Emaar Hospitality Group is a subsidiary company of Emaar Properties, one of the largest real-estate developers in the United Arab Emirates. It is a public joint-stock company valued at about US$9.7 billion as of 2018. The company runs its operations internationally and provides management and development services. Emaar Properties is known for its large-scale projects throughout the UAE and the MENA (the Middle East and North Africa) region. Probably the best-known project by Emaar Properties is Burj Khalifa, the tallest building in the world. Other large-scale ventures authored by Emaar Properties are Dubai neighborhoods with a recognizable signature design that draws on Arabic architecture traditions and adds modernity in the mix.
One of the company’s most successful subsidiaries, Emaar Hospitality Group describes itself as a global provider of “personal, innovative, and memorable lifestyle experiences.” It creates spaces for modern-minded visionaries to enjoy life and revive their energy. Emaar Hospitality Group focuses on high-end luxury hotels and restaurants that revolutionize the hospitality sector in the United Arab Emirates.
Due to a high diversity of projects launched and managed by Emaar Hospitality Group, this paper will only focus on one project – At.mosphere Burj Khalifa. Rising 442 meters above the ground, the restaurant is located on the 122d floor of the world’s tallest building. It offers its visitors breathtaking views of the Arabian Gulf as well as a wide array of critically acclaimed, gastronomical wonders. This paper assesses the market positioning and segmentation of At.mosphere and provides relevant theoretical underpinnings.
Literature Review
Market segmentation is critical to a marketing strategy; it drives organizations’ marketing decisions. The concept of market segmentation stems from the economic pricing theory that claims that it is possible to gain maximum profits via discrimination of pricing levels between segments (Venter, Wright & Dibb, 2015). Market segmentation helps to overcome market heterogeneity as in creating a product that would match the majority of people’s preferences (Venter, Wright & Dibb, 2015). Instead, it is suggested that companies group customers with similar product preferences and purchasing behaviors together, therefore, building homogeneous segments with defined needs and tastes (Venter, Wright & Dibb, 2015).
Market segmentation is important because it allows businesses to allocate resources in a more meaningful way and have a better understanding of their customer base. At present, researchers employ different segmentation variables such as demographic, geographic, psychographic, and behavioristic. These are the factors that are used to categorize customers and create homogeneous segments.
Once a company defines market segments, it proceeds with targeting. Not all segments are truly aligned with a company’s marketing strategy, which is why a choice needs to be made as to which of them make the most sense. Targeting means reaching out to the segments carefully selected based on their potential and commercial attractiveness (Chernev, 2018). According to Chernev (2018), the market size itself must be considerable enough to justify segmentation. Otherwise, grouping customers might result in even smaller segments, which would make accessing them challenging.
Segments must be different, and the differences between them should be readily observable and measurable (Chernev, 2018). Selected segments need to make sense financially as projected profits should be greater than the costs of additional marketing plans and other changes. Lastly, as suggested by Chernev (2018), accessibility of segments plays an important role in their selection: customers must be able to receive messages intended for them.
The next step that follows market segmentation and targeting is market positioning. Market positioning is a process through which a brand tries to shape consumer perception. It differentiates a product or a service from its competitors by giving it a distinctive identity. Chernev (2018) writes that market positioning establishes the image of a brand. If done correctly, it helps customers to associate a brand with a particular status, emotions, or experiences. Market positioning is needed to make a unique selling proposition: communicate values and benefits that would compel customers to switch brands (Chernev, 2018).
This can be achieved through cost leadership as in offering affordable products or differentiation – capitalizing on the unique features of goods or services. An effective market positioning strategy consists of three steps: determining company uniqueness, identifying its current market position, and analyzing its competitors – their interaction, influence, and leverage.
Segmentation Variables: Segmentation, Targeting, and Positioning
At.mosphere Burj Khalifa focuses on targeting market segments characterized by the following variables:
- demographic. At.mosphere welcomes customers of both genders with a focus on women. The restaurant hosts thematic female-only events where women can enjoy a company of like-minded individuals without having to worry about their safety. At.mosphere has the potential to appeal to customers of different ages. As for income, the present restaurant is in the upscale category: the minimum cheque is $220, which is not exactly affordable for broader audiences;
- geographic. At.mosphere is potentially appealing to both locals and tourists from all over the world. Regarding local tourism, the restaurant may be attractive to those living in the metropolitan area as well as to remote residents who do not come to Dubai too often;
- psychographic. At.mosphere is likely to attract customers with pronounced novelty-seeking behavioral patterns. Making it to the top of the world’s largest building is an adventure, and observing the Gulf while being almost half a kilometer from the ground is literally breathtaking. Apart from that, the restaurant might find its customers in people who like to make memorable impressions. At.mosphere could be a suitable place for a date, a business meeting, or an official celebration. Lastly, the venue can serve as a place for relaxation for men and women engaged in business during the day;
- behavioristic. It is readily imaginable that At.mosphere would be a part of travel programs, especially the short ones that only include the most impressive sights of Dubai. Tourists might be more open to new experiences, and their search for novelty might mitigate the high price of receiving a reservation at At.mosphere Burj Khalifa.
Porter’s Five-Force Model
At.mosphere is currently working on attracting well-off women who know what they want from service and who like to relax after a long workday in a company of like-minded individuals. Porter’s Five-Force model is a valuable tool for assessing the dynamics of the restaurant industry in the United Arab Emirates. Below is a breakdown of the key elements of the model:
- The threat of new entrants – medium. In 2019, the UAE ranked 11th in the Doing Business ranking that assesses the ease of doing business in particular countries. It shows good progress from 2018 when the country ranked 21st, indicating significant positive changes in business regulations. Logistically, starting a restaurant business in the UAE might not be as challenging as it used to be, but getting established surely is. The most attractive metropolitan areas of the UAE have sky-high rentals: opening a small, independent place might cost as much as AED 500,000 to AED 1.25 mn (“Top challenges faced by the restaurant industry in UAE And how to overcome them”, 2018).
- Bargaining power of buyers – high. Female customers, be it locals or tourists, are spoiled for choice. As the restaurants-to-customers ratio grows, they raise their expectations and will not settle for subpar service. Switching costs are quite low: in metropolitan areas, it takes a quick Internet search to find another decent place. Besides, Emirati women are experienced shoppers: according to the data provided by Societe Generale (2020), females make up to 80% of purchasing decisions in the country.
- Bargaining power of suppliers – medium. Due to the country’s climate, the Emirates’ agricultural capacity is not high enough. This means that if supplied locally, the food industry does not have a wide range of options to choose from. Alternatively, those companies that choose to supply their business with overseas production need to figure out logistics and maintain good relationships with partners. This is especially true for restaurants such as At.mosphere Burj Khalifa that are known for their exotic dishes.
- The threat of substitutes – medium. On the one hand, female customers have a wide range of options when it comes to the restaurant sector. On the other hand, there are not so many places that host ladies-only events, which makes At.mosphere Burj Khalifa stand out. Besides, its location on top of the world’s tallest building makes it one of a kind. Visiting At.mosphere is not only consuming the food: it is an experience that engages all senses.
- Industry rivalry – high. With almost twelve thousand cafes and restaurants, the restaurant industry in the UAE is among the largest and most competitive economic sectors. Statistically, per each million of UAE residents, there work up to 3,000 food places. The growing diversity of new restaurants alongside with low entry barriers and conducive business environment has ramped up the industry rivalry in the country. The food sector environment is shaped by the Emirates’ shifting demographics, flourishing tourism as well as the country’s unique location in the heart of the Middle East.
It should also be noted that luxury brands are popular with Emiratis. As reported by Societe Generale (2020), Dubai alone accounts for one-third of the Middle East’s entire luxury market. UAE residents spend as many as 30% of their monthly salaries on luxury goods and services. It means that the UAE is a market conducive to selling high-end products and experiences, which increases the competition between its players.
POP and POD of At.mosphere Burj Khalifa
POP and POD stand for points of parity and points of difference respectively. These concepts are essentially opposite: POP refers to the similarities between the analyzed brand and its contenders whereas POD refers to the differences. In the case of At.mosphere Burj Khalifa, the aspects of product offerings that are relatively similar to what competitors have to offer are the luxurious ambiance and fusion cuisine.
Dubai is known for its hospitality, high-end hotels, and upscale restaurants. At.mosphere is far from being an exception: it is a lushly furnished venue with a refined design that is in line with the trends dominating the UAE restaurant sector. Though highly appraised by food critics, its cuisine is not exactly unique. At the moment, it is a fusion of the world’s culinary traditions, which is understandable. The restaurant must be generating a considerable part of its revenue from tourists, which is why the cuisine is international to appease the most diverse tastes.
What makes At.mosphere Burj Khalifa unique is its location on top of the world’s tallest building. The restaurant benefits largely from the popularity of the building itself: today, Burj Khalifa can be found on any list of things to do in Dubai or the UAE. Being the highest restaurant in the world turns dining at At.mosphere into an unforgettable experience. For an extra payment, guests can take up coveted seats at the next level, even higher from the ground. The reviews on Google Maps and Trip Advisor are full of excitement: users refer to their experience as one of a kind. Some admit that they cannot find words to describe the beauty and the feeling of the place.
Perceptual Map: At.mosphere’s Market Positioning
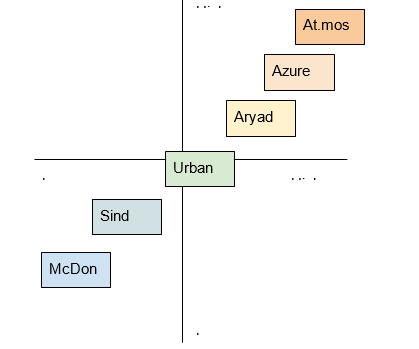
Perceptual maps are a valuable tool for defining a market positioning strategy. As seen from Image 1, perceptual maps have two axes: quality (X-axis) and price (Y-axis). Based on this distinction, the market is broken down into four positions – high price-high quality, low price-high quality, low-price-low quality, and high price-low quality. The second and the fourth options are rather exceptional: overall, in the restaurant industry quality seems to be proportional to price. Atmosphere is in the top right corner of the perceptual map: it is an extremely expensive place whose prices, however, are justified by high-quality gastronomy and unforgettable ambiance (Image 1). Eating at the top of Burj Khalifa cannot and should not be an ordinary experience, which is why At.mosphere rightfully markets itself as a luxury venue.
Azure Beach, Aryad Cafe, and Urban Bar & Kitchen are middle-range restaurants that still offer great food and service. Azure Beach stands out and, hence, is put higher on the trendline due to its location at a resort which gives the place an extra glamour and chic. The lower left square contains two low-price low-quality restaurants with ambiguous reputation and mixed reviews. Sind Punjab Restaurant does not capitalize on providing its customers with top service. Instead, it markets itself as a place where one can have a quick snack without spending too much money. McDonalds does not need an introduction: barely anyone associates the world famous fast food chain with anything glamorous. Its positioning is straightforward: calorie-rich food that is far from being healthy at low prices.
Conclusion and Recommendation
At.mosphere Burj Khalifa is one of the most successful projects by Emaar Hospitality Group, a subsidiary of the UAE largest real-estate developer. Located on top of the world’s tallest building, At.mosphere positions itself as a high-end luxury venue that offers an unforgettable ambiance and top-notch service. The high prices are balanced by the high quality of the food and the uniqueness of the experience of dining at the highest restaurant in the world. In the nearest future, At.mosphere might want to tap further into the market segment consisting of wealthy women seeking relaxation in female companies. By doing that, Atmosphere will further differentiate itself from its contenders and create a safe and friendly place for a promising market segment.
References
- Chernev, A. (2018). Strategic marketing management. Cerebellum Press.
- Societe Generale. (2020). United Arab Emirates: The market.
- Top challenges faced by the restaurant industry in UAE and how to overcome them. (2018). Web.
- Venter, P., Wright, A., & Dibb, S. (2015). Performing market segmentation: a performative perspective. Journal of Marketing Management, 31(1-2), 62-83.

