Introduction
This paper presents a detailed innovation action plan for Apple Inc. Apple is a leading manufacturer and distributor of high-end computers, smartphones, software, and multimedia devices. Some of the most important products of the company include iPhone, iPad, and iMac (Apple 2014). Founded in 1976 in the US, Apple has grown rapidly to become one of the largest companies by asset base and profitability in the world. The company owes its success to the creative utilization of cutting-edge technologies that enabled it to achieve product and process innovation. However, the level of innovation at the company has declined in the last three years. This is illustrated by its latest smartphones that lack features and functionality that can rival those of Samsung. Thus, the innovation action plan will evaluate the weaknesses and the strengths of Apple’s innovation management structure. It will also analyze the company’s innovation strategy. Based on these analyses, recommendations will be made to improve Apple’s innovation strategy.
Innovation Management Structure
Apple uses an organic innovation management structure in which product development and innovation activities are undertaken by various project teams. The teams report directly to the CEO and are fully responsible for their performance (Apple 2014). This innovation management structure has the following strengths and weaknesses.
Strengths
First, the structure enhances flexibility and learning in the company. This facilitates effective communication between the management and employees (Martinez & Garcia 2011, pp. 537-566). Effective communication enables employees to clearly articulate the technological and product innovation challenges that the company is facing. The resulting improvement in ideation leads to the creation of creative techniques and knowledge that ultimately enable the company to innovate.
Second, the structure is characterized by a low degree of formalization. The company does not use a unified command and control system. Behaviors are not highly formalized to enable employees to interact freely with their seniors (Apple 2014). The low degree of formalization promotes autonomy, which in turn improves accountability and responsibility. Accountability and responsibility motivate employees to develop innovative techniques to achieve their work targets.
Third, the innovation management structure facilitates the decentralization of decision-making processes. Each project team is allowed to make product design and production decisions. This promotes innovation by enabling as many employees as possible to participate in the process of making decisions that influence product quality and business processes (Abouzeedan & Hedner 2012, pp. 6-27). Also, the decentralization of decision-making processes eliminates the delays that often hinder innovation.
Fourth, the structure promotes horizontal specialization of labor. Apple’s employees focus on role integration within their areas of specialization. Undoubtedly, specialization improves employees’ knowledge, skills, and experience in specific business processes (Afuah 2003, p. 78). The resulting improvement in competency among employees leads to innovation.
Finally, the innovation management structure enables the company to satisfy customers’ needs. Specifically, the flexibility that the structure provides enables the company to focus on innovations that satisfy market needs rather than the objectives of the management (Trott 2008, p. 89).
Weaknesses
First, the organic innovation management structure is likely to work only if the employees are self-motivated. Since the employees have high levels of autonomy in their work, they have to motivate themselves to achieve innovation in their areas of specialization. This means that the lack of motivation among employees will limit the company’s ability to innovate (Sattler 2011, p. 92).
Second, high specialization among employees limits the extent to which ideas can be integrated to achieve innovation (Sattler 2011, p. 93). For instance, engineers who are in charge of product development might not understand the business case for product differentiation if they have no experience in business processes such as marketing.
Finally, the organic innovation management structure leads to the creation of a large volume of ideas. Undoubtedly, most of the ideas generated by the employees are not likely to be appropriate (Sattler 2011, p. 95). As a result, the company is likely to spend a lot of time and resources to evaluate ideas that might eventually not lead to innovation.
Sourcing New Ideas and Technologies
The Current Approach
Apple focuses on the internal generation of ideas and the development of cutting-edge technologies. The company does not believe in achieving innovation through huge investments in research and development or the acquisition of startup technology firms. For instance, in 2013 the company spent only $3.5 billion in research and development (Apple 2014). By contrast, its peers such as Samsung and Microsoft spent $10.2 billion and $10.6 billion respectively. Apple accesses new ideas and technologies by investing in staff development and training. The company employs the best engineers and marketers to achieve innovation. Moreover, it provides the best leadership and incentive programs to motivate its employees to be creative. As a result, ideation improves as the employees internalize the culture of creativity.
Effectiveness of the Current Approach
The main strength of the approach that Apple uses to access new ideas and technologies is that it improves ownership of the innovation process. Self-motivated employees are likely to go the extra mile to generate superior ideas and technologies that lead to real innovation (Assink 2006, pp. 215-233). For instance, the company’s employees developed the iPad because they were motivated to create a product that would improve their ability to communicate by combining the features of a computer, a phone, and a multimedia gadget in a single handheld device. Since the employees were passionate about their work, they achieved revolutionary innovation by creating a product with unprecedented functionality.
Another strength of the strategy is that it is cheap. Staff development is cheaper than acquiring readymade technologies or third-party ideas. This enables the company to reduce its operating costs, thereby improving its profits. The approach also facilitates knowledge transfer within the company. As employees interact with each other, they are likely to share their ideas and knowledge about various business processes.
Despite its strengths, the approach used by Apple to access new ideas and technologies is not sustainable. The company often loses its talented employees to its competitors such as Microsoft and Google. This limits its access to new ideas and the ability to develop advanced technologies through staff development. The approach also limits the company’s ability to access external ideas and knowledge (Jun & Park 2013, pp. 890-907). Undoubtedly, small startup technology companies have new ideas and technologies that can help Apple to achieve innovation. Moreover, failure to invest in research and development will reduce the company’s ability to develop new technologies.
Improvement
Apple should increase its investments in research and development programs. The new ideas that its employees can generate can be improved if they are subjected to rigorous scientific studies that involve external stakeholders and experts. As a result, the company will be able to develop advanced technologies that satisfy real needs (Thompsons 2010, pp. 29-31). Also, Apple should consider acquiring startup companies with advanced technologies and ideas that can leverage their products’ competitiveness. This will reduce the time required to develop innovative products and business processes. The current strategy for accessing new ideas and technologies should be improved by introducing effective staff retention programs. This will enable the company to avoid losing its best employees to its competitors.
Innovation Concepts
Lead-User Innovation
A leader-user is an extreme user of a particular product. Thus, his or her needs are likely to be more demanding than those of an average consumer. Lead-user innovation involves working with extreme users to identify future market needs. This involves achieving innovation by satisfying needs that customers have not realized. The application of the lead-user approach to innovation at Apple is limited by the fact that the company focuses on accessing new ideas from internal rather than external sources. Also, lead-user innovation is not likely to apply to Apple because of the company’s limited research and development budget. The ideas obtained from lead-users are often abstract and difficult to commercialize (Shehabuddeen 2007, pp. 12-135). This means that the company has to invest heavily in research and development activities to synthesis the ideas obtained from lead-users.
Open Innovation
Open innovation is based on the premise that companies can achieve real innovation by accessing and utilizing external ideas and technologies. Companies that use this approach to innovation focus on working with independent research organizations and customers to acquire new ideas and technologies (Alwis & Hartmann 2008, pp. 133-147). They also purchase startup companies to access new ideas. Companies that use open innovation share their ideas freely within their industries. Open innovation cannot work at Apple because of the company’s belief that the best ideas can be generated internally rather than externally. The company’s culture of secrecy and ‘invented here syndrome’ also limit the application of open innovation. Apple cannot easily access external ideas because it is not ready to share its ideas and technologies freely.
Disruptive Innovation
Disruptive innovation involves improving past successes to develop superior products, technologies, and business processes. This approach is applicable at Apple because it promotes access to internal rather than external sources of new ideas and technologies. Besides, the disruptive approach to innovation reinforces Apple’s blue ocean growth strategy. Specifically, it enables the company to use its internal resources to develop superior technologies and products that do not exist in the market (Apple 2014).
Apple’s Innovation Strategy
Apple focuses on disruptive innovation to challenge the status quo by developing superior products that fulfill unsatisfied needs. The company’s innovation strategy can be illustrated in figure 1.
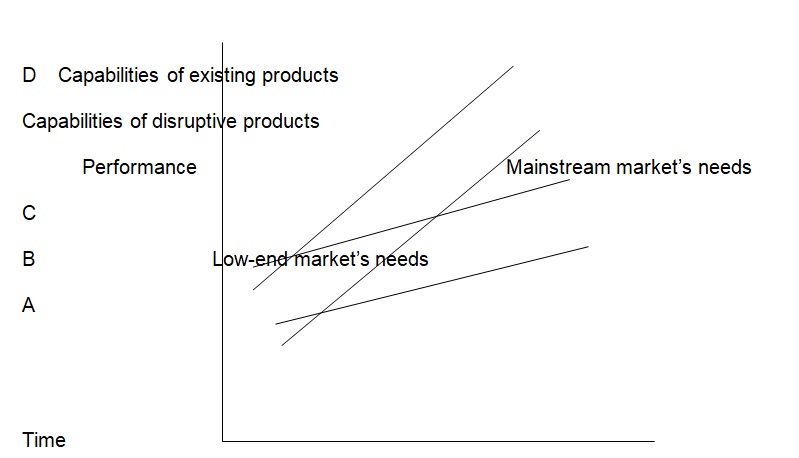
In figure 1, Apple introduces its disruptive innovations at point B by developing a product that does not meet the current needs of the mainstream market. Similarly, the product does not meet the needs of the low-end market (point A) where customers are price sensitive and do not require superior functionality. For example, the initial versions of the iPhone could not match laptop computers in terms of data storage capacity and the ability to access the internet (Apple 2014). Thus, they could not meet the needs of the mainstream market. However, they offered unnecessary features to the low-end market where customers were only interested in a handheld telecommunication device. As the needs of the mainstream and the low-end market increase, the company improves its products’ features. As shown in figure 1, the performance of the products improves with time. Thus, at a point, C Apple launches products that meet the needs of the mainstream market at a lower cost. As a result, customers shift to Apple’s products since the existing offerings are expensive and provide unnecessary features or capabilities (point D).
Improved Innovation Strategy
Product Dimension
Apple should embark on situation analysis to identify future market needs. This calls for road-mapping to identify and to respond effectively to future threats and opportunities. This can be achieved through the following steps. First, the company should predict the expected future changes in market trends and drivers. Specifically, it should determine the expected changes in social, political, economic, environmental, and political factors. A clear understanding of these factors will enable the company to predict future market needs (Shehabuddeen 2007, pp. 12-135).
Second, based on the analysis of market trends the company should identify product features that will be needed to satisfy future customers’ needs. This involves determining the level of performance in terms of information management, communication, and entertainment capabilities that smartphones and computers will require to meet future market needs. Finally, the company should determine the level of expertise and technologies that it will require to develop products with the features that will satisfy future market needs (Sattler 2011, p. 112). Thus, the company must assess its ability to access the technology that will be required for future product development. The assessment will inform investments in research and development, as well as, talent acquisition (Sattler 2011, p. 113).
Based on the situation analysis, Apple should identify the innovation strategy that will enable it to satisfy future market needs. Given the dynamics of the technology industry, Apple should focus on radical innovation to replace its products that are likely to be absolute in the future as other companies develop innovative products to satisfy emerging market needs (Assink 2006, pp. 215-233). This will enable the company to avoid losing customers to its competitors. Apple should also focus on incremental innovation to enhance the features of its existing products that are likely to continue being useful to customers. Incremental innovation will improve the relevance of the existing products, thereby boosting future sales. Given the high competition and the increase of commoditization in the technology industry, Apple should focus on being the first mover. Specifically, the company should launch new innovative products ahead of its peers to earn high-profit margins.
Process Dimension
Apple should establish effective structures and processes to manage innovation. The processes that must be established include the following. First, the company should establish a functioning idea management system (Shehabuddeen 2007, pp. 12-135). The system should include change leaders who will sensitize employees on the need for innovation. The leaders should inspire employees to generate creative ideas to solve existing innovation problems. The idea management system should have a database that stores employees’ ideas. Besides, the system should facilitate critical analysis of each idea and provision of valuable feedback to employees to improve their creativity.
Second, Apple should establish a resource allocation and management system. The main resources that the company will require to innovate include talented employees, time, and financial capital. Adequate time must be allocated to the innovation process to enable employees to engage in critical thinking, research, and discussions to find effective solutions to innovation problems (Alwis & Hartmann 2008, pp. 133-147). The company is likely to achieve the best outcome if it entrusts the innovation process to employees who have advanced expertise in product and process development. Moreover, employees should be self-motivated and passionate about innovation to achieve the best results. Undoubtedly, Apple will require a significant amount of financial capital to innovate. The funds should be used for research and development activities to test various ideas and technologies before commercializing them. This will help in reducing failure.
Finally, an effective communication management system will be required to develop and execute the innovation strategy. The company should facilitate effective communication between the management and the innovation team (Trott 2008, p. 123). One of the factors that hinder innovation at Apple is the culture of secrecy where employees are not aware of the innovations that the company expects to achieve in the future. This culture has to be abandoned and replaced by a communication system where employees discuss new ideas freely and make suggestions to the management concerning on-going innovation processes. The communication system should also enable the company to interact with its external stakeholders such as customers. Specifically, it should enable the innovation team to incorporate customers’ views and expectations concerning product features and functionality.
People Dimension
The success of any innovation process depends on the people who are involved in it. Cooperation and coordination among the innovation team members have to be ensured through an effective organizational culture (Shehabuddeen 2007, pp. 12-135). In this regard, Apple should improve its organizational culture in the following ways. First, the staff recruitment process should enable the company to hire employees who possess the traits of an innovator. The traits that facilitate innovation include being proactive, independent, persuasive, and open to change. Besides, prospective employees should be intelligent, resilient, and possess in-depth knowledge in their areas of specialization. The company should hire only employees who are ready to accept its culture of innovation.
Second, Apple should embark on staff development. Specifically, it should provide both on-the-job and off-the-job training to its employees to improve their knowledge and skills. On-the-job training will enable employees to acquire practical skills that they need to conduct their experiments to generate new ideas that facilitate innovation. Off-the-job training programs should be provided through colleges and universities to enable employees to acquire emerging knowledge and theories in their areas of specialization (Alwis & Hartmann 2008, pp. 133-147). The staff development program should also provide mentorship opportunities to inspire new hires to internalize the culture of innovation and creativity. Besides, the employees should be given all the tools and resources that they require to innovate.
Finally, Apple should put in place an effective reward and recognition system to encourage innovation. Reward and recognition are effective tools for inducing innovation since they shape the behaviors of employees (Afuah 2003, p. 142). The company should link employees’ compensation to work targets to achieve innovation. Apart from financial rewards, Apple should appreciate its employees who are committed to innovation by acknowledging their achievements. Acknowledgment or recognition enables employees to develop an emotional and psychological attachment to the innovation process. The resulting improvement in commitment among employees will lead to the achievement of the desired innovation.
Implementation of the New Innovation Strategy
Management of the Implementation Process
Apple should follow the following steps to implement an innovation strategy. In the first step, the company should focus on accessing diverse ideas that will enable it to innovate. The ideas should be obtained from internal and external sources to achieve the best outcome. The second step should focus on evaluating the effectiveness of the ideas (Shehabuddeen 2007, pp. 12-135). The evaluation should enable the company to identify the available business opportunities and the target markets that can be served using the identified ideas.
In the third step, the company should establish a business case for the new products to be developed. This will involve identifying the product features that create value to customers, protecting the innovation using patents, and complying with all regulatory requirements (Assink 2006, pp. 215-233). Besides, adequate resources should be allocated to commercialize innovation. The fourth stage should focus on the development of the product using the new technology or idea (Assink 2006, pp. 215-233). The manufacturing processes, as well as, distribution and logistics systems should be established at this stage.
In the fifth step, the company should test and validate the innovation. This will involve testing the functionality of the product, market acceptance, and the efficiency of the production system. The sixth step involves launching a new product. At this stage, the company should intensify its marketing activities to create demand. It should also train the sales and support team to boost sales (Trott 2008, p. 145). Finally, post-launch reviews should be done to identify and to resolve emerging challenges.
Change Management
An effective change management framework helps in aligning the behaviors of employees to the desired innovation outcomes. Based on Kotter’s change management model/ theory, Apple should implement its innovation through the following steps.
The first step in the implementation process should focus on preparing the company for innovation. Key leaders in the company such as the CEO and the COO should create a sense of urgency to enable employees to understand the rationale for innovation. The leaders should inspire the whole company to accept the proposed innovation strategy and to participate in its implementation (Sattler 2011, p. 213). In the second stage, the leaders of the innovation process should aim at building a guiding coalition. This will involve winning the support of the employees with immense influence in the organization. The rationale of this strategy is that the influential employees will use their power of persuasion to convince their colleagues to support the process of implementing the innovation strategy. This will help in averting internal resistance that might derail the process of implementing the innovation strategy.
In the third stage, the management should develop a clear vision to guide the implementation of the innovation strategy. The vision should provide a clear picture of the products and the competitive advantages that the company expects to achieve through the innovation strategy (Assink 2006, pp. 215-233). Besides, the vision should highlight the steps or procedures that must be followed to achieve the desired innovation. The fourth stage should focus on communicating the vision throughout the company. The company can use various communication vehicles such as management meetings, newsletters, focus group discussions, and informal meetings to discuss the vision with the employees. The communication activities should convey convincing messages that motivate employees to take action by participating in the process of implementing the innovation strategy.
In the fifth stage, the company should empower the employees to participate in the process of implementing the strategy. This will involve providing the necessary training, mentorship, and resources that employees require to perform various tasks during the implementation process (Martinez & Garcia 2011, pp. 537-566). In the sixth step, the management should achieve short-term wins. These include developing new product features, technologies, and production processes that facilitate the achievement of the desired innovation. Short-term wins will motivate employees to achieve the desired innovation.
After achieving short-term successes, the company should continue with the implementation process until all targets are achieved. Once the innovation strategy is fully implemented, the company should focus on embedding it in its organizational culture to ensure continuity.
Potential Challenges
The process of implementing the innovation strategy is likely to face the following challenges. First, the new strategy is likely to face resistance from the management and some employees. Accessing new ideas and technologies from external sources is likely to be resisted because it contravenes the company’s culture of secrecy and achieving innovation through staff development (Afuah 2003, p. 235). Changing this culture by increasing expenditure on research and development, as well as, collaborating with lead-users and independent technology companies is likely to create opposition to the innovation strategy.
Second, providing effective leadership to guide the implementation of the innovation strategy is likely to be a challenge. Following the death of the former CEO, Apple has been facing difficulties in finding a transformational leader who can integrate technical, marketing, and management skills to lead innovation in the company.
Third, the company is likely to face resource constraints. Specifically, it is likely to face time and human resource constraints. Since telecommunication and computer technologies have very short lifecycles, the company will have to spend as little time as possible to develop and launch new products (Jun & Park 2013, pp. 890-907). As a result, the company might not have adequate time to implement the innovation strategy.
The aforementioned challenges should be addressed through the following strategies. To begin with, the change management process should be used to avert resistance to the innovation strategy (Shehabuddeen 2007, pp. 12-135). The management should provide a strong business case and inspiration to convince employees to embrace the innovation strategy. The leadership gaps in the company should be filled by identifying several change leaders to support the CEO in leading the innovation process. Human resource constraints should be addressed through effective succession planning and staff retention programs. The company can reduce time constraints by collaborating with external research companies to develop and launch new products within a short period.
Monitoring the Success of the Innovation Strategy
Innovation is the “process of ideation, evaluation, selection, development, and implementation of new products or services” (Trott 2008, p. 10). Based on this definition, the objectives of innovation are to increase the number of new ideas, to enhance the quality of ideas, and to improve the financial performance of the company by implementing new ideas. Thus, the success of the innovation strategy can be monitored by assigning and measuring performance metrics to the innovation process and new products (Trott 2008, p. 10). The success of the innovation strategy can be monitored by measuring the number of new ideas that are generated per 100 employees, the percentage of new ideas chosen for implementation, the return on investments achieved by implementing new ideas. The success of the innovation strategy can also be monitored by calculating the return on product development expense (RoPDE). RoPDE measures the financial performance of products that have been developed using the innovation strategy (Sattler 2011, p. 178).
Conclusion
Apple uses an organic innovation management structure. This structure enhances flexibility and learning, thereby enabling the company to achieve the desired innovation. The company mainly depends on an internal source (its employees) to access new ideas and technologies. This strategy limits the company’s ability to access external ideas and technologies that it needs to innovate. Thus, Apple should increase its investments in research and development, as well as, collaborations with lead-users and independent technology companies to access new ideas and technologies. Additionally, the company should abandon its culture of secrecy to promote the sharing of ideas with internal and external stakeholders. Given the dynamics of the technology industry, the company should focus on both disruptive and incremental innovations to maintain its competitiveness in the future.
References
Abouzeedan, A & Hedner, T 2012, ‘Organization structure theories and open innovation paradigm’, World Journal of Science, Technology and Sustainable Development, vol. 9. no. 1, pp. 6-27.
Afuah, 2003, Innovation management: strategies, implementation, and profits, McGraw-Hill, New York.
Alwis, R & Hartmann, E 2008, ‘The use of tacit knowledge within innovative companies: knowledge management in innovative enterprises’, Journal of Knowledge Management, vol. 12. no. 1, pp. 133-147.
Apple 2014, Apple Inc. Annual Report: 2013. Web.
Assink, M 2006, ‘Inhibitors of disruptive innovation capability: a conceptual model’, European Journal of Innovation Management, vol. 9. no. 2, pp. 215-233.
Jun, S & Park, S 2013, ‘Examining Technological Innovation of Apple Using Patent Analysis’, Industrial Management and Data Systems, vol. 113. no. 6, pp. 890-907.
Martinez, I & Garcia, J 2011, ‘The influence of organizational structure on organizational learning’, International Journal of Manpower, vol. 32. no. 6, pp. 537-566.
Sattler, M 2011, Excellence in innovation management, Sage, London.
Shehabuddeen, N 2007, Innovation in Real Life: A Hands-on Guide to Genuine Innovation, Open Innovation, Liverpool.
Thompsons, 2010, ‘What do Apple, IBM, and P&G know? How open innovation can help business and yourself’, Strategic Direction, vol. 27. no. 3, pp. 29-31.
Trott, P 2008, Innovation management and new product development, John Wiley and Sons, New York.
