Introduction
The selected business is Harley-Davidson, which is a motorcycle producing company. It was founded in 1903 in Milwaukee, and, since then, have competed with many domestic and international rivals. Within a century, Harley-Davidson became the largest U.S. motorcycle manufacturer. The company’s mission is to promote freedom for the soul and timeless pursuit for adventure (“Our company,” 2020). It also values emotion, evolution, and innovation as the key legendary traits.
Descriptive Process
The descriptive process is based on the Process Chain Network (PCN) analysis. The given approach assesses the interaction between product producers and clients (Kazemzadeh et al., 2015). There is a tight relationship between Harley-Davidson and its customers. Therefore, the company needs to be highly adjustable with the processes to satisfy its customers’ needs. It primarily focuses on lean manufacturing, where the main goal is to minimize waste (Slack, 2015). The only essential elements are quality and efficiency, which means that there is no place for unnecessary time or material usage.
The starting point of lean manufacturing at Harley-Davidson is customer value. If one considers the activities of an enterprise from the perspective of lean production, then all processes and operations can be divided into those that add value to the product and those that do not add value. Then, anything that does not add value to the consumer in terms of lean manufacturing is a waste that needs to be eliminated. Lean manufacturing is a logistics management concept focused on optimizing business processes with maximum market orientation and taking into account the motivation of each employee. Lean manufacturing at Harley-Davidson is at the heart of the new management philosophy. The purpose of such production is to achieve minimum labor costs, minimum terms for creating new products, guaranteed delivery of products to the customer, and high quality at a minimum price.
Lean manufacturing at Harley-Davidson is a system, business approach to manufacturing and product lifecycle management. In addition, this includes relationships with suppliers and customers, which can reduce the need for manual labor and significantly increase the efficiency of the use of production space. When introducing a lean manufacturing system, it must be remembered that the reorganization of production is a project. This requires not only an attentive and thoughtful attitude but also a mandatory preliminary assessment of the feasibility of implementation. In addition, at present, there is an active development of information solutions for the automation of lean production, the use of which, together with traditional control systems, can greatly contribute to the optimization of this concept’s implementation.
Quantitative Process
The quantitative process is the design and effective capacity, which will greatly help to improve the overall understanding regarding the company. Effective capacity can be considered as one of the essential elements because it describes the maximum amount of work or output an organization is capable of completing in a specific period of time (Aghapour et al., 2019). In other words, it factors in the main constraints, which hinder the effective capacity, such as delays, quality issues, and material allocations. A York-based facility, which assembles Softail and Touring bikes, produces up to 600 motorcycles, and many of them are customized according to customers’ needs. Such an impressive output is possible due to Harley-Davidson’s Materials as Needed (MAN) system, where materials go into the assembly line on a just-in-time basis, as can be seen in Figure 1. There is a number of steps taking place in the York facility, which include:
- Tube bending
- Frame-building
- Machining
- Painting
- Polishing
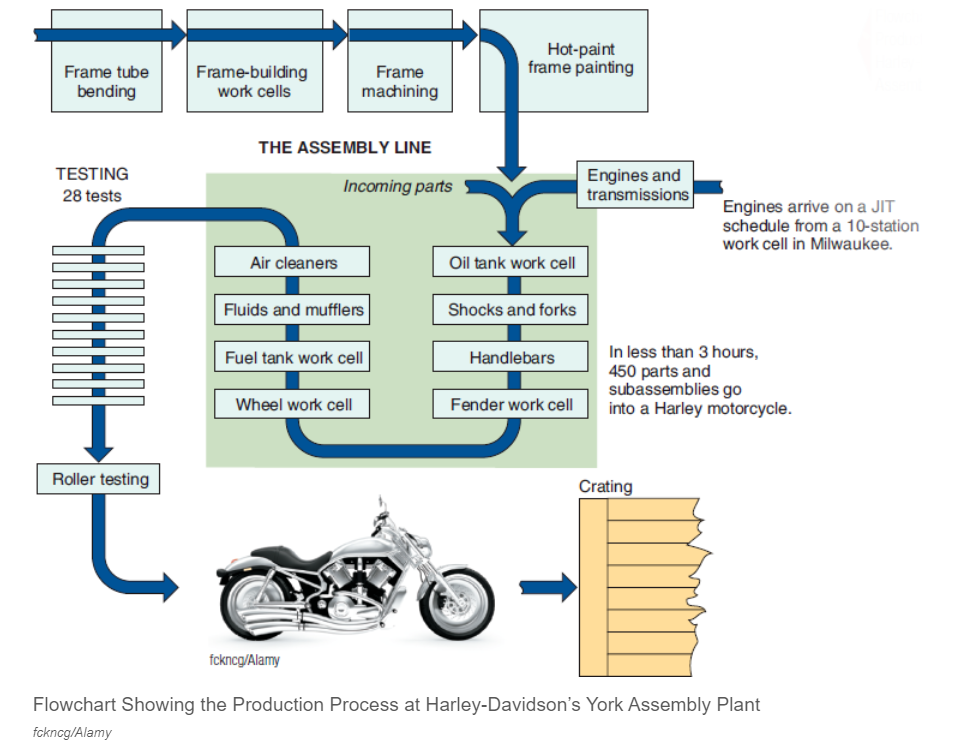
The alternative that lean manufacturing at Harley-Davidson offers is to rethink the role of functional services, departments, and the entire company so that everyone can contribute to value creation. In addition, their work must meet the real needs of employees throughout the value chain. When changing the organization of work, the first thing that can be seen is a significant reduction in the time between concept development and product release. There is a decrease in the period between sale and delivery, between the receipt of raw materials and the transfer of finished products to the consumer. Lean manufacturing at Harley-Davidson allows the company to freely change the sequence of production of any product and thereby respond quickly to changes in demand.
Thus, when introducing lean manufacturing, it is necessary to carefully and thoughtfully treat its application to carry out a mandatory preliminary assessment of the feasibility of implementation. In addition, Harley-Davidson is currently actively developing information solutions for the automation of lean manufacturing. Using technology in conjunction with traditional management systems can go a long way toward optimizing the implementation of lean manufacturing, which is, as shown by the research, worth it.
Conclusion
In conclusion, one should note that Harley-Davidson is one of the largest motorcycle manufacturers in the U.S. The company PCN analysis shows that it is highly customer-oriented where the company uses machines to sell emotions and experience. In addition, it also adheres to lean manufacturing operational management style, where the primary objectives are waste minimization and efficiency. Harley-Davidson utilizes the MAN system and just-in-time material control, which further improves its manufacturing. Therefore, the main strength of the company is the fact that its operations are highly automated and properly arranged. The challenges can be found in such efficiency being vulnerable to disruptions.
References
Aghapour, A. H., Yazdani, M., Jolai, F., & Mojtahedi, M. (2019). Capacity planning and reconfiguration for disaster-resilient health infrastructure. Journal of Building Engineering, 26, 1-13.
Kazemzadeh, Y., Milton, S. K., Johnson, L. W. (2015). A comparison of concepts in service blueprinting and process-chain-network (PCN). International Journal of Business and Management, 10(4), 13-25.
Our company. (2020). Web.
Slack, N. (2015). Capacity management. Wiley Encyclopedia of Management, 10, 1-2. Web.

