The modern business environment is characterized by numerous factors that can either hinder or support performance. Some of them include emerging technologies, competitive business models, availability of related products, and changing consumer expectations. Managers who consider these issues find it easier to formulate superior approaches to achieving the intended aims. Coca-Cola remains one of the most successful multinational corporations (MNCs) in the world today. It applies evidence-based strategies to produce high-quality products and market them successfully to the targeted customers (Kayabaş, Boyraz and Derdiyok, 2017).
It has been relying on the concept of Marketing Management (MM) to overcome the challenges of competition and add value to every stakeholder. The corporation’s managers identify and present additional strategies to improve its model and achieve more results.
At Coca-Cola, marketing management is a continuous process whereby those involved are constantly identifying new opportunities and practices for delivering additional benefits. The cyclical model means that the introduction of additional products will require a powerful strategy to deliver them to the identified customers (Kanesan, Ismail and Krishnan, 2018). Since the year 1888, Coca-Cola has managed to acquire timely lessons and ideas that different leaders replicate in every market to maximize efficiency and sales (Kanesan, Ismail and Krishnan, 2018). It collaborates with bottlers across the globe through the use of its franchised marketing and distribution systems.
The MM strategy at the Coca-Cola Company takes 6 major phases. The first one is known as market auditing whereby those involved in the department identify specific goals that should be realized within a stipulated period. For example, the launch of every new product in a given country compels the company’s marketing managers to identify the intended sales or profits (Kanesan, Ismail and Krishnan, 2018).
The same step is also useful when this corporation is pursuing a new marketing-related agenda, such as improving its corporate social responsibility (CSR) image or improving its brand image or size. This initiative is essential since leaders encourage all stakeholders and decision-makers to collaborate and consider practical strategies for guiding such objectives.
The second phase that this corporation pursues as part of its MM process is the analysis of marketing opportunities and the development of appropriate strategies. The involved departments work together to analyze the strengths and assets that can support the introduced product or goal. The acquired information is then compared and contrasted with the challenges, threats, and opportunities in the external environment. Such a procedure can take long before the involved workers present a detailed report to the relevant department (Kanesan, Ismail and Krishnan, 2018). The analytical stage becomes an opportunity to locate more customers or clients, monitor their demands, and consider superior practices to achieve desirable results.
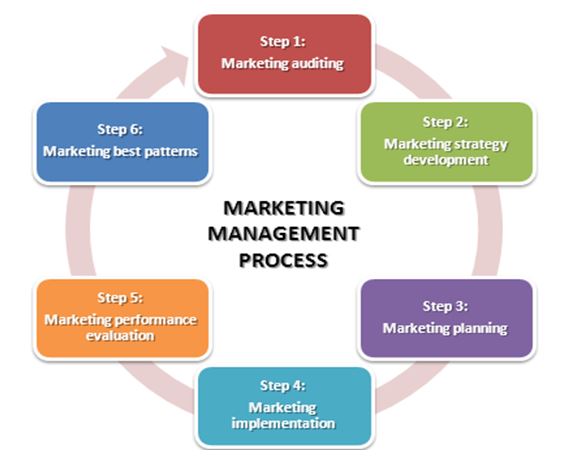
The next crucial stage that Coca-Cola follows as part of its MM strategy is known as planning (see Figure 1). This phase is an opportunity to define possible support systems and their efficiency. The targeted model is also aligned with the available resources, logistical operations, and the expectations of different stakeholders. The leaders engage in continuous learning to identify how similar procedures might have succeeded or failed in the past. The planners go further to consider the trends in the market and predict how different competitors might affect or disorient the anticipated goals. This corporation and its franchisees search for competent marketers who have the potential to execute the marketing plan effectively, solve emerging challenges, and introduce new practices to maximize performance.
The fourth phase of MM at this organization is that of marketing implementation. This is an area that Coca-Cola performs effectively due to its model of partnering with established restaurants, hotels, wholesalers, fast food companies, and supermarkets (Kayabaş, Boyraz and Derdiyok, 2017). The company uses the existing supply chain systems to deliver finished products to the targeted customers. This implementation phase is coupled with the concept of the marketing mix to ensure that positive results are realized. For instance, before releasing the product into the market the company finds out the product effectiveness and perform quality assurance tests. This attribute explains why Coca-Cola is associated with quality in different parts of the world. The leaders and marketing professionals go further to consider the power of competitive prices and engage in intensive promotion campaigns to support the entire implementation process.
Marketing performance evaluation is a process that Coca-Cola practices continuously. The relevant departments collaborate to identify areas of possible success and obstacles that might disorient the intended results. Any value addition activity goes through the same process to present additional approaches for improving performance (Mayureshnikam and Patil, 2018). The research and development (R&D) team are also involved in this stage to offer additional insights for maximizing productivity and addressing emerging issues.
The final stage of the cyclical MM process this company exhibits is known as marketing best patterns. This is the initiative designed to identify some of the ideas, tools, logistical support systems, and campaigns that work effectively for a specific product. These aspects become part of Coca-Cola’s marketing strategy and are eventually replicated in different regions to maximize performance and deliver the intended results.
The Coca-Company has always relied on the power of marketing management to introduce new products, improve the performance of existing ones, and launch new programs aimed at improving the welfare of different stakeholders (Kayabaş, Boyraz and Derdiyok, 2017). The involvement of all franchisees and departments has become an evidence-based strategy for minimizing the negative challenges of rivalry. Such a model will, therefore, continue to support the outlined marketing strategy and eventually make this corporation more competitive.
Coca-Cola has an effective marketing model that supports the way it distributes its carbonated drinks to the targeted customers. Its reputable and recognized brand image contributes significantly to its current performance and success. The above section has gone further to present the major processes that the leaders undertake to improve their business practices meet the needs of their business partners (Kanesan, Ismail and Krishnan, 2018).
This corporation’s management activities are appropriate and capable of supporting the outlined aims. The existence of powerful logistical and supply chain systems makes it possible for different players to support the marketing strategy. However, some suggestions can transform the current process and eventually make Coca-Cola more profitable.
Firstly, the company has been employing a standardized model for all markets in different parts of the world. The planning and implementation phases are founded on the outlined demands and expectations of potential customers. This strategy explains why different companies in the industry have managed to attract the same customers, thereby recording positive gains. Coca-Cola needs to consider the power of market segmenting and use appropriate targeting models (Mayureshnikam and Patil, 2018). Such an initiative will ensure that there are specific products that are intended to meet the demands of specific people, such as those with medical complications and children (Kotler et al., 2008). The success of Diet Coke in the United States should be replicated elsewhere to achieve additional gains and maximize profits.
Secondly, the use of technology remains a driving force behind Coca-Cola’s MM process. The company considers the superiority of its brand image to attract potential customers from different markets. Such a practice makes it hard for this organization to achieve additional gains (Kanesan, Ismail and Krishnan, 2018). The leaders can utilize various social media platforms and outlets to inform more people about the nature and effectiveness of the intended products. Customers can also be requested to provide additional insights that can improve the level of performance. Those in managerial positions will use the acquired ideas to formulate superior initiatives that resonate with the demands of the targeted individuals.
Thirdly, the leaders at Coca-Cola pursue new partnerships with different wholesalers and existing businesses to support the targeted marketing goals. However, this practice has the potential to affect the integrity or practicability of emerging marketing decisions. The introduction of additional outlets and stores whereby customers can purchase the products and consume them will transform the current situation (Kanesan, Ismail and Krishnan, 2018). This suggestion will become an evidence-based strategy because more people prefer a one-on-one experience with a given company to have most of their demands will be fulfilled. The consideration of such attributes will streamline the marketing management process and deliver high-quality results.
Reference List
Kanesan, S., Ismail, N.A. and Krishnan, K. (2018) ‘Identifying market segments and targets for marketing strategy plan of Coca-Cola Company in Malaysia’. International Journal of Business and Management, 7(4), pp. 77-80. Web.
Kayabaş, T.D., Boyraz, G. and Derdiyok, R. (2017) ‘Examining Coca-Cola and Pepsi brands under the basis of globalisation and multinational companies’, International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 7(12), pp. 351-358. Web.
Kotler, P. et al. (2008). Principles of marketing. 5th edn. London: Pearson Education.
Mayureshnikam and Patil, V.V. (2018) ‘Marketing strategy of Coca Cola’. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 1(1), pp. 77-85. Web.
What is marketing. (no date). Web.
