In addition to internal risks, organizations have to face various external risks such as economic or natural (Hopkin 139). Economic risks can be associated with financial constraints affecting industries, states, or countries. The emergence of such threats can lead to decreased revenues, a high rate of turnover, and an inability to innovate. In order to mitigate these threats, the operational manager will develop a risk management plan with recommendations concerning business insurance, the development of a fund for innovation, or a guideline for the allocation of funds during crises.
The operational manager will address financial department employees to come up with the plans. As for natural disasters, these can be storms or floods (and many other severe weather conditions). The operational manager should create a plan where employees’ activities during and after the disaster will be outlined. Some steps to ensure the safety of resources should be considered.
A risk management team is responsible for identifying and prioritizing threats, developing a mitigation plan, evaluating the effectiveness of the plan, and making corrections if necessary. Collaboration with other employees is essential for the success of the developed plans and their implementation. For example, when working on the part linked to external risks, operational managers should collaborate with financial department employees. It is important to describe specific measures that should be undertaken in particular situations. When developing the part related to natural disasters, operational managers will consult IT professionals on specific ways to ensure the safety of equipment.
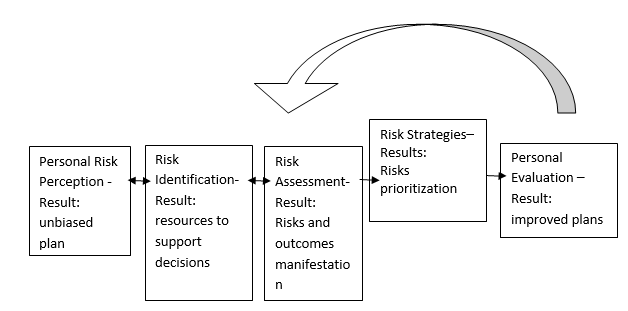
The risk assessment of the IT department was performed by means of the PRINCE2 model and generated a number of significant outcomes. The status and the legal compliance received the lowest scores of all the risk assessment criteria. I believe that this outcome is realistic and reflects the current situation as the status of the organization is sustained by the performance of the IT department (Rausand 43). All the legal requirements are carefully followed by the organization, so there is no doubt that these two criteria have little impact on the overall state of affair.
Human safety received the score that was a bit higher than those of the status and legal compliance criteria. This happened due to the fact that the work in the IT department of OMARCOM is connected to a number of hazards. In addition to that, working with a computer is connected to a number of health issues that are developing throughout an extremely short period of time (Rausand 47). The organization should take this into consideration in order to minimize the risk of decreased performance or staff turnover.
The next risk is the project schedule. The staff at the IT department of OMARCOM showed an average level of compliance when it came to the organizational discipline. This is supported by recurrent lateness among the staff, numerous skipped workdays, and inability to meet the set deadlines in almost 30% of the cases. If compared to the previously assessed criteria, the disregard of project schedule has a greater impact on the outcomes of a project.
The issues of discipline and schedule contempt should be resolved as soon as possible (Rausand 50). Nonetheless, the highest scores were received by the cost of the project and staff performance. These two criteria have the biggest impact on the department and the organization as a whole. The high cost of the IT projects may drain the budget of OMARCOM, and poor staff performance may result in the loss of income and client base.
Throughout the process of risk assessment, I have identified several advantages and disadvantages of the PRINCE2 risk management model. First, it helped me to divide the project into the stages, and the management of the risks became easier. Second, PRINCE2 is aimed at establishing an improved communication between the staff members and external stakeholders. Therefore, this approach provides more control to the risk manager (Rausand 102). Second, this risk assessment model gives the stakeholders the possibility to monitor the situation. Consequently, PRINCE2 is adjusted to identifying the IT department’s weak areas. On a long-term basis, this risk assessment model is useful in terms of correcting the flaws inherent in the department.
Third, PRINCE2 is a rather flexible model and allows the changes to be made in real time. The project team will be able to save resources and cut the costs of the project greatly. The biggest disadvantage of this risk assessment model is that it cannot offer a high level of flexibility that can be found in other contemporary risk assessment models (Rausand 111). The IT sphere develops quickly, and the users of PRINCE2 may encounter a number of specific difficulties when dealing with the modern projects.
Another two risk assessment methods that could have been used are GANTT and PERT. The first one is a graphic method of managing the risks of the project. There are several pros and cons that are characteristic of the GANTT model. The first advantage is that it generates a picture of the intricacy of the risk criteria. Second, this model allows the risk manager to set realistic time frames and develop a reasonable project schedule (Shapiro and Noe 123).
Third, the GANTT model is used to structure the ideas of the project risk manager and convey them to the staff. The key disadvantage of this model is that it can become too complex to understand it. Second, it is essential to constantly track the changes and update the graphs (Shapiro and Noe 128). Third, the graphs may seem confusing to the staff due to the fact that longer bars may represent an easier task that does not require much time and vice versa.
The PERT model is also based on the graphic representation of the risks. It specializes in the tactical level planning. The key advantages of this model are easy project management and critical path identification (Shapiro and Noe 155). The PERT model allows the project team to see the relationships between the risks and organizational performance and define the critical tasks that should be dealt with in the first place. At the same time, this model features confusing charts that may serve as the main factor motivating the team to disprove the use of the PERT model (Shapiro and Noe 157). Moreover, the predictions made by means of this model may be inaccurate due to the complexity of the project and high probability of unexpected events.
The two examples of risks that have a ubiquitous effect on the organization are conflicts within the project team and lack of resources. The potential implications of these risks can be identified as momentous due to their critical impact on the working environment, employee morale, and compliance with the set organizational objectives. The potential effects of these risks may include decreased performance and the failure of the project. Therefore, the effect of interpersonal relationships and improper allocation of resources is crucial. The results of the risk assessment showed that the PRINCE2 model provided an adequate evaluation of the risks present in the IT department of OMARCOM. The scoring method is relevant and reflects the upsides and downsides of the current project. The level of risk can be identified as “above average.” This can be explained by the mediocre level of accountability among the majority of the IT department staff and their unwillingness to comply with the vision of the organization.
When choosing the most appropriate strategies to mitigate risks, it is essential to estimate their operational effectiveness. The first approach is effective since it is characterized by efficient tools that can help the department avoid financial losses. Such steps as insurance, partnerships, and outsourcing have proved to be beneficial for addressing various financial risks (Hopkin 200). These measures are also associated with a comparatively modest investment, so can be appropriate for many companies including Omarcom.
The second approach that is concerned with employee morale can be difficult to maintain at the time of crisis. Continuous work on the relationships and working environment is essential since it can make people motivated and committed to organizational goals. This is a time- and effort-consuming process that requires certain investment. However, it is pivotal to maintain high staff morale in order to ensure the department’s excellent performance especially during a period of constraints. Since personnel’s morale is one of the priorities of HR professionals and managers, these stakeholders should collaborate and develop methods that will meet employees’ needs and expectations.
As for the third approach linked to resources allocation, the proposed activity can be rather ineffective operationally. Meetings can be a waste of time if the agenda is not set and the stakeholders are not motivated to participate. Employees can also express their concerns and focus on their needs without trying to find solutions. Therefore, it is necessary to make sure that the meetings will be held properly (with a detailed agenda, feedback, motivation). Employees should be encouraged to take an active part in the discussion, so it can be necessary to explain the objectives and potential outcomes of the meetings. Finally, training may be required, as employees may need to acquire communication, conflict management, and resources allocation skills.
Works Cited
Hopkin, Paul. Fundamentals of Risk Management: Understanding, Evaluating and Implementing Effective Risk Management. Kogan Page Publishers, 2018.
Rausand, Marvin. Risk Assessment: Theory, Methods, and Applications. Wiley, 2012.
Shapiro, David, and Angela Noe. Risk Assessment: Origins, Evolution, and Implications for Practice. Springer, 2015.

