Management decision support system is a platform that correlates volumes of data and information. Management support system is a decision-making tool that facilitates organizational operations. The architecture assists managers to understand, manage, organize, and redistribute, business processes. Management decision support system is not a decision model, but an aggregate component that supports business models and risk management. DSS systems can be classified into programmed and non-programmed decisions. The features of a programmed decision system include consistency, guideline and procedure.
The features of non-programmed decision system include inconsistency, no rules, spontaneous actions and instinct. However, the features of a decision support system include usability, adaptability, feasibility, efficiency, control, development, data integration, consistency and efficiency, compatibility, web-based interface. Business managers utilize a decision support system to analyze, support and facilitate the decision-making process in the organization. Thus, decision support system is a category of information system that facilitates business ideas and trends. The technology behind a decision support system includes differentiated databases, individual’s instincts and judgments, holomorphic models, and web-based integration. The study will provide managers the comparative advantage in a competitive market.
DSS combines business intelligence with human response to support the decision-making process. Thus, management decision support systems are interactive activities that ensure sustainability, growth and development of ideas and business operations. The benefits of decision support systems include spontaneous decision process, efficient organizational management, automated decision-making guidelines, adequate resource pool, information, personal efficiency and time management. Thus, managers must understand the practical use of decision support systems to influence business operations. As a result, managers can assess, compute, organize, and manage useful information to boost personal efficiency. We will review previous literatures of information systems and its uses in the business environment. Consequently, we will discuss the framework of decision support systems.
Literature Review
This section reviews previous literatures on decision support systems and management. The decision support system is a continuous chain in organizational management. Thus, the evolution of management decision systems began in 1978. Consequently, the major variable in the evolutionary process is time. Thus, we will analyze the evolution of decision support systems using previous literatures. Evolution describes the changes to a concept, procedure, and interface in an efficient form. Thus, the evolution of decision support systems can be analyzed with its features, technology, components, algorithms, knowledge, clients, and user preference. We must distinguish the terms used in this paper to avoid misunderstanding. Evolution is a gradual process that carries along all the aspects of change. However, revolution is a spontaneous change facilitated by evolution. Previous research revealed the evolution of DSS systems over time. The changes include user needs, technology, errors, user framework, structure, complexity, decision framework. Another documented review suggested that DSS evolution began with the sub-task level of web-based approach.
The aggregates of computer interface linked with volumes of data and information facilitates the management of decision support systems. The stages of the DSS evolution include detection, monitor, and predict. Thus, the evolution of each stage has been the pivot of the decision support model. Documented surveys revealed that hardware evolution improved the management of decision support systems. The hardware evaluation includes mainframe terminals, personal workstations, local network systems, Internet systems, and network devices. The evolution of the decision support system affected the server database, knowledge, and user interface. For example, the management of medical institutions with DSS has changed over time. Medical practitioners can trace the patient’s history with similar occurrence using the organization’s database. Thus, the evolution of decision support systems has enhanced the management of organizational operations.
The meaning of decision support
We discussed the evolution of decision support systems and its benefits in previous sections. However, we will describe the components of a decision support system. Decision support can be described as a technical skill that facilitates an individual’s activity. Thus, decision support facilitates the decision-making process of an individual or organization. Decision support provides assistance to communities, individual, organizations, and the nation. Decision planers are affected by limited resources, small budget, rigorous daily operations, and the incompetent data analyst. Thus, the need for efficient decision support systems will improve employee’s performance and productivity. Previous research classified decision support into decision support systems, analytical tools, and integrated framework of tools. We will discuss the components of decision support in the next section.
Decision support systems
An associated documentation of practical systems is called decision support systems. Consequently, decision support system is a collection of information that enhances productivity. Thus, productivity is a significant factor in a decision support system. Managers can forecast market or policy trends from a resource pool on the server database. Practical systems mean an aggregate resource used to solve problems. A collection of smart tools that facilitates the decision-making process is called DSS. However, these tools can be used to analyze different task. As a result, the decision analysis tool is an interface that integrates the practical system.
Decision analysis tool
Decision support tools are the main frame architecture for a DSS. The support analysis includes a graphical user interface and the GIS. The main feature of the decision analysis tool is accessibility. A client can access the interface from an online database. Thus, customers can communicate ideas and business patterns using a web-based approach. Consequently, the evolution of the DSS is influenced by research.
Decision support research
Decision support research facilitates the decision-making process. Management decision support system is based on competent research methodology conducted over time. Thus, an aggregate of research data can be used to solve various organizational challenges. Technology and data foster decision support research. As a result, decision makers can combine a pool of resources with an advanced graphical interface to facilitate the decision-making process. Thus, decision support research is an interoperable tool that supports organizational management. For example, environmental analysts utilized the DSS to resolve land conflicts across the Mediterranean region of Spain. Decision analysts collate volumes of information from different databases to support local communities and resolve complex land dispute.
Management decision support system
Documented reports revealed that urban sprawl has been managed with the DSS. Environmental analyst designed a user interface that analyzed the effects of soil and water quality. As a result, local communities could manage flood patterns and environmental risk assessment with the decision support system. Consequently, data analysis and interpretation have been used to educate wildlife personnel in North Dakota. Environmental town planners utilized the decision management tool to design urban and semi-rural towns. Thus, management decision support system has been used to eliminate the challenges encountered by decision makers.
Management decision support system framework
We have carefully analyzed the components of a decision support system and its benefits to managers. However, management decision support system is different from a decision support system. The decision support system is a collection of interoperable tool box for decision-making. As a result, the user interface must be incorporated with other components of the DSS. However, recommendations and action-driven analysis must be conducted by competent personnel. Thus, decision management technique is a factor in a support system. We will summarize the difference between management and support systems under five headings.
Structure procedures and defined actions
A DSS model is a resource pool for decision makers. Thus, an individual can analyze problems using available e options on the DSS database. However, management decision support system uses predictable tools to analyze similar problems. For example, toxic waste management decision support system was designed to assist communities manage toxic waste. As a result, environmental analysts can manage toxic waste using a DSS resource pool. Thus, the actions and procedures of management decision support systems are predictable and defined.
Competence and efficiency
DSS architecture influence competent users to facilitate the decision-making process. Consequently, a decision support system can be used accurately when the user is experienced and competent. Thus, decision management is a factor in the DSS model.
A specific interface and tool
In DSS architecture, the client user is responsible for business interpretations and application. However, management decision support systems functions with a specific user interface. For example, waste management organizations design specific interface that supports its objectives. Thus, management decision support system addresses a specific challenge within the organization.
Data analysis
DSS architecture can be used to analyze resource data. Thus, the user must apply various methods of data analysis to ensure the validity of the decision research. However, management decision support system relies on program analytics to ensure research validity. Thus, mathematical interpretations are applied in DSS architecture.
Repeated outcome
DSS architecture has a level of freedom in applying repeated actions. Thus, certain variables may change the possible outcome. However, management decision support system combines different analytic methods to derive a valid result.
Management decision support system and its applications
The organization of different support systems is called decision management. Decision management systems have been incorporated into business marketing, health institutions, military, catering, environmental waste management and engineering. The benefits of decision management system outweigh the economic and financial status. Thus, decision models are classified according to case patterns and structure. Decision types can be human judgment or a combination of web-based approach. However, a decision support system can be used to structure problems, identify alternatives and analyze organizational challenges. Thus, decision models can be used to analyze organizational challenges.
Linear decision models have been widely accepted in a different domain. This suggests that human judgment evolves with time. As a result, modeling decisions can be used to organize, analyze and decide a firm’s daily operations. The components of a linear decision model include preference, data availability and uncertainty. Preference influences the choice of action from a pool of resources and alternatives. Consequently, the availability of the resource pool influences the quality of the decision-making process. Uncertainty describes the user’s instinctive judgment on a particular situation.
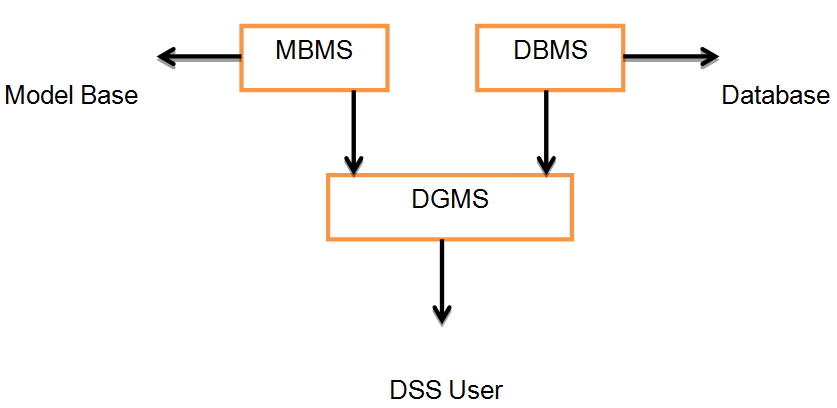
Management decision support systems have three fundamental components. The components include database, model-based, and dialog generation management systems. The database management system is an array of systems that store case variables in logical structures. A DBMS functions as a modulator to different classes of problem. Thus, users can distinguish between structure and process using the database management system. Model-based management system supports client’s independence. The model-based management system is an analogous copy of the DBMS. It transforms volumes of information into analytical interface. As a result, the user can manage complex problem. Dialog generation system describes the instinctive judgment of the user. The system is equipped with a human user interface that facilitates the decision-making process.
Normative and descriptive systems
Decision makers apply two distinct approaches with the DSS architecture. Managers utilize these approaches when considering human instinctive patterns. The expert system combines human instinctive judgment of the DSS architecture. Expert systems have been designed to imitate human judgment and patterns. However, expert systems also imitate human flaws and errors. Thus, managers may encounter the flaws of its designers. Consequently, managers prefer the descriptive approach, which relies on the development of small data sets.
As a result, complex decisions are considered using a small set of data to ensure reliability. The decision support system consists of a data bank, analytical tool, normative or descriptive models, technology and a user interface. However, management decision support systems require three fundamental components to function efficiently. The components include the database management system, dialog management system and the model-based management system.
The decision support concept includes the Gorry, Scott Morton, and Alter’s model. Gorry and Scott models classify problem into structured, semi-structured and unstructured patterns. Consequently, the management level includes operations, management and strategic control. The management level depends on the type of problem structure. However, Alter’s decision technique includes information elements, retrieving files, reports, decision consequence, initial decision, and final decisions. The decision support systems can be used to analyze, organize, and manage various organizational challenges. However, we must apply distinct user interface when analyzing specific problems.
Conclusions
Management decision support systems can be used to manage various organizational challenges. The components of a decision support system include databases, analytical tools, user-interface, and decision models. Management decision support system is a platform that correlates volumes of data and information. Management support system is a decision-making tool that facilitates organizational operations. The architecture assists managers to understand, manage, organize, redistribute, and decide business processes. Management decision support system is not a decision model, but an aggregate component that supports business models and risk management. Decision support can be described as a technical skill that facilitates an individual’s activity. Thus, decision support facilitates the decision-making process of an individual or organization. Productivity is a significant factor in a decision support system. Managers can forecast market or policy trends from a resource pool on the server database.
The organization of different support systems is called decision management. Decision management systems have been incorporated into business marketing, health institutions, military, catering, environmental waste management and engineering. The benefits of decision management system outweigh economic and financial status. Finally, the decision support systems can be used to analyze, organize, and manage various organizational challenges. However, we must apply distinct user interface when analyzing specific problems.
Bibliography
Callon, J.D., Competitive advantage through information technology, 6th edn, McGraw-Hill, Higher Education, Melbourne, 2006.
Laudon, J.P., & Laudon, K.C., Management information systems: managing the digital firm, 10th edn, Prentice Hall, New York, 2007.
Martin, E.W. et al., Managing information technology, 5th edn, Prentice Hall, New York, 2005.
McNurlin, B.C., & Sprague, R.H., Information systems management in practice, 7th edn, Prentice Hall, New York, 2005.
O’Leary, D.E., Decision support system evolution: Predicting, facilitating and managing knowledge evolution, Macmillan Press, Los Angeles, 2012.
Turban, E. et al., Information technology for management: transforming organizations in the digital economy, Prentice Hall, New York, 2005.
