Introduction
Cost accounting in general denotes the process of determining and accumulating the cost of production of any specific product or service. The process involves accounting for the incurrence and control of the cost of production (Horngren et al., 2002). As an accounting discipline, it covers the classification, analysis, and interpretation of various elements of cost in any manufacturing setting. Costing is a system of accounting that provides information about the ascertainment and control of costs of a product or service through which the operating efficiency of an organization can be measured. Cost accounting is adopted to provide cost data and information on costs to enable the management to make well-informed business decisions. Cost reports form the basis of an efficient cost management system (McNair, 2000). This report studies the usefulness of the cost report for the individual loans section of Landshark Co and details how the costing information can be used for making better managerial decisions by the company.
Objectives of Identifying and Recording costs
The major objective of costing is to record and analyze the information relating to direct costs and revenues so that a system of cost control can be established. Usually, budgetary control system helps in this process by identifying the cost elements to which the costs can be allocated. For example identifying the cost of direct materials, labor, and other direct cost items and estimating the budgeted requirements will tell upon the competence of the production department when the actual costs incurred in these heads are recorded, analyzed, and compared against the budgets.
From the costing information about the individual loans section of Landshark Co, the overall cost of running the individual loan section can be ascertained. The costing information also provides a complete break up of employee costs, direct service costs, and departmental overheads. The statement presents information not only on the actual cost incurred by the division but also on the budgeted costs on the various heads and the deviation from the budgets. This analysis will help in assessing the performance of the division concerning the individual cost elements on which information is available. In a financial services company like Landshark Co, one of the most important cost items is the employee cost. Based on the volume of activities in the individual loan section, the management may decide to vary the size of the workforce. The escalation in the employee cost should justify the increase in the volume of business handled by the section. The management may be reluctant to increase or decrease the workforce due to the existing company policies and the cost of selecting and training the workforce, especially people like mortgage examiners. However, the management should be convinced that the employee cost justifies the level of activity. The performance of the individual loan section can be easily assessed by comparing both budgeted and the historical figures of employee cost and volume of activities handled by the section. This is one of the objectives of identifying and recording costs.
Next to the employee cost the direct services cost and the administrative overheads assume importance as they determine the profitability of the division. Based on the costing information provided it is possible to identify the areas where cost can be controlled so that the efficiency of performance of the division can be improved.
The direct service costs like photography, tracing and mimeograph are directly proportional to the number of loan accounts moving through the department. Therefore any increase in the expenses on the direct service costs should be because of an increase in the accounts handled by the department. An efficient collection of costs on these heads and analyzing them would reveal the performance of the section in this respect. Even though the section may not have any control over the other fixed costs like rent and prorated company services, there are other items of administrative expenses such as office supplies, travel, telephone, and postage where the section could exercise caution to control the expense within the budget established. A comparison of the budgeted and actual expenses of individual loan section for the first six months period can be represented as below:
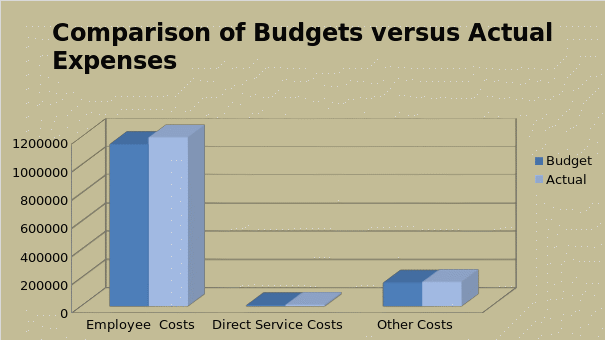
From the figure, it can be observed that the individual loan section has just exceeded the budgeted costs. In the absence of the number of accounts handled by the section, it would be difficult to identify whether the excess spending by the section is justified or not.
Information Qualities of Costing Data
In general, there are some basic qualities that any information should possess such as effectiveness, efficiency, confidentiality, availability, and reliability (Gelinas & Dull, 2009). All these quality attributes apply to the costing information also. To be effective the costing information should be relevant to the business process. The information should also be delivered in a timely, correct, and consistent manner to be useful to the users of such information. Accuracy and completeness of the information is another essential quality which the costing information needs to possess to be meaningful and to enable managerial decision-making. Availability of information at the appropriate time when required by the business process will help the organization safeguard its resources and associated capabilities by enhancing the productivity of the organization. Reliability is to be regarded as the most important aspect in the realm of cost, as the management will depend to a large extent on the costing information for taking important decisions concerning pricing and product mix.
In the case of the costing report for the Individual loans section, the information on the employee cost should be highly reliable and effective. The individual loan section is responsible for the legal processing of loans made to individuals and secured by mortgages on real estate properties. Since then the major function of the individual loans section is to perform the legal work necessary on all the new as well as existing loans purchased by the company, the section employs attorneys, mortgage examiners, and supporting secretarial staff. The staff has been recruited and trained by the company to do this routine job of checking the documents under the supervision of the attorneys. The efficiency in the performance of the section can be assessed based on the number of loan accounts cleared by the section. This has a direct bearing on the time spent by the employees and therefore the employee costs are the relevant performance index. The employee cost when compared to the budgeted level and the number of accounts checked by the section will tell upon the efficiency of the section. This makes the collection of reliable costing information on the employee costs important. The information should be made available in time so that the management would be able to control the employee cost.
Use of Budgets for communicating Financial Information
The basic objective of the budget process is to enable the division heads to plan and report in advance the scope of operations in their respective divisions for the following budget period. The budgets are prepared to take into account the anticipated changes in the activity levels from the current period and then arrive at the cost implications of these proposed changes. Management usually checks the individual budget for reasonableness and the total expected cost and revenue to ensure that the company can expect to achieve the desired profitability during the following year. Once approved, the budget can be used as a tool for communicating the relevant financial information to the division head so that he can plan the activities of his division in congruence with the overall financial planning of the organization. The financial information conveyed through the device of divisional budgets acts as the measure of the ability of the divisional head to plan the operations of the division and align the divisional operations with that of the organization as a whole. With a periodic review of the financial results of the division as compared with the financial information communicated through the budgets or costing reports, the actual performance of the division can be compared with budgeted performance and wherever deviations are there, the divisional heads may be asked to submit their explanations on large deviations in the financial results as against the projected estimates (Anthony et al., 1972). The costing report on the individual loans section can be used as a device to communicate the budgeted financial estimates of employee costs as well as other administrative costs so that the divisional manager can ensure effective control over the expenses under these heads.
Impact of Cost Report on the Operations of a Division
The cost report serves as an effective tool for providing valuable information and data for making sound business decisions. The manager in the day-to-day running of the operations of the division he heads is confronted with several decision-making scenarios, where he needs some financial information to arrive at the best decision. When the actual accounting figures for the period are not ready for his consideration, the costing report or the budgeted estimates provide an effective base on which he can rely for making the decisions on alternative solutions available. In manufacturing setup, defining the cost by variable and fixed costs enables the managers to calculate the contribution margin from any particular product which can be used in the cost-volume-profit analysis for deciding on the production volume of a specific product among different options (Fleming & Mary, 2000). For making this calculation, the manager can as well use the costing report which contains the budgeted revenue, variable costs, and fixed costs. In the case of the individual loans section, the manager based on the estimated volume of work expected to be passing through his department can decide to increase or decrease the number of staff in the section. The costing information on the employee costs and a comparison of the cost with the likely volume of activity will guide the manager to decide on the number of staff needed in the department for the following year. This is vital especially because the company spends a lot of time and money in recruiting and training staff required to deal with the legal documents for discharging the operations of the section. The manager has to keep the number of employees at an optimum level and should decide to employ additional staff only when he is confident that the need for additional hands in the department is permanent and is justified by the increase in the level of activity. Thus the information contained in the cost report enables managers to make sound business decisions concerning the operations of the respective division.
Additional Cost Details for forming a Clear Idea on Cost Situation
Since the function of the individual loans section is the legal processing of loans made to individuals the volume of activity in this section depends largely on the loan amount that the company earmarks for the following budget period. Normally the investment division of the company is made responsible for establishing the terms of the proposed loans including the number of loans, the respective interest rates, and maturity periods (Anthony et al., 1972). The individual loans section has to check all the loan instruments to ensure that the instruments protect the interest of the company as required by law and by the investment division of the company. Therefore to effectively decide on the volume of activity it is important that the manager of the individual loans section gets an idea of the total amount of loans budgeted to be purchased by the investment division in the ensuing period. It is also important that the investment division advises the individual loans section the estimated number of loan accounts that it proposes to undertake in the next budget period so that the individual loans section manager can estimate the level of activity in his section and decide on the number of staff required to handle the anticipated volume of operations by his section. This information will help the manager to estimate the employee costs as well as direct services costs. Based on the volume of work estimated the manager would be able to decide on the other costs like travel, telephone, and office supplies.
Communicating Cost Information in a Retail Shop
A retail shop can be considered as a responsibility center which can be further classified as a revenue center for control purposes. In a typical revenue center, an optimal relationship cannot be established between the input and output and the output can be measured physically in terms of the profit the center makes (Anthony et al., 1972). The revenue centers are not given the authority to set selling prices and the manager is held accountable for the expenses incurred directly within the unit. The primary measurement of performance is revenue. In a retail setting, the cost information is to be communicated to the manager who holds the position of responsibility for the revenue to be earned by the revenue center. He needs to know the percentage of discounts he can offer to prospective customers to increase the revenue. The absence of the cost information with the revenue center manager may result in loss of sales. On the other hand, there is no need that the cost information to be provided to the sales staff as they need not be made part of the pricing decisions. For any pricing decisions, they need to get confirmation from the manager of the revenue center and the authority in this respect is to be centralized with the manager. Revealing the cost information at the salesmen level would dilute the authority and in such a situation the manager may not be held accountable for the revenue maximization.
Need to Record the Costs of Loans Section
Individual loans section being an administrative and support unit the output of this section cannot be measured in monetary terms. This section is a discretionary expense center and therefore the management’s judgment as to optimum cost can be more a haphazard estimate and depends largely on the policies of the management. For instance, the company may decide on the number of staff in the individual loans section based on the cost of training the staff as mortgage examiners. In a discretionary expense center, normally the difference between the budget and actual expense is not considered as a measure of efficiency (Anthony et al., 1972). The cost of the loans section depends on the level of activity in the investment section. However, it is for the manager of the section to live within the budget amount and the management can control this aspect only when costs in the individual loans section are recorded and compared against the budgets.
Recommendation
The management may be able to achieve control within the individual loans section by using the services of the loan section staff to the functions of the investment section. Even though the investment section may not be able to provide some complete batch of work, part of the work can be transferred to the loans section whenever there is slack in the loans section. Similarly, the mortgage examiners may be trained to handle foreclosures whenever there is a lesser number of loan applications to be processed by the loans section. This would greatly help control the cost of individual loans section.
Conclusion
Each operating unit within a business organization develops its long-range plans and short-term budgets. The objective of budgeting is to have effective control over the cost to be incurred by the respective unit or division. The management looks at the budget and cost reports as a performance measure. The performance of any operating division can be measured by the deviation of the actual cost incurred by the respective division against the budgeted cost. The cost report thus forms the tool for the management to institute corrective actions wherever the management finds discrepancies in the budgeted and actual performance levels. The divisional managers are made responsible for meeting the budget estimates both in terms of revenue and expenses. Apart from the controlling function, the cost reports can be used as a communication device for informing the divisional managers of financial information based on which the managers can plan the level of operations in their departments. It is to be noted that in a revenue center the cost information needs to be communicated only to the person who is to be held accountable for the performance of the division in terms of revenue. Communicating cost information to the people at a lower level would dilute the authority and will absolve the manager from the responsibility for the revenue targets. In discretionary expense centers recording the cost, information becomes necessary to assess whether the manager stayed within his budgetary limits.
Reference List
Anthony, R.N., Dearden, J. & Govindarajan, V., 1972. Management Control Systems. New Delhi: Tata McGraw-Hill.
Fleming, K. & Mary, M., 2000. Towards Diversified Cost Accounting Systems. Web.
Gelinas, U.J. & Dull, R.B., 2009. Accounting Information Systems. USA: Cengage Learning.
Horngren, C.T., Foster, G. & Datar, S.M., 2002. Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis. New Delhi: Prentice Hall of India Private Limited.
McNair, C.J., 2000. Defining and Shaping the Future of Cost Management. Journal of Cost Management, 14(5), p.32.

