Introduction
Quality management includes many aspects such as quality plan, phase quality requirements, applying quality methods, reviewing the quality phase and the project quality review. Techniques and tools available for quality improvement today include information technology, quality function deployment, quality circles, total production management (TPM), total quality management, among others. A quality plan is driven by objectives, must have requirements, quality methods, standards and procedures.
To understand quality management, the International Organization for Standardization defines it as “a business tool focused not only on a product’s quality but also on how the product will be achieved thorough quality planning, quality control, quality assurance and quality improvement” (2). The organization also notes that the process of managing quality has over the years adopted a number of principles discussed below. Different businesses have different ways through which to apply this important business tool. To ensure customized management abilities and adapt to the many changes in business today, more businesses view it as an effective tool, one that allows them to keep the quality of their products consistent. “Quality management principles include customer focus, leadership, process approach, system approach to management, continual improvement, factual approach to decisions and relationships with different stakeholders” ( International Organization for Standardization 2).
Quality management principles
There are seven principle management principles. The first one is customer focus. Since organizations depend on their customers for the success of their business, it is important for them to understand their current and future needs and expectations. Benefits of customer focus as a quality management principles include increased market share and revenues. By understanding customers and what they need, the principle allows businesses to respond fast to market opportunities and enhance customer satisfaction. The results are higher brand loyalty levels and stability.
The second principle is leadership. According to the International Organization for Standardization, “leaders establish unity of purpose and direction of the organization and should create and maintain the internal environment in which people can become fully involved” (3). Benefits of leadership as a quality management principle include a better understanding of a business’ goals, proper activities alignment and implementation, as well as proper communication between different organizational levels.
Another important principle of quality management is involvement of people. Every business today realizes that human resources are its biggest asset and people are the essence of the business. By involving people fully, a business enables its abilities. Key benefits include committed, innovative, motivated and accountable people. When people are involved, they are eager to give their contributions to a business for the sake of continual improvement. Other quality management principles include process approach, continuous improvement, system approach to management and a factual approach to decision-making.
The affinity diagram as a quality planning tool
“The affinity diagram is a management and planning tool used to organize ideas and data, and group similar things into more focused areas” (Pyzdek 9). The process involves three major steps all aimed at taking large amounts of data and information and arranging it into classes and groups depending with how they relate. It is among the many management and planning tools used today, the others being the prioritization matrix, the process decision program chart, the interrelationship diagram, the tree diagram, the matrix diagram and the activity network diagram.
The affinity diagram is easily applicable when a business is solving a quality problem, brainstorming for ideas or analyzing complains. It is an effective tool when a business is trying to assimilate all the information into sensible and manageable categories. “The diagram is an important tool when synthesizing large amounts of data by finding relationships between ideas, as information is gradually structured from the bottom up into meaningful groups” (Pyzdek 31). As a quality management tool, it is very useful especially in the information management department so that they only share information to other departments when it is already organized and easy to interpret. For a company such as NBAD, it would be an effective tool when it is doing a market analysis on why the market share is reducing. It is expected that the results for such a survey would be large volumes of data, which would create many random ideas. The affinity diagram can be used in such a situation to categorize the results into service, market trends, competition, strategy and many other relevant categories.
Nominal group technique
To encourage equal participation in business, more companies are embracing the nominal group technique. The tool gives every person an opportunity to participate in resolving problems in their departments and organizations. It allows every person a chance to brainstorm, come up with ideas and present them to the rest of the team without fear of being judged for coming up with the best ideas. A secret voting for the ideas ensures that people vote genuinely without the need to impress their friends or team members. According to Carmosion’s definition “it is a decision making method for use among groups of many sizes, who want to make their decision quickly as by a vote, but want everyone’s opinions taken into account as opposed to the majority vote having their way” (11).
Like every other business tool, the nominal group technique has disadvantages and advantages. Its disadvantages include the fact that “opinions may not converge in the voting process, cross-fertilization of ideas may be constrained and the process may appear to be too mechanical” (Carmosino 13). Some of its advantages include the fact that voting is anonymous allowing the team to be true and real in their judgment. It also allows members equal participation and minimizes distractions during voting. It is time-saving as it allows a team to identify a problem and solve it as a team. Since no criticism is allowed during presentation, members of the team who are afraid of criticisms are more willing to suggest ideas. It eliminates differences between members of a team and ensures equal participation and consideration.
Using Nominal group technique in NBAD
National Bank of Abu Dhabi
“The National Bank of Abu Dhabi id the UAE’s second biggest bank by asset, has a network of 83 branches across the region and its overseas network stretches from Oman, Kuwait and Bahrain to Egypt and Sudan in Africa, London and the US” (National Bank of Abu Dhabi 1). The bank’s fourth quarter profits went down by 35%, a factor largely attributed to a reduced market share due to competition. Abu Dhabi Investment Authority (ADIA) have the majority shareholding in the bank with a 70% stake in it.
The following example uses nominal groups technique to establish key problems and issues in the National Bank of Abu Dhabi (NBAD).
Step 1: Introduction and explanation
This step involves presenting a clear explanation of the purpose of the meeting and raising a question to the team. The question in this case was; What are NBAD’s major problems and key issues?
Step 2: Silent generation of ideas
In this step, the facilitator provided each participant with a written problem and asked them to silently brainstorm and note down all the ideas they have concerning the question. As they did that, no consultations, discussions or criticisms were allowed.
Step 3: Sharing ideas
After everyone is done writing their ideas down, they are each invited to share them. Participants’ presentations are recorded and this is done until everyone is done. At this stage, very little attention is given to whether an idea is relevant or not even though participants are encouraged to stay within the topic. It is also important to note that no debates or criticisms are allowed. The other participants are encouraged to pay attention and note any new ideas that may arise from the ongoing presentations.
Among the issues and problems came up in this step include: lack of employee loyalty due to less pay, reducing revenues due to reduced market share, effects by international markets due to the banks presence in many regions, lack of training, lack of employer-employee relationship, sustainability issues, high level of exposure to political risks in different countries such as Egypt, lack of strong strategies to deal with competition and criticism over little involvement in environmental issues in the UAE region.
Step 4: Discussions
At this stage, the participants are allowed to seek clarification on any point that they think has not been well explained. Every person is allowed to participate in the discussion. The participants discussed the points raised in step three and from the discussions, it was easy to decide on which ones to vote for.
Step 5: Voting and ranking
This step involves prioritization of all the presented ideas. Everyone votes on an idea depending with how much sense it makes to them. Priority is based on how the idea relates to the original question. In the case of NBAD, the voting process revealed that the biggest problems in the company are; lack of employee loyalty due to less pay compared to market rates, reducing revenues due to reduced market share, effects by international markets due to the bank’s presence in many regions, high level of exposure to political risks in different countries such as Egypt, and criticism over little involvement in environmental issues in the UAE region.
Flow charting and its use in quality management
Flow-charting is one of the tools that allow businesses maintain consistency in their products. “It is a tool for analyzing processes by allowing a business to break any process down into individual events and activities and display them in shorthand form showing the logical relationship between them” (Pyzdek 56). It helps a business develop a common and an easy understanding of a situation and adopt a problem solving approach that makes it easy to solve ambiguous problems. It also helps business create consistency by establishing a standardized way of going through a particular process. The process promotes a better understanding of different processes in a business, which promotes improvement. Flowcharts can be used to clarify and communicate processes and ideas.
As a quality management tool, flow-charting helps businesses respond to changes in customer demands, market trends, products’ requirements, and regulations. These changes may not always fit and suit a business especially if they are not understood on time. In addition to understanding change, there is a constant need by businesses today to search and implement new ideas in order to retain their competitiveness and the advantages they enjoy in the market. Since many organizational activities involve many small events and tasks, a flowchart allows one to put them together into an easily understandable format.
Using a flow chart to identify gaps in work flow
The example below explains the procedure followed in NBAD to hire a messenger
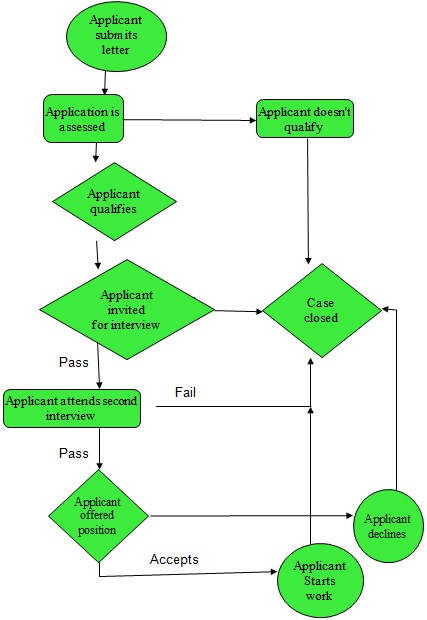
Conclusion
As businesses struggle to stay relevant and profitable in different global markets, quality management tools and techniques continue to find a place in many organizations’ operations. They play an important role in customer satisfaction, effective management and timely delivery of products and services to customers.
Quality management techniques include information technology, quality function deployment, quality circles, total production management (TPM), total quality management, among others. Flow charts, the nominal group techniques, the affinity diagram, data analysis tools and many others are important brainstorming tools in any business today.
As the globalization of markets cause more information overload, these tools enable businesses organize and manage information in a way that is helpful during decision-making processes. Information technology techniques and quality management software have also made it easier for organizations to manage quality and adopt to changes. “Quality management principles include customer focus, leadership, involvement of people, process approach, continuous improvement, system approach to management and a factual approach to decision-making” (International Organization for Standardization 1).
Works cited
Carmosino, Jeffer. Nominal Group Technique: Involving the Public. California: California University, 2005. Print.
International Organization for Standardization. Quality Management Principles, 2011.
National Bank of Abu Dhabi. About NBAD, 2011.
Pyzdek, Godfrey. Quality Management: Tools and Techniques. New York: Routledge Publishers, 2007. Print.
