Abstract
With the rise of conscious consumption, companies are financially incentivized to become more socially responsible. One of the companies that decided to adopt the so-called CSR (corporate social responsibility) approach is McDonald’s, the largest fast-food chain in the world. These days, fast food companies often receive criticism due to their negative impact and contribution to the burden of disease. Because of this controversy, it makes even more sense for them to make more effort to give back to the community. An important thing to be taken into account is the role that ongoing communication and gathering feedback from the customer plays in forming a CSR strategy. The present study concerns the perception and expectations of fast-food chain customers in regards to McDonald’s business ethics and CSR activities. To achieve the research goals, a survey was designed that has demonstrated that participants were not exactly aware of McDonald’s CSR practices. The participants put an emphasis on nutrition and wellness, environmental protection, and employment opportunities. The majority of customers were loyal to the brand in one way or another with behavioral loyalty prevailing over attitudinal.
Introduction
Nowadays, there is a growing need for companies to improve their business ethics and become more socially responsible in order to retain the customer. A recent American Customer Satisfaction Index (ACSI) (2015) report has shown that it has become more difficult for US companies to keep their customers satisfied. After surveying more than 9,000 people online, the ASCI has discovered that since 2014, the customer satisfaction rate slid by 3%. There are a number of reasons for this trend, one of which is customers’ changing needs and preferences. Millennials, the generation that spans between the early twenties and mid-thirties and consists of individuals involved in the workforce and having the most purchasing power, have different standards compared to their predecessors.
The new customer has a faultless command of gadgets, short attention span, and distaste for unethical business practices. Hall and Towers (2017) explain that millennials show the readiness to go through diverse, long, and complicated processes before making a purchase. They seek social validation of their decision, compare multiple alternatives, and do a background check on the company whose product or services they are considering. These new trends compel businesses to readjust and transform their strategies to stay afloat. One way to do this sustainably is to embrace corporate social responsibility: a business model that helps entities to control the negative impact of their operations and make meaningful, positive contributions. However, the relationship between CSR practices and customer satisfaction may not be precisely straightforward, which calls for continuous assessment and monitoring.
Theoretical Framework and Topic Statement
Corporate Social Responsibility
Corporate social responsibility is a self-regulating business model that seeks to contribute to social goals by holding a business accountable for its impact. By practicing corporate social responsibility, a company makes itself aware of the ways it influences the world. To be responsible in this regard means to moderate and prevent the negative impact and instead commit to continuous improvement. One framework that many companies adopt to evaluate their performance from a broader perspective is the so-called triple bottom line: social, environmental, and financial. Evidently, the triple bottom line is not the only framework to exist: for instance. Wu and Chen (2015) cites a theory put forward by Inoue and Lee that breaks CSR down into the following five elements: (1) employee relations; (2) product and service quality; (3) community relations; (4) environmental issues; (5) diversity issues. The triple bottom line may also be extended to include the stakeholder and the voluntariness. Lastly, some companies devise their own framework, building on the available theoretical approaches and existing evidence.
Typically, it is large corporations that decide to adopt a CSR strategy as they reach the point where they can afford giving back to the community on par with pursuing higher profits. In part, they may be forced to do it: large corporations have more publicity and scrutiny, which makes them more cautious and calculating about their business ethics. Because of their leverage and potential to both do harm and contribute to social progress, big companies are held to higher standards and are compelled to act on their promises.
In order to be seamlessly implemented into everyday business operations, CSR needs to become part of the corporate internal decision structure. The said structure prevails over individual actions and decisions and essentially forms the direction in which the company is going with the purpose of achieving its predetermined goal. The corporate internal decision structure operates on a specific set of beliefs and values; in other words, what is generally considered as right or wrong in the corporation. Together, they form an organizational culture that influences the company’s decisions at every level: starting with how it operates internally (manufacturing, hiring, treating employees) and ending with its external operations (sales, marketing, community initiatives). Aligning all these elements takes time and effort, and in the end, commitment to promoting sustainable organizational culture and building an internal decision structure that is compatible with it accounts for more integrity.
The question arises as to why a company would want to adopt a strategy that is this challenging to implement, time-, and resource consuming. From the standpoint of utilitarianism, being socially responsible means improvement in collective welfare despite the inconvenience of the initial effort. For the company, organizing or partaking in social actions may forestall legislation and render a corporation more independent from the government. The positive image of a company that it owes to its CSR may attract more qualified cadres who are motivated not only by remuneration but also fighting for the right causes. The customer, on the other hand, benefits from better services and may also enjoy community programs. Therefore, in terms of utilitarianism, corporate social responsibility is mutually beneficial and adds to the net well-being of all the participants.
CSR and Customers’ Preferences, Responses, and Satisfaction
As it has been mentioned earlier, committing to CSR and upholding a good reputation may as well be considered a long-term investment that has the potential of yielding positive financial results. The defining consumption trend of the last couple of decades has been a strong leaning toward consciousness. Mintel Press Team (2015) reports that more than half of US consumers (56%) would stop buying from companies that do not meet their ethical standards. Furthermore, one-third of American consumers go as far as rejecting an unethical brand entirely, even in the absence of a viable alternative. Another finding by Mintel Press Team (2015) that is worth mentioning is that 27% of consumers would switch to another supplier that they consider more ethical even if it meant purchasing goods or services of lower quality.
These figures showcase the importance of taking CSR seriously, devising CSR strategies with consideration, and understanding consumers’ responses. Customers’ favorable attitudes toward CSR campaigns undertaken by a company may encourage their continuation and further development. Wu and Chen (2015) cite capstone studies that have shown that positive social responsibility image was associated with a higher purchase likelihood and long-term brand loyalty. Other studies have suggested that a company’s positive CSR branding creates goodwill that may later serve as a protection against political, social, and economic fluctuations (Wu & Chen, 2015). The association between CSR, customer satisfaction, and brand loyalty receives further attention from researchers and may lay a foundation for sustainable CSR practices.
The present research project investigates both customer satisfaction and brand loyalty: two phenomena that have received diverse interpretations in modern literature. For the sake of clarity, customer satisfaction will be defined as an overall estimation based on the customer’s purchase and consumption experience of a product or service over an extended period of time. Customer loyalty can be defined as the customer’s willingness to use a company’s products or services again, for which customer satisfaction has been found to be a prerequisite. Rashid, Rani, Yusuf, and Shaari (2015) point out two categories of loyalty: attitudinal and behavioral. The former consists of such elements as emotional attachment, emotional connection, trust, and commitment. The latter relates to what customers do as opposed to how they feel: behaviorally loyal customers may take actions such as spreading word of mouth referrals and repeating their purchase.
Rashid et al. (2015) explain that the two types of loyalty may or may not be connected: attitudinal loyalty may indeed precede the desired behavior. However, sometimes, customers may be satisfied with their experience and feel positive emotions without taking further action. According to the researchers, customer satisfaction and loyalty are two complex concepts that have become even more complicated at present (Rashid et al., 2015). Today, they expand beyond the actual quality of a product or a service and encompass the purchasing experience and relationship with a provider or a supplier as a whole. Given the new context and consumption trends, companies can no longer ignore the role of CSR in attracting the customer, yielding financial gains, and improving their social standing.
CSR and Fast Food Industry: The Case of McDonald’s
The topic of the present research paper is McDonald’s CSR practices from the perspective of young North American customers. Kim and Ramos (2017) state that upholding a socially responsible image is especially challenging for large fast food companies such as McDonald’s. The researchers explain that because of the global burden of disease caused by obesity, the fast-food industry has faced intense criticism and counter-movements. The opponents of the fast-food industry range from self-organizing parent groups, nutrition groups, and healthcare professionals to state and national legislators. Weathering such harsh criticism requires a response in the form of sustainable practices that give back to the community. McDonald’s preaches their commitment to the following three key areas:
- ethical practices;
- environmental protection;
- long-term economic viability.
Some of the most notable programs and initiatives launched and maintained by McDonald’s include the inclusion of fruits and vegetables in the menu, the Youth Opportunity program, and Ronald McDonald House charities. Youth Opportunity helps unemployed and underemployed young people to receive relevant training and work experience. Ronald McDonald House Charities help families with sick children stay together during hard times by providing dwelling adjacent to hospitals. It is assumed that even though these initiatives undertaken by McDonald’s do help form a positive, socially responsible image, not so many customers might be aware of them. Therefore, the goal of the present research is to understand the expectations and perceptions of McDonald’s’ CSR strategies among young American customers. The second research goal was to investigate customers’ knowledge of McDonald’s’ CSR. It has been hypothesized that despite regular reports and extensive publicity, McDonald’s might not be reaching broad audiences.
Methodology
To meet the aforementioned research goals, a questionnaire was devised the answers to which were evaluated on the Likert scale. The survey consisted of “I”-statements with multiple answers ranging from 1 – “Does not apply to me at all” to 5 – “Completely agree.” The questions were broken down into five categories:
- consumers’ eating out behaviors;
- expectation of CSR;
- perception of CSR;
- loyalty to and satisfaction of McDonald’s;
- demographics of the respondents.
For this research, it was essential to operationalize the concept of CSR in a comprehensive way due to the plurality of approaches and definitions. In order to make it robust and also pertinent to the fast-food company in question, the key aspects were drawn from relevant studies on CSR and McDonald’s sustainability report. They included:
- corporate governance;
- business ethics;
- sustainability;
- nutrition and well-being;
- environmental responsibility;
- employment experience;
- community service.
The perception of CSR part of the questionnaire explored whether participants were aware of McDonald’s’ CSR initiatives: they were enlisted with the purpose of checking respondents’ knowledge about them. For this part, the Likert scale was slightly readjusted because agreement and disagreement statements no longer applied. Therefore, it was decided to assign five for “I know exhaustive information about this initiative” and one for “I do not have the slightest clue about this initiative.” Lastly, the third part of the survey, loyalty and satisfaction, built on the previous research in those two concepts. Loyalty was categorized as attitudinal and behavioral; therefore, the following exemplary statements applied: “I talk positively about McDonald’s” and “I dine at McDonald’s often.” Satisfaction was broken down into three essential elements: product experience, customer service experience, and visitor experience.
The present research recruited ten participants near three major student campuses to inquire about their experiences with the selected brand. The convenience sampling method proved to be time- and cost-efficient; besides, the majority (90%) of the people approached consented to participate. Six (60%) of them were women, and 4 (40%) were men. Four (40%) of participants were enrolled in an undergraduate program; two (20%) were in graduate school, and four (40%) were already working. The average age was 24.6 years old (SD = +- 5.2 years). The information submitted by the participants was analyzed using popular software SPSS for descriptive statistics. Descriptive statistics were used to explore the demographics of the sample, the most important aspects of CSR, and participants’ knowledge of McDonald’s’ CSR efforts.
Results
Eating Out Habits
The survey has shown that around 70% of respondents eat out in fast-food restaurants at least every week. A minority of the respondents (20%) reported eating fast food daily. Around half of the participants (50%) go to McDonald’s’ restaurants at least once a month. For a minority of the surveyed individuals (20%) McDonald’s was the go-to option: others expressed their preference for other fast-food chains such as KFC, Subway, and Burger King. Overall, the results of the first part of the survey have two implications: the sampled individuals have a stable eating out habit, they show brand awareness and have experience with eating at McDonald’s, even though it is not their top choice.
Expectation of CSR
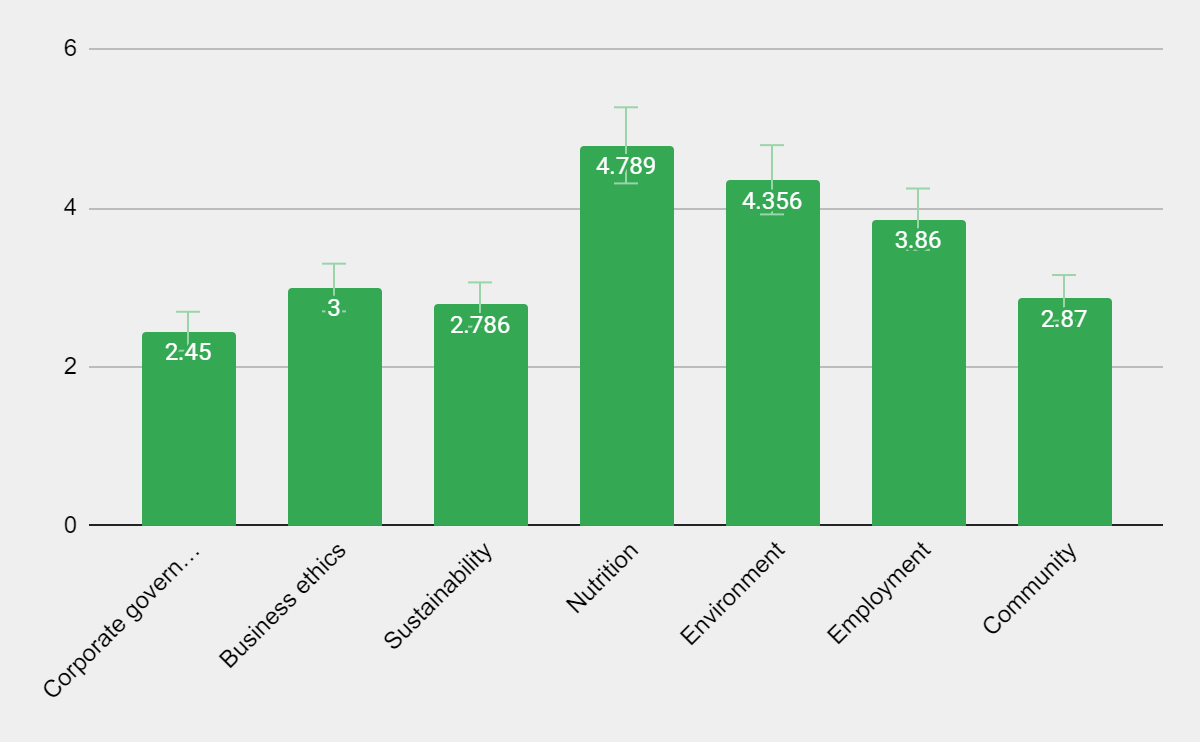
As seen from Graph 1, the most important aspect according to the respondents is wellness and nutrition (the average evaluation of 4.789 out of 5). The second best is environment: on average, the respondents were giving it 4.356 points. McDonald’s employment opportunities, job programs, and initiatives have also resonated with the surveyed individuals: the aspect scored 3.86 out of the possible five points. At three out of five points, business ethics proved to be of moderate importance to the respondents. The aspects that have proven to be the least important as per survey results were corporate governance (2.45), community service (2.87), and sustainability (2.786).
Perception of CSR
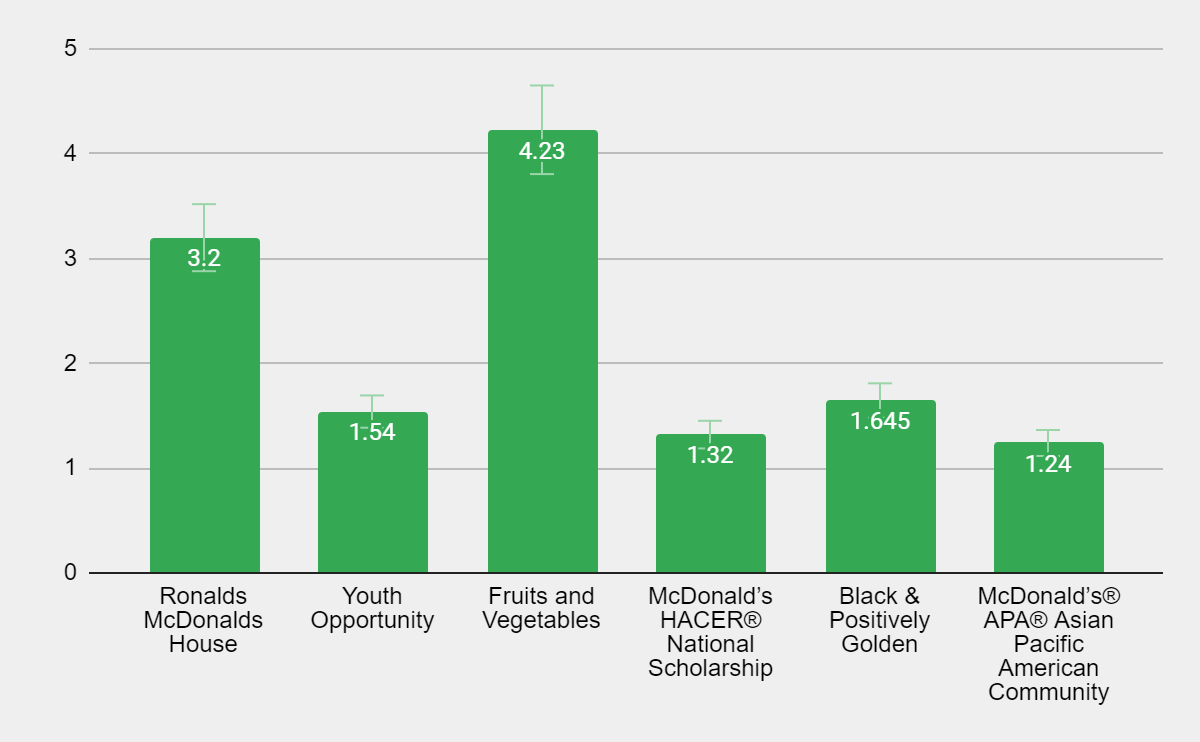
Overall, the third part of the survey has confirmed the hypothesis that customers are not exactly aware of the brand’s CSR efforts. The most recognizable initiatives were Ronald McDonald’s House and fruits and vegetables on the menu: they scored 3.2 and 4.23 respectively. The rest of the initiatives were recognized by very few people. A program for young people, Youth Opportunity, scored 1.54 while Black people awareness campaign received an evaluation of 1.645. The least recognizable activities were McDonald’s National Scholarship (1.32) and McDonald’s APA (Asian Pacific American Community) (1.24).
Loyalty to and Satisfaction
The results show that 60% of respondents are loyal to McDonald’s in one way or another. Behavioral loyalty was more widespread than attitudinal: while 80% of participants reported going to McDonald’s more than once only a minority (10%) admitted their emotional attachment to the brand. A small part of the sample (20%) recommended the food chain to their family and friends. As for satisfaction, respondents have demonstrated very moderate excitement about their experiences.
Discussion
The first part of the survey investigated respondents’ eating out habits, and the results differed from expectations. They seem to diverge from other studies ’ findings: as Safety and Health Magazine (2018) claims, about one in three Americans (36.6%) consume fast food every day. Therefore, the respondents’ patronage of fast food is lower than the national average. This might have two explanations: firstly, due to the subjectivity of the self-reporting method, some respondents might have underestimated their habits. Second, given that the present study researched the behavior of young people, it might have captured their inclination to eat healthier. This is consistent with a recent report provided by L.E.K. (2018) that has demonstrated that consumers are not only actively seeking products that would offer some health benefits but are also ready to pay more for it. Moreover, 63% of the respondents reported that they want to eat healthily every day.
The second part of the survey is also reflective of the trend mentioned above. Participants named nutrition as their priority when it comes to evaluating a food company’s social responsibility. The next most significant concern is the environment, which may be explained by the comprehensive news coverage of natural disasters and climate change as well as global environmental education. The negative impact of environmental issues is becoming common knowledge and a cause for concern for many customers. 81% state that they care whether a company whose products or services they are choosing is environmentally friendly (“Global consumers seek companies that care about environmental issues,” 2018).
One more explanation for the ranking of aspects lies in the theory of agency and self-interest. As Montada and Maes (2016) explain, humans are inherently selfish, and they tend to prioritize things that impact their lives directly. A similar theory that can also be entertained in this context is the one put forward by Adam Smith. The thinker stated that individuals overwhelmingly pursue maximization of their own pleasure. Taking this into account, it comes as no surprise that the respondents of this survey have emphasized something that they must have personal experience with nutrition and employment.
The same applies to customers’ perception of McDonald’s CSR efforts. The results have confirmed the hypothesis that despite the overall popularity of the brand, the philanthropic aspect of it is not well known. Again, akin to customers’ expectations, the perception was driven by self-interest and personal experience too. Respondents were aware of the presence of vegetables and fruits on the menu, presumably because they encountered it in real life. Ronald McDonald’s house charities were familiar to a minority while other initiatives, mostly focusing on disadvantaged communities, were not. Lastly, the fourth part of the survey has shown that attitudinal loyalty and behavioral loyalty were indeed not precisely connected. While many respondents continued to purchase McDonald’s products, only a small fraction reported actual emotional connection and practicing word-of-mouth.
Recommendations
The present study has contributed to the field of business ethics by showcasing the importance of maintaining communication between the business and the customer. As seen in the literature review section, the concept of CSR is quite complicated and encompasses many aspects. While generic business and management literature does not point out exactly which elements have the most weight when it comes to building a solid reputation, the reality tells otherwise. The survey conducted for the present study has demonstrated that customers do prioritize some aspects over others. This may imply two things for business practitioners: firstly, it shows the impossibility and impracticality of filling every niche that there is to CSR.
Secondly, business practitioners might want to give more publicity to those initiatives that seem more relevant to customers. Another valuable recommendation is for businesses to understand the realities of the industry that they are in. As it has been mentioned before, serving fast food puts suppliers at an immediate disadvantage due to the negative reputation that this type of production has. To overcome these difficulties, companies should target them exactly when working on a CSR strategy. For instance, a fast-food corporation might want to address the issues with the unhealthiness of the food first and expand its menu to offer more options.
Conclusion
The present study sought to understand the perception and expectations of fast food consumers in regards to McDonald’s CSR activities. The need for such a study is motivated by the rising conscious consumption and healthy eating trends, which make consumers change their purchasing behavior. While McDonald’s has already been building a substantial effort to promote the right causes – financial, social, and environmental, they might still struggle to improve CSR awareness. The study employed a comprehensive survey that explored customers’ eating out habits, perception of the company’s CSR initiatives, and expectations. The results have shown that the majority of the participants were not exactly aware of McDonald’s social programs and initiatives. As for their expectations, respondents highlight the importance of wellness and nutrition, environmental protection, and employment opportunities. The majority of the respondents proved to be loyal to the brand in one way or another, even though McDonald’s is not their top choice when it comes to fast food.
References
American Customer Satisfaction Index. (2016). ACSI retail report 2015. Web.
Flammer, C. (2015). Does corporate social responsibility lead to superior financial performance? A regression discontinuity approach. Management Science, 61(11), 2549-2568.
Hall, A., Towers, N., & Shaw, D. R. (2017). Understanding how Millennial shoppers decide what to buy. International Journal of Retail and Distribution Management, 45 (5). pp. 498-517
Kim, Y., & Ramos, M. L. Z. (2018). Stakeholder responses toward fast food chains’ CSR. Corporate Communications: An International Journal, 23(1), 117-138
Laprade, E. (2018). Corporate social responsibility: McDonald’s. Web.
McDonald’s. (2020). Community. Web.
Mintel Press Team. (2015). 56% of Americans stop buying from brands they believe are unethical. Web.
Montada, L., & Maes, J. (2016). Justice and self-interest. In Handbook of social justice theory and research (pp. 109-125). New York, NY: Springer.
Rashid, I. M. A., Rani, M. J. A., Yusuf, B. N. M., & Shaari, M. S. (2015). The impact of service quality And customer satisfaction on customer’s loyalty: Evidence from fast food restaurant Of Malaysia. International Journal of Information, Business and Management, 7(4), 201.
Saeidi, S. P., Sofian, S., Saeidi, P., Saeidi, S. P., & Saaeidi, S. A. (2015). How does corporate social responsibility contribute to firm financial performance? The mediating role of competitive advantage, reputation, and customer satisfaction. Journal of Business Research, 68(2), 341-350.
Safety and Health Magazine. (2018). Nearly 37 percent of Americans regularly eat fast food, study shows. Web.
Wu, S. I., & Chen, J. H. (2015). The influence of CSR on brand relevant aspects. Journal of Management & Sustainability, 5, 17.
Appendix
Respondent 1
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No Yes
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 3;
- Sustainability 2;
- Nutrition 5;
- Environment 4;
- Employment 3;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 1;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 4;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once?
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s?
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family?
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience?
Respondent 2
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No Yes
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 3;
- Sustainability 3;
- Nutrition 4;
- Environment 5;
- Employment 4;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? Yes
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? Yes
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 3
Respondent 3
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No Yes
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 3;
- Sustainability 4;
- Nutrition 5;
- Environment 4;
- Employment 3;
- Community 3.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? Yes
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? Yes
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 4
Respondent 4
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No Yes
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 4;
- Sustainability 4;
- Nutrition 5;
- Environment 4;
- Employment 3;
- Community 3.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 5;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 4;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? Yes
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? Yes
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? No
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 2
Respondent 5
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No Yes
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 3;
- Business ethics 4;
- Sustainability 3;
- Nutrition 5;
- Environment 5;
- Employment 4;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? Yes
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? No
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 3
Respondent 6
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No No
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 3;
- Business ethics 4;
- Sustainability 3;
- Nutrition 4;
- Environment 4;
- Employment 4;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? Yes
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? No
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 2
Respondent 7
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No Yes
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No No
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 3;
- Sustainability 3;
- Nutrition 4;
- Environment 5;
- Employment 4;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? Yes
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? No
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 4
Respondent 8
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No No
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No No
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 5;
- Sustainability 3;
- Nutrition 5;
- Environment 5;
- Employment 4;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? No
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? No
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 3
Respondent 9
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No No
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No No
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 3;
- Sustainability 3;
- Nutrition 4;
- Environment 5;
- Employment 4;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? No
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? No
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 2
Respondent 10
Part I
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every week? Yes/ No No
- Do you eat at fast food restaurants every day? Yes/ No No
- Do you frequent McDonald’s at least once a month? Yes/ No No
- Is McDonald’s your go-to option when you are choosing a fast food restaurant? Yes/ No No
Part II
What do you think is important about McDonald’s social efforts and activities? Evaluate the importance from 5 (very important) to 1 (not important):
- Corporate governance 2;
- Business ethics 3;
- Sustainability 3;
- Nutrition 4;
- Environment 5;
- Employment 4;
- Community 2.
Part III
How familiar are you with the following initiatives of McDonalds? Evaluate their familiarity on a scale from 5 (know very well) to 1 (hearing about if for the first time):
- Ronald McDonald’s House: an American independent nonprofit organization whose stated mission is to create, find, and support programs that directly improve the health and well-being of children 4;
- Youth Opportunity: a new initiative called Youth Opportunity, with a global goal to reduce barriers to employment for two million young people by 2025 2;
- Fruits and vegetables: healthier items on the menu 5;
- McDonald’s National Scholarship: a scholarship for Hispanic students 1;
- Black and Positively Golden: a new movement to uplift communities through education, empowerment and entrepreneurship. It tells stories of truth, power and pride, and focuses on the people and places that are the greatest expression of Black excellence 1;
- McDonald’s® APA® Asian Pacific American Community: capturing and sharing Asian Pacific American stories for the masses 1.
Part IV
- Have you been to McDonald’s more than once? Yes
- Do you feel positive emotions associated with McDonald’s? No
- Have you ever recommended McDonald’s to your friends and family? No
- On a scale from 5 (very satisfied) to 1 (not at all satisfied), how happy are you with your McDonald’s experience? 3
