Business Models and strategies
Ecommerce refers to a business model where the activities of the business are conducted electronically via the internet. There are various types of eCommerce as indicated below:
Business -to- Business (B2B)
This type of eCommerce refers to an electronic business activity whereby companies transact business activities with each other (Harvey Norman warms 2011). An example of such business is www.alibaba.com, where wholesalers sell their goods to retailers. For a B2B eCommerce to be effective, business models such as brokerage must be taken into consideration. In this case, brokers become the market- builders for a commission in return.
Business- to- consumer (B2C)
This kind of eCommerce involves businesses and consumers. Through electronic systems, businesses are able to sell goods and provide services to the general public (Harvey Norman’s new website 2011). A good example of a B2C business is Amazon where businesses sell goods to consumers. Manufacturers can use a manufactures’ model if they want to supply directly to the consumers since the model aims at compressing the distribution channel.
Consumer- to- consumer (C2C)
This kind of eCommerce refers to a situation whereby consumers sell goods to other consumers electronically via sites offering classifieds, forums, and auctions for free. An example of a C2C kind of eCommerce is eBay where consumers post their goods free for sale. For a C2C e-commerce brokerage model is inevitable. This is so because consumers need someone to come in and incur the cost of bringing them together (Harvey Norman reveals 2011). Other business models that could be useful for C2C include the advertising model, community model, subscription model, and utility model.
Consumer- to- business (C2B)
This refers to consumers posting individual or group projects giving a clear indication of a budget constraint. Within a few hours, companies can review the requirements of the consumer and bid on the posted projects. A good example of such eCommerce is www.elance.com, where freelancers all over the world provide their services via the platform. Without the brokerage model in C2B, this kind of eCommerce would not be possible. Consumers need the means to pass their message to potential companies and this can only be possible through the brokerage model (Five things Gerry Harvey 2011).
System Building- processes, tasks, and techniques
A reach picture model refers to a diagrammatic representation of the stakeholders in a company, their concerns, and a number of structures in a work context. Rich picture diagrams can be used to affirm the findings of an observation thereby being used as evidence for the final report. In order to come up with a rich picture, model one has to visualize the model (Harvey Norman reveals 2011). This aids the viewer’s understanding and imagination. Below is a rich picture model of freelancers’ websites. The website is a consumer- to- business e-commerce where consumers post projects and companies submit their proposals.
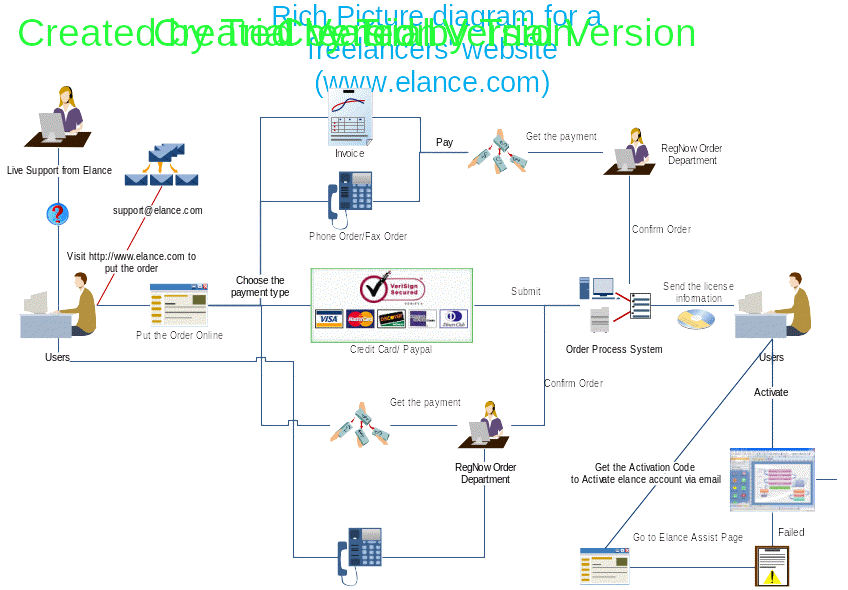
The key stakeholders from the rich picture diagram above are elanced, consumer, PayPal, and freelancing companies. Elance act as the brokerage model linking the consumers and the freelancing companies for a commission (normally 8.75% of the total cost of the project). Freelancing companies are registered on the website free of charge. They are then required to file up their payment details and personal information once their accounts are activated.
Consumers are also required to follow the same procedure as the freelancer and thereafter they can post their project details and start reviewing the project proposals. Once a consumer selects a freelancer, he or she is expected to escrow the funds for the proposal via PayPal. Elance then releases the funds to the freelancing company less their commission once the consumer is satisfied that the project is completed to his satisfaction.
Rich picture diagrams are advantageous in that they do not require expertise to draw them. However, they can be complex to understand if the situation in hand involves a complex environment such as online business (Lau 2006). The rich picture diagram above is an indication of complex eCommerce businesses that involve customers and buyers all over the world. Ecommerce is a global market that has untapped potential. More individuals are joining the online business, sharing business ideas, and increasing competition among businesses.
Business and I.T Strategies
There are five aspects that must be looked into in order to understand the kind of competition within an eCommerce environment. These aspects include the threat of new market entrants, degree, and nature of the competitive rivalry, customers’ bargaining power, suppliers’ bargaining power, and competition brought about by a substitute product (Bonera 2011). Without these five key factors, one can never understand the intensity of rivalry within the eCommerce industry.
Newmarket entrants are a threat to businesses in the eCommerce world. If new entrants join the industry, they are likely to dominate a share of the market. This will lead to intensified rivalry and thereby reducing the profit margins due to competition. The bargaining power of suppliers is also a key factor that must be looked into when it comes to internet business. If suppliers exercise their bargaining power, they are more likely to sell their products at higher prices thereby squeezing profits earned via eCommerce.
The bargaining power of customers is also an important aspect to be considered when doing online business. Online business involves stakeholders all over the world. There are numerous suppliers of a particular product or service and each supplier sells his products at his own convenient price. This makes customers be more powerful as they are spoilt for choice. This also gives customers an opportunity to dictate the prices for goods and services. If the customers are powerful, they will be able to pull down the prices for goods and services.
Ecommerce is a growing business trend. New and efficient products are being sold via an electronic business portal. Products that meet the same needs as old products are made readily available to consumers via the internet. With such substitutes being provided in the eCommerce market, prices of goods sold online are likely to drop due to competition. This will in turn reduce the profit margins for companies engaging in eCommerce.
Given that online business engages business participants all over the world, competitive rivalry is likely to be intense. This will lead to price wars and in turn price reduction. Competitive rivalry in eCommerce is also likely to bring about investment in new products and innovation in order to cope with the stiff competition.
The online business is fast-growing with new ideas and trends emerging to conquer the market. Consumers are beginning to trust online transactions thereby increasing the revenue collected from e-commerce related activities. With internet providers working hard to enable consumers to access the internet from the comfort of their homes, more consumers are likely to join the online market. This will give the businesses that have already taken advantage of e-commerce an opportunity to increase their sales revenue. More secure and efficient payment systems are also likely to be set up to reduce the cost of transactions and also reduce the incidences of fraud.
With I.T, online business is likely to become efficient as technology is more likely to reduce paperwork and depending on digital databases to store crucial business information (Kinder, 2002). Information technology also allows businesses to connect easily regardless of the distance. Such communication systems reduce the time and cost that would have otherwise been wasted if the traditional communication methods were to be used.
Systems Analysis Techniques and Tools
A use case diagram is a horizontal ellipse that describes a system of actions providing measurable ideas. The diagram below shows a use case diagram of a freelancing website.
A use case diagram for Elance
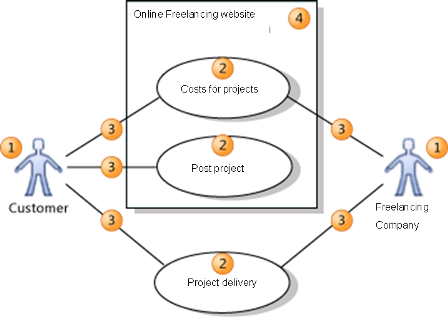
A use case diagram has three main components as indicated in the diagram above. These include; an actor (1), a use case (2), and a system (4). An actor refers to a group of persons with a common objective, devices, or organizations that interact with the main system (Website). As for a use case, it refers to actions that are usually accomplished by an actor in pursuit of a particular goal. A system refers to whatever that has been developed. In order for the use case to be effective, there must be associations (3). These are indicated by straight lines. In order for an association to exist, there must be an actor that relates to the system described through a use case.
From the use case diagram, it is visible that the website acts as a brokerage model. Through the website, customers are able to transact with freelancers thereby being able to increase their sales (Xing, 2001). Through the website, customers are also able to view the price quotes for specific projects hence making them able to set their own project prices. The use case diagram also shows that only the customer can post the project. The website allows customer-freelancer communication to allow them to effectively deliver on each partner’s end of the bargain.
Ecommerce is a business industry that is growing at an alarming rate. New businesses are coming up and taking advantage of the untapped online market. Even with this untapped market, businesses are faced with various challenges regarding eCommerce. One such challenge is trust; most consumers still do not trust online businesses and this acts as a hindrance to the already set up websites. Another challenge that is faced by internet businesses is the fact that they need to work on-site SEO (McCarthy, William & Pascale 1997).
This is an inbound marketing strategy that is used by online businesses to drive traffic to their sites. Most internet business owners do not understand this marketing tactic and this makes their sites to be placed at the bottom of the search engine result page. Business owners can also increase traffic to their sites by taking advantage of social media. If these businesses do not know how to maximize the potential of social media, then they are likely to find online competition to be unfavorable. It is therefore important for business owners to keep updating themselves on upcoming online business trends.
List of References
Bonera, M. 2011. ‘The propensity of e-commerce usage: The influencing variables’, Management Research Review, vol. 34, no.7, pp. 821-837.
Foo, F. 2013. Harvey Norman warms to online sales but rivals far ahead. Web.
Hammond, M. 2011. Harvey Norman’s new website incorporates franchisees. Web.
Khin, E W, Fatt, C K, & Kaur, S. 2010. ‘The implementing of business-to-business E-commerce application: An australian case study’, Enterprise Risk Management, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 1-23.
Kinder, T. 2002. ‘Emerging e-commerce business models: An analysis of case studies from west lothian, Scotland’, European Journal of Innovation Management, 5(3), 130-151.
Lau, S Q. 2006. ‘Domain analysis of e-commerce systems using feature-based model templates’, University of Waterloo (Canada). Web.
McCarthey, EJ , William, D P & Pascale, G Q. 1997. Basic marketing, Irwin, Sydney.
Salek, N. 2011. Harvey Norman looks to e-commerce, CRN Connecting the Australian Channel. Web.
Stafford, P. 2011. Five things Gerry Harvey must get right on his new website. Web.
Xing, J 2001, ‘Commitment-based interoperation for e-commerce’, North Carolina State University. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses, 140-140 p.
Zappone, C 2011. Harvey Norman reveals online move. Web.

