Introduction
The business environment in which organizations operate today is frequently changing, and it is becoming more and more complex. Organizations, both private and public, feel increasing pressures that force them to react quickly to changing conditions and to be innovative in the way that they operate (Turban, et al. 2007). The response has always been setting up strategies with regards to quality improvement. It is not always the concept of better product branding and prices, but quality products.
For instance, Caterpillar, the giant in machine manufacturing, offers quality products at low prices accompanied by good promotional activities; making it acquire competitive advantage in the industry. This implies that customers not only consider prices, but also quality products and services. This report analyses different facets of quality, including quality imperatives, the strategic importance of quality, quality philosophies, quality tools and strategic alliances of managing quality. In essence, Hexaware Technologies is used as the preferred organization in elaborating quality issues.
Background of Hexaware Technologies
The selected organization used in the first and second assignment will be integrated in this analysis. Hexaware Technologies is a service company offering information technology services and business process subcontracting solutions in various institutions. The company’s clients include banking institutions, health care services, and airline industry. The company is situated in India with several branches worldwide (Hexaware Technologies Limited (HTL), 2010). Quality is a major concern in the field of software management because the existence of customers in many cases depends on the reliability of services. Hexaware has constantly applied quality improvement in its services through proper management of the company’s development centers. This has helped the firm to maintain good reputation from customers.
The Quality Imperative
Quality imperatives are the very important factors that drive organizations towards quality improvement. This section discusses the major factors behind the materialization of quality issues in the last fifty years, and to which extent has become an important aspect that can threaten organization’s survival. According to Beckford (2002), the three main factors are: the economic, the social, and the environmental imperatives. The last subsection explains the imperative behind Hexaware’s involvement in quality improvement.
The Economic Imperative
When evaluating the world market today with that of fifty years ago, it is evident that there are major changes in demand, competitive level, labor and material costs, and customer buying behavior. After the completion of the Second World War, production companies were dealing with customers with high demands, who could accept any products, whether good or bad. With affordable production requirements and lack of stiff competition, the main concern was production in large quantity at the expense of quality. Customer’s unawareness also contributed to the trend of accepting products with poor quality.
Recently, such things are not in existence anymore. Manufacturers are now dealing with hard market environment, where they cannot even determine their competitors. There are also significant upsurge of labor and material cost and emergence of well informed customers who make buying decisions inline with quality products (Narasimhan & Nair, 2004). All these changes have forced manufacturers to change their methods of production and chase for new solutions in order to survive. “The Gurus promise that achieving quality will reduce cost and improve productivity, and certainly many of the tools will lead towards these things”. (Beckford, 2002, p.7).
The Social Imperative
Providing bad quality products implies that organizations are wasting human resources. The human capital, skills, and talents need to be used wisely by giving employees proper work security. Workers need to be good steward of organizational resources, and likewise, managers have to be good steward of the human resources. Managers have to ensure that employees are socially responsible and assigning them tasks relevant to their capabilities (Bullen, n.d). More so, improving quality of workers minimizes costs and thus increasing the general productivity, which is an essential managerial goal.
The Environmental Imperative
Governments and authorized environmental entities are applying obligations on organizations with regards to reducing environmental damages. In order to achieve this, organizations are encouraged to enhance their business processes and some time the type of raw materials they use so as to minimize environmental degradation. This implies that improving quality of the business process and using better quality materials result to a better environment.
Hexaware Technologies and Quality Imperative
The major forces behind quality improvement in Hexaware are economical and social imperatives. When talking about economic imperative, the best example is the competitors and customer status. In the information technology (IT) industry, there is stiff competition because of constant changes in technology. This has lead to the drop of prices in IT products and solutions (Stair & Reynolds, 2006). Likewise, the human capital in the industry is demanding because of the need of diverse ideas. These factors has led Hexaware to set up a Quality Improvement Program which is concerned with the business needs, technological advances, customer responses, and process development. It is notable that the company has achieved remarkable quality standards such as ISO 9000:2000, TickIT, and CMMI Level V, in its bid for quality improvement (HTL, 2010).
The Strategic Importance of Quality
Quality plays an active role in different stages of decision making. Beckford (2002) asserts that such management decision making can be implemented in four different levels: operational, administrative, strategic, and normative levels.
Quality in Operational Level
Operational level of management is concerned with the daily activities carried out in an organization that help in achieving organizational objectives (Laudon, 2006). For instance, in manufacturing industry, these activities include designing, machining, welding, and packing. Any delays or errors result in glitch in the final output, which can be a product or service or anything else. Different quality tools can be used at this level to reduce errors and increase production. These tools are discussed in section 5.0.
Quality in Administrative Level
Administrative management involves controlling, directing, and allocating operational resources toward achieving the organization’s goals. Administrative managers are required to take appropriate action when a situation that requires critical decision arises. Thus, poor quality in this level will adversely affect the degree of output from the operational level. It is imperative that top managers ensure that sufficient quality management system is applied in the administrative process within their companies. By doing so, they will guarantee the system’s ability of meeting customer expectations (Beckford, 2002).
Quality and Strategy
Organizational goals, plans, policies, and human resources are things that are not supposed to be taken lightly. These aspects are likely to remain within the company’s lifetime and thus the decision process should be determined by strategies. Quality is an important determinant in strategic planning. It acts as a foundation of plans and proper communication structure (Swift, et al., 1998).
Quality and Normative Decision
Normative decisions are those decision concerned with future changes which an organization is required to integrate within its strategic plans. These decisions need to be taken in advance to ensure that the organization survives. For example, existence of customer acceptance of a certain level of product quality might change in future. This change should lead to immediate action in the quality level; otherwise, the organization is deemed to fail in meeting customer expectations (Beckford, 2002).
Hexaware Technologies and Quality in Different Levels
The daily operations in Hexaware are run by supervisors in each subunit. The supervisors delegate duties to workers and subsequently document records. These documents are revised daily to ensure that they conform to strategic plans and quality standards. Such procedures improve the quality in operational level and make it easy for top level managers to review them. The quality in administrative level can be seen in transparent software dealings among managers, employees, and customers. The strategic managers normally receive reports and suggestions from supervisors, thus making informed decisions.
As a result, the major strategic target of Hexaware is to increase its competitive niche in offering software solutions. This is both a long term and a competitive goal. To meet this target, the company strives to provide quality services supported by expanding its market base. For example, Hexaware is concerned with offering on-demand computing services to institutions which consider the minimization of IT investment. In this case, companies can lessen their investment in IT infrastructure by spending just enough to handle normal processing requirements and paying for as much extra computing power as the market demands (Laudon, 2006).
Quality Philosophies
Quality management concepts mostly originated from individuals who successfully applied several statistical techniques and management knowledge in quality improvement. Those researchers and practitioners are known as “gurus”, since their philosophies and tools have been tried and adopted in the current quality practices (Beckford, 2002). This section looks at the philosophies of such gurus and consequently analyses the philosophy adopted by Hexaware technologies.
W. Edwards Deming
Deming is always considered as the “father of quality control”. Deming argued that a lot of effort should be placed on the management and business processes, in addition to workers’ performance. He outlined that 15 percent of quality issues originate from employee error and a significant 85 percent are due to poor management and lapses in business processes. Deming said that the management is required to correct system faults and develop an atmosphere that increases quality and enable employees to perform well. This calls for proper direction and supervision within the organization (Reid & Sanders, 2007). In his philosophy, Deming introduced 14 principles that can guide organizations in realizing quality improvement.
Philip B. Crosby
Crosby believed that quality is free and stressed that there should be proper inspiration and planning. He argued that the cost of preventing errors is lower than correcting them and therefore organizations should be ready to implement quality measures in order to meet customer requirements. He invented the term “Do it right the first time” and the principle of “zero defects”, stressing that no errors should be assumed (Reid & Sanders, 2007, p.145).
Other Gurus
Other gurus who also played a big part in quality improvement include: Feigenbaum (overall quality control), Ishikawa (systems approach, cause-and-effect diagrams), Juran (created the notion of cost of quality), Shingo (defect avoidance), Taguchi (emphasis on product design quality) (Beckford, 2002). Despite having different philosophies, the fundamental thing is improving quality.
Looking at Hexaware Technologies, the company follows the principles of Deming and Juran. Since it is a service company, the quality improvement concepts are: courtesy and friendliness of staff, time management, and consistency. The management strives to offer quality awareness to its employees at all levels of governance, thus having a quality improvement plan that fits in their system program.
Communication of philosophies
When examining philosophies or concepts from different thinkers and scientists, it is essential to outline the common aspects between them. These common principles represent extract results that those people came with, and have high degree of accuracy. The following are some of the points that most gurus agree with: quality is an important aspect in company success; quality realized by individual effort; quality is a continuous requirement; and quality is a total concept. Thus, our study organization, Hexaware, communicates the above mentioned philosophies to its workers, stakeholders, and customers through a Quality Improvement Program that incorporates a company wide Defect Prevention Program and Metrics Program (HTL, 2010).
Quality Tools
Quality is an application plan that requires tools and techniques in order to be measured. By incorporating problem solving and statistical process control tools and techniques in quality improvement, different members of organization can be able to evaluate and determine the performance within their organization. In addition, it will help in making the right decisions with the aim of improving performance. The following subsections explain some of the quality techniques and tools.
Statistical Process Control
According to Beckford (2002), Statistical Process Control is “a quantitative approach based on measurement of process performance” (p.305). It is an essential method of identifying errors among processes in the manufacturing industry. Histograms, Control Charts, Run Charts, and Normal Distribution Curves are the common Statistical Control tools. In this case, we consider the use of Histograms.
Histogram is an important arithmetic tool that helps in evaluating process performance using frequency distribution graph. The output of a process is normally represented by a pattern similar to the behavior of that process. If the pattern or rather distribution goes over or below the normal expected shape, then it implies that there are some defects in the process (Hradesky, 1995). Histogram shows whether the distribution is normal or symmetrical in nature. Figure 1 illustrates a normally distributed variable.
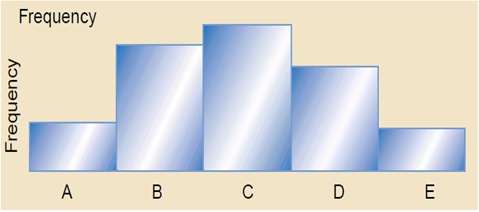
Benchmarking
Benchmarking is the method of constantly comparing a company’s strategy, products, and business processes with other top organizations in the same industry. This is deemed as a way of enabling an organization to learn how others achieved excellence and thus setting new strategies to match out or even improve the whole process (Swift, et al., 1998). In principle, benchmarking technique can be started by asking some questions and trying to get their answers. For instance, how are going to classify our self and what are we going to measure? What criteria shall we use to compare our self with the other firm? How to gather data about our competitor? When benchmarking is applied, a company can be able to realize some benefits with regards to cultural change, process improvement, and employee participation in different methods of improvement.
House of Quality
House of Quality is an important tool that supports quality deployment. It is used to define the requirements from market research and translate them to products and services that reflect quality (Swift et al., 1998). The House of Quality technique encompasses the following six major components:
- Customer Requirements: Incorporate the customer needs before building the product.
- Planning Matrix: Relationship matrix include customer needs, technical requirement, processing requirements, and product features.
- Technical Requirements: The requirement in which the company needs to perform in the specific product or service.
- Inter-Relationships: The connection between technical requirements and customer requirements.
- Roof: It shows the effect of any new requirement need to be developed in the rest of technical requirement.
- Targets: The conclusion from the entire matrix.
Pareto Chart
Pareto chart is used in Pareto analysis. Pareto analysis is a method used to determine quality problems inline with their level of importance. The concept in this technique is that only certain quality issues are significant, while several others are not important. Thus, by developing a Pareto Chart, the causes of bad quality can be categorized in decreasing order by considering their respective percentage of defects. For example, figure 2 shows how the percentages of defects (A to E) can be represented in a Pareto chart. In essence, Pareto proposes that if the first two causes are worked out, the problem can be solved.
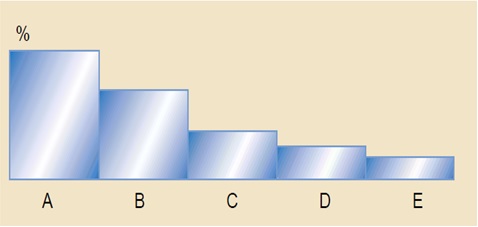
Baldrige Awards
Baldrige Awards is a regional quality program which was developed by the United States. The award has developed a general protocol for quality, and many firms use the criteria in their application form as a basic management conduct for quality improvement programs. It is similar to ISO standard, but the later is more concerned about scope. Bildrige Awards is more comprehensive program than ISO standard, and addresses more specific aspects like human resource dimension. Generally, when talking about certificates, Bildrige Awards is considered to better than ISO standard and harder to get (Swift, et al., 1998).
Six Sigma
Previously, rejection of three items out of one thousand was applied and acceptable by different factories. This was known as Three Sigma standard. Today the standard is not acceptable any more. For the last three decades, a new standard called Six Sigma has been approved. It is more accurate than the old one because it accepts three defects or errors out of a million items. Six Sigma is a very thorough technique that applies acceptable quality principles and techniques. Non Six Sigma companies spend more money in fixing problem than those who apply Six Sigma standard (Reid & Sanders, 2007). This is simply because applying Six Sigma standard requires major improvement in performance by having close interaction with customers, workers and suppliers, and applying high level of training to all employees from top to bottom levels.
HRM Influences
Human resources can be considered as the main element in achieving quality improvement. Specifically, the HRM department can play an active role in applying Total Quality Management (TQM) in organization. This can be achieved by implementing TQM in the HRM department as the main quality agent and creating HRM values that enhance quality orientation in the rest of organization. In many organization, HR department lead the quality improvement programs. This can be explained by representing the different duties in HR department like selections, staffing, motivation and so on. (Bowen & Lawler, 1992).
Hexaware Technologies and Quality Tools
Most of the tools which have been mentioned above are not used in Hexaware Company except for a selected the tools. The reason simply is that most mentioned tools are familiar in manufacturing and mass production industries or even in services institutions. However, Hexaware applies benchmarking standards in its software solutions. The company constantly compares itself with leading companies like Oracle in ensuring quality.
Strategic Alliances and Methods of Managing Quality
Strategic alliances are important creators of wealth. Organizations enter into relationships with suppliers, clients, and other companies with the aim of achieving competitive niche in quality, innovation, and cost. To achieve the expected interaction of these alliances, the partnering parties must build long-term relationships (Laudon, 2006). Managing quality in such alliances requires new quality control, intensive supplier prerequisite systems, and shared technique and development information. This section looks at supplier development, TQM, ISO 9000, quality assurance, and skill based quality management inline with quality improvement.
Supplier Development
The connection between buyer and supplier has great effect in the success of business operations. They rely on each other. For example, in automobile industries, the car manufacturers mostly assemble 20% of the cars within the company, and about 80% come from suppliers. The major question in this scenario is: how efficient and reliable is the supplier? The relationship with supplier must be narrow and seamless. It must include intensive involvement from the buyer and in some cases, the buyer can offer free training program for supplier to ensure that right products are supplied. This will save time and money, hence long-term relationship.
Total Quality Management (TQM)
TQM is an incorporated managerial effort to enhance quality in terms of functions and process at all levels of management (Reid & Sanders, 2007). It can be considered as a system approach concerned with applying quality issues in every interaction between the basics of the organization. Hradesky (1995) asserts that TQM is a philosophy, a set of tools and process whose result guarantee consumer approval and constant enhancement. It is something that all participations in the organization should be involved in. Some important elements of TQM can be summarized as follows:
- Designing of critical business success factors.
- Implementing of cultural change, values which match to strategic planning.
- Align the organization with internal customer satisfaction.
- Initiate a suitable sizing which is matching of human resources to functional requirements.
- Implementing of techniques and standard such as, Quality Function Deployment and ISO.
- Establishment of quality management scheme which includes strategy, measures and work orders thus Quality Assurance.
ISO 9000 Series
ISO 9000 series are quality management systems standards which were developed in early 1940 as quality standards for defense industry (Beckford, 2002). These standards are the core of quality system standards applicable to a board range of industry and economic sectors. They are not standards for products as some people think. Instead, they are standards for governing quality management systems.
ISO 9000 is divided into different series; for example, ISO 90001 is concerned with quality system and models of quality assurance, ISO 90002 involves quality system and assurance in production and installation, ISO 90003 is about the same but mainly concerned with quality testing and inspection. ISO 90004 is the most relevant in this study, since it talks about quality tools; it is the general guideline for services, processes, materials and quality improvement. An organization can realize the following with regards to ISO certification: customer loyalty, improved market share, higher stock prices, reduced service calls, greater productivity, and cost reduction (Swift et al., 1998).
Quality Assurance
Quality Assurance is about making sure that quality is realized through applying systematic quality improvement program. This ensures that there is confidence in product or service in order to guarantee a given condition for quality strategy. The government is tasked with ensuring quality certification within organizations. In addition, Quality Assurance program documents quality plans, processes, and procedures which are adopted from quality standards and it is important that an organization follows these steps (Stair & Reynolds, 2006). It should lead the organization in processing planned and continuous improvement. Much of Quality Assurance is not about economics; it is about corporate culture to get everything to be done in right way. It can be started by applying ISO 9000 which has been discussed before.
Skill Bases Quality Management (SBQM)
This report has discussed the different fields where quality management can be applied; for instance, in processes, strategic planning, relationships, and so on. SBQM is applied when the quality of product or services depends on the employee’s skills and level of education. This is very common in services sector where applying customer requirements depend on the skill of the technician, or in teaching, the level of student understanding depends on how good the teacher is.
Beckford (2002) asserts that SBQM “is an approach to the construction of an effective and manageable quality management system (QMS) based on development and recording of the skill base of service organization” (p.279). This can be achieved through defining the necessary skills and level of education required by the system before employing people. The best-fit people in specific departments are then chosen. By doing this, the organization can achieve SBQM approach which is part of TQM.
Hexaware Technologies and Quality Strategic Alliances
Part of quality strategic alliance in Hexaware Company is the relationship with the customer. This interaction provides the necessary information about the stresses in equipments which determine the suitable type and scheduled service. In addition, Hexaware was able to acquire FocusFrame in 2006 as its constituent company in software testing. This has enabled the company to enhance quality in all levels of management. However, Hexaware needs to restructure its business processes in order to survive in the highly competitive software industry; new alliances should be formed with suppliers of software products, such as Microsoft.
Conclusion
This report has discussed different issues in quality improvement and emphasis has been placed on a real organization: Hexaware technologies. Different factors have lead to the quality imperatives, especially after the Second World War; these include economical, social, and environmental imperatives. The strategic importance of quality in different levels of organization has been discussed and therefore quality needs to be improved and applied in all levels in order to get the desired result, otherwise, it will be waste of time and money.
Some of quality gurus and their philosophies were reviewed to illustrate the sources of quality knowledge and tools. Generally, investing in quality issues deserve attention from all organization especially the profit-oriented organizations. The reason is the fact that investing in quality, in overall view, helps in fixing problems, maintaining, and increasing of customer attitude. Improving quality leads to customer satisfaction hence increased market share.
References
Beckford, J., 2002. Quality. 2nd Ed. Routledge Taylor & Francis Group: New York.
Bowen, D. & Lawler, E., 1992. Total Quality-Oriented Human Resource management. An Official Article. Web.
Bullen, P., n.d. Quality Improvement. Management Alternatives for human services. Web.
Hexaware Technologies Limited (HTL). 2010. Hexaware Technologies. Fresher Avenues. Web.
Hradesky, J., 1995. Total Quality Management Handbook. McGraw-Hill Inc: US.
Laudon, K. & Laudon, P., 2006. Management information Systems: Managing the Digital Firm. 9th Ed. Pearson Prentice Hall Inc: Upper Saddle River, NJ.
Narasimhan, R. & Nair, A., 2004. The antecedent role of quality, information sharing and supply chain proximity on strategic alliance formation and performance. International Journal of Production Economics, 96, pp. 301-313. Web.
Reid, D. & Sanders, N., 2007. Operations Management: An Integrated Approach. Rev Ed. John Wiley & Sons: New York.
Stair, R.M. & Reynolds, G.W., 2006. Fundamentals of information systems. 3rd Ed. Thompson Course Technology: Boston.
Swift, J., Ross, J., & Omachonu, J., 1998. Principles of Total Quality. 2nd Ed. CRG Press LLC: US.
Turban, E., Aronson, J.E., Liang, T., & Sharda, R., 2007. Decision Support and Business Intelligence Systems. 8th Ed. Prentice Hall: New Jersey.

