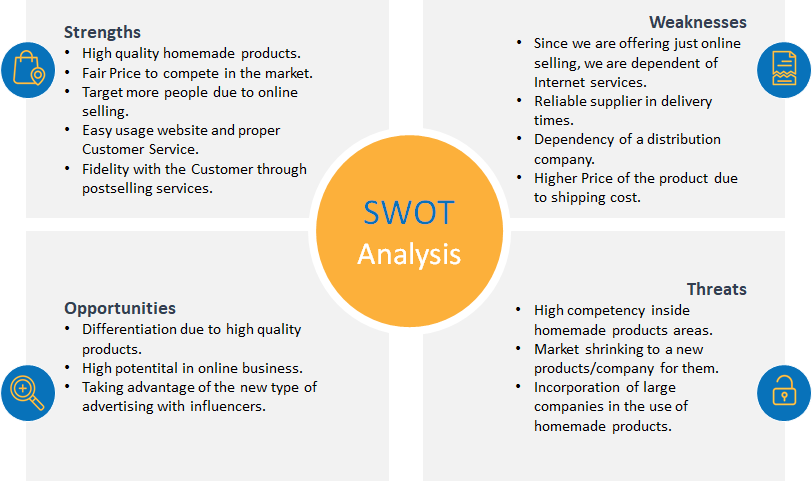
Conclusion
The modern world scenario allows businesses to find their clients in almost all countries. The variety in race, ethnicity, religion, and mentality places many challenges in keeping new entrepreneurship ideas viable for a long period in the global market. Moreover, multinational companies with employees as representatives of many cultures face many challenges to building a unified team which can perform. Therefore, it is essential to comprehend the nuances of different cultures and their impact on business strategy decisions. Our team decided to analyze and compare five countries following the Hofstede’s Cultural Dimension Theory which share significantly different geographic locations, religions, values, and mindset (China, Libya, Saudi Arabia, France, and Spain). The theory suggests that there are six dimensions which mainly determine the culture.
It was found that different religious beliefs in five countries play one of the most crucial roles in the disparity of mentality between the nations. The spread of the three largest religions often seems to lead to misunderstandings between the followers of Islam, Christianity, and Buddhism. In addition, the dissimilarity in everyday choices and organizational values such as the division of leisure time from work and career achievement orientation instead of familial values frequently become a cause of conflicts. The gender roles substantially differ between Asian and European countries where the latter group has a more feministic approach. At the same time, the differences pose potential benefits for productive cooperation for many business industries. This is because the business can use a variety of resources and geographic locations for creative development and easy expansion.
The E-commerce area was chosen as a collaboration business plan due to the ability of the industry to use the variation in culture to the fullest extent and the modern innovation offers. Craft Bazaar is an ideal online platform which allows different handmade items retailers to introduce their products to the worldwide community. The user can register and customize his or her products in a convenient way and in a short time. The downfall of the online store are potential delivery issues and high dependence on internet services.
References
Omar, A., Ali, F., & Imhamed, S. (2020). Exploring Entrepreneurial Framework Conditions in Libya: A National Experts’ Perspective. Journal of Entrepreneurship, Business and Economics, 8(1), 15-53.
XX. Edward T. Hall. Intercultural Communication Jérôme Rive, Alain Roger In Top Authors in International Management (2014), pages 375 to 390.
