Introduction
Technology and trade are inextricably linked in today’s networked globe, influencing international Trade. This essay investigates the complex interrelationships between commerce and technology, looking at how developments in the field have transformed economic competitiveness, altered market dynamics, and changed trade practices. Technology advancements have radically changed how firms do business, from the introduction of the Internet to the emergence of digital platforms and automation (Sturgeon 2021). This essay seeks to clarify the changing relationship between commerce and technology and the ramifications for many stakeholders in different sectors and regions by analyzing significant trends, obstacles, and possibilities.
The Development of Trade and Technology
Historical Background
Commerce has consistently increased with the help of technological advancements. Long-distance transportation and navigation were made more accessible by the invention of the wheel, the compass, and shipbuilding methods, all of which significantly enhanced commerce between ancient cultures (Kelly et al., 2021). The 18th and 19th centuries Industrial Revolution marked a turning point in economic growth by bringing mass production and industrialization (Zeidan, 2021). Significantly increasing trade volumes, these innovations altered industrial processes. Innovations like the steam engine, automated looms, and railroads significantly lowered transport times and production costs. The basis of the global economy was laid during this time by the unparalleled growth of both local and international Trade. The influence of technology on trade growth and economic progress is considerable, as demonstrated by these historical advances.
The Digital Era
The late 20th and early 21st centuries saw the emergence of the Information Age, characterized by fast advancements in information and communication technologies (ICT). The Internet, digitalization, and mobile technologies have changed how firms operate and conduct business. The emergence of digital payment systems, global supply chains, and e-commerce platforms that facilitate quicker, more transparent, and practical trading is directly related to these technical advancements (Putrevu & Mertzanis, 2023). Big data analytics and cloud computing have further transformed corporate operations by enabling better consumer experiences and real-time decision-making. Furthermore, digital marketing and social media have created new channels for accessing international markets. These advances have streamed conventional trade procedures and produced new company prospects and models.
Utilizing Technology to Promote Trade
Greater Efficiency and Productivity
Technological advancements significantly increase the productivity and capacity of industrial operations. Automation, robotics, and artificial intelligence (AI) are innovations that lower production costs while boosting productivity and enhancing product quality. Because of these developments, the worldwide market has become more competitive, propelling commerce growth. For instance, businesses may manufacture complex, high-quality products at lower costs because of new production techniques, which makes their products more appealing to consumers abroad (Putrevu & Mertzanis, 2023). By enabling accurate and scalable manufacturing, advanced technologies help businesses satisfy customer needs and stay competitive. Greater market reach and more worldwide trade prospects result from this greater competitiveness.
Reducing Barriers to Trade
Technology reduces costs and logistical challenges to cut trade barriers dramatically. Digital platforms provide global linkages between buyers and sellers, providing small and medium-sized businesses—which may otherwise find it challenging to penetrate international Trade—with access to overseas marketplaces. Additionally, blockchain technology improves transaction security and transparency, which reduces the possibility of fraud and fosters confidence between business partners (Meyer et al., 2023). Automated border and customs administration systems speed up the passage of products, cutting down on related expenses and delays. These technical technologies improve the efficiency and seamlessness of cross-border transactions by streamlining trade procedures.
Facilitating Global Supply Chains
Technological developments have had a profound impact on global supply networks. The Internet of Things (IoT) enables sophisticated logistics and tracking systems that give real-time data on commodity movement, improving transparency and control throughout the supply chain. Due to this technical visibility, firms can expedite their processes, cut down on delays, and quickly adapt to changes in the market. Inventory control and forecasting are further optimized by automation and AI-driven analytics (Meyer et al., 2023). The efficiency of these global supply networks is essential to international Trade because it ensures the dependable and timely cross-border delivery of commodities. Increased customer satisfaction and competitiveness in the global market are two benefits of improved supply chain efficiency and cost savings.
Trade’s Contribution to Technological Advancement
Obtaining New Markets and Resources
Technology advances significantly due to Trade, which introduces companies to new markets and resources. Companies are incentivized to develop novel goods that cater to different client preferences and regulatory needs by having access to various markets. This exposure to many markets inspires innovative ideas and product development, promoting an innovative culture (Meyer et al., 2023). Furthermore, access to raw materials and intermediary commodities that might not be available locally is made possible by international commerce. Companies may experiment with new materials and procedures, improving their production capacities and maintaining their competitiveness in the global market, thanks to this access, which is crucial for innovation in manufacturing methods and technical breakthroughs.
Originality and Competition
International commerce exposes businesses to global competition, which greatly encourages innovation. Businesses spend much on research and development (R&D) to improve their goods and processes and stay competitive. Making this investment is essential to be competitive in a global market where customer preferences are changing, and technology is advancing quickly (Insee & Suttipun, 2023). This worldwide competition creates a competitive strain that propels technological advancement, resulting in the development of new technologies and the ongoing enhancement of preexisting ones. Businesses speed up innovation as they try to beat their international competitors. Therefore, the state of international commerce directly affects the competition among enterprises for technology, creating a climate in which success and survival depend on constant innovation.
The Role of Law and Governance in Technology and Trade
Trade Policies and Agreements
Governments have a big say in how commerce and technology interact through agreements and legislation. Technology and innovation sharing is greatly aided by trade agreements like the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) and the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA), which reduce tariffs and promote collaboration (Insee & Suttipun, 2023). These agreements assist in removing obstacles that could otherwise prevent the interchange of technology developments by improving trade circumstances. Furthermore, protecting intellectual property (IP) requires rules vital to innovation. These laws support technological advancements that boost Trade and stimulate economic growth by upholding artists’ rights and guaranteeing the legal protection of their innovations. This structure of rules and agreements produces a stable and predictable environment, which promotes global Trade and technical cooperation.
Innovation and Industrial Policies
Government programs that support innovation and industrial growth greatly impact how technology and business interact. Subsidies, tax exemptions, and R&D grants all contribute to the advancement of technology by encouraging businesses to make innovative investments. Furthermore, new trade opportunities are produced by industrial policies supporting advancing cutting-edge technologies like biotechnology and renewable energy (Insee & Suttipun, 2023). Governments raise their countries’ competitiveness in the global market by fostering an atmosphere that encourages innovation. Strategic investments in workforce development, education, and research infrastructure further strengthen the innovation ecosystem, which promotes economic growth and trade expansion.
Trade-Technology Relationship: Opportunities and Difficulties
The Digital Divide and Inequality
The digital gap severely challenges the relationship between Trade and technology. Poor infrastructure and limited technological access sometimes cause developing countries to lag behind developed ones, even while advanced economies benefit from technological developments. This disparity has the potential to worsen economic inequality and obstruct the growth of equitable international trade (Insee & Suttipun, 2023). Two things that need to be done are reducing the digital gap and ensuring that every country can benefit from technological advancements and international Trade. In addition to financial improvements in infrastructure, closing this gap would need regulatory changes and educational programs that promote fair access to digital resources and chances for economic engagement.
Cybersecurity and Data Privacy
As Trade increasingly moves toward digital platforms, worries about cybersecurity and data privacy are intensifying. Data leaks and cyberattacks can potentially sabotage Trade and undermine trust amongst business partners. Protecting personal information and putting strong cybersecurity measures in place is essential to ensuring international trade integrity and smooth functioning (Alanazi, 2023). Cooperation and international standards are crucial to a safe digital trading environment. Stakeholders may reduce risks and increase confidence in digital trade transactions by proactively resolving these issues, enabling seamless and safe international trade interactions.
Sustainability and Ecological Impact
The combination of technology and business brings up significant environmental and sustainability concerns. Although technology may lead to increased resource consumption and pollution, it can also increase productivity and decrease the environmental effect of business. While fostering economic growth, adopting sustainable behaviors and utilizing technical advancements can reduce adverse ecological effects. To ensure that commerce contributes to long-term economic development and environmental well-being, it is imperative to balance environmental sustainability and technological innovation (Alanazi, 2023). To preserve the condition of our planet for future generations, governments, corporations, and individuals must work together to create and implement policies prioritizing sustainability in Trade and technological advancement.
Research Studies
The Growth of E-Commerce in China
China has become a significant player in the global e-commerce sector because of its quick technical improvements. The nation’s adoption of cutting-edge technology, including blockchain, big data, and artificial intelligence (AI), has improved operational efficiency and user experience on critical platforms like JD.com and Alibaba (Figure 1) (Falcone et al., 2019). Many customers and businesses are drawn to these technologies because they provide safe transactions, customized shopping experiences, and effective supply chain management.
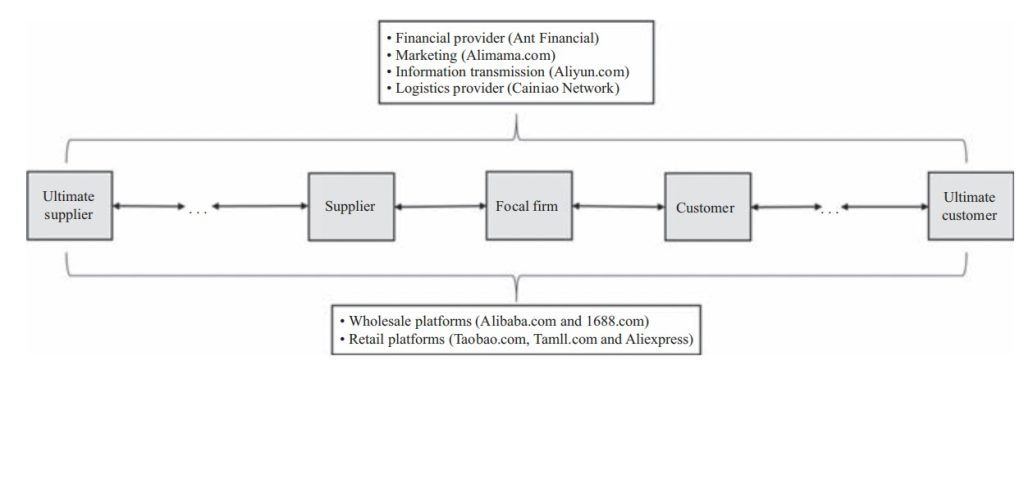
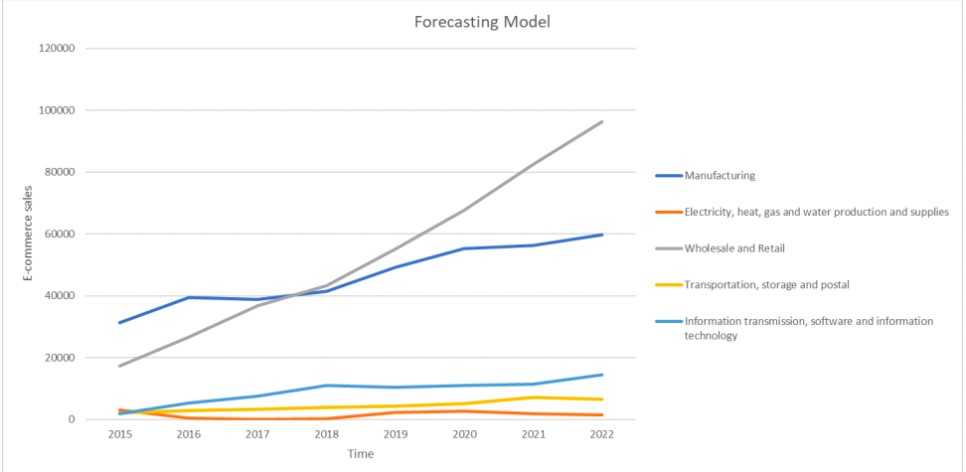
This development has been made possible mainly by the Chinese government’s encouraging policies and calculated investments in the infrastructure of information and communication technologies. Policies like the “Internet Plus” plan and significant investments in tech firms have created a favorable climate for the expansion of e-commerce (Lukács et al., 2022). The industry’s vitality has also been aided by the growth of high-speed Internet, ubiquitous mobile connection, and logistics network advances, making online transactions and delivery easier. China’s ascent in the e-commerce sector aptly illustrates the advantageous relationship between Trade and technology. Furthermore, Figure 2 illustrates that the wholesale and retail sector is seeing a more rapid growth compared to the manufacturing business. By 2022, the e-commerce income of the wholesale and retail business is projected to surpass RMB 10,000 billion (Li & Zhou, 2023). These findings indicate that the wholesale and retail business will see a growing share in the future due to the advancement of e-commerce. This synergy illustrates how a country may become a global trade leader by adopting innovative technologies and supportive policies.
The German Industry 4.0 Project
The German initiative known as Industry 4.0 perfectly illustrates how technological innovation may stimulate business. Germany has expanded its export markets and significantly improved its industrial competitiveness globally by assiduously integrating cyber-physical systems, artificial intelligence (AI), and the Internet of Things (IoT) into its manufacturing processes (Rainnie et al., 2020). The project highlights the need for well-thought-out plans and robust governmental backing when utilizing technology to enhance Trade. Germany is a role model for nations hoping to leverage Industry 4.0 to drive trade and economic growth because of its proactive embrace of cutting-edge technology and promotion of industry-government cooperation.
India’s Software and IT Export Explosion
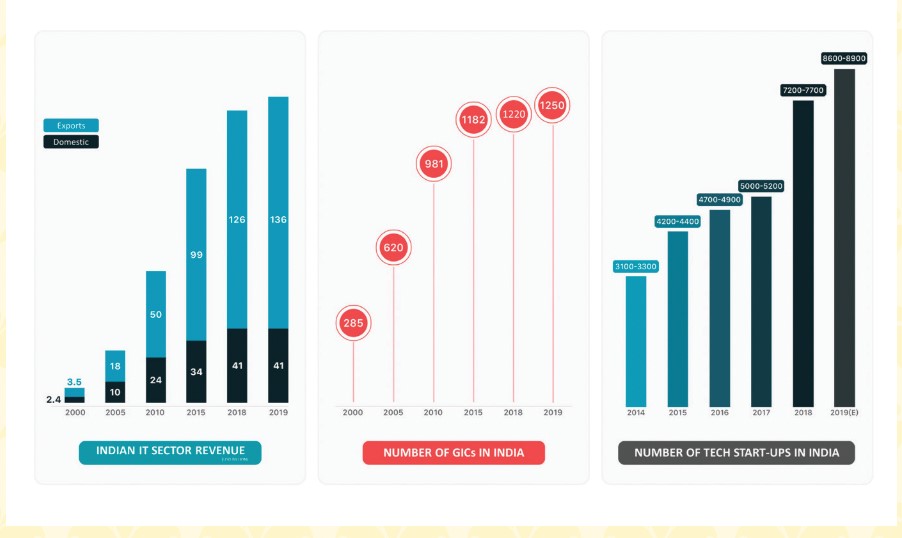
India’s IT and software services industry has become a significant factor in its economy and foreign commerce. By utilizing ICT breakthroughs, businesses like Infosys and Tata Consultancy Services (TCS) have emerged as global leaders, providing clients with state-of-the-art solutions (Deshpande 2021). This accomplishment emphasizes how important it is for governments to have policies that support the relationship between commerce and technology. India’s success in the IT sector may largely be attributed to initiatives supporting infrastructure development and IT education (Figure 3) (Jalote & Natarajan, 2019). These policies have catapulted India to the forefront of the global IT services sector, boosting economic growth and international commerce by fostering an atmosphere conducive to technical innovation and entrepreneurial spirit.
Outlook and Trends
Advancements in Technology
The continuous development of new technologies will significantly influence technology and commerce in the future. AI, blockchain technology, and quantum computing have the power to dramatically change international trade by fostering productivity, security, and creativity. Blockchain can streamline supply chains, lower fraud, and increase transaction transparency and trust (Figure 4) (Afrin & Pathak, 2023). Quantum computing has the potential to completely transform our ability to solve problems by improving data analysis and complicated logistics in ways that were previously unthinkable. By streamlining operations and customizing consumer experiences, AI may streamline workflows, enhance decision-making via predictive analytics, and create new business opportunities.
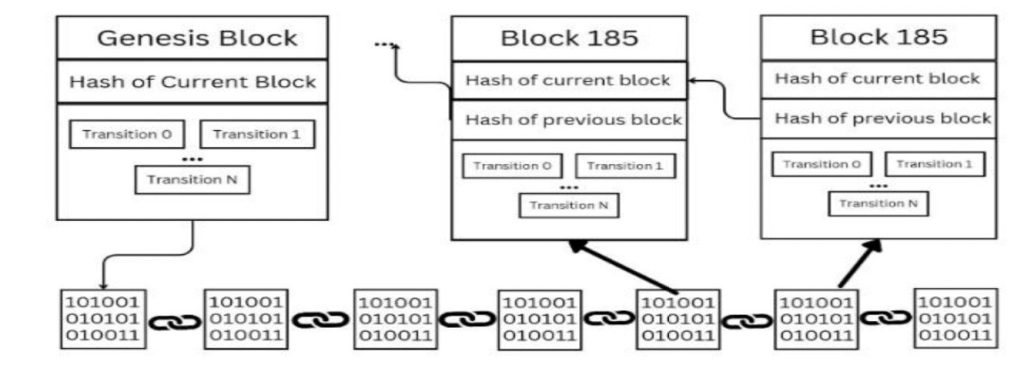
These technologies provide unseen opportunities to improve decision-making, streamline processes, and create new commercial opportunities. For nations and companies hoping to stay competitive in the global economy, staying up to date with these advancements will be essential (Jaiswal et al., 2022). Countries prioritizing skill development, infrastructure, and education will be better positioned to exploit these developments. Likewise, companies investing in state-of-the-art technology and cultivating an innovative culture will be leaders in their respective fields. It will be crucial to embrace innovation and devote significant resources to research and development to fully realize the potential of emerging technologies and support future trade and commerce expansion. Governments, academic institutions, and the commercial sector must work together to foster an environment that encourages technology developments and their incorporation into frameworks for international commerce.
Regional Integration and Trade Blocs
Trade blocs and regional integration will continue to impact the relationship between business and technology significantly. Programs like the African Continental Free Trade Area (AfCFTA) are designed to lower tariffs and promote cooperation among member nations to increase intra-African Trade (Ndonga et al., 2020). These initiatives can encourage regional economic growth and development by promoting the sharing of technology, expertise, and innovative ideas. Regional blocs that are more connected and collaborate provide synergies that double the advantages of technology improvements and spur innovation and competitiveness. In the coming years, commerce blocs will play a more significant role in influencing the interaction between technology and Trade as nations understand the benefits of regional integration.
Inclusive and Sustainable Trade
In order to create a more robust and just global economic system, future commerce must prioritize sustainability and inclusiveness. It is essential to close the digital divide, ensure cybersecurity, and adopt sustainable practices. Policies and initiatives that promote technology transfer, capacity building, and environmental sustainability will be crucial to achieving these goals (Corsi et al., 2020). Countries can close the digital divide and provide excluded populations more influence by guaranteeing fair technological access and encouraging digital literacy. In an increasingly linked world, strong cybersecurity measures are required to defend against cyberattacks and secure critical data. Furthermore, sustainable practices are essential for preventing environmental deterioration and fostering long-term economic resilience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Trade and technology have much in common and are advantageous. Technological developments promote commerce by improving supply networks, lowering obstacles, and increasing productivity. Automation and artificial intelligence, for example, increase productivity and lower manufacturing costs, increasing the competitiveness of products on the international market. In addition, Trade stimulates innovation by introducing businesses to fresh markets and rivalry, forcing them to make R&D investments to maintain their competitive edge. In order to solve issues, take advantage of opportunities, and establish this connection, government policies and international collaboration are essential. Making the most of Trade and technical synergies will be essential to attaining sustainable and equitable global economic development as the globe changes.
References
Afrin, N., & Pathak, A. (2023). Blockchain-powered security and transparency in supply chain: exploring traceability and authenticity through smart contracts. International Journal of Computer Applications, 85(49), 5–15.
Alanazi, A. (2023). Clinicians’ perspectives on healthcare cybersecurity and cyber threats. Cureus, 15(10).
Corsi, A., Pagani, R. N., & Kovaleski, J. L. (2020). Technology transfer for sustainable development: Social impacts depicted and some other answers to a few questions. Journal of Cleaner Production, 245, 118522.
Deshpande, V. (2021). Innovations and innovative practices in start-up it companies in Pune. Ashok Yakkaldevi.
Falcone, E., Kent, J., & Fugate, B. (2019). Supply chain technologies, interorganizational network and firm performance. International Journal of Physical Distribution & Logistics Management, 50(3), 333–354.
Farboodi, M., Jarosch, G., & Shimer, R. (2023). The emergence of market structure. The Review of Economic Studies, 90(1), 261-292.
Insee, K., & Suttipun, M. (2023). R&D spending, competitive advantage, and firm performance in Thailand. Cogent Business & Management, 10(2).
Jaiswal, A., Arun, C. J., & Varma, A. (2022). Rebooting employees: Upskilling for artificial intelligence in multinational corporations. The International Journal of Human Resource Management, 33(6), 1179-1208.
Jalote, P., & Natarajan, P. (2019). The growth and evolution of India’s software industry. Communications of the ACM, 62(11), 64–69.
Kelly, M., Gráda, C. Ó., & Solar, P. M. (2021). Safety at sea during the Industrial Revolution. The Journal of Economic History, 81(1), 239-275.
Li, Z., & Zhou, W. (2023). Research the impact of e-commerce on China’s Economy. Advances in Economics, Management and Political Sciences, 37(1), 211–218.
Lukács, E., Völgyi, K., Kovács, N., & Tóth, Á. (2022). American versus domestic digital companies in the Chinese market. Decision Making: Applications in Management and Engineering, 5(2), 120-139.
Meyer, K. E., Li, J., Brouthers, K. D., & Jean, R.-J. ‘‘Bryan’’. (2023). International business in the digital age: Global strategies in a world of national institutions. Journal of International Business Studies, 54(4), 577–598. Ncbi.
Ndonga, D., Laryea, E., & Chaponda, M. (2020). Assessing the potential impact of the African continental free trade area on least developed countries: A case study of Malawi. Journal of Southern African Studies, 46(4), 773-792.
Putrevu, J., & Mertzanis, C. (2023). The adoption of digital payments in emerging economies: challenges and policy responses. Digital Policy, Regulation and Governance.
Rainnie, A., & Dean, M. (2020). Industry 4.0 and the future of quality work in the global digital economy. Labour & Industry: a journal of work’s social and economic relations, 30(1), 16-33.
Sturgeon, T. J. (2021). We are upgrading strategies for the digital economy. Global Strategy Journal, 11(1), 34-57.
Zeidan, A. (2021). Industrial revolution. In Encyclopedia Britannica. Britannica.
