Business Companies Problems
It is well known that business companies planning expansion in the near future should conduct a thorough analysis of current economic problems in order to achieve maximum efficiency in the procedure of increasing the staff and volume of goods or services produced. At the same time, it should be noted that the main problem faced by an entrepreneur in trying to scale his organization is the financial component (Robertson & Robertson, 2012). Traditionally, the business has been expanding through an increasing variety of assortment, distribution of retail space, and geography. Each of these operations is expected to require significant financial investment in order to go smoothly and smoothly.
In this example, Cool Widgets Inc., a collection company handling thousands of letters, does not say that it has financial problems. On the contrary, Sandra, the CEO, plans to expand geographically into California, New York, and Nevada, and increase its staff both physically and remotely. This scenario describes a common problem among many business companies, namely the establishment of internal processes. Organizations need to be confident that their forces can handle the full volume of incoming correspondence and streamline accounting transactions. Cool Widgets Inc. focuses on creditor activities and includes three categories — accounts payable, accounts receivables, and account collections. Finally, the confidentiality of information is not an insignificant problem for companies that collect data, and even more so for clients’ financial transactions (Pullen et al., 2019). Companies must ensure that their work materials are fully protected and respond prematurely to potential hacker attacks and leaks.
CWI’s Problems
The company handles more than a thousand letters per day, and the projected expansion in the three states contributes to the growth of turnover. Indeed, such a scale of letters, including not only client appeals and complaints but also financial reports, accounting balances, bank statements, checks, UPS, Fed-Ex, and courier deliveries, requires attention and professionalism in processing. Cool Widgets Inc. handles letters physically, which means that staff is responsible for sorting, redirecting, and reporting correspondence. That is the company’s problem: it cannot set up internal processes to handle such a large volume of mail, therefore, according to the scenario, some of the mail is delivered to the wrong address, routing is disrupted, and fines arise. From this point of view, it is assumed that the scaling of the company will only exacerbate the situation as the number of mails will increase.
Influence on Stakeholders
This situation affects not only the company’s customers but also other stakeholders, such as employees, suppliers, and investors. Broken correspondence turnover and incorrect routing mean that letters, invoices, and payment notices are not delivered on time or are not delivered at all to customers. As a result, customer expectations are not met, and they decide to stop using the services of Cool Widgets Inc. The inability to deal with mail is similarly problematic for employees, as the workload of the company’s departments seems high. This can cause professional stress and fatigue, which are not known to have a positive effect on organizational performance and productivity (D’Arcy & Teh, 2019). The person in charge, Tyra, may feel more concerned because she is most likely to be under pressure from her supervisors. Finally, if a company’s structure implies investment, investors and shareholders may not be interested in a business that receives many complaints.
Needs and Solutions
The decision that needs to be made to achieve the efficiency of internal processes at Cool Widgets Inc. is the automation of mail processing. In the modern world, developed companies are seeking to move away from work to automated processes, and the processing of incoming mail requires no human effort and can be replaced by machines (Mendling et al., 2018). In particular, with the help of automation, it is possible to simplify the work of the accounting department on the movements of the company’s financial flows considerably. Finally, a significant advantage of automated letter processing will be increased data confidentiality, as this approach eliminates the human factor and creates a culture of transparency.
On the other hand, the company faces the need not only to sort and redirect letters in a high-quality and timely manner but also to conduct analytical work on business scaling. As mentioned above, Cool Widgets Inc. plans to open additional branches in Nevada, New York, and California, and at the same time to hire new employees. The HR department of the company needs to develop a recruitment strategy, because if at the moment the company does not have a high rating and attractiveness in the eyes of applicants, then failure is guaranteed (IIBA, 2015). HR may consider the variant of tangible and intangible benefits both for new employees and for those who have been working for a long time. If Cool Widgets Inc. introduces an automation system for mail processing, employees should be trained to work on this. The company turns out to be interested in conducting training sessions as well.
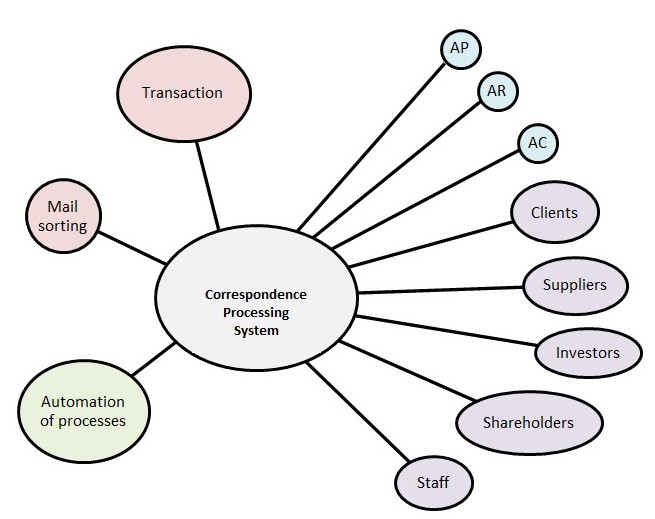
Context Diagram
The context diagram allows to visually reflect the connections present in the system for processing letters, accounts, payments, and bank statements. Cool Widgets Inc., being not a small company, has a branched diagram that includes the internal business structure and external connections and process management. There are several color categories on the chart that need to be explained.
- Blue are those departments of the company that deals more with mail. For Cool Widgets Inc., these are the accounting departments that deal with payment poisoning, revenue management, and processing of incoming financial flows.
- Purple is the system’s stakeholders.
- Red is the process that underlies the mail processing.
- Green is the projected improvement in the system.
Correspondence Processing System
References
D’Arcy, J., & Teh, P. L. (2019). Predicting employee information security policy compliance on a daily basis: the interplay of security-related stress, emotions, and neutralization. Information & Management, 56(7), 1-7.
IIBA. (2015). A guide to the business analysis body of knowledge. BABOK Guide Mendling, J., Decker, G., Hull, R., Reijers, H. A., & Weber, I. (2018). How do machine learning, robotic process automation, and blockchains affect the human factor in business process management? Communications of the Association for Information Systems, 43(1), 19-28. Web.
Pullonen, P., Tom, J., Matulevičius, R., & Toots, A. (2019). Privacy-enhanced BPMN: Enabling data privacy analysis in business processes models. Software and Systems Modeling, 18(6), 3235-3264. Web.
Robertson, S., & Robertson, J. (2012). Mastering the requirements process: Getting requirements right. Addison-Wesley.

