Executive Summary
Burberry is a fashion house with a long history of providing luxurious apparel. The company operates in various countries globally and employs many people. This paper aims to perform a financial analysis of their annual report for the year ended March 2020. The results from their income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statement will be scrutinized. The internal report will examine the absolute figures, and a horizontal analysis will also be performed from 2019. 2020 was not a pleasant year for many businesses across the world, and it will be interesting to see the impact on their finances.
One aspect of being checked will be their asset valuation, both short-term and long-term, and their comparison to 2019. The pandemic affected sales worldwide, which likely affected their current assets with so many stores shutting down. Burberry, like many businesses, finances its operations through debt such as loans from banks or bonds. The paper will look at their liabilities and the effect of reduced revenue on their debt settlement; equity and retained capital earnings will also be looked at.
On the income statement, parameters to be analyzed are gross profit, revenue, operating income, earnings per share, and dividend per share. The cash flow statement will look at various activities that affect cash flow. Mainly, the paper will analyze operating, investing, and financing operations that have different effects on the cash flow, with some providing cash while others are consuming it. After examining financial position, the paper will look at the external environment, specifically Israel, and the factors that could affect their business operations there. The recommendation for Burberry is to continue bolstering their luxury reputation since it has been established that the company suffers when they deviate from this. Another suggestion is for them to expand to emerging luxury markets.
Introduction
Burberry PLC is one of the world’s largest fashion companies. It is a British luxury fashion house founded in 1856 by Thomas Burberry (Kitson, 2016). The company is involved in the design and distribution of ready-to-wear apparel, such as leather products, footwear, eyewear, fashion accessories, fragrances, and cosmetics. As of March 2020, the organization operated more than 468 stores in 59 countries worldwide and has more than 9000 employees (Kitson, 2016). The company was family-run until 1955, when General Universal Stores(GUS) acquired a majority stake; GUS would divest their share in 2005 (Kitson, 2016). Interestingly, Burberry is famous for its trench coats which got its name from soldiers wearing them in battlefield trenches during the First World War; they later became popular with civilians (Kitson, 2016). This paper will analyze the company’s financial position, external environment, and risks surrounding its operations in Israel.
Burberry’s objective is to drive creativity to unlock new opportunities for the company, its customers, and the communities. This is based on the values of being driven creatively, being caring and open, forward-thinking, and pushing its heritage (Strangmueller, 2017). The company places importance on its short- to medium-term targets and believes these to be essential in allocating resources, setting policies, planning schedules, and streamlining processes.
Burberry is recognized in the world as a luxury brand. Therefore, the company desires to maintain its brand standing even as it grows its business network. It seeks to remain relevant in the global market with evolving consumer tastes and preferences. Burberry’s business strategy is maintaining its luxury reputation. In the early 2000s, the company had become associated with hooliganism after their products had lost their luxury touch (Rohwedder, 2009). After restructuring and change of CEOs, they regained their prestigious reputation by pulling products from the market. Burberry has received criticism for its habit of burning products to avoid cheapening its brand.
Current Financial Position
Balance Sheet
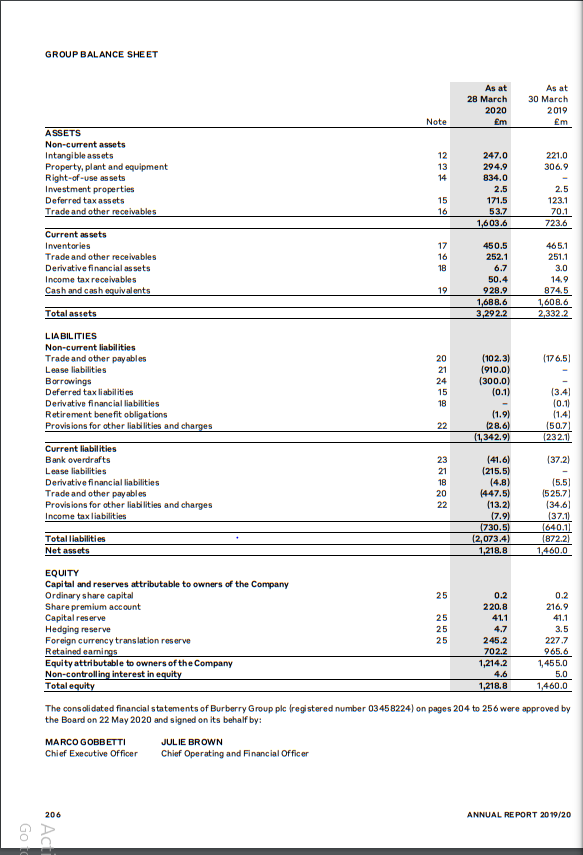
Burberry realized significant growth in the asset base. The total assets increased from 2.3 billion pounds in 2019 to 3.3 billion pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The non-current assets shored up from 724 million pounds to 1.6 billion pounds, pushed by 834 million pounds right-of-use assets (Burberry PLC, 2020). The current assets increased marginally from 1.61 billion pounds in 2019 to 1.69 billion pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The total liabilities climbed from 872 million pounds in 2019 to over 2 billion pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). There was a significant increase in non-current assets from 232 million pounds in 2019 to over 1.3 billion pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The growth is attributed to lease liabilities (910 million pounds) and borrowings (300 million pounds) (Burberry PLC, 2020).
The borrowings were sourced from a multi-currency revolving credit facility with a group of banks; the facility matures in November 2021 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The current liabilities also went up from 640 million pounds in 2019 to 730.5 million pounds in 2020, largely due to lease liabilities (215.5 million pounds) (Burberry PLC, 2020). The company’s total equity declined from 1.46 billion pounds in 2019 to 1.22 billion pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). In 2020 and 2019, the ordinary share capital was 200,000 pounds for both years. Retained earnings declined from 965.6 million pounds in 2019 to 702.2 million pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). In general, Burberry’s capital base received a boost in 2020 from lease liabilities and borrowings from a consortium of banks.
Income Statement
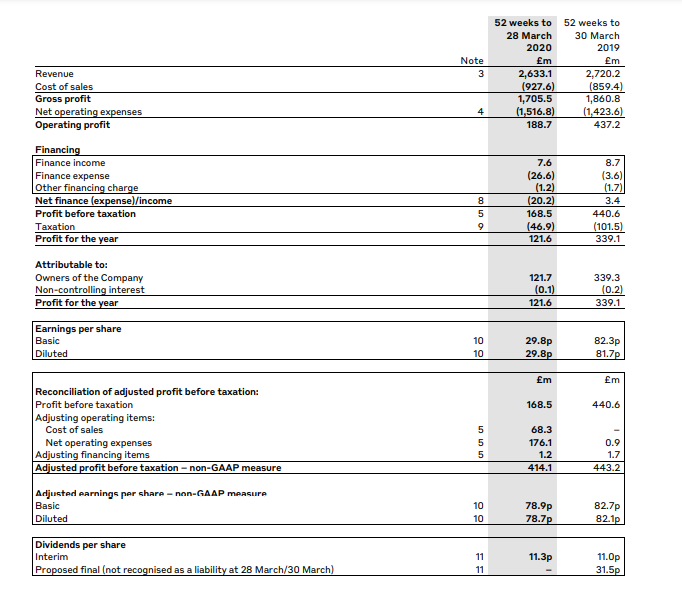
The revenue declined by 4 percent from 2.72 billion pounds in 2019 to 2.633 billion pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). Before COVID-19 hit, business in Asia was on the rise, driven by China’s youth in anticipation of the Luna Year. However, after January, the sales dwindled following the closure of stores. In Europe and Middle-East, sales growth was weakened by the COVID-19 impact after stores’ closure and reduced traveling. America’s growth was sluggish, further pulled down by reduced tourist activity and closure of businesses due to COVID-19.
The company’s profitability dropped in 2020, as illustrated by various factors. Gross profit reduced from £1860.8 million in 2019 to £1705.5 million in 2020. The gross margin went down by one percentage point from 68.4 percent in 2019 to 67.4 percent in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The operating profit went down significantly by 57 percent, from 437 million pounds in 2019 to 189 million pounds in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The decline was primarily due to a 244 million pounds adjustment for operating items connected to provisions for inventory, store losses, and other charges relating to the projected effect of the COVID-19 epidemic on future trading.
The operating margin declined by a similar percentage, from 16.1 percent in 2019 to 7.2 percent in 2020. The company’s net income for 2020 was £121 million, a 66.22% drop from 2019, causing the net margin to drop from 12.47% in 2019 to 4.62% in 2020. The company paid dividends per share of 11.3p, down 73 percent from 42.5p issued in 2019 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The reduction was a measure aimed at protecting the company’s future cash position. Earnings per share(basic) reduced from 82.3p to 29.89, while EPS (diluted) reduced from 81.7p in 2019 to 29.8p in 2020 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The results have further illustrated the average year it was for Burberry.
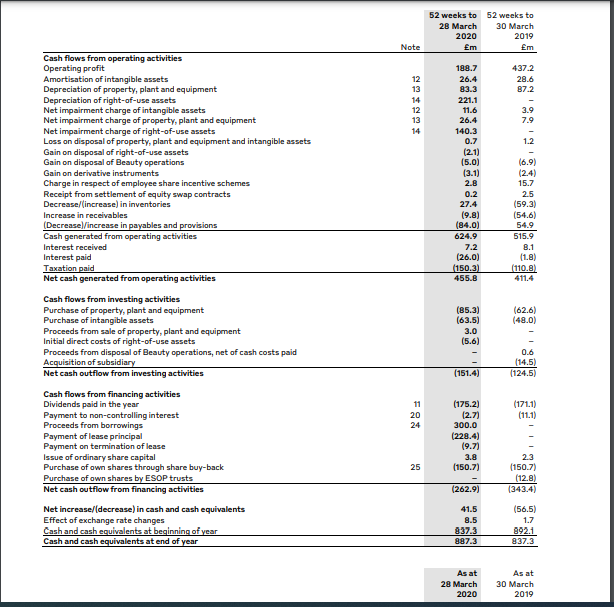
Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement indicates cash movements involving the company. The activities that are involved are divided into operating activities, financing activities, and investing activities. The company earned a net of 455.8 million pounds in 2020 from operating activities, a 10 percent increase from 411.8 million pounds earned in 2019 (Burberry PLC, 2020). Burberry spent 151.4 million pounds on investing activities compared to 124.5 million pounds in 2019 (Burberry PLC, 2020). On financing activities, Burberry spent a net of 263 million pounds in 2020 compared to 343.4 million pounds for 2019 (Burberry PLC, 2020).
As of March 28, 2020, Burberry had cash of £887 million, comprising £300 million obtained through a revolving credit facility in March 2020 and returning 325 million pounds to shareholders through dividends (175 million) and share repurchase worth 150 million pounds (Burberry PLC, 2020). In general, the company realized an increase in cash and cash equivalents boosted by money borrowed.
External Economic Analysis
The Israeli economy performed well in 2019 due to sound fiscal management and reduced spending. However, a decline in government spending could have reduced consumer spending in the economy. With reduced consumer spending, Burberry would be affected by people spending less. In 2020, the country’s economy contracted by 5.5 percent due to the effect of COVID-19 (Burberry PLC, 2020). The poor growth is characterized by reduced buyer spending on luxury goods as many people prioritize spendings on basic supplies like food, health, and shelter.
Future Risks
Risks are uncertain events that occur and can significantly affect the operations of the company. Burberry considers competition as the most significant risk to its operations. The apparel industry is also vibrant, with enormous potential for long-term growth. Moreover, the regulatory environment poses risks in terms of the laws formulated that may impact the company’s operations in terms of doing what is right. New technology is also likely to impact the business due to consumer spending habits (Burberry PLC, 2020). Other risks include changes in foreign exchange rates, adverse weather conditions,
Risk assessment is an essential element of Burberry’s overall strategy. Managing the risks forms the basis upon which the company executes its strategy, creates value for the shareholder, protects its brand, and ensures good governance (Burberry PLC, 2020). The board is tasked with determining the company’s risk affinity and inspiring the management to implement effective systems to detect risks, assess the risks, and institute mitigation measures. The Internal Audit goes through these actions and other control roles, which assures the Risk Committee, and in the end, the board.
Swot Analysis
Strengths and weaknesses
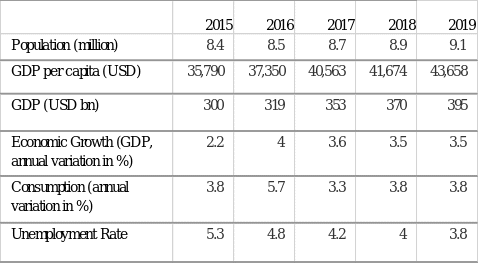
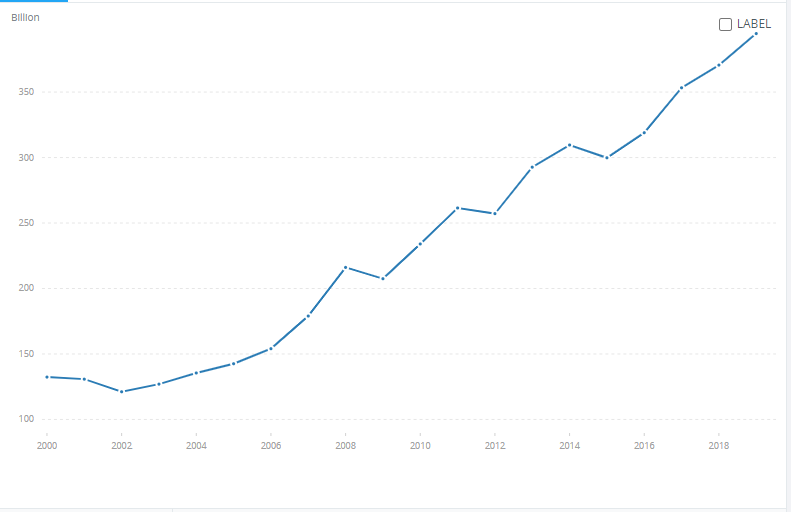
The biggest strength Burberry has in Israel is the country’s economy which is thriving. It has a GDP of 395 billion as of 2019; that is an impressive figure for a country with just 9 million people (FocusEconomics, 2020). Their GDP per capita is also at par with other developed countries, indicating that Israelis can afford luxury products. Millennials dominate the luxury consumer base in the Middle East; luckily, Israeli’s population is also relatively young, with only 10% aged above 65 (Demirci, 2019). This is an indicator that Burberry is positioned to have a market for a while. From table 1, Israel is not a large country; there are only so many customers to buy luxury products. The economy has also been affected by the COVID-19 pandemic, and growth has slowed down.
Opportunities
Burberry’s opportunity in Israel lies in Israel’s continued economic growth. As of 2019, the country has 130000 millionaires, and the number is expected to hit 174000 by 2024 (Tress, 2019). This represents a ready market for their luxury products. Israel is punching above its weight in this category, ranking fifth globally and having the same numbers as populous nations such as Brazil.
Threats
Burberry is faced with stiff competition from other established brands in the industry, such as Gucci, Zara, Swatch, and Michael Kors, who have also set up operations in Israel. The top three leading companies control over 50 percent of the global industry revenue, and the top ten control around 80 percent (Oltenau, 2020). These patterns are likely to reflect in Israel too. Therefore, the company has limited control in the industry and must compete aggressively to maintain and acquire new customers.
Recommendations
As an established top luxury brand, Burberry should aim to grow its market share to boosts sales. The company should strive to improve its current standards. Moreover, it should continue the expansion strategy to introduce the brand to new markets. The use of technology ought to be enhanced to shore up its competitiveness and attract new customers by creating awareness (King and Lawley, 2016). COVID-19 remains to be a challenge. Therefore, the company must innovate ways to navigate the challenges brought about by the disease. There are many other threats to the company that needs to be managed by growing the product portfolio and entering new markets.
Conclusion
Burberry is an established brand in the fashion industry. The company has a long history and has survived in the industry through innovation and expansion. It has employed modern technology to survive the current competition from established brands. In the year 2019/2020, Burberry reported a decline in revenues and profits mainly due to the COVID-19 impact as well as changes in the regulatory framework. However, the results remained impressive, showing resilience in the industry supported by its uniqueness and company capabilities.
Reference list
Demirci, S. (2019). Millennials dominate the luxury market in the Middle east. IESF. Web.
FocusEconomics. (2020) Israel Unemployment Rate – Israel Economy Forecast & Outlook. FocusEconomics. Web.
GDP (current US$) – Israel | Data (no date). Web.
King, D. and Lawley, S. (2016) Organizational behaviour. Second edition, Oxford; New York, NY: Oxford University Press.
Kitson, B. (2016). Burberry days: an insider’s account of the clothing business. London: Austin Macauley Publishers.
Olteanu, L. (2020). ‘Rebranding strategies and their boomerang effect—The curious case of Burberry.’ The Journal of World Intellectual Property, 23(5-6) pp. 777-797.
Rohwedder, C. (2009) Burberry Goes Back to Basics. Wall Street Journal. Business. Web.
Strangmueller, M. (2017) Economic Strategies. Potential Improvements of Burberry. Musselburgh: Queen Margaret University.
Tress, L. (2019) Israel has 131,000 millionaires, and its wealth is growing quickly, report finds. Web.
Appendix A
Burberry PLC Income Statement 2019/20
Appendix B
Burberry PLC Balance Sheet 2019/20
Appendix C
Burberry PLC Cash flow statement 2019/20