Introduction
Background
Leadership styles of the successful business leaders have attracted many academicians. Especially the leadership styles of tycoons like the Russian monopolists and oligarchies (Kets De Vries, 2000). There are various researches, which have tried to identify a link between personality trait and leadership style (Kornør & Nordvik, 2004; Bono & Judge, 2004). Further research has also identified a difference in leadership styles due to variances in culture of the leader (Hofstede, Deusen, Mueller, & Charles, 2002; Martínez & Dorfman, 1998). Another study specifically deals with the effect on personality trait on entrepreneurial leadership style (Zhao & Seibert, 2006). These researches show that there has been extensive understanding regarding the approaches towards identifying a leadership style and to the leader’s personality.
Problem Statement
The main problem that is studied in the paper is the personality traits and leadership style of Carlos Slim. In this paper, I will use these researches on leadership style to establish a link between the personality traits of a leader as identified through previous work, and link it to my present study wherein I will do a case study analysis of Carlos Slim. After Carlos Slim featured as one of the richest men in the world (Winter, 2007), interest regarding his personality and leadership style is an interesting proposition to study. Further, the study will also provide insight into the leadership style of a businessperson who did all his business in Mexico, which is not a developed country while maintaining undisputed leadership in the market. This will deal with the prevalent literature on personality and leadership theories, show the theoretical correlation between the personality and leadership styles, and analyze Carlos Slim’s character based on this. Therefore, the paper proposes to study the leadership style and personality of the Slim and try to ascertain what kind of personality and leadership traits he possesses.
Hypotheses
As we have seen earlier, the personality of Carlos Slim through the Big Five model of leadership has demonstrated that he appears to be low on extraversion and average on neuroticism. He is high on openness to experience and is low on agreeableness. Slim is high on conscientiousness. With this brief understanding, I will now present the problem statement for the study. For the study, I have taken three hypotheses, which are –
- Carlos Slim’s personality demonstrates a transformational leadership style.
- Carlos Slim as a leader does not have an extravert’s personality unlike other leaders.
Carlos Slim’s leadership style has the following characters growth of the business, personal wealth, power, and reputation
Delimitation
The study is a case study of the life of Carlos Slim. So the geographic delimitation of the work in restricted to the places where Slim had his business, especially Mexico. This paper will be dealing solely on the operations of Carlos Slim. So the delimitation of the research is restricted, more so because it is a case study research. The study is conducted through a questionnaire survey and thus the paper cannot be generalized. Further, as the scope of the paper did not allow interviewing people reporting to Carlos Slim, we have used an experimental research method, which is again limited to the sample group. Therefore, the problem for the present study is to identify the leadership style of Carlos Slim using my understanding of his personality, which is demonstrated using Big Five personality Trait theory. Thus, we divide the study into three sections. First, we will do a brief review of the literature and then identify the hypothesis that we can construct through our understanding of the literature. This will lead to a discussion of the various leadership styles that Carlos Slim demonstrated using his personality traits and his other works.
Limitations
The limitations of the study are in its scope. The best way to ascertain leadership personality and style is through conducting questionnaire survey of the immediate subordinates of the leader, but this is not possible for this research. Further, the study does not try to understand the personality of Slim though empirical finding. Personality is ascertained through secondary research. In addition, most of the literature on personality and leadership theory are based in developed countries, which constrict the view of the researcher and avoid looking at other cultural influence on personality or leadership style.
Literature Review
The study of leadership and personality is a well-traversed path. There are various researches on the personality traits of leaders (Van Eeden, Cilliers, & Van Deventer, 2008; Aronson, 2001). However, mostly studies have concentrated on assessing leadership personality through quantitative research. A qualitative method of study in personality study has been limited. This paper aims to do a leadership personality study using case study method. The personality whom we aim to study is Carlos Slim, the richest man in the world according to Forbes magazine (Winter, 2007). The study will try to ascertain different aspects of Slim’s personality vis-à-vis the leadership personality theory. This research will to establish a relationship between Slim’s behavior and their outcomes. The following section will undertake a brief study of the theoretical background of leadership personality.
Slim’s Background
This is a true story of rags to riches. Carlos Slim had transformed himself and his company into a $59 billion empire (Winter, 2007). To provide a brief background, Slim is the Mexican business tycoon who is a self-made man. He owns the Mexican telecom giant Teléfonos de México or Telmex. There are various controversies regarding Slim’s monopolistic growth and corrupt handling of political alliances (Winter, 2007). Nevertheless, the fact remains that he is presently the richest man in the world and an excellent leader who had transformed his company into an empire, which has spread from “cigarettes to airlines” (Winter, 2007). Presently he has put in a lot of money into philanthropic activities, which drives away his reputation of being a capitalist competition killer.
This paper tries to ascertain the Slims’ leadership and traits with the help of leadership theories and researches.
Theoretical Background
The leadership characters and their personality traits are different for all individuals and cannot be generalized (Goffee & Jones, 2006). Still we encounter personality trait theories like Big Five Personality Theory or leadership theories like Transactional and Transformational Leadership. The Big Five Theory of personality asserts that the there are five basic personality traits which in combination provides a personality type. The personality traits are neuroticism, extraversion, and openness to experience, conscientiousness, and agreeableness. Neuroticism implies an individual’s ability to adjust and his emotional stability. Therefore, a person with high degree of neuroticism will suffer from depression, anxiety, hostility, etc. Extraversion implies an individual’s assertiveness. Openness to experience shows a person’s intellectually curious mind and his desire to seek new ideas. Agreeableness shows a person’s interpersonal skill. Conscientiousness implies the level to which an individual is organized, hard working, and motivated. For leaders it is believed that the level of neuroticism, openness to experience, agreeableness, and conscientiousness is high (Zhao & Seibert, 2006). However, their degree of extraversion may or may not be low (Zhao & Seibert, 2006). Taking this research study to be our benchmark, we try to ascertain from a qualitative case study approach, what traits Slim posses.
Personality Traits
From various articles and interviews of Carlos Slim, this research will try to draw a personality trait of Slim using Big Five Personality Theory. The following section will describe Slim’s character vis-à-vis a personality trait. This will provide a clear picture of Slim’s personality as a leader.
Neuroticism: people who have a high degree of neuroticism are said to be calm, confident, relaxed, and even sometimes tempered (Zhao & Seibert, 2006). Slim is relaxed and confident which is demonstrated with his visit to Washington D.C. quietly and not informing anyone. He is self-composed as he is not over enthusiastic to show-off his possession of wealth and went around in a hired Ford Sedan when he visited the United Sates (Winter, 2007). He is confident when he speaks of his humble past and present humble living. Nevertheless, his lack of confidence in himself and in his organization has made him undertake false means to stop the growth of completion in the telecom sector of Mexico (Ipsen, 2008). His intention to curb competitors to grow shows his hostile attitude of doing business, which is indicative of a low score on neuroticism. However, we did not get any instance of his personality, which showed temper, but he appears to be a person who usually remains calm. Therefore, in terms of neuroticism we cannot conclusively state his personality trait.
Extraversion: Slim is not an extravert. Previously he had shield away from media and kept his whereabouts, operations, dealings, and strategies a closely guarded secret. He seldom gave interviews or appeared before media. His workings were so secretive that he reached United States unannounced and quietly went about doing his business dealings (Winter, 2007). His appearance before media is just a recent phenomenon after he has been stated as the world’s richest man; “Slim only this year has given up a long habit of cultivating anonymity” (Winter, 2007). Clearly, this shows that Slim has an introvert’s character.
Openness to experience: Slim is open to new ideas. This can be understood from his expanse into business. Slim owns right from a cigarette company to an airline’s company. This shows that the man does not fear to venture into new areas. Further, his passion for football shows that he is open to the idea of a sport which requires a lot of openness to experience (Winter, 2007). As Slim himself states, “I like numbers…Words speak to some people; to others of us, its numbers.” He credits this trait with his success as a financier” (Winter, 2007). A man who believes in numbers will always accept an idea, which shows him profitable “numbers”. His open ideas have made him a recent philanthropist. Therefore, Slim has a high degree of openness to experience.
Agreeableness: Whether Slim is an agreeable man or not, it is difficult to ascertain. Nevertheless, it can be said with high degree of conformity that he has eccentric ideas (Winter, 2007). Many of his ideas are based on whims and not on any solid business logic. A man who works on his personal whims is not likely to be agreeable of other’s ideas. Further, a close observer of Slim would call him “disarming, austere, and even humble” (Winter, 2007). This character actually makes him look stern and strict. A strict man will not be agreeable as to be agreeable he has to “cooperative” and must have “high interpersonal relationships” (Zhao & Seibert, 2006). Further, Slim’s interaction with other corporate and media shows that he is not very friendly to either of the two, which shows that his ability to mix with others is not very strong, thus making him have a low degree of agreeableness.
Conscientiousness: Slim is definitely a man who can work hard. He has built an empire from a small entrepreneurial setup of his father. He knows his past and has no intention to hide it. He leads a very humble life as compared to a man of his stature. He has built a fortune only based on hard work. Therefore, he scores high on the scale of conscientiousness.
Study Hypotheses
Personality of a person is thought to have a significant effect on the development of the person’s leadership style, especially that of an entrepreneur (Zhao & Seibert, 2006, p. 259). Leadership has mostly been studied by researchers from an individual’s perspective and has been defined in terms of individuals’ personality traits, leadership behavior, pattern of interaction, relationship with subordinates, relationship with followers, etc. (Yukl, 1989, p. 252). I use entrepreneurial leadership style as a main potent for our study as I believe that Carlos Slim’s empire has been developed from an entrepreneurial venture and thus requires understanding from this standpoint. The leadership theory, which forms the focus of the leadership study, is transformational leadership theory.
Transactional and transformational leadership styles were identified in the 1970s. Transactional leader is one who takes initiative to contact others to exchange something; here the transaction does not go beyond the exchange of things. A transformational leader, on the other hand, is one who interacts with other sin such a way that the leader follower relationship brings out motivation and morality. A transformational leadership is important for the leader to understand the true needs of the followers. A transformational leadership helps in higher performance of the organization. According to this theory there are four components of the leadership style and they are “idealized influence, inspirational motivation, individualized consideration, and intellectual stimulation” (Khatri, 2005, p. 20).
Khatri (2005) argues that the four components of leadership as thought to comprise in the personality of transformational leaders can be brought down to two components. According to him, the two components, which are the most important elements of a transformational leader, are charisma and vision (Khatri, 2005, p. 21). His model suggests that leaders who have high charisma and high level of vision for his company are transformational leaders.
Bono and Judge (2004) have argued that transformational leadership is a neo-charismatic leadership theory, which shows a hybrid approach to leadership. They identified the leadership behavior to be based on “idealized influence” indicating the leadership have high standard of moral or ethical conduct and are held at high personal regard by others (2004, p. 901). The second behavior is “inspirational motivation” which describe the leaders whose visions are strong and futuristic and are based on their ideals (2004, p. 901). The third is called “intellectual stimulation” which refers to the leadership behavior through which they challenge organizational norms, encourage, and cultivate innovation among followers. The fourth behavior is called “individual consideration” where the leader has attention towards the follower’s training and developmental needs and believes in participative management. While transactional leaders believe in contingent reward which indicates leadership stress on exchange of resources and management by exception which indicates leader’s monitoring of the follower’s performance and taking corrective action as and when necessary (Bono & Judge, 2004, p. 902).
Kornør and Nordvik (2004) have studied the correlation between personality traits of a person to the leadership behavior of the individual. They have used Norwegian leaders as their sample for the study and have used Big Five Personality Trait theory and factor and correlation analysis for the research (2004, p. 50). They studied 106 respondents who had participated in leadership and career development programs (2004, p. 50). They used correlation analysis, regression analysis and factor analysis to identify the relationship between the personality traits and the leadership dimensions. In their study, they identified three common factors which affect leadership style, viz. “looking for new possibilities,” “hard working,” and “dealing with people”, which they believe affect the leadership style the most (Kornør & Nordvik, 2004, p. 53). Their study shows that individuals who have high degree of extraversion and open to experience are open to Change (2004, p. 53). High conscientiousness in personality indicate that the person have their attention on getting things done (2004, p. 53). According to their study, extraversion and conscientiousness are the best predictors of leadership style (2004, p. 53). However, van Eeden, Cilliers, and van Deventer (2008) found that is a leader uses transformational or transactional leadership style depends on his interpersonal style and social ethics. From this research, we come to our first hypothesis.
Hypothesis 1: Carlos Slim’s personality demonstrates a transformational leadership style.
Bono and Judge (2004) conducted a meta-analysis to understand the relationship between leadership personality and their inclination to become transactional or transformational leaders. They used the Big-Five model of personality and they were related to the three dimensions of transformational leadership i.e. charisma, intellectual ability and individualized consideration (2004, p. 903) and with three dimensions of transactional leadership i.e. “contingent reward”, “management by exception–active”, and “passive leadership” (2004, p. 903). Their study revealed that extraversion in character of a leader has a strong influence and mostly strongly correlate to transformational leadership characters (2004, p. 908). They believe that extraversion and its dimensions “dominance and positive emotionality” can be used as dimensions of extraversion while analyzing the character of a transformational leader (2004, p. 908). Extraversion can be described as the degree to which people are “assertive, dominant, energetic, active, talkative, and enthusiastic” (Zhao & Seibert, 2006, p. 260). Further people who are high on extraversion are usually cheerful or like to a part of a large group. People who are low on extraversion tend to keep quiet and be alone and are usually reserved and independent in nature (Zhao & Seibert, 2006). As believed by Zhao and Seibert (2006) entrepreneurs are extraverts. As Carlos Slim started his business from scratch, he can be considered an entrepreneur in the Mexican market. Thus, we reach our second hypothesis
Hypothesis 2: Carlos Slim as a leader does not have an extravert’s personality unlike other leaders.
Carlos Slim as a leader does not have an extravert’s personality unlike other leaders. Cultural differences affect leadership styles as it affects the goals of the leaders (Hofstede, Deusen, Mueller, & Charles, 2002, p. 784). Goals affect the personality of the person (2002, p. 787). Research has demonstrated that different leaders from different nations have different goals. So Hofstede et al. (2002 ) has shown that in Latin American countries the inclination of the leaders “tycoons” are “growth of the business, this year’s profits, continuity of the business, personal wealth, power, honour, face, reputation” (2002, p. 793). Their study shows that it is distinctly different from US culture of doing business of a leader. From Hofstede et al.’s study we come to our third hypothesis.
Hypothesis 3: Carlos Slim’s leadership style has the following characters growth of the business, personal wealth, power, and reputation.
Methodology
The methodology adopted for this research is case study analysis. A case study analysis is a valid qualitative methodology. In this research, we use this qualitative methodology to understand the leadership style and their dependence on personality traits through a case study model of Carlos Slim. I choose Carlos Slim as his story is intriguing and has not been studied so far. Further being the third richest man in threw world, he has made a journey from being a stockbroker to building a conglomerate single-handedly. He has shown exceptional leadership and strength of personality in doing so. In this study, we thus use a case study approach to understand the leadership style of Carlos Slim.
The study being a case study analysis of Carlos Slim’s leadership style and personality, I have adopted a qualitative research methodology wherein I develop the case study of the entrepreneur. The detailed methodology is presented below.
The case study data is collected from secondary sources and the relation between personality and I use an alternative model of transformational leadership by Khatri (2005) to understand the leadership characters of Carlos Slim. In this section, I will explain the model that was presented by Khatri to identify transformational leadership and use it frame a survey questionnaire.
Figure 1: an alternative model for transformational leadership, source N. Khatri, an alternative model for transformational leadership, 2005
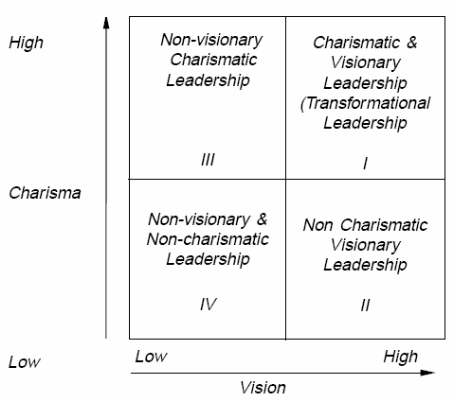
As figure, 1 shows Khatri divided leaders into four quadrants, which represents four broad categories. The model considers leaders who are high on vision and charisma or low in both or those who fall somewhere in-between. So here, we consider leaders who are high on either charisma or vision but not both, and so are unable to transform the organization. Leaders in quadrant 1 are transformational as they are high on both charisma ad vision, whereas leaders in quadrant IV are low on both the characters, thus are expected to be least effective. Further in quadrant III and II the leaders are either highly charismatic or vision thus making them moderately effective in the company’s success. Using this model, I will try to understand the leadership style of Carlos Slim.
To conduct the research, a sample of 30 respondents is randomly chosen from a university business management undergraduate class. The students are first given an biographical article about Carlos Slim written to demonstrate the background of Slim and his rise from a small businessman in a less developed country. Then based on their understanding about Carlos Slim in the article they are asked to answer a structured questionnaire regarding Slim’s personality and leadership style. The survey questionnaire is provided in the appendix. This methodology was chosen, as it was difficult to contact people who reported directly to Carlos Slim. Due to the limitation of scope, this method was thought to be the most effective way to understand the general perception that is derived about Slim after going through his life as an entrepreneur of a conglomerate.
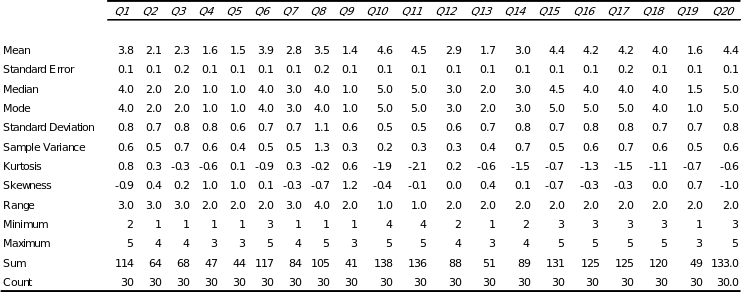
The questionnaire was presented to a group of 35 students of whom 30 completed the survey properly. The sample was randomly chosen and was first thoroughly briefed about the survey and was asked to read the article on Carlos Slim. The average age of the respondents was 20 years and male is to female ratio was 3:2. The analysis is done using descriptive statistics based on the responses in Excel.
Research Findings
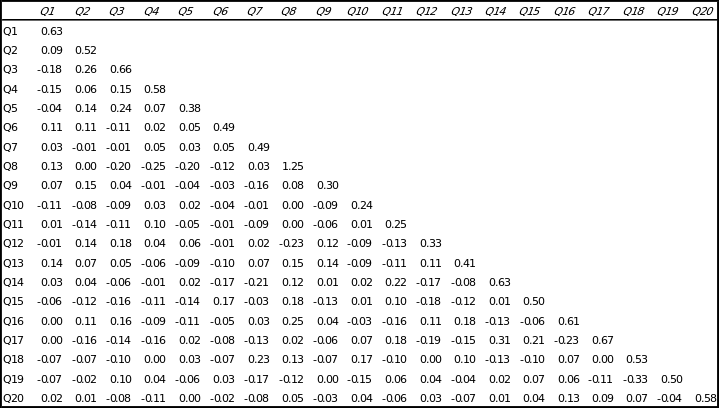
The questionnaire had twenty questions related to four main characters of a leader, which was derived through the literature review. The three main characters were charisma, vision, extraversion, and ethics. The twenty questions were then cultured to form the four categories (see table 1). As table 1 show, the questions in the questionnaire as presented in the appendix are categorized based on these four characters. Based on this categorization, the correlation analysis of the questions for each category is done. Further each category has a direct question asking directly if the respondents feel that Carlos Slim is charismatic, or a visionary leader, or is an extrovert or ethical leader. Based on these questions the other questions in the category are correlated to understand if the questions, which indicate the four characters, are fulfilled. When charisma and vision related characters are clubbed together, they represent the first hypothesis. Extrovert correlates to the second and Latin Leader correlated to the third characteristics. The last character represents if the leader is ethical or not which will again related to the transformational character to the leader.
Hypothesis 1: For this hypothesis, we consider the model presented by Khatri (2005) on transformational leadership. Khatri has shown that charisma and vision are the two main characteristics of a transformational relationship (figure 1). Table 2 shows that the correlation between Q3, Q1, Q5, Q8, Q12, Q13, andQ14. The main criteria for this analysis are to understand if the respondents feel that Carlos Slim shows charismatic leadership qualities and if it is high. Q3 directly asks the question if Carlos Slim is a charismatic leader. For this question, the descriptive statistics in table 3 shows that the mean of the responses are 2.26, which indicate that the respondents feel that Slim is not a charismatic leader. Further the standard deviation being just 0.15, indicates that the variation in the responses are low which indicates a valid mean. So seeing the correlation between the remaining the questions with Q3 in shown in table 2. This indicates that the correlation is negative with Q1, which shows that Slim is the ultimate decision taker in the company, which is against the charismatic leadership quality, which is high in Slim’s character with a mean of 4, and so a negative correlation is obtained. When respondents were asked to rate Slim on his media friendliness as compared to Richard Branson, Slim scored a very low mean of 1.46 and a positive relation with Q3. As the relation between the questions Q5, Q12, and Q13 are positively related to Q3 indicating that Slim is low on the scale of being a charismatic leader, and a negative relation with Q1, Q8, and Q14 indicates that they are desired characters in a charismatic leader, which are not present in Slim again indicating his low charisma. Therefore, Carlos Slim is found to be low on the scale of charisma indicating non-charismatic leadership quality.
While considering vision of Slim, we correlate Q2 with Q6. Here both the questions are related to Slim’s vision and his sharing of the vision with others which is actually the role of a visionary leader (Bono & Judge, 2004; Khatri, 2005). Table 5 shows that for both he questions the median are 2 for Q2 and 4 for Q6 which indicates that Q6 is believed to hold true and Q2 is not true. A correlation analysis of the two questions indicates a positive relation indicating that the Carlos Slim is a visionary leader.
From the two discussions of charisma and vision, we find that Carlos Slim is low on Charisma and high on vision. Thus, according to Khatri’s model he belongs to quadrant II (figure 1) indicating that Slim is not a transformational leader but has certain characters of a transformational leader, thus will be able to bring about some changes in the organization but being more of a transactional leader. This shows that hypothesis 1 does not hold true.
Hypothesis 2: It is believed that Carlos Slim does not have an extrovert’s personality. Here extraversion is measured according to Zhao and Seibert (2006) where they have shown that an extravert’s personality is judged by assertiveness, exposure and his talkativeness (which is taken here to be quietness). Thus, the mean of Q4 which asks a direct question i.e. if the respondents feel Slim has an extravert’s personality or not, the mean was 1.5 indicating that the respondents believe that Slim does not have an extravert’s personality. This indicates that the respondents do not feel that Slim has an extravert’s personality. When correlating this question to the other question it can be observed that Q7, Q10, and Q11 have a positive correlation with Q4 and the correlation coefficients being high indicate that all agree that all other characters of extraversion are low in Slim indicating that he has an introvert’s character. Thus, Slim is not believed to have an extravert’s personality.
Hypothesis 3: Leaders have an effect on their personality and their leadership style due to cultural discourse (Hofstede, Deusen, Mueller, & Charles, 2002). Following this, I tried to find if the leadership style if Carlos Slim had any effect of the Latino culture. The cultural traits of a leader was found by Hofstede et al. in their study which has been used to identify the main characters of cultural constraints on Slim. The main components in a Latino culture as identified by Hofstede et al. are the leadership value for power, wealth, and philanthropy. The individual means for the following are high for power and wealth and low for philanthropy, which is characteristic of Latino cultural leadership. Further, in correlations we see that they are positive for the value of power and wealth, which is considered high while the value of philanthropy is considered low. Further while considering the ethical trait in Slim’s leadership the analysis has found that Slim did not have high consideration for ethics with the mean score for all the ethics related questions to be low. In addition, showing that Slim’s orientation towards profit making is higher than philanthropy indicating a character indicating selfishness, which does not befit a transformational leader but a transactional leader. He values personal wealth more than any other thing thus showing that Slim is more oriented towards personal profit than shareholder profit. In addition, he values power. Which shows that Slim values power, personal wealth and profit highly as are the characters of a leader from the Latino countries (Hofstede, Deusen, Mueller, & Charles, 2002 ) and shows transactional type of leadership (Bono & Judge, 2004). This indicated that Slim’s leadership style is highly conditioned by the Latin culture-holding hypothesis 3 true.
Summary, Conclusions & Recommendations
From the above research findings, we see that the personality and leadership style of Slim is not that of a transformational leader. As the hypothesis, 1 does not hold true, it shows that the leadership style of Slim is more of transactional nature. Now I will correlate the empirical finding with that of the findings of the secondary analysis. Carlos Slim’s personality has been found through secondary research that he is hard working. A conscientious person has a strong sense of direction and work very hard to achieve it. Carlos Slim is a person who does this. These people are conscious, self-disciplined, and tend to be neat in their work. Slim seems to be a person who represents these characters. Slim’s dedication to his business and his entrepreneurship venture has shown that he is a man dedicated to his goal. He is a tycoon who believes in building his company and works stringently to achieve his goal. His capacity to work hard and adhere to his goal can be best described through the following statement: “Slim, long known for his ability to spot undervalued companies and turn them into efficient, profitable enterprises, has often been called the “Warren Buffett of Latin America.” (Smith, 2007, p. 3). Thus, this indicates that Slim demonstrates a characteristic blend of hard work, dedication, and focus. Further, he is open to changes that occur in his business as well as life. One foremost example for this is his insistent anonymity from the media was removed once he featured as the richest man in the world in 2007: “… Slim only this year has given up a long habit of cultivating anonymity. He has even begun talking regularly to the press. Perhaps he realized his ascension to Forbes’ No.1 spot would fan public interest; perhaps he has grown less protective of his privacy as he retires and bequeaths his business interests to his children” (Winter, 2007, p. 36). This shows Slim’s acceptance to change and intention to change with need. Thus, he has transformed his company from a small entrepreneurial venture into a conglomerate but there are areas where he shows no extraverts’ character or charisma. Thus from the secondary research as we did from the primary research findings, Carlos Slim is not a transformational leader. However, he is high on vision but low in charisma, which puts him half way in-between.
Slim is more of an introvert. His character fails to show any character of an extravert. This finding is demonstrated through the empirical research that I conducted. Most of the respondents felt that Slim liked to keep alone and shy away from the media. Secondary research I conducted showed similar finding. Slim has demonstrated his character as an introvert. Slim’s earlier anonymity from the media and then his shows that his aversion to be an open book and deal with all. He kept his whereabouts, operations, dealings, and strategies a closely guarded secret. He seldom gave interviews or appeared before media. His workings were so secretive that he reached United States unannounced and quietly went about doing his business dealings (Winter, 2007, p. 36). His appearance before media is just a recent phenomenon after he has been stated as the world’s richest man; “Slim only this year has given up a long habit of cultivating anonymity” (Winter, 2007, p. 36). Clearly, this shows that Slim has an introvert’s character. Following Bono and Judge (2004) it can be stated that Slim being an introvert tends more to be a transactional leader than a transformational leader. Thus, I dub that Slim Does not have an extravert’s character and is essentially an introvert.
Hypothesis 3 is proven true with Slim’s character having characteristics of a Latin leader. Cultural effect on leadership style of Slim is apparent through his business. Slim’s contention is to deal with profits which is seen through his company’s insistence on cost cutting (Mehta, Bergtraum, Neering, & Ruiz, 2007, p. 23). His character shows a distinct Latin American character when it comes to accumulating personal wealth. His personal wealth is at $59 billion (Winter, 2007, p. 35) and has majority shares in “at least 222 companies” (Winter, 2007, p. 36). This shows that he has a distinct character to collect wealth. He cares about his reputation and that is why Slim has undertaken to provide to the world a view of his life and business to the world.
Slim is a powerful man and likes being powerful. He utilizes it to gain his objective. His sense of power is shown when he states the following while discussion in his misplay with political allies to gain a deal: “Slim dismisses the whole controversy as irrational. “We won because we paid more,” he says, “by about 8 cents per share” (Winter, 2007, p. 36). Thus, Slim’s character is heavily depended on his cultural background. This finding holds true the third hypothesis, stating that culture has an influence on leadership style which has also been found by Hofstede et al.’ findings (2002 ).
The limitations of the study are in its scope. The best way to ascertain leadership personality and style is through conducting questionnaire survey of the immediate subordinates of the leader, but this is not possible for this research. Further, the study does not try to understand the personality of Slim though empirical finding. Personality is ascertained through secondary research.
Appendix
Table 1: Carlos Slim Leadership Survey
Directions
This questionnaire contains statements about leadership style beliefs. Next to each statement, circle the number that represents how strongly you feel about the statement by using the following scoring system:
- Almost Always True – 5
- Frequently True – 4
- Occasionally True – 3
- Seldom True – 2
- Almost Never True – 1
On the article based on Carlos Slim and his growth as the world’s richest man, please answer the following questions regarding Slim’s perceived personality and leadership style. Think of Slim as your boss and then respond to the questions below. Be honest about your choices as there are no right or wrong answers – it is only for your own self-assessment.
Cover Letter
Dear Respondent,
I am a student of Business Management at Palo Verde College and I am conducting a survey on the leadership and personality style of Carlos Slim, one of the richest men in the world according to Forbes and the business mogul of Mexico. The research project is a term paper, specifically for the purpose of academic pursuit. This research intends to identify the leadership style of Carlos Slim. Through your participation, I intend to find the same.
Enclosed with the letter are a brief questionnaire and a biographical write-up on Carlos Slim’s life and business. I request you to read the write-up, then, if you choose to, fill the questionnaire, and return it back.
If you choose to participate, I will request you not to write your name as this is an anonymous survey. Your personal details are not required for the survey and your participation in the survey will never be revealed.
I hope you will take out some of your valuable time and help me complete this research.
Sincerely,
Name:
Reference
Bono, J. E., & Judge, T. A. (2004). Personality and Transformational and Transactional Leadership: A Meta-Analysis. Journal of Applied Psychology Vol. 89 No. 5 , 901-910.
Hofstede, G., Deusen, C. A., Mueller, C. B., & Charles, T. A. (2002 ). What Goals Do Business Leaders Pursue? A Study in Fifteen Countries. Journal of International Business Studies Vol. 33 No. 4, 785-803.
Kets De Vries, M. F. (2000). A Jpurney into the “Wild West”: Leadership Style and Organizational Practices in Russia. Organizational Dynamics (Spring) Vol. 28 No. 4 , 67-81.
Khatri, N. (2005). AN ALTERNATIVE MODEL OF TRANSFORMATIONAL LEADERSHIP. Vision Vol. 9 Issue 2 , 19-26.
Kornør, H., & Nordvik, H. (2004). Personality traits in leadership behavior. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology Vol. 45 No. 1 , 49-54.
Martínez, S. M., & Dorfman, P. W. (1998). The Mexican Entrepreneur. International Studies of Management & Organization Vol. 28 No. 2 , 97-124.
Mehta, S. N., Bergtraum, L., Neering, P. A., & Ruiz, L. (2007, August 20). Carlos Slim. (cover story). Fortune , pp. 22-29.
Smith, G. (2007, July 5). Carlos Slim’s Fat Fortune. Business Week Online , p. 3.
van Eeden, R., Cilliers, F., & van Deventer, V. (2008). Leadership styles and associated personality traits: Support for the conceptualisation of transactional and transformational leadership. 253-267.
Wah, S. S. (2004). Entrepreneurial Leaders in Family Business Organizations. Journal of Enterprising Culture vol. 12 no. 1 , 1-34.
Winter, B. (2007). How Slim got Huge. Foreign Policy vol. 163 , 35-42.
Yukl, G. (1989). Managerial Leadership: A Review of TIneory and Researcti. Journal of Management Vol. 15, No. 2 , 251-289.
Zhao, H., & Seibert, S. E. (2006). The Big Five Personality Dimensions and Entrepreneurial Status: A Meta-Analytical Review. Journal of Applied Psychology Vol. 91 No. 2 , 259-271.
