Introduction
The market often poses several challenges that a firm must know how to deal with to remain competitive in the market. Enterprise risk management has become a critical part of management as firms struggle to find ways of managing the challenges they face in their normal operations (Marchetti 2012). As Monahan (2008) says, it is only those firms that can manage the risks they face that can achieve success in the current turbulent market.
Apple Inc., one of the most successful technology firms in the global market, can only continue registering great performance if its management is capable of identifying and managing risks both in the internal and external environment. Timely and effective management of these risks is what differentiates successful firms from ordinary firms. In this paper, the researcher will look at the risks that Apple Inc. faces and how it can overcome these risks to remain competitive in the global market.
Aims of the Organisation
Apple Inc. is a multinational technology company that offers a wide variety of products (O’Grady 2009). The firm in 1976 and has experienced massive success in the market over the years despite the challenges that exist in both its internal and external environment. The company aims and objectives are clearly outlined in its vision, mission, and value statements.
According to Lashinsky (2012, p. 67), “the aim of Apple Inc. is to produce high-quality, low cost, easy to use products that incorporate high technology for the individual.” Achieving this aim requires a deep understanding of the environmental forces that may act against the firm. The management must realise that these forces cannot be ignored because they have the potential of crippling the operations of this company.
Apple Inc. faced serious challenges in the late 1980s and early 1990s especially on the issue of designs of the personal computers and cost of manufacturing. Its products became less popular because of poor workmanship in design and development (Marchetti, 2012). After making attempts to find better ways of addressing these problems, the board of directors decided to bring back jobs in 1997.
Identified Threats and Opportunities
Threats
The top management unit of this firm must have effective strategies for dealing with these two categories of threats.
External threats
The external business environment poses serious risks to this firm that may threaten its very existence in the market. The main risk that Apple Inc. faces in the global market today is stiff competition (Gillam 2012). Samsung is currently the biggest rival that Apple Inc. has to deal with in the market because of most of the similarity of the products that both firms offer. Other major competitors in the market include Google, Microsoft, HP, Dell, and Toshiba among a host of other companies (Stoelsnesa 2007).
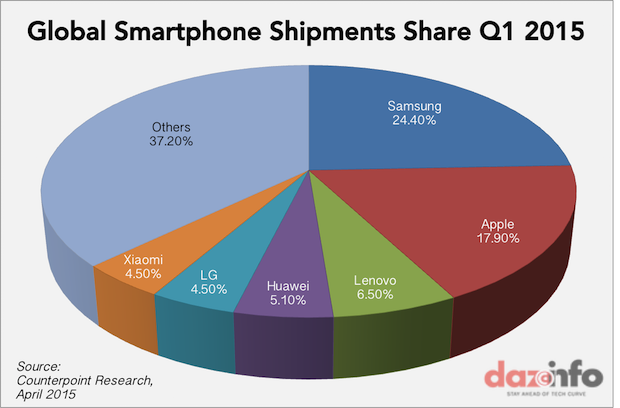
Managing the stiff market competition can help define the ability of this firm to achieve success as it tries to expand its market share. Other new firms such as Tecno and Huawei are also emerging and they offer similar products in the market (Girling 2013). Some of these firms may consider entering the American and European markets which means that competition is expected to stiffen shortly. The figure in appendix 1 shows that Samsung has already outsmarted Apple Inc. in the smartphone market.
Counterfeiting is another major threat that Apple Inc. is facing, especially in the global market. The United States is the main market for this firm’s products. However, the management has been trying to expand its market share by trying to capture the global market. Its operation in the global market has often been affected by the existence of some counterfeit products, especially from some unscrupulous Chinese firms (Conrow 2003). These counterfeits not only deny this firm the revenue it deserves but also affects the brand strength in the market.
Clients who are unlucky enough to purchase these counterfeits get dissatisfied and lose trust with the brand not knowing that what was sold to them was a counterfeit product. As Bach (2007) says, dealing with counterfeited products in some countries is very challenging because of the ambiguous laws which are often not properly enforced. Counterfeiting has been one of the main factors that have made it difficult for this company to successfully launch its products in some of the emerging markets in parts of Asia and Africa. The fear of having counterfeit products in these markets has made the firm to forfeit the profits that would be generated in these new markets.
Apple Inc. has positioned itself as a technology firm that is a major driver of change in the global market. Its performance in coming up with new products has been very impressive. However, these emerging technologies are a threat to this firm despite its ability to adapt them as quickly as possible. The firm is often forced to spend a lot of money to remain innovative in the market. A large amount of its revenues is set aside for research and development to help it come up with new products and production methods.
Sometimes it forces the firm to sacrifice developmental projects to focus on new product and production methods. According to King, Lu, and Pastén (2008), spending on innovation and new product development is important for a firm that seeks to achieve success in the modern market. However, it becomes problematic if the firm considers it the only way of overcoming market competition. Currently, it seems this is the main approach that Apple Inc. is using to manage the stiff market competition (Olson & Wu 2010).
The problem with this strategy is that a firm ends up spending a lot in research as the pioneer of the new technology. As Marchetti (2012) says, as an innovator, a firm gets to enjoy the benefits of being the first to invent a given concept, but it has to meet the associated costs. When using this strategy, this firm should emphasize idea screening to lower the associated costs.
The current emergence of constant terror attacks is another major issue that Apple may have to deal with shortly. The firm has not faced any form of attack from these terrorists and is not considered as one of their targets. However, future patterns of the attack remain unclear. ISIS, unlike Al Qaeda, is very aggressive and calculative in its attacks. It has been successful in recruiting people from all over the world to execute its attacks. It is not clear how this terror group identifies its targets.
However, some of its attacks have proven devastating. The management of this company must realise that being one of the United States’ most prosperous and admired firm, it may be a primary target of ISIS as the group increases its attack on Western nations. They may consider an attack of this company a sign that they have the potential of shaking the nation, just like Al Qaeda did about fifteen years ago. The attack may not necessarily be a physical one using guns and bombs. A cyber-attack is a very probably approach that they may use to bring down this giant firm.
Internal threats
As this company tries to deal with external threats, the management must be aware that some threats may emerge from its internal operations. One of the main internal threats that this firm faces in the market today is the loss of a highly-skilled workforce to rival companies in the market. Although the rate of employee turnover at the firm is relatively low, the firm has lost several talented employees to top technology firms like Google Inc. and Microsoft Corporation. As Sadgrove (2005) notes, training employees and equipping them with the necessary experience takes a lot of time and resources.
When they are lost, the firm not only loses an employee but also all the resources that had been used to equip him or her. Tim Cook, the current chief executive officer at Apple Inc., has successfully galvanised leadership at the firm and provided a sense of direction to the firm. However, there is the fear that at one point leadership wrangles may become an issue, especially during successions. During such delicate times, the top executives may struggle to get to the top spot. Such struggles may compromise the internal environment of the firm.
Loyalty is one of the most important qualities that employees of a firm should have, especially when dealing with a highly competitive technology-based industry. In this industry, the threat of stealing designs and other copyrights is real and very dangerous given the time and investment involved. Given that employees of this company are often trusted with these designs if they are not loyal enough then they can sell such designs to rival firms. Apple Inc. has not faced this problem before, but it is a real threat that cannot be ignored. Das (2006) warns that such a problem may arise when employees start feeling that they are not treated with respect as they desire. Such disgruntled employees may easily be used by the rival companies to bring down this firm in various ways.
Opportunities
In the above section, the researcher has identified some of the very likely threats that this company faces both in its internal and external environment. It is important to look at some of the opportunities that this firm may take advantage of in the current turbulent market. According to Khatta (2008), electronic firms such as Apple Inc. have a great opportunity to tap into the global market because of the emerging economies. The emerging economies make it possible for the firm to increase its market share through globalisation.
The markets in South America, Africa, and parts of Asia offer this firm opportunity to expand its market share. The company can increase its revenues by ensuring that its products are available in these emerging markets. The technological advancements in the fields of transport and communication also benefit this firm. It offers its opportunity to manage its overseas branches with ease and to coordinate its activities more effectively. Its products can also reach the international market with ease.
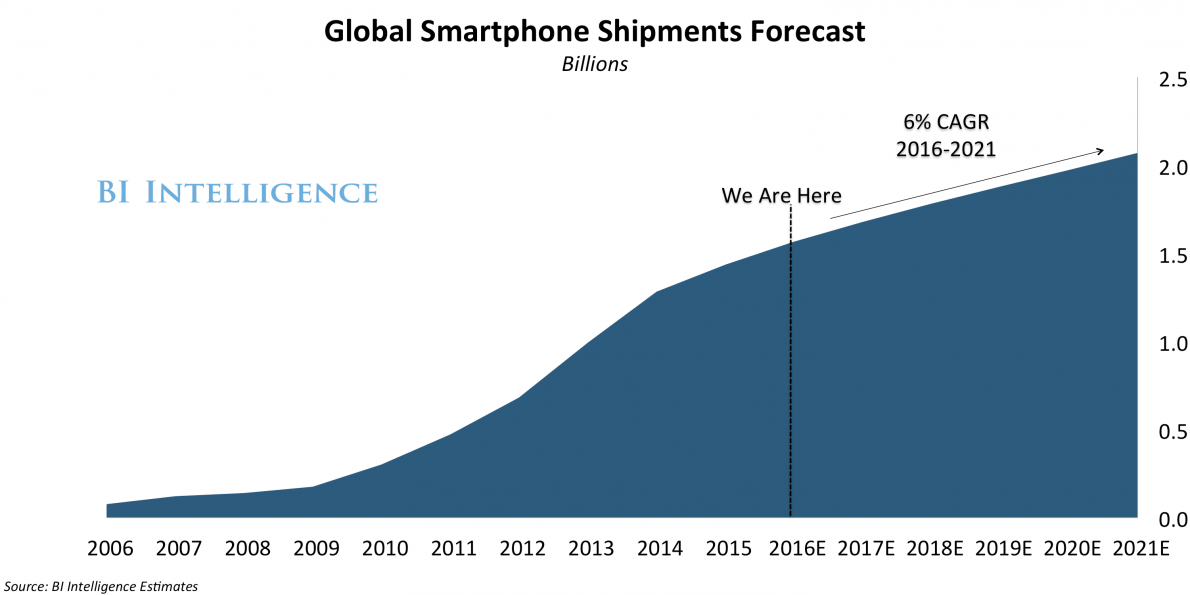
The growing economy in the United States, especially after the 2008 economic recession, has helped in improving the local market’s purchasing power. More people can afford high-quality Apple brand products. This would translate to increased revenues generated within the country. Other major markets where this firm currently operates such as Europe, China, and Japan have also registered impressive economic growth over the recent past. The figure in appendix 2 shows the forecast for the growth of the smartphone market within the next five years based on records.
The management of Apple Inc. will need appropriate strategies that will enable it to take advantage of the expected market growth in the coming years.
Existing Controls
The management of Apple Inc. has come up with several strategies to help deal with some of the threats identified in the section above. To deal with the threat of stiff competition in the global market, the top management unit of the firm has decided to introduce innovation both in production and marketing of its products.
The company uses some of the latest production equipment to ensure that its products are of high quality and produced at the lowest cost possible. In terms of marketing, Apple Inc. has embraced social media marketing as a way of boosting its sales. It has not stopped using mass media marketing, but more focus is now put on social media marketing where the firm can reach out to its clients in a simplified manner. These innovative strategies have helped this firm to strengthen its brand in the local and international market. Its strong brand gives it a competitive edge over its market rivals. A study by Lüsted (2012) shows that Apple is the most trusted brand in the electronic market for its top quality products.
According to Wagner (2009), the management of Apple Inc. is greatly concerned with the threat of counterfeit products. The management often patents all its designs to legally prohibit any firm in any part of the world from copying them. Currently, the emerging markets of Africa and parts of Asia form the major market for the counterfeited products although most of these products are manufactured in China. Currently, Apple has avoided some markets because of the problem of counterfeiting. The management is trying to come up with measures beyond patenting to help it deal with the problem of counterfeiting.
Apple Inc. is one of the firms with a unique capacity to retain its most important employees. According to a report by Linzmayer (2004), this company has one of the lowest rates of employee turnover in the recent past. The management is keen to ensure that its human resource remains highly productive and motivated. At this firm, employees are allowed to participate in top decision-making processes, especially if the decisions will affect them or their places of work. The firm believes in embracing innovations driven by its employees. It offers these employees a platform where they can think beyond the obvious and come up with a unique solution to the existing problems (Gillam 2012).
As such, these employees feel highly valued by the management. They feel they are part of this successful company other than just being mere employees. Besides the attractive remunerations offered to them, this firm also takes care of the social needs of its workforce such as paying part of their social security benefits among others. Its commitment towards its human resource has not only reduced the rate of employee turnover. It has also increased loyalty among the employees because they feel betraying the firm is like betraying themselves.
Calculation of Risk and Risk Threshold
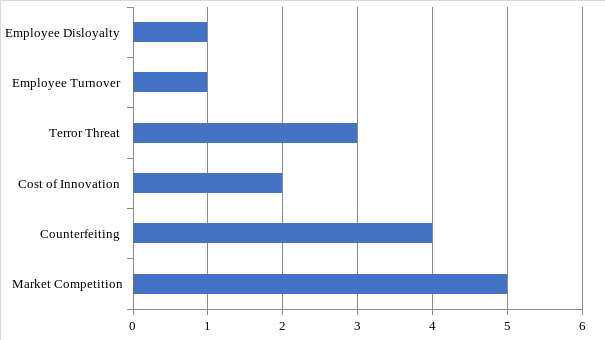
In the section above, the researcher has identified the major threats that Apple Inc. faces in the global electronic market. Each of these risks has a varying magnitude in terms of their impact on the normal operations of this company. Calculating the risk threshold helps in determining their significance and how urgent the management needs to focus on addressing them. Basing the threats on a scale of 1-5 (where 1 means least consequential and 5 mean most consequential), the tables in appendix 3 and 4 were generated.
As shown in the above scale, external threats are more severe and will need to be addressed as soon as possible to ensure that they do not affect the operations of this company negatively. Stiff market competition tops the list of external threats that Apple Inc. currently faces. It is known that Samsung has already overtaken Apple Inc. in the smartphone market.
For a long time, Apple dominated this market following its invention of the iPad and iPhone. However, Samsung came up with very similar products which were available at relatively low prices compared to what Apple was offering. This made it easy for Samsung to enter the United States’ market and other global markets all over the world. Competition forced Apple Inc. to relocate its production plant from the United States to China in its attempt to cut down the cost of operations. As mentioned in the section above, the current trend shows that market competition will get even stronger as some new firms emerge locally and in the international markets.
Counterfeiting and stealing of copyrighted designs is another significant threat in the external market. Apple Inc. and Samsung Corporation have been held in long court battles over issues of abuse of copyrighted designs. Apple has accused Samsung of stealing some of its designs. The problem of counterfeiting has been a major concern in China. The existing copyright laws in China are not effective enough in protecting companies from theft of patented designs (Hampton 2009). It forces this company to avoid some markets because of the need to fight this vice. The firm is yet to come up with an effective way of addressing this problem.
The terror threat is real, though it is given the least considered by the firm at the moment. The trend taken by the terrorist’s’ groups shows that individual companies maybe their current targets. It happened in France when Charlie Hebdo was attacked by the terror group, leaving top editors at this firm dead. The attack was well planned and properly executed. If such attacks may continue, then this firm may be at risk of losing its valuable employees and assets. The risk is remote, but it is a possibility that should be taken seriously.
The cost of innovation has also been an issue, especially given the fact that sometimes the firm spends a lot to come up with a new invention only for the rivals to copy it at no cost. Innovation itself is strong, but the cost associated with it is an issue. The firm is still working on ways of ensuring that it may continue being innovative without posing any threat to its resources. Internal factors such as employee turnover and lack of loyalty among the employees are not posing any significant threat to this firm.
Mitigation Actions
Apple Inc. remains one of the top brands in the electronic market despite the stiff competition that it faces in the market (Girling 2013). The issues discussed above have the potential of slowing the growth of this company or even forcing it out of the market entirely. However, this firm can come up with measures that can help it deal with the threat in a very effective manner. The following are some of the possible mitigation actions that it can use to deal with each of the above-discussed threats.
Managing competition
Market competition is the main threat that this firm has to deal with based on the discussion above. To deal with this problem, the management should consider expending its product line. It should consider introducing low-cost products that can compete favourably with products from firms such as Samsung. The management should take advantage of its strong brand to diversify its product offering.
In so doing, Gillam (2012) advises that it should not compromise on quality. Like Samsung, it should consider massive production of other electronic products such as music systems, fridges, iron boxes, washing machines, among others. As Lüsted (2012) suggests, diversification can help it increase its revenues within its current markets.
Fighting counterfeit
Fighting counterfeit products is a big challenge that the firm is yet to find a way of fighting, especially in the global market. As a firm that offers high-quality products, Apple Inc. can open up speciality shops in markets outside the United States and Europe, especially in places where counterfeiting is rampant such as in China (Girling 2013). The firm can then warn its customers against purchasing products from outlets outside its speciality shops. In its adverts, it can explain to its clients where to purchase genuine Apple-branded products. The strategy may help discourage counterfeiting of the firm’s products (Lashinsky 2012).
Reducing the cost of innovation
The cost of innovation at this company is relatively high. To deal with this problem, the management may consider new approaches that will cost less (Marchetti 2012). For instance, the management may come up with a policy where new ideas are taken through a thorough screening to ensure that they are viable before investing a lot in them at advanced stages only to realise that they cannot apply to the firm.
Managing terror threat
Managing the threat of a terror attack is a major concern that is not only troubling this firm but also the entire country. To manage this threat, the firm may need to introduce a new security apparatus at its premises, especially its head office in California but also its production plants and major outlets. The employees should also be trained to respond to possible cases of terror attack (Shenkir & Walker 2007).
Improving employee loyalty and reducing their turnover rate
To improve employees’ loyalty and reduce their turnover rate, the management should come up with human resource management strategies which are engaging. Employees should be involved in decision-making processes. Girling (2013) says that they should be made to feel that they are respected and considered an important part of this company.
Conclusion
Risk management is currently one of the most important areas of management that firms are keen to focus on. Apple Inc., one of the leading American companies, faces numerous threats in the market that may have a significant impact on its operations. Stiff competition in the market, counterfeiting, terror attacks, employee turnover rates and employee loyalty are some of the issues that this firm will have to deal with to improve its competitiveness. Having effective ways of managing these threats may determine its ability to survive these forces.
Table 1: Apple Risk Register
List of References
Bach, B 2007, Implications of enabling technologies for Apple Inc: Cybermarketing & enabling technologies, GRIN Verlag GmbH, München.
Conrow, E 2003, Effective risk management: Some keys to success, American Institute of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Reston.
Das, S 2006, Risk management, Wiley, Hoboken.
Fraser, J & Simkins, B 2010, Enterprise risk management, Wiley, Hoboken.
Gillam, S 2012, Steve Jobs: Apple icon, ABDO Publishers, Minneapolis.
Girling, P 2013, Operational risk management: A complete guide to a successful operational risk framework, Wiley, Hoboken.
Hampton, J 2009, Fundamentals of enterprise risk management: How top companies assess risk, manage exposures, and seize opportunities, American Management Association, New York.
Khatta, R 2008, Risk management, Global India Publications, New Delhi.
King, R, Lu, Y & Pastén, E 2008, Managing Expectations, Journal of Money, Credit and Banking, vol. 40, no. 8, pp. 1625-1666.
Lashinsky, A 2012, Inside Apple: How America’s most admired-and secretive-company really works, Business Plus, New York.
Linzmayer, O 2004, Apple confidential 2.0: The definitive history of the world’s most colourful company, No Starch Press, San Francisco.
Lüsted, M 2012, Apple: The Company and its visionary founder, Steve Jobs, ABDO Pub, Minneapolis.
Marchetti, A 2012, Enterprise risk management best practices: From assessment to ongoing compliance, Wiley, Hoboken.
Monahan, G 2008, Enterprise risk management: A methodology for achieving strategic objectives, John Wiley & Sons, Hoboken.
O’Grady, J 2009, Apple Inc., Greenwood, Press Westport.
Olson, D & Wu, D 2010, Enterprise risk management models, Springer, Heidelberg.
Sadgrove, K 2005, The complete guide to business risk management, Ashgate Pub, Aldershot.
Shenkir, W & Walker, P 2007, Enterprise risk management, Tax Management, Washington.
Stoelsnesa, R 2007, Managing Unknowns in Projects, Risk Management, vol. 9, no. 4, pp. 271-280.
Wagner, K 2009, Apple talk network system overview, Addison-Wesley, Reading.
Appendices
Appendix 3: Risks scale rate