Introduction
The notion of the government’s role in a country’s economic growth is relatively recent. D’Anieri (2010, p.246) asserts that changes in a country’s economy were perceived to result from natural calamities. This means that there is nothing that the government could do in order to influence economic growth. However, there has been a significant transformation over the past few decades arising from the increased acceptance by politicians and economists that the government can influence a country’s economy. This can be achieved through the effective formulation and implementation of fiscal and monetary policies.
In order to be effective, the role of macroeconomic policies in the US is undertaken by both the state and the Federal Reserve. The Federal Reserve’s operation has been enhanced by the firm’s efficiency to operate without any form of interference from the political class (Watchel, 2010, p.1). As a result, the US has managed to maintain a relatively high rate of economic growth over the past few decades. For example, a report published by the CIA World Factbook in 2007 estimated the country’s Gross Domestic Product (GDP) to be $13.84 trillion. This is approximate s 3 times more compared to that Japan which is the next largest economy in the world. Its GDP was $ 4.4 trillion in 2007.
As a result of the 2007 economic recession, the US economy was adversely affected. For example, according to Kyser, Sidhu, Ritter and Sedgwick, the country experienced a slowdown in its GDP growth. In 2008, US GDP grew with a small margin of 0.8% during the 1st three quarters. However, this trend was reversed with the GDP plunging with a margin of -3.8% during the last quarter of 2008 (2010, p.1).
In order to improve its economic growth and stability, the United States government and the Federal Reserve have been committed to stimulating the country’s economic growth. This has been achieved through the effective formulation and implementation of macroeconomic policies. As a result, the economy is on its path to recovery. In order to understand how the US government is achieving this, this paper evaluates the main macroeconomic policies implemented by the US government. The research is based on the objectives of the US government which include enhancing economic growth, minimizing the rate of inflation and unemployment and ensuring stability in the country’s balance of payment.
What is needed to increase economic growth?
Economic growth refers to the long-term expansion of an economy’s productive potential. As a result of sustained economic growth, the living standard of a country’s citizens is improved significantly. In order to stimulate the country’s economic growth, the US federal government makes use of a wide range of economic tools (that is fiscal and monetary policies). Some of these tools include taxation and controlling the money supply. Additionally, the US government also controls the activities of private businesses so as to prevent the emergence of monopolies.
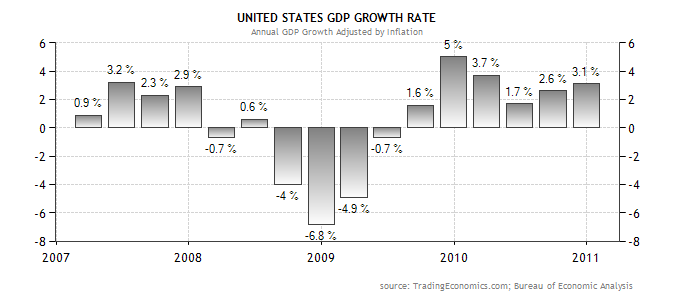
A country’s economic growth is measured by determining the percentage change in real Gross Domestic Product. Real GDP refers to the total output produced domestically using local resources. In 2010, the United States experienced an increment in its GDP with a margin of 3.1% during the 4th quarter of the year compared to the previous quarter. The table below illustrates the percentage change in the United States real GDP during four quarters in 2009 and 2010.
Increase in government spending
Over the past two years, the US government has increased its level of spending. This has played a significant role in stimulating the country’s economic growth. An increase in government spending through various avenues for example improvement in infrastructure causes expectations in the economy. As a result, private investors may increase their level of investment in such an economy despite other factors such as the rate of interest being high. In the past two years, the US government has increased its spending with regard to research and development and human capital (Jackson, 2011, p.3).
Research and development
For a country to experience high economic growth, it is vital for the government to be committed to research and development. One of the ways through which this can be achieved is by funding basic research and development projects. The US Federal government devotes a significant proportion of its resources to research and development. Private businesses do not mostly invest in research and development projects since the associated returns may be below. However, research findings may be used by other businesses in the process of undertaking their investments.
During the 2010 financial year, President Barrack Obama increased US funding in research and development to $ 147.620 billion which represents a $ 555 million or 0.4% increment from the 2009 financial year (Sargent, 2010, p.5). In its research and development funding, the US government is mostly committed to strengthening the country’s competitiveness and innovation. As a result of its commitment to research and development, the US witnessed significant breakthroughs with regard to scientific and new technologies (Sargent, 2010, p. 5). The US accounts for approximately 40% of the world’s patented new inventions.
Foreign direct investment
A country’s economic growth also arises from increased Foreign Direct Investment (FDI). The United States appreciates the role of FDI in a country’s economic growth. Over the past few years, the US experienced significant growth in FDI. However, in 2009, the US experienced a significant decline in the level of FDI undertaken in the country. During this year, the total FDI in the US declined to $ 152.1 billion from $319.7 billion in 2008 which represents a decline with a margin of more than 50% (Organization for International Investment, 2010, p.1). During this year, the country experienced the lowest level of FDI in a span of 4 years. The table below illustrates the decline in the trend in the country’s FDI during the period ranging from 2004 to 2009.
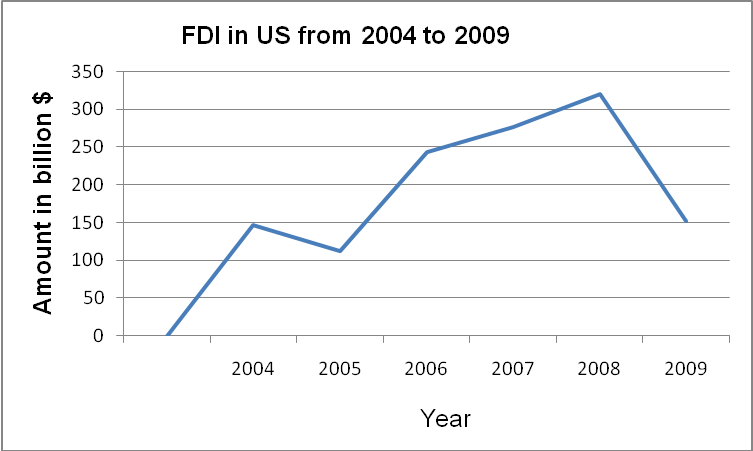
One of the factors which led to the significant decline in the country’s FDI is the 2007 economic recession. The reduction in the country’s FDI was a reflection of the decline in the level of credit available. Despite the sharp decline in the country’s FDI, the US government is committed to improving its economic growth by stimulating FDI. In an effort to achieve this, the country implemented the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act in 2009 (Brickman, 2010, para. 7). Through this Act, the US government developed a number of incentive programs to stimulate foreign investments.
Human capital
According to Brickman (2010, para. 8), a country’s economic growth is also enhanced by the quality of human capital. Human capital refers to the various skills, abilities, talents and education possessed by human workers in addition to the value they add to the labor market. By investing in education, training and health, a country is able to have a strong workforce that will contribute to the production of high-quality goods and services. In addition, an economy that invests in training is likely to be more technologically advanced. This arises from the fact that there is effective utilization of natural resources.
The US government spends a substantial amount of its budget on funding the country’s education system. For example, in 2010, President Barrack Obama indicated his commitment to improving the US education system by allocating $81.1 billion to education in the US Recovery Act. In addition, education was boosted with a further $ 46.7 billion allocation in the federal budget (Brickman, 2010, para. 8). As a result, the country has been able to develop a productive workforce. This has played a significant role in motivating investors in the US. The country is the global leader with regard to labor productivity. Currently, the labor productivity of every employee in the US is valued at $ 63,885 (Brickman, 2010, para. 9).
Inflation
Inflation is defined as the general rise in commodity prices against the consumers’ purchasing power. In 2009, the US Federal Reserve set the country’s interest rate at Zero. This resulted in an increment in the price of stocks. However, consumer goods were not affected. The zero percent interest rate also enhanced growth in the country’s Gross Domestic Product. The chart below illustrates the trend in the US inflation rate in 2009 and 2010 respectively.
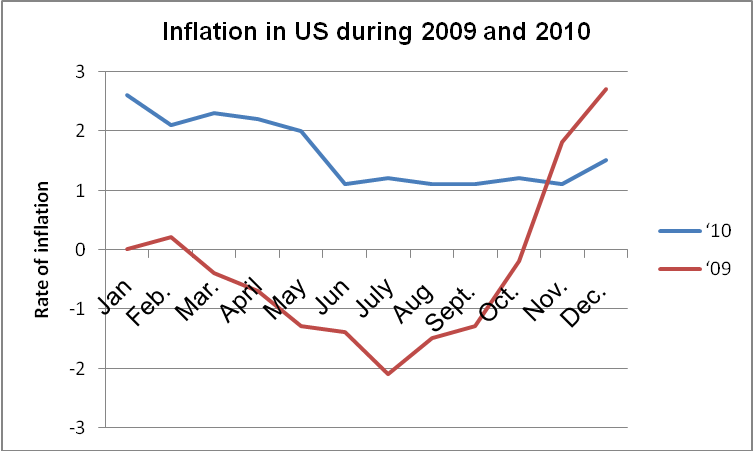
From the graph above, it is evident that US has experienced an increase in the rate of inflation over the past two years. In order to control the rate of inflation, the Federal Reserve is increasing its effort to reduce the amount of money circulating in the economy. One of the ways through which this is being achieved is by increasing the rate of interest applicable to financial institutions. As a result, it is not possible for individuals to access credit from financial institutions.
Unemployment
Prior to the 2007 economic recession, the US had a relatively low rate of unemployment as illustrated by the curve below. However, the occurrence of the recession led to a rise in the rate of unemployment. This resulted from the fact that most firms were undertaking downsizing strategies so as to cope with the recession. As a result, a large number of individuals lost their jobs.
In an effort to deal with the rise in unemployment, the US government through Congress developed an economic stimulus package whose worth was $ 787 billion (Kelly, 2009, para. 1). From this stimulus package, the unemployed were to benefit in a number of ways. For example, the government increased the period in which the unemployed could seek unemployment benefits for more than 33 weeks from the regular 26 weeks (Kelly, 2009, para. 1). This means that the unemployed could seek unemployment benefits for 59 weeks. Approximately 3 million people were expected to benefit from the bill. In addition, the US government suspended taxation applicable to unemployment benefits. This meant that the unemployed did not have to pay income for the first $2400 they receive. However, any amount above $2400 was subject to income tax.
By increasing its payment to the unemployed, the US government played a significant role in stimulating the country’s economic growth. This arises from the fact that unemployed people are likely to consume the amount offered. The resultant effect is that consumption which is a major factor in a country’s economic growth was boosted significantly.
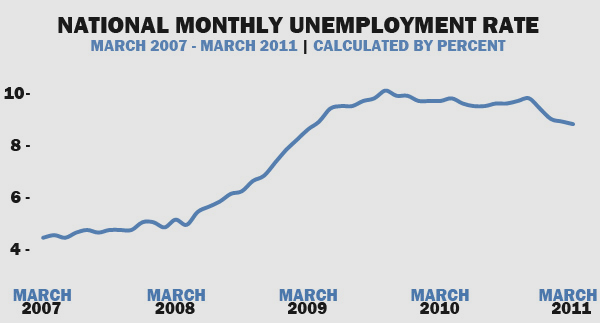
Source: Web.
Balance of payments
Balance of payment indicates the total of the financial transactions conducted between a country and all the other countries of the world. BOP indicates the total amount spent by a country’s citizens on imports and how successful its firms are in exporting to the international market. During the 2010 financial year, the US experienced a deficit in its current account. The country’s deficit in goods and services during its 2010 fiscal year increased to $ 495 billion from $ 374.9 billion in 2009. One of the factors which led to the increase in the trade deficit is an increase in the volume of imports relative to exports (Scott, 2009, para. 9).
In an effort to improve the BOP, the government has incorporated a number of macroeconomic policies. One of these is aimed at improving exports. The policy entails offering incentives such as tax reduction and subsidies to specific industries. As a result, these firms are able to produce cost-effectively thus lowering their prices. The resultant effect is that the country has been able to deal with foreign competition.
The US government has also integrated monetary measures which entail lowering the interest rate. Through the Federal Reserve Act, the government lowered the rate of interest so as to stimulate economic growth.
Conclusion
As a result, of the 2007 economic recession, US economic growth was adversely affected. However, the above analysis illustrates the US government and the Federal Reserve’s commitment to stimulate the country’s economic growth in 2009 and 2010. This has been achieved by evaluating the factors which enhance a country’s economic growth. Additionally, the researcher took into consideration various macroeconomic policies. One of the macroeconomic policies which the US government and the Federal Reserve utilized is increasing the level of government spending in various economic sectors.
For example, by increasing its spending on research and development, the US government was able to boost its domestic investment. This is due to the fact that investors relied on the research findings to conduct the investment. In addition, the government increased its spending on enhancing human capital by increasing its funding for education and training. As a result, the US has been able to enhance its labor productivity. As a result of the decline in the FDI in the US, Congress devised the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act in 2009 which included a number of incentives so as to attract foreign investments.
To control inflation, the Federal Reserve has increased the applicable rate of interest thus decreasing the amount of money in circulation. With regard to unemployment, the US government has instituted an economic stimulus package to enhance individual consumption. Additionally, the US government has issued export incentives to promote the country’s exports. As a result, the country has been able to control the balance of payment deficits.
References
Brickman, A., 2010. The USA opens for business 2010. Web.
D’Anieri, P., 2010. International politics: power and purpose in global affairs. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning.
Jackson, J., 2011. Foreign direct investment in the United States: an economic analysis. New York: Congressional Research Service.
Kelly, M., 2009. Stimulus funds boost number of federal jobs. Web.
Kyser, J., Sidhu, N., Ritter, K. & Sedgwick, S., 2010. 2009-2010 economic forecast and industry outlook. Web.
Organization for International Investment. 2010. Foreign Direct Investment in the United States. Web.
Sargent, J., 2010. Federal research and development funding. FY2010. New York: Congressional Research Service.
Scott, S., 2010. U.S. international transactions: fourth quarter and year 2010. Web.
Watchel, P., 2010. Central banking for the 21st century: an American perspective. New York: New York University.
