Abstract
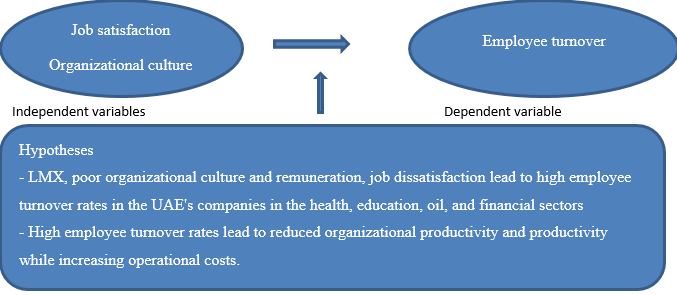
Employee turnover is a global challenge affecting all business set-ups, whether multinationals or small and medium enterprises. The objective of this study is to investigate the causes and impacts of high employee turnover rates in different business sectors in the UAE. Organizational culture and job satisfaction will be investigated as the causes of employee turnover, and thus they will be the independent variables.
On the other hand, the turnover rate will be used as the dependent variable. A quantitative research approach will be used, and data will be collected using interviews and questionnaires. 160 participants will be recruited for the study with 120 employees and 40 managers drawn from different companies based in Dubai in the health, education, financial, and oil sectors. Different research questions and two hypotheses based on the topic of staff turnover will be developed for the study. The importance of this study is to provide organizations with evidence-based data and results that can be used to plan strategically on employee retention methods to avoid high turnover rates.
Introduction
Employee turnover is one of the major challenges that contemporary organizations face, as it affects performance negatively. In the United Arab Emirates (UAE), cases of employee turnover have been increasing in the recent past. Therefore, this research paper will be used to explore the causes and impacts of employee turnover rates in different firms in the UAE. The findings of this study are important as they would shed light on the nature of this problem, and thus human resources management (HRM) teams can use this information to reduce the number of employee turnover rates and improve organizational performance.
Currently, the UAE depends mostly on expatriate workers, and thus the recruitment process and training are costly and time-consuming. Consequently, companies cannot afford to lose employees due to human resources management issues that can be solved through research. The major causes of high employee turnover rates in organizations include job satisfaction, remuneration packages, poor career prospects, the management-employee relationship, leadership style, and organizational culture.
Therefore, the UAE is currently experiencing high staff turnover rates, and this research will investigate the causes and impacts of such phenomenon on organizations across the region. Understanding the causes of this problem and its impacts on organizations will allow human resources to reflect on their employee retention strategies to evaluate whether they are solving the issue or not. The quantitative research methodology will be used to collect data through questionnaires and interviews. The dependent variable is staff turnover, while the independent variables are job satisfaction and organizational culture.
Literature Review
According to James and Mathew (2012), staff turnover is a global human resources problem that needs to be addressed as a way of improving organizational performance. For instance, between July 2010 and June 2011, the Malaysian retail sector experienced employee turnover rates of 18 percent (Nair, Salleh, & Nair, 2014). Employee turnover is characterized by the quitting of employees from a firm due to diverse reasons.
Labor is one of the important factors of production, and thus whenever employees quit, productivity is affected, and profitability declines. According to human capital theory, employees are critical assets that play a major role in the organizational success (Zulu, Chetty, & Karodia, 2017). Organizational culture determines the nature of the work environment that employees enjoy in the course of executing their duties.
In a study to understand the causes and impacts of staff turnover on non-profit organizations in South Africa, Zulu et al. (2017) found out lack of training and career development opportunities contributed significantly to this problem. Employees will stay in companies that offer career advancement opportunities, but they will leave if the same is lacking. James and Mathew (2012) add that workplace structures, such as autonomy, social support, job stress, and pay scale, determine the rate of employee turnover in an organization.
In another study by Liu, Cai, Li, Shi, and Fang (2013), leadership style, which is part of organizational culture, determines employee turnover. The leader-member exchange (LMX) theory, which explores the relationship between leaders and employees, is embedded in the leadership style practiced in an organization, and it contributes significantly to turnover intentions. Abu Elanain (2014) argues that employees are likely to stay in an organization of their relationship with the management and leadership is healthy. However, they are likely to leave in case of conflict between the two. Ultimately, organizational culture is directly linked to job satisfaction, which is another significant cause of high staff turnover rates.
Job satisfaction is a function of organizational culture aspects, such as LMX, remuneration terms, career advancement opportunities, organizational commitment, remuneration, job stress, and leadership style, among other factors, which contribute to employee turnover (James & Mathew, 2012; Zulu et al., 2017; Liu et al., 2013; Abu Elanain, 2014). The issue of high staff turnover rates has significant negative effects on the performance of an organization.
According to Zulu et al. (2017), employee turnover leads to decreased productivity and high operational costs, thus affecting the profitability and sustainability of organizations. The productivity of any company or institution depends on the available human capital. As such, after workers leave an organization, the capacity of production declines. Besides, the labor gaps created by such employees have to be filled by hiring replacements, which increases operational costs.
In the process, the profitability and sustainability of the involved organizations are affected negatively. The LMX theoretical framework will be used in this research to explore the relationship between supervisors and subordinates as part of an organizational culture that determines job satisfaction, which ultimately contributes to employee turnover.
The rationale of the Study and Hypotheses
The importance of conducting this research is twofold. First, the study will create a deep understanding of the causes of employee turnover in different companies in the UAE. In a bid to address a problem, the causes should be understood thoroughly to allow the creation of problem-specific intervention measures. As such, the intervention measures will be effective, and the probability of achieving positive results increases significantly.
Consequently, this proposed study is important to firms in the UAE, as they will use evidence-based strategies when addressing the problem of high employee turnover rates. Second, the study will fill research gaps on the topic of staff turnover in the region. Current studies on this subject focus on one sector, such as the oil industry or the financial industry. Therefore, the available literature lacks comprehensive cross-sectoral and comparative information concerning employee turnover in the UAE. This study will collect data from four sectors, including the health, oil, banking, and education sectors.
Therefore, the information gathered will be used to establish whether the causes of this problem are shared across industries, or they are specific to some sectors. This information will be important for HR managers in different sectors when tailoring employee-retention strategies as a way of addressing the problem of staff turnover.
The study will attempt to answer several questions based on organizational culture, job satisfaction, and the impacts of employee turnover. The questions include –
-
- What are the causes of employee turnover in the health, education, oil, and financial sectors in the UAE?
- What is the relationship between LMX and staff turnover intention?
- What is the role of remuneration in employee turnover?
- What are the impacts of employee turnover on organizational performance, productivity, profitability, and sustainability?
Research Methodology
- Participants – participants for this study will fall into two categories. The first one will be 120 workers drawn from different companies operating in Dubai in the health, oil, education, and financial sector. Each sector will provide 30 participants of different ages and genders, both locals and expatriates. The second category will be 40 managers drawn from the mentioned sectors – 10 from each sector.
- Study Design – Explanatory study methodology will be used. Data will be collected through questionnaires and interviews based on the availability and preference of the participants. This study design was chosen because it is easy to measure data and present results clearly using objective data. One of the limitations of this study design, and especially the data collection part of it, is that participants can give biased information.
- Measures – Five-point Likert-type scales (ranging from 1 to 5) will be used to measure items related to organizational cultures, such as opportunities for career advancement, decision-making policy, organizational justice and fairness, leadership style, and turnover intentions. The same scales will be used to measure items related to job satisfaction, such as LMX, role ambiguity, role conflict, remunerations, and reward systems.
- Procedure – The first step will involve sending letters of request to the participants asking for their permission to participate in the study. Those that give informed consent will indicate how they would prefer to provide information – through either interviews or questionnaires. A convenient date for the interviews will be scheduled. Questionnaires will be sent through email.
- Statistics – the hypotheses will be tested using SPSS for data analysis. SPSS uses measures of central tendencies, such as mean and standard deviation. Correlation and regression analysis will also be used in the process of examining the strength of the relationship between different variables.
Conclusion
The available literature shows that employee turnover rates are high in different business sectors in the UAE. Therefore, this study will seek to understand the causes and impacts of employee turnover on four business industries in the UAE, including education, health, oil, and financial sectors. Some of the major causes of high turnover rates among workers are poor remuneration and organizational culture, which lead to job dissatisfaction. Ultimately, employees quit employment, hence the high turnover rates. Participants will be drawn from the mentioned sectors and questionnaires, and interviews will be used as data collection methods. The data will be analyzed using SPSS and regressive analysis to test the stated hypotheses.
References
Abu Elanain, H. M. (2014). Leader-member exchange and intent to turnover: Testing a mediated-effects model in a high turnover work environment. Management Research Review, 37(2), 110-129.
James, L., & Mathew, L. (2012). Employee retention strategies: IT industry. SCMS Journal of Indian Management, 9(3), 79-87.
Liu, Z., Cai, Z., Li, J., Shi, S., & Fang, Y. (2013). Leadership style and employee turnover intentions: A social identity perspective. Career Development International, 18(3), 305-324.
Nair, M. S., Salleh, R., & Nair, S. K. (2014). Employee turnover in the Malaysian retail industry. Global Business and Management Research, 6(4), 283-289.
Zulu, K., Chetty, N., & Karodia, A. M. (2017). The impact of staff turnover on organizational performance: A case of the three non-profit organizations in Verulam (Republic of South Africa). Arabian Journal of Business and Management Review (Oman Chapter), 6(11), 1-31.

