Introduction
Gucci, an Italian fashion house company based in Florence, is a highly popular luxury brand. Some of the products include fragrances, handbags, shoes, makeup, home decoration, and accessories. It operates worldwide with several stores, generating billions in the form of sales revenue. It has maintained its position against other luxury brands such as Louis Vuitton. However, Covid-19 has affected the sales, hence a decline in the income generated, especially in 2020 (Dalton, 2020). An in-depth SWOT analysis, a BCG Matrix, and intensive growth strategies are instrumental in facilitating the company’s recovery after the end of Covid-19. Understanding the company’s former and present position is crucial to help outline strategies to ensure the company’s future success.
SWOT Analysis
Strengths
Gucci has highly qualified employees who are extensively trained in the company’s programs. For instance, in 2018, the company launched a training program titled “École de l’Amour,” from French “School of Love.” The program, dubbed “a laboratory of ideas” by Marco Bizzarri, Gucci’s president and CEO, accepts school graduates and teaches employees art and management, focusing on raising the next generation of skilled cadres (Carrera, 2018). Gucci is established on all continents, except for Antarctica, with the biggest revenues stemming from Asia-Pacific (38%), Western Europe (28%), and North America (20%) (Statista Research Department, 2020) The brand has competent dealers where the sales team is taught how to explain to the consumers how to reap maximum benefits from the goods. Therefore, the sales team conducts promotional adverts and ensures the customers receive the utmost satisfaction from the Gucci products (White, 2018). The company boasts a diverse portfolio of products that includes shoes, accessories, leather goods, apparel, fragrances, and even decor pieces.
Weaknesses
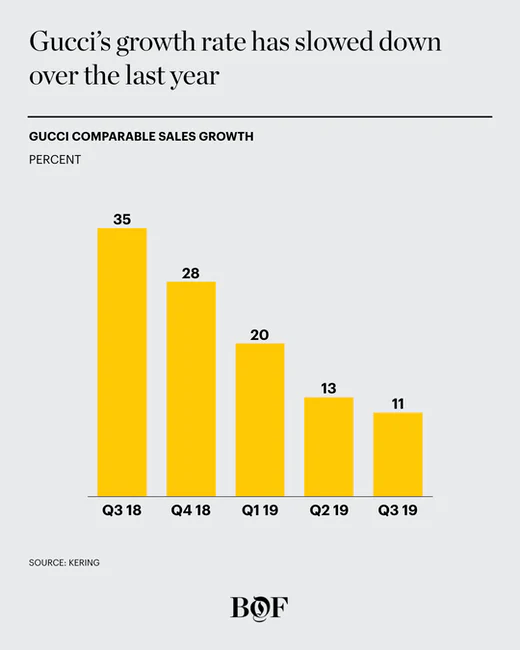
There is a higher attrition rate compared to the rivals; hence, more resources are spent training and developing the workforce. They are also required to invest in advanced technologies as the company expands into various geographical regions. Inadequate and inefficient financial planning is evidenced in the company’s debt-equity ratio and the current asset ratio.
The company also has an elevated day inventory; thus, more capital is required to invest in the brand. The company’s meteoric sales in the previous years have been replaced with more modest numbers as seen in Graph 1 (Fernandez, 2019). Wendlandt (2014) suggests that Gucci may be suffering from oversaturation and brand fatigue in some of its key markets such as Asia-Pacific. According to the analyst, the brand has been increasing prices each year without offering fresh ideas and making use of trends. The inaccessibility with little value has likely driven some customers away and encouraged them to discover smaller brands.
Opportunities
The low inflation rate in the market creates more stability; hence consumers obtain lower interest rates (“Historical Inflation Rates: 1914-2020,” 2020). The formulation of new environmental policies such as the utilization of renewable energy and “the polluter pays” principle makes corporate responsibility a competitive advantage. At present, Gucci works on reducing waste, optimizes transportation, and saves energy in all Gucci stores, offices, warehouses, and supply chains (“Environment,” 2016). The core competencies can facilitate the diversification of the company into other product lines and commodities.
Higher purchasing power due to an economic rebound is an opportunity for the company to attract more customers and raise its share. In 2017, President Trump introduced the Tax Cuts and Jobs Act that decreased corporate taxes from 35 to 21% (Congress.gov, 2018). Since the US is one of Gucci’s key markets, its overseas office is enjoying lower taxation. The availability of new technology allows the company to maintain loyal customers and attract new ones due to establishing a good pricing strategy.
Threats
Increased wage levels, such as $15 per hour and higher costs in China are likely to lower its profitability (Richter, 2019). Fluctuating policies on standards across different countries in which the company operates can subject Gucci to multiple lawsuits. The irregular supply of innovative products leads to an inconsistent rate of sales volume in the company. Liability regulations differ across various countries hence exposing Gucci to various liability claims. The higher cost of raw materials is likely to reduce the company’s profits in the long run (“Rising raw material prices significantly impact on business performance,” 2017).
The increase in the number of luxury brand companies exposes the company to unlimited competition; thus more efforts have to be spent advertising and establishing strategies to counter competitors.
BCG Matrix
The Boston Consulting Group, also known as the BCG matrix, is a tool designed to assist businesses with long-term strategic planning. The matrix utilizes two variables: relative market share (horizontal axis) and market growth rate (vertical axis). Based on these two determinants, there are four variations of businesses: stars (high share/ high rate), cash cows (high share/ low rate), question marks (low share/ high rate), and dogs (low share/ low rate). According to Fashion United (2016), Gucci is among the most recognized and prosperous clothes and accessories brands in the world, ranking ninth on the list with a value of approximately $9.6 billion.
When excluding the non-luxury brands from the ranking, Gucci takes the fourth position after Hermes, Rolex, Louis Vuitton, and Cartier (Fashion United, 2016). There are no exact figures reflecting Gucci’s shares in all markets where the brand operates. However, based on the facts mentioned above, it is safe to assume that Gucci would score high on the relative market share scale.
In 2020, the luxury fashion market was worth US$94,313 million. It is projected that in the next five years, the fashion industry will be growing by 6.6-7% annually (Statista, 2020). Given the fast growth rate, Gucci takes up the top left quadrant of the BCG market: the brand is a star. However, there are some reservations that should be made about keeping this status. At present, the market’s largest segment is luxury apparel that generated more than US$62 million in 2020 (Staista, 2020).
As suggested by Statista Research Department (2020), only 13% of Gucci revenue comes from ready-to-wear items. Furthermore, the United States is the best market for luxury brands, responsible for more than a quarter of all revenue generated in 2020 (Statista, 2020). However, Gucci makes only 20% of its revenue in the United States (Statista Research Department, 2020). Therefore, the next strategic moves could include focusing more on apparel and strengthening brand presence in the US.
Ansoff Matrix
It is used to help companies decide their market growth strategies and suitable products. The main elements are diversification, market penetration, market development, and product development, depending on whether to enter new markets or remain in the existing ones. The company’s most appropriate strategy is diversification of its products to cater to the various changes experienced in lifestyles, socio-cultural elements, increased cosmopolitan culture, migration, and evolution of media technology (Gili, 2019). Features such as social media platforms have changed the scope of operation of several businesses since customer feedback and advertisement can be conducted to reach many people across the globe.
Growth and Expansion Strategies for Gucci
There are several steps Gucci can implement to facilitate its growth and expansion in light of Covid-19 and even after the eradication of the virus. Some of the measures include maintaining relevance to consumers by reassuring them the company is taking necessary steps to protect them, and upholding social distancing by establishing a stronger online presence. Adjusting capital expenditure and the operational costs are vital to prevent unnecessary spending through outdoor advertising campaigns and refraining from opening stores in the affected companies (Ronchetti et al., 2020).
Other long-term measures include adopting a 360-degree consumer model to plan all functions relating to customers and reinventing the existing supply chain by prioritizing vendors and suppliers while maintaining the quality of commodities. Motivated suppliers will enable the company to acquire quality raw materials in a timely and efficient manner. Implementing rigorous digital advertising will also help the company reach more customers, hence penetrating new markets. Even without opening physical stores, consumers can obtain commodities through online delivery companies.
References
Carrera, M. (2018). Gucci kicks off new training program. WWD. Web.
Congress.gov. (2018). H.R.1 – An Act to provide for reconciliation pursuant to titles II and V of the concurrent resolution on the budget for fiscal year 2018. Web.
Dalton, M. (2020). Gucci’s sales fell 34% in first half. Wall Street Journal. Web.
Environment. (2020). Gucci. Web.
Fashion United. (2016). Most valuable fashion brands. Web.
Fernandez, C. (2019). Gucci’s slowdown continues but Bottega Veneta is picking up steam. Business of Fashion. Web.
Gili, G. (2019). The elasticity of demand in the luxury market and Gucci’s case study (ID No. 212501) [Master’s thesis, Luiss Guido Carli]. Luiss.
Historical inflation rates: 1914-2020. (2020). Web.
Rising raw material prices significantly impact on business performance. (2017). Inverto. Web.
Ronchetti, M., Nobile, T. H., Oliveira, N. K., & Cantoni, L. (2020). Digital fashion competencies: Market practices and needs during Covid19. Web.
Statista. (2020). Luxury fashion – worldwide. Web.
Statista Research Department. (2020). Global revenue share of Gucci in 2019, by product category. Web.
White, L. (2018). Brand identity and web atmospherics in luxury fashion brand website design. (ID No. UP786100) [Undergraduate Dissertation, University of Portsmouth]. LiamWhite.
Wendlandt, A. (2014). Gucci needs new ideas, talents to combat brand fatigue. Reuters.
Richter, F. (2019). 50 years of US wages, in one chart. World Economic Forum.

