Introduction
Emirates Airline is an immensely growing airline company that is situated in Dubai. It started its operations in 1985. The airline has won many intercontinental awards. One such award is the 2011 Airline of the Year given by the Air Transport World. Emirates Airline observes, “The award was based on recognition of Emirates Airline’s commitment to safety and operational excellence, customer service, and financial conditions, including a 22-year consecutive annual profit” (par.6).
Emirates Airlines is the biggest flag carrier in the Middle East region. The CEO of an airline organization serves the principal functions of carrying the vision to the desired future position. A team of dedicated managerial staff does the rest of the work to make sure that the vision is realized. For Emirates Airlines, these managerial staff members include the administrative vice-chair (Sir Maurice Flanagan), the Emirates Airline’s head (Tim Clark), and the administrative vice president in charge of operations.
Others include engineering director (Adel Ahmed), the managerial vice president in charge of human resources (Abdulaziz Al Ali), and the supervisory vice president in charge of passengers and sales across the world (Thierry Antinori) among others. These leaders have played a credible role in promoting the airline’s organizational culture. Without the unending efforts of the employees, including the cabin crew, Emirates Airline could not have grown into a highly profitable organization.
Through the management, as part of the organizational behavior, the company has been able to articulate strong roots of organizational ethics as the basis of setting moral values together with standards of work. Through the tireless effort of human resource management, Emirates Airlines has managed to employ approaches to human resource management in terms of recruitment of the appropriate staff for handling various corporate values. In any organization that seeks global competitiveness, all staff members need to focus on promoting a positive culture of work. Emirates Airlines has established a strong culture that is organized around ensuring the delivery of optimal benefits to all customers.
Major competitors of Emirates Airlines accuse it of pursuing anti-competitive strategies claiming that this move has enabled it to achieve its continuous success. However, the company maintains that its business model has immensely contributed to its success. All airlines that operate in Dubai’s open skies are competitors. Ten of these organizations are Qatar, Air France, Qantas, BA, Lufthansa, Air Arabia, Etihad, Flydubai, Dubai Royal Air, and Abu Dhabi Amiri. Emirates Airlines targets all groups of customers by ensuring it delivers service utilities that meet their needs. For example, it operates the economy and sumptuous classes.
Concepts or Theories
The Travel Industry
The travel industry encompasses one of the most lucrative service sectors in the UAE and around the globe. The industry houses various companies that offer different travel services such as vacation reservations via the internet, tour operations, and travel agency professional services. Other sectors in the industry include cruise lines, airlines, restaurant service businesses, car renting, rail travel companies, conferences, parks, sporting and entertainment companies, publication organizations, marketing research organizations, and regulatory agencies. Each of the sectors has various organizations, which operate under stiff competition.
For instance, in the marketing sector, different organizations engage in offering marketing research services to various businesses that deal with travel services in a bid to help them analyze their industry trends and/or derive better strategies to retain and increase their market share.
Competition occurs between organizations in different sectors. For example, the airline sector competes with companies that offer alternative means of travel such as rail travel. For Emirates Airline, competition is one of the major factors that pose challenges to its industry of operation (air travel industry). Another important challenge entails human resource problems. Other issues include technological challenges, mechanisms for improving service productivity and methods to improve service quality. Dealing with these challenges requires visionary leadership. Indeed, the success of Emirates Airlines in dealing with the problems is attributed to his highness, Sheikh Ahmed.
He is the chairperson and the chief manager of the airline. Through the past two and a half decades, he has been proactively involved in Dubai economic development. Consequently, apart from being involved in creating the appropriate environment for business to thrive in Dubai, he has also been resourceful in fostering the expansion of the aviation industry in the United Arab Emirates. He has been involved in the formulation of investment, economic strategies, and fiscal policies to support the vision of the airline industry.
Challenges in the Service Sector
Service sector organizations operate under intense competition from rival organizations, which provide substitutes or compete in the same line of service. While the threat of substitutes such as road and rail is not significant for Emirates Airline, the threat of other airlines taking away the company’s market share remains high, especially when several international carriers merge to achieve a higher competitive advantage. Although the Dubai administration operates Emirates Airlines, the company’s success has been achieved in a highly competitive environment. This situation is contrary to some competitors’ position that protectionism has played an incredible role in influencing Emirates Airline’s growth into an international brand.
Alcacer and Clayton assert that Emirates Airline encounters competition from major brands such as Gulf carriers coupled with other international strategic alliance airlines (13). The number of carriers that fly the Dubai open skylines continues to rise. This rise is attributed to the government policy for maintaining an open skyline. Emirates Airline’s support for this policy suggests that it remains vulnerable to competition as an important challenge that faces service sector organizations.
Service sector organizations depend on employees to deliver organizational value to customers. Hence, employees are the main source of competitive advantage. Organizations experience challenges when they pursue policies that do not serve the interest of employees who deliver suboptimal services or lead to the development of poor customer relationships because of the resulting low motivation and work commitment.
However, HR can handle employees’ complaints to ensure their satisfaction through their union representatives. Nevertheless, being constituted in the UAE, Emirates Airline’s policies do not support employee unionization. Hence, workers cannot champion or make bargains with the company through labor unions. Consequently, the challenge of effective management of employee relations to enhance satisfaction, work morale, and commitment remains problematic in Emirates Airlines, just like in any other service sector.
Technology in the Service Sector
Technology is important in the service sector to help in reducing operational costs or improving customer experiences with the service. This plan is important in the airline industry since organizations in the sector serve people of different social-economic status. Therefore, people would like to associate with an airline that offers services that meet their unique needs. Emirates Airlines first provided custom-made video for all ranks. It also leads the industry in providing clandestine suits coupled with showers. The company always incorporates the latest technology into its new aircraft to ensure it remains relevant, amid the technological changes. In terms of customer service, Emirates Airlines provides customers with an opportunity to make online bookings and/or check their flight status through the platform.
Ways to Improve Service Productivity
Improving service productivity is incredibly challenging because of services “lack ownership, are intangible, inseparable, and have heterogeneity” (Rust, Zeithaml, and Lemon 113). This claim suggests that it is challenging to measure the productivity of service sector organizations due to the intangibility of their services. Therefore, one cannot know how productivity has changed over time. One way of ensuring that an organization that operates in the service sector provides better customer experiences is by serving customers at a faster rate. However, a situation where many customers are served within a limited time does not imply that they will purchase the service in the future. They may feel they have been taken through the service too fast to the level of regarding the service as being of low quality.
Methods to Improve Service Quality
Customer satisfaction with services offered in the service sector is incredibly important to ensure that clients purchase the same service in the future.
Helping many customers cannot be an indication of the quality of services delivered. It is important to incorporate other perspectives into it, other than speed, as a method of improving the service quality. For example, Khosla observes, “helping the highest number of clients possible and keeping them satisfied at the same time is the best determinant of service quality” (223). Indeed, Emirates Airlines seeks to ensure that it delivers quality services by emphasizing offering professional and personalized approaches to managing customer relationships.
Analysis of the Service Sector
Government Support to the Sector
Dubai has open skies. Hence, all global carriers can use Dubai as an operational hub with minimal or no interference from the government. However, some airlines have complained over the government’s interference with the competitive structure of the airline industry in the UAE by offering direct support to the Emirates Airline. For example, Qantas and Air France claim that Emirates Airlines directly benefits from government subsidies.
It also retains and supports cozy dealings with the Dubai Airport Authority. Alcacer and Clayton support this line of argument by claiming states, ” Air France, Lufthansa, and Air Canada claimed that government policies such as subsidized fuel, no income tax, and strategic synergies with the government at its principal hub were major sources of success for Emirates that disadvantaged other airlines” (13). The president of Emirates Airlines failed to accept this criticism.
Even though Emirates Airlines denies benefiting from the government’s support through subsidies, other facts indicate that the organization directly benefits from government support. For example, Partnership for Open & Fair Skies asserts that in a 2015 legal filing, Etihad, Emirates, and Qatar Airways admitted having received direct government support (par.2). In the case of Emirates Airlines, the company accepted that the Dubai Investment Corporation (ICD) participated in contracts that involved fuel hedging. This situation prevented the airline from reporting on hedging losses, which led to artificial modification of profits to depict higher profits that the market situations could practically support.
Quality Standards
In any services sector organization, people are important sources of competitive advantage. Such an advantage is acquired through the delivery of quality services. Considering that it is challenging to measure quality levels in the service sector industry, the main challenge that Emirates Airlines is facing is how to manage its people to ensure they deliver better clientele satisfaction. Indeed, customer satisfaction is necessary to attract and retain existing customers. Emirates Airlines seeks to ensure that it maintains its first-time customers while attracting others, including those who have developed service loyalty to other airlines.
The management understands that this goal can only be accomplished if the company remains true and committed to its service quality standards. The company has a four-star certification under the Skytrax rating system. As detailed by Skytrax, the system assesses airline organizations based on their quality of onboard products and staff services (par.1). It also considers airline operations’ quality in home-based airports.
Sector Performance/Growth
The global airline industry has faced various challenges in the recent past to the level of prompting many organizations to fall or focus on exit strategies, including forming strategic partnerships. Many challenges arise from fuel-price fluctuations that lead to increased operational costs. This situation implies lowering the profitability of the global airline’s service sector. However, as illustrated in Graph 1, despite these challenges, Emirates Airline has been reporting positive profitability. This profitability was sustained even from 2008 to 2009 when major airlines suffered heavily due to the global financial crisis.
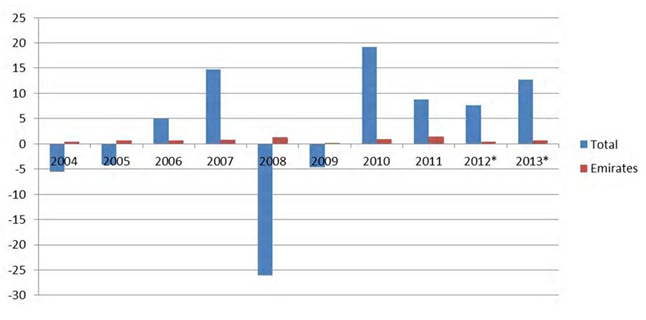
Although Emirates Airlines has recorded positive profitability as shown in Graph 1, the company faces problems that threaten its capacity to maintain optimal profits. For example, it faces competition from Gulf Airlines and Turkish Airlines. However, Alcacer and Clayton confirm that Emirates Airline explores anti-competitive strategies, which ensure sustained positive performance (15). To survive in a highly competitive business environment, Emirates Airlines struggles with the problem of product innovation coupled with continuous improvement of services.
Emirates Airline’s growth story has caught other competing airlines with a shock. For example, Shaban reckons, “the airline created history in 2007 by announcing a historic civil aviation aircraft order for 120 Airbus A350s, 11 A380s, and 12 Boeing 777-300ERs, worth an estimated $34.9 billion at Dubai Airshow” (par.5). Later, during the 2010 Berlin Air Show, Emirates Airlines announced that it had ordered 32 Airbus A380s. During the Farnborough Air Show, the company announced having ordered 30 Boeing 777-300ERs. Hence, the company’s growth strategy focuses on expanding its fleet size and increasing its number of travel destinations in its market that currently comprises destinations that are located on six continents.
Contribution to the Economy
The airline industry has been instrumental in promoting economic activities in the UAE. Dubai Airports asserts the “Aviation will contribute $53.1 billion to Dubai’s economy, 37.5 percent to its GDP, and will support over 750,000 jobs by 2020” (par.3). Indeed, at the start of 2013, the company and the entire airline industry, including support organizations such as Dubai Airport made an economic donation of close to $27 billion.
This amount totaled to about 27% of Dubai’s GDP. By the same year, the industry supported an excess of 416,500 people in terms of employment provision. Hence, the segment employs about 20% of the entire number of residents in the emirate. Indeed, each $100 of economic involvement in the UAE airline industry is accompanied by close to $70 in support sectors in the neighborhood financial system such as logistics networks and the hospitality quarter. The creation of 100 jobs in the airline industry translates into 116 jobs in other sectors of the UAE economy (Dubai Airports, par.7). In 2013, Dubai received about 10 million visitors who contributed about $13 billion. This amount was 1% of the total global expenditure by foreigners.
Conclusion
The service sector is one of the lucrative quarters in the UAE. It attracts many players, including the airlines, which focus on offering air travel and cargo carriage services. Emirates Airline operates in this sector. Starting its operation in 1985, the company has grown significantly in terms of fleet size and the number of destinations. The company emphasizes delivering high-quality services both at Dubai Airports Authority and onboard.
Some competitors complain that the airline receives direct subsidies and other forms of support from the government, which have enabled it to maintain positive performance in a dynamic highly competitive operational environment. Emirates Airline’s operational model has been instrumental in supporting and maintaining positive profitability. However, on the global platform, the airline industry has had periods of high losses.
Recommendations
- Emirates Airlines should ensure it competes fairly in open skies in case complaints raised by its competitors are true. Any support from the government that places other organizations at a disadvantage should be withdrawn.
- To increase its global reach, the organization should consider forming more strategic alliances.
- Employees’ affairs are critical to the success of any service organization. Although Emirates Airline cannot breach the UAE law, which does not authenticate unionization, the company should consider alternative ways of mitigating employee conflicts with it to guarantee motivation and satisfaction.
- The company should provide incentives to frequent customers to maintain them.
- To expand its clientele, Emirates Airlines should intensively establish markets in the Asia-pacific region.
Works Cited
Alcacer, Juan, and John Clayton. Emirates Airline: Connecting the Unconnected, Havard: Havard Busness School, 2014. Print.
Dubai Airports. Quantifying the Economic Impact of Aviation in Dubai, 2015. Web.
Emirates Airline. The Airline: Emirate Airline. 2011. Web.
Khosla, Swati. “Consumer Psychology: The Essence of Marketing.” International Journal of Educational Administration 2.2 (2010): 220–225. Print.
Partnership for Open & Fair Skies. Emirates Confirms Billions in Government Subsidy for Airport Terminal. 2015. Web.
Rust, Ronald, Valarie Zeithaml, and Katherine Lemon. “Customer centered brand management.” Harvard Business Review 82.4(2004): 110-118. Print.
Shaban, Sadiq. Emirates is the Fastest Growing Airline in the World. 2015. Web.
SkyTrax. Emirates 4-Star Airline Rating. 2016. Web.
