Management Consultancy
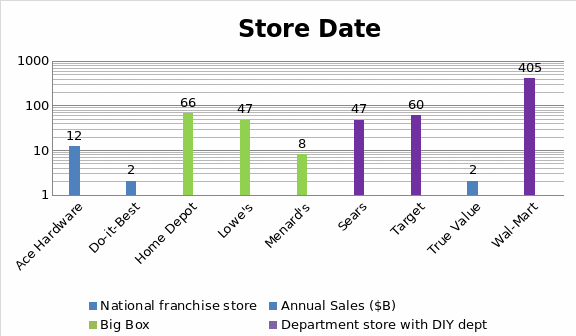
Misleading Sales Figures
The sales figure is merely a representation of any company’s activities in the market. If not analyzed properly, these figures can be misleading. First of all, it needs to be understood that the published sales figures are a result of financial engineering, and they have less to do with the actual operations or cash flow of the company. However, even if these sales figures are considered legitimate, they can still be misleading for several reasons:
- Keeping in mind the given case, it has been mentioned that the holding company has bought several chains of stores in Belgium, England, France, Germany, Italy, and Spain; all of which are European countries. Whereas, the given sales data is from American companies, which would not be of much help for any sort of comparison, and would most likely only misguide the decision-making process. The two continents are far apart from each other geographically and economically, as well. The world has become a global village because of the present levels of globalization, but still the two continents maintain a unique economic and business environment. Each country has its own challenges and opportunities, the conditions of demand and supply are quite different, and so are the competitors. So, the sales figure of companies from a different country would mislead the entire process right from the beginning.
- Secondly, even though the sales figures are of companies from the retail sector, they still are pretty different. The company under discussion specializes in Do-It-Yourself stores, since all the chains it had bought are of such stores. However, the data of the stores provided here are not strictly from the same industry. Some of them are hardware stores, some are Big Box stores and a few are Do-It-Yourself stores. Due to this reason, the sales figures of these stores might look promising, but the lack of experience of the holding company may result in significantly lower sales. Thus, rendering the sales data misleading.
- Furthermore, the sizes of the mentioned companies are incomparable. Do-It-Best and True Value are too small stores to be compared with Wal-Mart. The problem here is that only the sales figures are mentioned, which show that Wal-Mart is capable of generating more than $400 billion in sales, whereas True Value can only make sales up to $2 billion. This might make the investor think that Wal-Mart is a much better option to invest. However, what would be more useful is the sales-per-store data, or sales-per-square-foot-of-store-space data, because that provides better comparable numbers. Such data would be more relevant, and not misleading.
- Lastly, focusing on the sales figures is also misleading because people may confuse sales with profits. However, sales and profits are totally different things. If a company does not keep a strict control over its costs, or does not establish a healthy profit margin, it would still be able to attract customers and make sales, but the profits of the company will be significantly low, or it may even end up making losses.
Therefore, due to the mentioned reasons, the sales data can be quite misleading from a stakeholder’s point of view.
The Decision-Making Rationale Characterized by the Holding Company Executives
We all make decisions every day; some are trivial, whereas some are fairly significant. However, decision-making is one of the most important jobs of a manager. One of the qualities that differentiate a good manager from a bad one is the ability to make the right decision at the right time. Decision-making has now developed in to an established subject, and typically decision-making can be divided into three main categories:
- Normative decision-making
- Descriptive decision-making
- Prescriptive decision-making
Lately, a fourth type has also been added, Naturalistic decision-making. An analysis of the decision taken by the executive of the holding company shows that their approach is closer to Naturalistic decision-making, and there are several reasons for me to believe so. Firstly, the traditional approaches often assume that any decision-making problem can be divided into a series of features or outcomes, that the decision maker deems valuable (positively or negatively) in some way, and that the person making the decision will base his decision upon the achievement or avoidance of these outcomes. Orasanu and Connolly (1993), however, suggest that these approaches do not take into consideration several aspects of the decision-making process that the decision maker may find relevant (Orasanu & Connolly, 1993). For instance, like in the given case, the problem at hand has very high stakes, it is ill-structured, very uncertain, and interests of a lot of people are involved and not only of the decision maker. Under such circumstances an approach that takes these things into account, even if it means dropping formal ideas such as outcomes and probabilities, is valuable.
Furthermore, one of the key characteristics of the naturalistic approach is that it does not believe in over thinking the decision. The focus is a “good enough” decision and not strictly the “best” decision, and that is exactly what the holding company executives have done. Rather than going through each and every decision alternative in detail, they have settled on an option which they deem to be “good enough”.
Also naturalistic decision-making involves preparation before the decision is made, and an analysis of different types of stores in the U.S shows the same attribute.
Who should be Involved in the IT Platform Decision?
Like in every other decision, all the related parties who have a major stake or expertise in the matter should be involved in the decision. In this case, all the executives, the IT director and most importantly the unidentified buyer should be involved.
The executive should be involved because they are the top management of the company, and they should always be at the top of any decision that is of this much importance. This decision involves several chains of retail stores, and the impact of the decision will be of significance for the entire organization.
The IT director should be involved because he is the person here with the technical expertise regarding the matter at hand. He knows even if the option is technically viable or not. He would be well aware of the state of the present system, and also the time, effort and money needed to make the required upgrades.
Lastly, the unidentified buyer needs to be involved, because he is the one with the greatest stakes involved. If the present management decides to modify the system, but the present system is what would have suited him better, he would not only lose precious time but money, as well. On the other hand, if he requires a modified IT system, then probably the present management would be able to do it in a better and more efficient manner, thus making the situation more favorable for all the related parties.
Cognitive Styles Best Suited for this Problem
Everyone has a unique approach to problem-solving. The way we perceive the world and operate, process and register data, is known as our cognitive style. The cognitive style of a manager is of critical importance in the way he acts and makes the decisions. It is also important to understand that the cognitive style is different than the cognitive strategy; cognitive style has a broader scope than a cognitive strategy. John Hayes and Christopher Allison have divided cognitive styles into 26 dimensions (Hayes & Allinson, 1994).
In the given scenario, I believe, there is a need of analytical perspective. Therefore, cognitive styles that allow for a distinction between the alternate options would be best suited. I believe an analytical dimension would be best to perceive the problem. Once the problem has been perceived and registered, a logical reasoning approach should be taken for the problem solving purposes, which would involve a logical survey of all the alternatives available before reaching to any conclusions. Lastly, for the sake of task execution, an active approach should be taken, which prefers to gaining insight into the problem by active involvement instead of separated observation.
Best Creative Approaches in this Case
I would recommend mind mapping as a creative approach to analysis, for the reason that whenever creativity and innovation is the primary concern, the first person the consultant should be communicating with is himself. Contrary to popular belief, we do not have instantaneous access to our subconscious. In order to improve the analysis, we need to constantly communicate with ourselves, to get access to our thoughts, ideas and memories. Doing so engages us in a personal dialogue, which improves analysis, and one of the most effective such techniques is mind mapping.
Mind mapping is very different from writing ideas down on paper, because when we do so, it essentially becomes a linear exercise, which significantly limits its scope. However, practicing the same exercise in the mind makes it a semantic network, in which each idea is connected with a host of other ideas. Mind mapping is particularly very useful when there is need of creativity and innovation because the only rule in mind mapping is that there are no rules.
Furthermore, I would also recommend the Delphi auditing in some cases, where the decision maker himself has limited knowledge about the subject or is not an expert. In such cases, one should follow the Delphi method, which means that expert opinion should be taken on the development of such issues. By doing so a lot of time and effort can be saved and a better quality decision can be made, as well. The Delphi method has two major steps, 1) identifying the issue at hand and 2) making a list of the credible people who have expertise in the relevant area.
References
Hayes, J., & Allinson, C. (1994). Cognitive style and its relevance for management practice. British Journal of Management , 22 (2), 53-71.
Orasanu, J., & Connolly, T. (1993). The reinvention of decision making (3rd ed.). New Jersey: Ablex Publishing Corporation.

