Executive Summary
The pandemic caused the oil cost reduction, affecting Kuwait’s total revenue during the past year. Although the government strives to balance the production and export of its natural resources, there was a 2% drop in this sector’s contribution to its GDP within one year. Since the global oil demand decreased during the pandemic, Kuwait had to diminish its crude oil production in 2020 to adjust the budget for lower prices and income. The overall situation suggests that the government should develop other non-oil sectors to make the state’s economy more independent from price changes in the global oil market.
Introduction
The present report investigates the effect of an oil price decrease on the economy of the State of Kuwait. The report aims to show that this phenomenon has an overall negative impact on the country’s revenue in the long term. Another goal is to specifically explore various business sectors that may be affected by the drop in oil cost. In particular, the report attempts to answer the following questions:
- Question one: What percent of revenue drop occurs in case of a decrease in oil prices?
- Question two: What factors contribute to the revenue drop?
The report comprises three main sections: background, analysis, and conclusion. First, the background section discusses historical and modern examples of oil price fluctuation and its influence on Kuwait’s development. Then, the analysis section presents the data from three sources regarding two aspects of the topic at hand, such as the effect of an oil price increase and decrease. The report ends with conclusions from the analysis and recommendations on adjusting the country’s economy to rely less on the price of its natural resources.
Background
Natural gas and crude oil are two primary resources contributing to Kuwait’s growth domestic product (GDP). The economy of the countries in the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC) is heavily dependent on the price fluctuations that occur in the global oil market (Vohra, 2017). Kuwait and other GCC members benefited from the increase in the cost of crude oil in the early 2000s, but these states were affected by the price drop in 2008 (Vohra, 2017). The rise in oil prices has an overall positive effect on the economies that rely on it. On the other hand, the drop in oil cost diminishes the revenue of countries like Kuwait, but this negative impact can be minimized due to the high demand. This country’s economy seems strong enough to tolerate an extended period of low oil prices.
Analysis
Kuwait is the country that mainly produces and sells oil and gas, making its economy significantly dependent on these resources. Kuwait’s government strives to balance oil and gas production, export, and consumption (Central Statistical Bureau [CSB], 2020). Therefore, this country is one of the leading producers and exporters of crude oil and natural gas for a relatively low production cost (Kisswani & Elian, 2017). Figure 1 demonstrates that the amount of natural gas produced in Kuwait from 2016 to 2020 remained approximately the same (CSB, 2020). However, crude oil production slightly reduced in 2020 compared to the preceding years since the pandemic caused the decrease in demand, causing the price drop (Figure 2). According to Vohra (2017), “low oil prices have undoubtedly left the GCC nations with budget problems” (p. 12). When a similar situation happened in 2008, Kuwait and other GCC members had to cut their public expenses to balance the budget (Vohra, 2017). It suggests the country’s economy demands changes because social welfare is one of the essential fields that should not suffer from the unipolar direction of the economy.
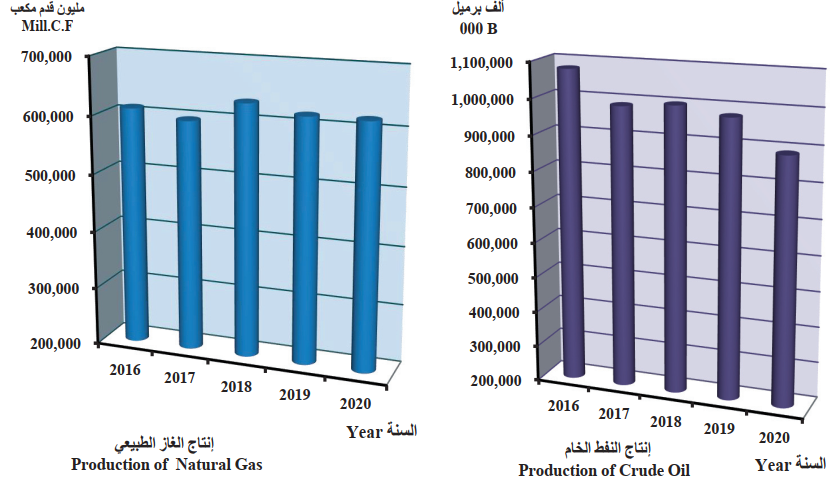
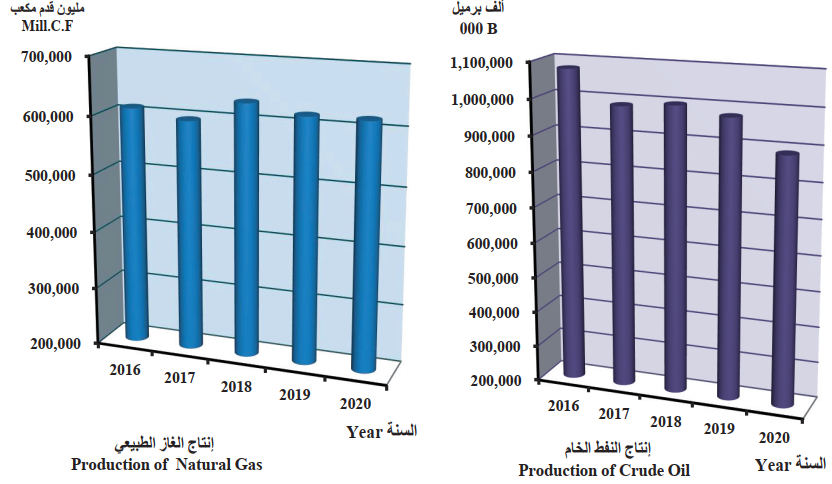
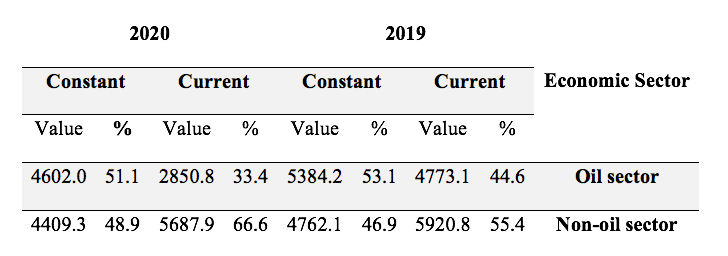
The ongoing COVID-19 crisis significantly affected various sectors of the global economy. Since international transit and transport were limited at the beginning of the pandemic, it caused a decline in oil demand, resulting in lower prices and production. For instance, the oil and gas contribution to Kuwait’s GDP declined from 53% in 2019 to 51% in 2020 (Table 1). Furthermore, Table 1 shows that the quarterly percentage of the oil sector in the country’s GDP also significantly decreased from 44.6% in 2019 to 33.4% in 2020 (CSB, 2021). The crisis also affected the non-oil sector, but it does not represent the most significant portion of Kuwait’s economy, so its effect was less dramatic.
Table 1: Percentage Distribution of Quarterly GDP in Oil and Non-Oil Sector (CSB, 2021)
Conclusion and Recommendations
In summary, the oil price drop decreased Kuwait’s revenue primarily because its development heavily depends on oil and gas production and export. The overall long-term impact of this situation on the country’s GDP was negative at all times because it requires significant frugality that damages the public sector. Thus, Kuwait’s government should try to diversify the economy by encouraging the growth of other sectors, opening new employment opportunities, and investing in the population’s education. Moreover, creating more jobs will allow maintaining the social and political stability of the state. In fact, these measures will not only make the country more resilient to the oil market disturbances but will also attract foreign investors to develop other non-petroleum fields.
References
Central Statistical Bureau. (2020). Annual statistical abstract, 2020-2019 (54th ed.). Web.
Central Statistical Bureau. (2021). Estimates of quarterly gross domestic product at current and constant prices. Web.
Faheem, M., Azali, M., Chin, L., & Mazlan, N. S. (2020). Asymmetric effect of oil price changes on trade balance in Saudi Arabia, Kuwait, and United Arab Emirates. Pakistan Journal of Commerce and Social Sciences, 14(3), 685-714.
Kisswani, K. M., & Elian, M. I. (2017). Exploring the nexus between oil prices and sectoral stock prices: Nonlinear evidence from Kuwait stock exchange. Cogent Economics & Finance, 5(1), 1-17. Web.
Vohra, R. (2017). The impact of oil prices on GCC economies. International Journal of Business and social science, 8(2), 7-14.
