Introduction
Ford Motor Company is one of the leading vehicle producers globally, with large markets and several strategies for their business growth. They are one of the leads in profitability and market ventures overseas. To achieve all these, the company uses several strategies, which are responsible for its current position in the market. These include corporate-level, business-level, and functional-level strategies, all of which are important and effective for the company’s business. These companies’ success mostly depends on how the management chooses to use these strategies. The focus remains on the diverse strategy used by the company concerning its current success and entry into new markets.
Strength and Weakness Matrix in Ford’s Internal environment
Figure 1. Ford’s SWOT Analysis
Corporate-level Strategy
Corporate-level strategies are primarily used by companies with control over their supply chain and sales. This means they are responsible for making most decisions and planning how the market will stand for maximum profitability. For this reason, these strategies are formed by the top management, who then translate the same to medium and low-level managers. This means that the company runs under a single rule from the top in the power hierarchy.
The company has total control of its markets, hence responsible for valuations, which its suppliers use in the sales. Making such decisions is difficult for the company, as some supply chains are far from the focal company, so they have to dig a lot to make the best choices. Its resources also have a role in corporate-level strategies, as they make decisions depending on what it can control using its finances. The organization ensures that they align with their company’s short and long-term goals and objectives, which the company aims to achieve over a specific period.
Ford Motor Company possesses several strengths, which play critical roles in ensuring the whole organization is successful in all its activities. Firstly, the company has a vast global brand image, which works to its advantage in many cases. It is a well-known motor company whose brand is in most countries globally. Some customers focus on brands, ensuring that they are well known. Ford motors have already established a big name for itself in most markets overseas and in the United States (Donadone, 2019). The organization has a simple logo engraved with the name ‘FORD’. Good production often leads to increased sales, especially with a huge brand name, which is the case with Ford.
Another strength of the firm is the solid global supply chain that they have established. With minimal diversification, the company has positively focused on the global supply and increased the quality of produced cars. Over the years, the company has put a lot of intensity on market penetration, making it their long-term goal. This means expanding their global supply chain by venturing into new markets and dominating their already established markets. This strategy’s success depends on the fact that they do not have a lot on their hands (Anbinder, 2018). The firm takes advantage of its strong brand, which means it should have the ability to give more products to its markets without struggle. Having a competitive advantage is very crucial in the current global vehicle market.
Minimal diversification is another strategy that allows the company to focus on market penetration and increase productivity, one of its main strengths. Despite venturing into some markets, like the sale of luxury cars, to keep up with the global competition, that is not Ford’s focus in their sales (Popkin, 2019). With increased sales in its market, the company is likely to increase its productivity and ensure its products are of the highest quality. This is a crucial strategy that the company may use to succeed in its activities.
Despite the corporate strategies being merit to the company, they also have several weaknesses, which hinder the achievement of company goals over time. The company has experienced a few recalls over the past years. Their vehicles had a problem with side doors in 2016, which saw the recall of around 830 thousand cars. A similar case occurred in 2015, where the airbags were not functional, meaning they had to recall their vehicles for repair. In many cases, such issues see companies lose more customers as the brand name is tarnished.
Ford is well known for its dependence on the production of trucks and SUVs. More than half of their output is trucks. Despite the high quality of these trucks, the company is also required to be more flexible, as they focus on the market trends. With emerging global warming cases, most people opt to drive smaller vehicles with minimal fuel consumption, hence. protecting the environment. The company plans to increase SUVs rather than smaller vehicles (Popkin, 2019). This has seen their total sales reduce by far, as other companies with variety continue to gain a competitive advantage over Ford.
Diversification should also be in marketing, as the country should consider new markets. Ford chooses to increase sales to its already existing customers in many cases. Other companies have focused on producing vehicles with low consumption to meet the needs of their customers. On the other hand, other companies have focused on emerging markets for maximum sales. These organizations end up having a substantial competitive advantage, seeing Ford drown in their sales.
IFE Matrix
The IFE Matrix is developed by focusing on key internal factors that affect the company both positively and negatively. These include strengths and weaknesses, preceded by the weight the carries on the company. These include brand recognition, which positively affects the company, being part of its strengths. On the other hand, they have weaknesses like downsizing, which weigh down the company. The IFE matrix basically evaluates how strengths and weaknesses affect Ford motors. In many cases, they have several implications for the company, which affect diverse sectors. These include factors like lack of innovation in manufacturing. This gives other companies a competitive advantage over Ford, which greatly affects their sales. The same case applies to positive factors like the affordability of their vehicles. They translate to increased sales, hence the prosperity of the brand.
Figure 2. IFE Matrix
The company offers autos and commercial vehicles, whereas the Lincoln brand sells premium cars. It has also manufactured heavy vehicles, tractors, and automotive components in the past. Ford holds modest shares in Mazda and Aston Martin, both of which are based in the United Kingdom. Based on 2010 car sales, Ford is the second-largest manufacturer in the United States and the fifth-largest in the world. Ford was Europe’s fifth biggest carmaker at the end of 2010. Based on worldwide sales of $118.3 billion in 2009, Ford is the eighth-ranked overall American-based firm in the 2010 Fortune 500 ranking. Ford manufactured 5.532 million cars in 2008, employing roughly 213,000 people across 90 sites and locations across the globe.
Grand Strategy Matrix
The grand strategy matrix was developed through comparison with other companies. It shows where Ford stands in the market. As shown in the matrix, they have a low competitive advantage compared to other companies in the global market. At the same time, they experience rapid market growth, hence their position in the grand strategy matrix. These have several strategic inferences in corporate and business-level units. In the case of competitive advantage, the corporate unit is involved as it affects the whole company. Other vehicle manufacturers are doing extra in their headquarters to ensure they remain on top while Ford is lagging behind. It means that Ford is nor putting its focus on outdoing other companies in the market. Business level units are also affected as the market growth is mostly present in their domain. They experience most of these issues, including the lack of competitive advantage, as they work on distributions and other branches.
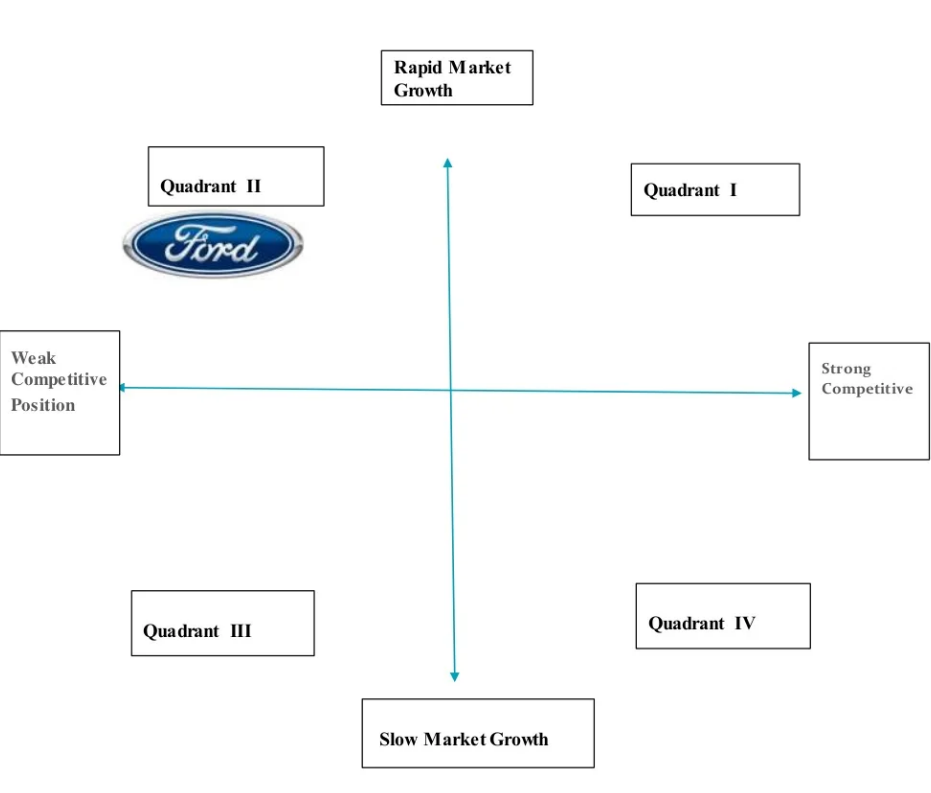
Ford is in the second quadrant of the grand strategy matrix as its experiencing large losses and its competitive position has also been harmed by new entrants in the automotive business thus, it has a poor competitive position, and the market growth is quick. A rise in customer expectations has boosted competition in part because it has created more opportunity for innovation. However, owing to the continual rise in costs of raw materials and natural gas and the change in currency rates, it has been challenging for businesses to introduce new models regularly.
However, they remain tight with emerging market trends giving a different perspective. Most customers opt for low-fuel-consumption vehicles for several reasons. These include the reduction of environmental pollution and cars, which are cost-effective. In many situations, they find themselves in a weak competitive position in the current markets, which makes it difficult (Thai-Tang, 2019). However, they have joint ventures with other companies like Mazda and the Lincoln brand. All these partnerships aim to increase the total sales and ensure that competition remains stiff. They give them the best position to compete with global companies, which have also established a stable ground for their success in overseas markets.
Business-level Strategies
Ford’s product line mainly includes its trucks, which they are more famous for. The company has a global supply chain for most of its trucks. Ford motors work with automotive and mobility, which they put as their primary focus in production. Ford motors also have other vehicles apart from trucks, which have helped them build a name. Moreover, the company has also partnered with the Lincoln brand to produce a variety of luxury cars to keep up with the competition. Ford’s product line consists of a variety of automobiles, which have created the brand name they possess. Multinational corporations have a robust supply chain for their products and long-term market dominance (Di Minin, Ferrigno, & Zordan, 2019). They aim to increase their total production over the years to bring them a competitive advantage in their markets.
Through producing high-quality products, they are likely to earn more from the loyalty of their customers. Statistics show that Ford’s initial target market was the millennials, young people in the technology field (Diekfuss et al., 2021). Being the most energetic, they have a strong network connection, hence efficient customers for the company’s products (Sanci et al., 2021). They have also produced some vehicles like the Ford Fiesta with a focus on young people and women as their market. This vehicle is affordable for most people that age, hence having them as potential customers (Lin, Bruning, & Swarna, 2018). That is why Ford Motor’s products have high-power vehicles, which will give individuals longevity in terms of service.
Ford uses market penetration as their main business-level strategy. They aim to increase customer satisfaction by adding value to their products. This ensures that the company promotes dominance in its markets and new markets(Seifzadeh & Rowe, 2019). However, sales replicate the high quality of products that the company produces. This means that they do not come at the lowest cost in the market (Link, 2018). Production at a lower price gives the company an advantage as they can sell them at a relatively low cost, attracting more customers to their products. In some cases, this cost leadership strategy may be effective as other companies find it difficult to copy.
Functional Level Strategies
Ford has a dual matrix structure with both centralized and decentralized forms. They have single corporate management in charge of all their activities (Ali, bin Ahmad, & Johari, 2017). Simultaneously, they also have decentralized distribution strategies, where the delegate parties are in order. Ford has a unique organizational culture, where they allow shared opinions and beliefs with their workers (Warrick, 2017). The company suggests that all employees have the potential to pursue their visions, creating an employee-based culture. Ford Motors believes that every individual has the freedom to pursue their will for the good of the whole society (Morgan, & Liker, 2020). In the marketing production sector, they ensure that they set prices that replicate the current market trends. It remains a unique strategy, giving them a competitive advantage over other organizations, hence their success in the fields. Its operations revolve around automobile production in its specific branches globally. They have centralized management from the home company, which becomes decentralized in other places to support the manufacturing operations. They have a finance branch, Ford Motor Credit Company LLC, responsible for their accounts (do Carmo et al., 2019). Their financial institution has also made it easier for dealers and customers who benefit from credits from the company. It is also responsible for the finance of company activities. Being a transparent company, they have presented most of their research and development results on the website for public viewing. Most of the information about the company, including finances and its variety of products, can be found on its sites.
Ford ensures that the functional level strategies align with its vision and mission in several ways. In marketing production, they ensure that the prices meet their customer’s needs. This brings immense customer satisfaction, which is one of the company’s missions. With the affordability of their products, they can meet their mission and vision of promoting mobility globally. Their organizational culture also aligns with their mission, as they focus on fostering a good work environment for the good of society. This means ensuring people can travel affordably across the world.
Financial Analysis
Total Debt Ratio
The debt-to-asset ratio of a firm is calculated by multiplying total debt by total assets. A debt-to-asset ratio of more than one, or one hundred percent, indicates that a business has more debt than assets, while a debt-to-asset ratio of less than one hundred percent indicates that a firm has a surplus of assets over liabilities. Total Debt Ratio = 1 – (1 / Equity Multiplier). Since the firm has an equity multiplier of 1.5,
= 1 – (1 / 5.3)
= 0.8113
Therefore, the company has Total Debt ratio of 0.81
Quick Ratio
is the measurement of the Liquidity of a company. In other words, we can say it is a measurement that tells how well a company can meet its short-term liabilities. Using the quick ratio instead of the current ratio is regarded a more cautious method of determining the company’s ability to pay its debts.
Quick Ratio = (Current Asset-Inventory) / Current Liability
It is also called the acid-test ratio.
($116744 million – $10808 million) / $97192 million
Standard Quick Ratio is 1:1
Quick Ratio of Ford is 1.09( As of December 2020)
Asset turnover ratio
In order to determine how well a company’s assets create income or sales, asset turnover ratios are computed. The monetary quantity of sales (revenues) is compared to the total number of assets, and an annualized percentage is computed. Net sales or revenue divided by the average value of all assets may be used to determine the asset turnover ratio (ATR). Asset turnover ratio is calculated by the following formula:
Asset turnover ratio = Net Sales / Total assets
= 17.9 billion USD / 257 billion USD
= 0.07 Times
Return on Assets
It is possible to measure a company’s productivity by looking at its return on total assets ratio, which demonstrates the extent to which its investments generate value. When you take the firm’s earnings after taxes (EAT) and multiply it by the total value of its assets, you get the net income for the company. The return of assets Ratio for Ford Motors is calculated as follows:
Return on Assets Ratio = Net Income ÷ Average Total Assets
= 19.94 billion ÷ $258537 million
= 7.71%
The above ratios give the financial position of the company. Investors use the ratios to make crucial decisions while buying and investing in the firm’s shares. Businesses may evaluate their own performance and compare it to that of other firms in their field using the four analyzed ratios. Using financial ratios, it is possible to assess the relationship between two or more financial statements. They are the most powerful instruments for comparing long-term results.
Conclusion
Ford has several strategies that it uses in its daily company performance. Most of them are advantageous to them as they aim at increasing their sales and total company profitability. Its strengths include a famous brand name, which essentially boosts its sales globally. This brings recognition from their customers, most loyal to the brand, hence increasing profitability. However, they also have some disadvantages like low-quality products, which have caused several recalls over the years. However, the external environment offers stiff competition; hence, they should gain a competitive advantage over other organizations.
References
Ali, K. S., bin Ahmad, F., & Johari, H. (2017). The mediating effect of job engagement on the relationship between organizational structure and organizational performance: a theoretical model. International Journal of Economics, Commerce and Management, 5(3).
Anbinder, J. (2018). Selling the World: Public Relations and the Global Expansion of General Motors, 1922–1940. Business History Review, 92(3), 483-507.
Diekfuss, J. A., Grooms, D. R., Hogg, J. A., Singh, H., Slutsky-Ganesh, A. B., Bonnette, S.,… & Myer, G. D. (2021). Targeted application of motor learning theory to leverage youth neuroplasticity for enhanced injury-resistance and exercise performance: OPTIMAL PREP. Journal of Science in Sport and Exercise, 3(1), 17-36.
Di Minin, A., Ferrigno, G., & Zordan, A. (2019, July). Technological Discontinuities and Dominant Designs: The Case of Ford, 1896-1914. In Academy of Management Proceedings (Vol. 2019, No. 1, p. 14659). Briarcliff Manor, NY 10510: Academy of Management.
do Carmo, M., Neto, M. S., & Donadone, J. C. (2019). Financialization in the automotive industry: Shareholders, managers, and salaries. Journal of Economic Issues, 53(3), 841-862.
Lin, H. C., Bruning, P. F., & Swarna, H. (2018). Using online opinion leaders to promote the hedonic and utilitarian value of products and services. Business Horizons, 61(3), 431-442.
Link, S. (2018). The Charismatic Corporation: Finance, Administration, and Shop Floor Management under Henry Ford. Business History Review, 92(1), 85-115.
Morgan, J. M., & Liker, J. K. (2020). The Toyota product development system: integrating people, processes, and technology. Productivity Press.
Popkin, C. A., Bayomy, A. F., & Ahmad, C. S. (2019). Early sport specialization. JAAOS-Journal of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, 27(22), e995-e1000.
Sanci, E., Daskin, M. S., Hong, Y. C., Roesch, S., & Zhang, D. (2021). Mitigation strategies against supply disruption risk: a case study at the Ford Motor Company. International Journal of Production Research, 1-21.
Seifzadeh, P., & Rowe, W. G. (2019). The role of corporate controls and business-level strategy in business unit performance. Journal of Strategy and Management.
Warrick, D. D. (2017). What leaders need to know about organizational culture. Business Horizons, 60(3), 395-404.
