Introduction
The global business environment has changed significantly in the recent past. Certain developments such as the internet, management theories, outsourcing, and online banking have transformed how different organizations pursue their objectives. Many players in the global banking sector have been focusing on various approaches that can promote performance and profitability (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). The increasing level of competition in the banking industry has encouraged business owners to come up with quality products that resonate with the changing demands of the targeted customers. Such products should also be available at friendly prices. Hao and Yazdanifard (2015) go further to acknowledge that flexibility has become something crucial for firms that want to remain competitive in these changing times. Flexibility can guide banks and financial institutions to change accordingly depending on the situations experienced in the business environment. The literature review below examines past studies and theoretical models that have been presented to support the implementation of effective change in the banking industry.
Literature Review
Understanding Organizational Change
Oreg (2003) indicates that organizational change is a continuous or episodic event executed in a company in an attempt to foster performance. This means that the process can be implemented and supported for a given period to achieve the targeted results. Within the past three decades, change is always synonymous with improved organizational performance. Organizational change has gained much attention because of its potential to ensure different firms (and banks) improve their situations (Ikinchi 2014). This means that the process is supported in a firm to foster new activities and practices that can eventually result in improved performance.
Transitional change has emerged as the commonest approach embraced in banks that want to achieve their goals much faster. This kind of change is aimed at introducing gradual or minor practices in a given institution. As a result, the change can be used to produce new strategies, organizational cultures, or initiatives that can support every new goal (Fernandez & Rainey 2006). An organization introduces change depending on several factors such as intended objectives, available resources, current workforce, and the nature of its departments. More often than not, changes are introduced in specific departments without interfering with the functions of the others (Oreg 2003). These are usually short-term changes aimed at promoting or supporting various functions. Ikinchi (2014) argues that such changes tend to deliver positive results when a given department in an organization becomes less effective.
Developmental change has emerged as a powerful model that can guide companies to realize their potential much faster. This kind of change has been applied in many financial institutions to foster development and continuous growth. Oreg (2003) observed that developmental growth was appropriate for firms that wanted to transform their cultures. The move is capable of promoting a dynamic environment characterized by a wide range of competitive advantages. During the change process, leaders (or managers) should scan their organizations carefully in an attempt to identify specific areas that need improvement (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). When this information is acquired, it can be possible to design a powerful model for supporting and implementing the proposed change (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). Modern theories in change management have supported several evidence-based practices to support the process. For instance, past scholars have indicated that organizational managers should be able to identify the existing gaps and come up with adequate solutions.
Past studies have supported the role of various practices such as motivation, empowerment, and preparedness towards supporting organizational change. Individuals should be encouraged to form teams to achieve targeted goals much faster (Oreg 2003). New theories have been emerging every day to explain how leaders can support and sustain change in their respective firms. For instance, change models have been designed to empower more firms to overcome the major hurdles arising from technological advances. Managers should be able to explore and interpret numerous factors known to impact organizational performance such as politics, economic performance, and government policies (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). This knowledge has been supported by many scholars because it has the potential to result in successful organizational change in different banks.
Change Management
Change is an inevitable event that takes place in companies, institutions, and people’s lives (Ikinchi 2014). When change is about to take place, more people will tend to be dissatisfied with the process. Many scholars have gone further to accept the fact that change cannot occur smoothly without hurdles. Similarly, the targeted employees in a given bank tend to be opposed to new changes because they can affect their positions, personal expectations, and career goals (Hao &Yazdanifard 2015). The ability to change to disorient people’s comfort zones is something that has been captured by many organizational theorists. The occurrence of opposition during change implementation is a major challenge that makes it impossible for many firms to achieve their goals. Experts in change execution have gone further to support the use of adequate approaches (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). This is the reason why change management has become a common phrase in various organizational theories.
Ikinchi (2014) defines change management as a powerful approach implemented to transform how various duties are done in an institution. The theoretical approach has been developed further to focus on the worker and the organization (Fernandez & Rainey 2006). To ensure the change management process is successful, organizational leaders should implement a powerful model and use adequate strategies. Without proper guidance or support, the targeted individuals will be in a position to support the initiative and deliver positive outcomes. This kind of support is essential since many workers will be against the process unless adequate incentives are available. Failure to implement and manage any form of change in a company can result in disastrous outcomes (Fernandez & Rainey 2006). This can be the case because more stakeholders and employees can become disoriented and fail to support the existing business model.
There are unique approaches that can be embraced by banks and institutions that want to manage change efficiently. Culture is the first issue to consider whenever improving a firm’s performance. Various attributes such as leadership can be used to reshape a firm’s culture. The level of trust between the managers and the targeted employees should be desirable. When the two read from the same page, it becomes easier to address emerging challenges, share ideas, and promote new practices that can eventually support the implemented change (Hao &Yazdanifard 2015). A positive culture in a given firm alone cannot produce tangible results. Many researchers acknowledge that a friendly culture catalyzes new behaviors and attitudes that can maximize collaboration (Oreg 2003). The second approach focuses on the issue of leadership. Competent leaders will offer insights and guidelines that can make the targeted change a reality. The third aspect that has produced positive outcomes in many industries is that of communication. Oreg (2003) indicates that effective communication is one of the magical attributes capable of transforming the performance of every company across the world. Communication is a powerful strategy that makes it easier for persons to interact, share opinions, and promote trust. The practice results in a new bond whereby the targeted workers can work as a team and overcome every emerging problem.
Ikinchi (2014) goes further to acknowledge that change management is a wide area that can be implemented using numerous approaches. For instance, teamwork and leading can be combined by managers to empower the targeted employees. It is also appropriate to communicate frequently to targeted persons. The vision should be known and understood by the workers. Throughout the change management process, organizational leaders must ensure the employees have the best environment to support their goals. The workers will come up with innovative concepts or ideas that can be translated into positive organizational results.
Leadership and Change
Past scholars in the field of organizational theory have indicated that leadership is one of the best tools for fostering effective change. For instance, Hao and Yazdanifard (2015) link the possession of adequate leadership dexterities to the successful implementation of change in the banking industry. This means that an organizational leader capable of applying his or her competencies will find it easier to empower every follower and eventually record desirable results. Leadership is a wide field that focuses on numerous functions such as mentoring, empowering, and guiding others. Throughout the change process, the manager must ensure different employees are guided and empowered. By doing so, every worker will be willing to support the process, present his or her viewpoints, and address emerging challenges before they disorient the entire process. A study conducted by Ikinchi (2014) revealed that leaders who failed to support the change management process encountered a wide range of barriers from their respective followers such as increased employee turnover. This became a wakeup call for different managers planning to implement change in their respective firms (Hao &Yazdanifard 2015).
Ineffective leadership has been associated with various gaps capable of affecting the process of change in an organization (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). Managers who do not exhibit some of the best leadership qualities tend to encounter various barriers whenever implementing change. Incompetent leaders will be unable to mentor or come up with the right vision for their respective workers. Such managers have been observed to catalyze different obstacles such as poor communication and resistance (Ikinchi 2014). The affected employees find it hard to support the intended objectives or goals of the institution. Some researchers have presented convincing connections between inappropriate leadership and organizational barriers especially when planning to implement new changes (Hao &Yazdanifard 2015). Some of these barriers include reduced levels of communication, lack of employee motivation, and increased business risks. On the other hand, skilled leaders use their competencies effectively by motivating, empowering, and mentoring their workers (Anjani 2013). Different individuals should be recognized, motivated, and rewarded depending on their inputs to the organization. When such strategies are put in place, it becomes easier for the workers to promote a better environment and eventually realize their potential.
Leadership theories offer diverse aspects that can be applied in organizations to support change management (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). According to leadership trait models (or theories), successful managers possess specific peculiarities that can be applied in an organization to support the entire change process. Leaders with specific traits such as the desire for success, decisiveness, integrity, self-assurance, and supervisory capabilities will empower their followers accordingly (Anjani 2013). Individuals with such dexterities will tend to be democratic while at the same time being able to give appropriate directions. The beneficiaries will engage the leader and eventually promote the most desirable practices in the organization.
As described earlier, past analysts have outlined various skills that are critical whenever supporting new changes in business agencies. Behavioral theorists have acknowledged the fact that traits can dictate the performance of a given leader. Some abilities have been grouped to support the role of behavioral therapy in the field of change management. Coaching has been identified as a powerful leadership competence capable of empowering many change leaders. Coaching is a practice that makes it possible for leaders to communicate with their followers, create awareness, and mentor them accordingly. According to Hao and Yazdanifard (2015), coaching can be outlined as one of the attributes used to foster change. A leader who is willing to coach his or her followers creates a sense of resilience. The practices will encourage targeted employees to remain optimistic and focus on the targeted outcomes.
Leadership theory supports the need to engage and involve others throughout the change implementation process (Ikinchi 2014). Anjani (2013) indicated that the involvement of different workers was a powerful trend capable of promoting organizational responsiveness to new changes. The use of various programs could mentor and widen the competencies of more workers. Every empowered participant finds it easier to make accurate decisions, innovate, and identify new practices that can enhance organizational performance. Leaders should get adequate feedbacks from their respective followers. A new practice characterized by decision-making and collaboration emerges thereby supporting the change process. Competent leaders should reward and motivate their workers using diverse strategies (Hornstein 2015). Organizational theories have indicated clearly that an empowered worker will be willing to work harder to ensure the targeted goals are achieved promptly.
Evidence-Based Factors for Effective Change
Business organizations that fail to consider various factors such as the inclusion of a proper plan find it hard to implement change successfully. Fernandez and Rainey (2006) outlined specific factors that were essential whenever implementing a new change in an organization. The first one is to ensure there is a need for change (Ikinchi 2014). This can be achieved by creating and communicating the most appropriate vision to the workers. The second thing is to ensure there is a course of action to be followed throughout the process. Internal support is necessary to minimize resistance throughout the change process. The top management must be involved throughout the process. This practice will ensure the followers are guided and supported. Such individuals will find it easier to be involved and focus on the benefits of the proposed change. The provision of adequate incentives and resources is necessary whenever planning to implement a new change (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). These resources include the acquisition of new machines or training to ensure the workers are empowered to go to the next level.
Managerial leaders should come up with powerful approaches to support change based on the issues experienced in their respective firms. The change process should therefore be aligned with the targeted end state in the organization (Ikinchi 2014). The emerging challenges that can affect the change process should be addressed immediately. This is the reason why some theorists in change management have proposed specific models to support the process (Naveed, Jantan & Ahmad 2016). The use of a proper model will ensure the process is managed successfully. The approach will be used to empower every stakeholder, address emerging challenges, and deliver the intended goals.
One of the best theoretical frameworks used in change management is Kurt Lewin’s model. According to the model, change is a complex journey that should be supported by every participant in an organization. Since people tend to resist every kind of change, the model has been suggested by many scholars because of its potential to create the best environment in an organization. Lewin came up with a powerful approach that has made it possible for many firms to implement change successfully. The first stage described in Kurt Lewin’s model is known as unfreezing (Hussain et al. 2016). During this phase, managers should use their competencies to inform their workers about the proposed change. They should go a step further to prepare their followers to support the process. The urgency of the organizational change process should be communicated to the right individuals.
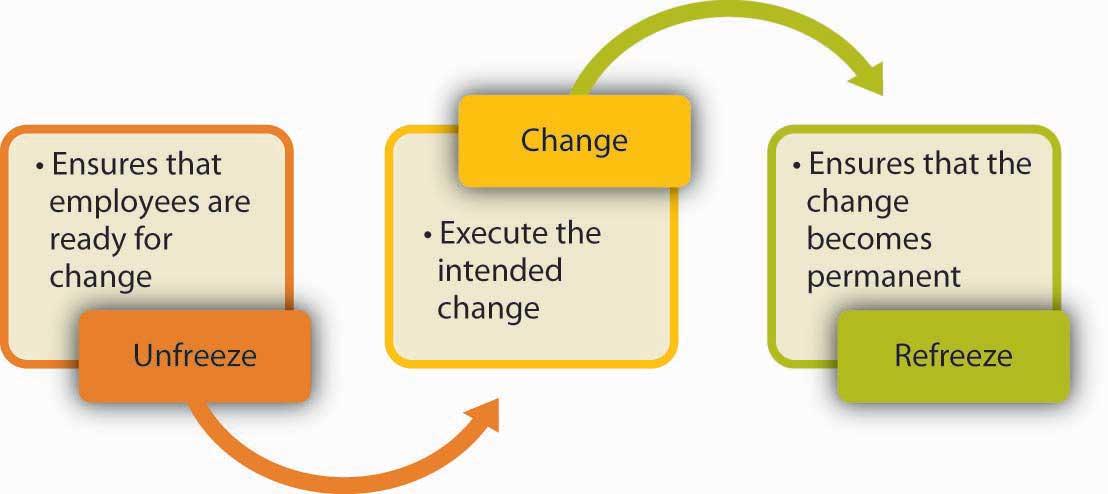
The second stage described in the model is a transition (or change). Since change is not an event, the manager should ensure the right resources and incentives are available to support the journey. The leader must deal with resistance and empower the employees using appropriate programs. Teams can also be created to foster communication. The third stage is known as the refreezing phase (Hussain et al. 2016). This will become the new state of productivity and performance. During the phase, the change leader must promote the best behaviors and empower the workers continuously. The best practices should be supported continuously and empower stakeholders to focus on the targeted goals (Hussain et al. 2016). With this theoretical model in place, it will be possible for every financial institution to implement change successfully and eventually become profitable.
Conclusion
The above literature review shows conclusively that leadership is a powerful model capable of promoting and supporting any form of change in the banking industry. Change managers who portray appropriate leadership competencies will enhance collaboration and teamwork. With a proper vision and an evidence-based theoretical framework, such managers can guide their followers to engage in new practices and deliver positive results (Ikinchi 2014). They should use reward initiatives or programs to empower their workers. These practices can make it possible for the targeted employees to remain committed, develop new skills, engage in lifelong learning, address problems, and eventually create a competitive advantage. This gain can make it easier for banks to deal with competition and eventually remain relevant in their sectors.
Hypothesis and Questionnaire
Hypotheses
The hypotheses below will be used to support the proposed study:
- Change will be implemented successfully by leaders who support the outlined strategy than those who do not.
- Change will be effective when organizational units promote various practices and norms that support the process than when they do not.
- The manager’s ability to support the proposed change using a powerful model will enhance positive outcomes.
Questionnaire
This questionnaire is aimed at understanding the major issues to consider whenever implementing change in a bank. The questionnaire will guide the researcher to get quality information that will be used to come up with a model for supporting effective change in the banking industry. The survey has 10 questions and can take less than 20 minutes to complete. Every response will be handled in a confidential manner.
- What is your current position or job title?_______________________________________________________________
- What is the current status of your position? [Select tick one]
- Full time employee (FTE) { }
- Contract
- { }
- Other [specify]_____________________________________________________________________________
- What is your understanding of change management?______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- What measures are undertaken in your bank to implement change(s)?______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- How does leadership (management) implement and support organizational change?______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- What issues are considered whenever planning or executing change in the bank?______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- How has your bank implemented change successfully in the recent past? What initiatives are usually taken seriously?______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- Which (and how) change models are embraced by managers in the firm? Please elaborate._______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- What new lessons have you gained from the bank regarding the effectiveness of change management?______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
- What is the impact of effective change on organizational performance?______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Reference List
Anjani, P 2013, ‘Impact of readiness for change organizational change of banking sector in Salem District’, International Journal of Business Management, vol. 3, no. 4, pp. 353-371.
Fernandez, S & Rainey, H 2006, ‘Managing successful organizational change in the public sector’, Public Administration Review, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 168-176.
Hao, M &Yazdanifard, R 2015, ‘How effective leadership can facilitate change in organizational through improvement and innovation’, Global Journal of Management and Business Research, vol. 15, no. 9, pp. 1-6.
Hornstein, H 2015, ‘The integration of project management and organizational change management is now a necessity’, International Journal of Project Management, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 291-298.
Hussain, S, Lei, S, Akram, Y, Haider, M, Hussain, S & Ali, M 2016, ‘Kurt Lewin’s change model: a critical review of the role of leadership and employee involvement in organizational change’, Journal of Innovation and Knowledge, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1-7.
Ikinchi, S 2014, ‘Organizational change: importance of leadership style and training’, Management and Organizational Studies, vol. 1, no. 2, pp. 122-128.
Naveed, R, Jantan, A & Ahmad, N 2016, ‘Organizational culture and organizational change in Pakistani Commercial Banks’, International Journal of Research in Business Studies and Management, vol. 3, no. 8, pp. 15-18.
Oreg, S 2003, ‘Resistance to change: developing an individual differences measure’, Journal of Applied Psychology, vol. 88, no. 4, pp. 680-693.
