Introduction
Motivation refers to the force that drives an individual or a group of persons toward achievement of certain goals (Calver, 2001). Motivation can either be intrinsic or extrinsic (Miner, 2002). There are various theories put in place to explain as to why employees should be motivated. Some of the main theories are:
- The McClelland theory of needs.
This theory is based on three motivational aspects that includes the urge for power, affiliation as well as the urge to achieve.
- The motivational hygiene theory.
This theory is by Frederick Herzberg. It is also known as the factor theory. Frederick argued that in the corporate life there are satisfiers (intrinsic factors) and dissatisfies (extrinsic factors). He also talked of hygienic factors such as security, status, salary, organization policies and even the working conditions that the employees are exposed to. He also explained that there are motivational factors such as the possibility of growth, promotion and even greater challenges within an organization.
- Equity theory
This is by J. Stacy Adams in which he talked of the give and take issues in an organization. He compared “give” to the inputs that employees give to an organization and “take” to the output derived from an organization.
- Hierarchy of need theory.
This theory was developed by Abraham Maslow, who categorized human needs in a hierarchical manner. The theory postulates that human needs are either physiological, safety, belonging, being loved, self-esteem or self-actualization needs.
- Theory X and theory Y
This theory is by Douglas McGregor. Theory X assumes that the leader perceives employees as lazy and has to coerce them so that they can work. Theory Y on the other hand assumes that the leader perceives employees as being highly motivated, ambitious and ready to work as they take work to be natural.
We shall base our study on the last two theories that is the Hierarchy of need theory by Abraham Maslow and theory X and Y by Douglas McGregor.
Hierarchy of need theory
As illustrated above Abraham Maslow theory is a hierarchical theory. The following is a diagram showing the hierarchical order of Maslow’s needs (Fincham and Rhodes, 2005).
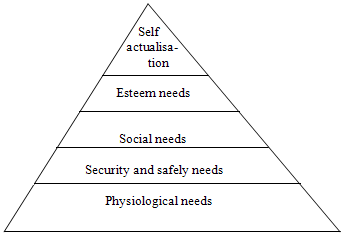
In this theory employee needs are categorized as:-
The physiological needs which entail the things that a person requires to sustain his life such as food, shelter, medical care, education, sleep and even clothing.
In the second level that is security and safety a person will be checking on the security based on his employment, his health safety and the safety of his family. Social need is achieved through virtues such as being loved by others, affection and being allowed to be part of a particular group that is the freedom of forming groups. Esteem need is achieved through the confidence people have in you, the great achievements you make in life, respect from other people and also the self esteem in you.
Finally self actualization is gained when one achieves his or her individual potential in it one is able to solve problems which may arise within the organization. There is general lack of prejudice. In this theory the lower order level is generally considered as the physiological need whereas the top level as the growth needs (Quick and Debra, 1996). In this an individual will first satisfy the needs falling under a lower level and when he or she has satisfactory catered for them then he shifts his attention to a much higher level of need.
Theory X and Y
In respect to theory X the assumptions leaders make are:
Work is generally distasteful and the team members will do anything to avoid work (Quick and Debra, 1996), a lot of people are not ambitious, they hate responsibility and have to be driven for them to work. There is overall low level of creativity among people in tackling problems within the organization.
Many people are generally greedy or self centered hence they must be controlled and forced to work so as to achieve the overall corporate goals, also the employees are perceived to resist change within the organization (Miner, 2002). Finally this theory assumes that the leaders see their work force as people who can be easily cheated.
When we turn to theory Y the assumptions that leaders make include:
When working under favorable conditions work can be as natural as play (Calver, 2001). Also once the employees are committed to creativity and are self directed they can easily achieve the organization goals. This theory also assumes that creativity is always present and spreads out within an organization. The final assumption under theory Y is that, majority of the employees can deal with responsibility within the organization they work in.
A leader who generally applies theory Y model is normally seen as being optimistic in his or her leadership approach (Fincham and Rhodes, 2005).
Comparing Abraham’s theory of need to Theory X and Y
Both Abraham Maslow and Douglas McGregor appreciate the fact that people are motivated to achieve higher levels of needs. A person will feel more motivated once he meets his needs (Calver, 2001)).
Comparing the two theories it’s clear that McGregor theory is based on Abraham Maslow’s theory of hierarchy of needs in the sense that, the lower level needs of Maslow that is physiological and security needs can be compared to theory X whereas the social, esteem and self actualization needs( higher level needs), can be compared to theory Y.
Also both theories Y and Maslow’s hierarchy of need theory are similar as both show that work can be a source of satisfaction to employees. This two theories(Y and Maslow) advocate for a stable employment thus leading to an increased productivity due to high employee morale and job satisfaction (Bruce and Patrick, 2000)
Though theory X and theory Y are two different assumptions there is one great similarity in them in that both theories see a leader as a person whose primary role is to consolidate and organize the resources of an organization, workforce included, for the overall benefit of the organization.
Contrasting issues
A number of contrasting issues also emerge such as:-
First unlike the Abraham Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory, McGregor does not consider the fact that the lower level needs have to be met first before one shifts his attention to the higher level needs. McGregor treats all needs uniformly.
Also unlike the Abraham Maslow theory which is one fold, theory X and Y are two alternative sets of folds or assumptions in which theory X denotes assumptions held by leaders which are false and theory Y are assumptions which are real ( John 2002).
Another major contrast in the two theories is that Maslow’s theory focuses on ways of increasing team member’s loyalty to an organization through provision of a job that focuses on one’s well being both in and out of the organization as compared to theory X in which McGregor stipulates that employees dislike work and have to be driven for them to work.
Unlike the Maslow’s theory Douglas McGregor’s theory X and Y focuses on identifying factors motivating a team member based on the team member’s perception that is hating work in the case of theory X and perceiving work as natural in the case of theory Y. However, Maslow’s theory is based on individual needs that is the Physiological needs, security needs, social needs, esteem needs and the self actualization needs.
Also Maslow’s theory focuses mainly on both the attitude and responsibility of employees to their work whereas theories X and Y put much of their emphasis on the management and the motivational aspects of a leader and the overall perception of the organization at large.
Ways of motivating team members
Under Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory a leader can do the following to motivate his team members:-
Starting with the lower order a leader can cater for the physiological needs of his team members by checking on the salary they earn and their employment stability. In it the leader will ensure that his team gets adequate pay for their services and also they are working under stable environment. In so doing the team leader will be motivating his team physiologically.
The second level to check on is the team member’s security needs. In this the team leader will ensure that the working environment is safe, his team members are entitled to benefits such as pension and also ensure that his team is being exposed to fair and favorable working practices.
The third level to check on is the on the sense of belongingness. The team leader can get this by encouraging and allowing his team to form social groups. Human beings are social being and thus the employees will feel appreciated if allowed to relate with others. In so doing team members will feel both respected and wanted in the organization and thus be more motivated. This form of motivation can also be given through ensuring that there is appropriate managerial communication within the organization.
In the fourth level that is the self esteem a team leader can motive his team members by ensuring that it acquires a positive personal image, respect and even gets recognized. This is especially to issues such as the job title they get, having favorable working space and even having prestigious work tasks or assignments.
The final level to check on under Maslow’s hierarchy of needs theory is the self actualization. In it the team leader should focus on both the individual member growth and development. This will easily be achieved if the team leader ensures that his members have autonomy in their work and also they get more challenging work. In so doing the team leader will be motivating his team members to both develop and grow their careers. In respect to Douglas McGregor theory we will focus on the two theories separately. We start with theory X whereby we can categorize it under either hard or soft approach. In the hard approach the leader can choose to coerce, threaten or even instill tight control over his team members.
In the soft approach the team leader can opt to be permissive or seek harmony with his team members with the expectation that they (team members), will be cooperative when need arises. However the team leader should be highly careful when applying this theory as both approaches can easily lead to negative outcomes such as hostility in the case of hard approach or blackmail in the case of soft approach
Turning back to theory Y a leader can motivate his team members by:-
Ensuring there is both decentralization and delegation of work. This will ensure there is equitable distribution of both power and responsibilities. In so doing the team members will feel having more responsibilities to the organization and thus be more committed and motivated to work. Secondly the team leader should routinely carry out job enlargement. This will ensure there is a broader scope of job and thus satisfy egos of his team members. More to this a leader should ensure that his team members participate in management and decision making processes. This will make them feel appreciated and recognized in their various roles within the organization.
Conclusion
The team leader can have his team set out their own objectives and targets for performance appraisal purposes. This will motivate them as the team members will feel that targets are not imposed on them rather they (team members) are having the responsibility of setting them with respect to their varied capabilities.
It is therefore clear that both Abraham Maslow and Douglas McGregor’s theories have a lot of potential to both business and corporate world. It is therefore the responsibility of all leaders to determine the level in which their team members are so that they (leaders) can determine the best rewards to give to their team members.
List of References
Bruce C. and Patrick M. (2000). Management: NY: Baron Education Series Publishers.
Calver, C.S (2001). Self reduction of behavior: New York: Cambridge University press.
Fincham R and Rhodes P. (2005). Principles of organizational Behavior: Oxford: Oxford University Press.
Miner J. (2002). Organization behavior, foundations, theories and Analysis: Oxford university Press.
Quick J. and Debra N. (1996). Organizational behavior, London: West publishers.
