Differences between Data and Information
Data refers to raw facts or observations such as values or measurements. Data is considered to have little or no value until it has been processed and transformed into information. Examples of data include a series of symbols not obtained randomly, numbers and words, a series of ideas obtained by observation or research recorded and kept for future reference. Similarly, a collection of non-random facts and even records of an event or a fact can constitute data. Information on the other hand is data that has been processed so that it is meaningful and can be interpreted. Examples of information include: data that has been processed for a purpose, interpreted and understood by the recipient. Due to that data undergoes a transformation process which has various constrains such as labor, cost and transformation skills before it becomes information. Data is stored in databases where it is obtained when needed through data mining. Information involves transforming data using a defined process. It also involves placing data in some form of meaningful context.
Information is produced in response to an information need and therefore it serves a specific purpose. It helps reduce uncertainty thereby improving decision behavior of managers. The kind of decisions that managers make and how they affect their organizations depend largely on the information they have at hand. As a result, managing information and knowledge is very important to organizations. Transformation of data to information of high quality is therefore required for proper decision making of any organization. Organizations get data and information from various sources. Sources of management data is either from primary or secondary sources and falls into three categories that include existing data and information, people, pictorial records and observations. Existing data can be obtained from newsletters, academic research reports, theses, statistical reports, technical reports, market research reports and online sources like specific government sites and specific research journals that are accessible through various search engines.
Such data and information is reliable but may be expensive because it might involve the use of online data and information collection tools that are costly. People such as key informants, focus groups, competitors, sponsors, policy makers, volunteers and consumers on the other hand make good sources of raw data. For instance, a company may decide to collect data about consumers’ perception of its products by conducting surveys or use of questionnaires that are issued to the specific willing people who will participate as data providers. Such data can help the given company in production of commodities that meet consumer needs. However, some groups of people may be unwilling to take part in data provision while others may give wrong information and this may lead to wrong decision making. Pictorial records and observation data sources include videos, film documentaries, speeches, photos, minutes of meetings and recorded presentations of various events and programs.
Various organizations collect and select data in a way that will allow only the relevant data to be collected to reduce chances of incurring expenses in the collection process. There is no method of data collection and selection that is right or wrong because the selection criteria depends on several factors that ensure quality and integrity of the collected data for better decision making. One of them is the purpose of the evaluation where an organization will choose a given method for collecting data depending on the kind of questions it needs to answer. Target audience is another factor that needs to be considered to make sure that collected data is of high quality. The method chosen should be able to gather as much relevant data and information as possible from the targeted audience. An organization will choose a method of data selection and collection which is cheap and feasible because data collection is expensive, time consuming and laborious.
UK Legislation on Data and Information
In the United Kingdom, data collection, handling, use, Data Protection Act of 1998 (DPA) governs sharing and storage. The act states that data controller in any organization should comply with the DPA and breaching of DPA terms and conditions can lead to prosecution of data controller of any organization. Data and information of any organization is under the hands of the data controller and in case of any loss, he/she will be held accountable. On collection of data, the act advocates that data should be collected when there is need to collect it. Collection of data for personal reasons or unauthorized collection of data about specific people is strictly forbidden. DPA states that data collected should be audited often so that irrelevant data can be dismissed. This ensures that there is unnecessary junk data retained in many organizations and only the relevant data is retained. Actually, DPA clearly states that all the data that is not needed should be deleted.
UK Data Protection Act states that personal data should be kept secure and should not be available to the public. It is only specific and entrusted people that should have access to personal data or data from various companies. On the question of sharing data, adequate level of protection should be maintained during data sharing to make sure that there is no leakage of any information and data locally or internationally. The act allows people to have specific rights on their collected data such as the ability to change the collected data if it is wrong, the right to stop personal data for marketing purposes and the right to access the collected data besides other rights.
UK DPA act ensures that organizations take utmost care of any collected data they have. This is because collection of data involves labor, time, collection ability and it is expensive. If the collected data falls in the wrong hands, expenses might be incurred trying to recover such data and problems might arise and this may be solved in the court, which is time consuming and unnecessary. As a result, most organizations today have employed efficient data management systems that are governed by database controllers. Indeed every organization today has an IT expert responsible for data management. Database management systems (DMS) provide database security and allow efficient data mining. These systems also ensure effective data transformation that results in high quality information for decision-making.
Scenario application of data and information protection is in the Barclays Banking group that has been involved in collection of various customer data and information through surveys. All Acts regarding protection of confidential information of its clients have protected the Barclays banking group. In addition, it has all patents to any collected findings that relate to its activities including trends in the banking industry.
Decision Making Models
Different decision-making models are used by various organizations in decision-making. The choice of the decision model to be used depends on the size of the organization, political interference, shareholders, type of information available, timing of decision-making and the expected decision implementation outcome. Some of the decision-making models employed by organizations today include rational-economic model, administrative model, implicit favorite model and political model.
The rational-economic model focuses mostly on how decisions should be made. The decision maker under this model is assumed rational and impartial. Rational-economic model gives the decision maker full mandate to make decision on behalf of the organization after considering various choices since he/she has all the capabilities and resources.
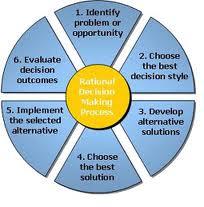
Generally, the decision-making process follows a series of steps starting with identification of the specific problem, followed by evaluation of various alternatives from which the best option is selected and then implementation is done at last. This model is used when a portion of shareholders has a larger investment than the other whole group in a given organization. It is also used when a specific expertise is needed in decision making hence some people are given the mandate to make decisions for the given company. Rational-economic model is advantageous in that decisions are made within the shortest time possible since the overall decision-making process is in the hands one person.
Administrative decision-making model is a model that is involved with how decisions are made. It involves simplification of the decision-making process by focusing on solving those problems that the organization can solve in its current state. In this model, decision makers work within boundaries and are not completely rational like in rational-economic model. As a result, decision makers only identify few alternatives about solving a particular problem of which most of them have been proved to be working there before. It is from such limited alternatives that the best choice is chosen and then later implemented.
Lastly, we have the political decision making model in which the decision maker is neither rational nor unbiased. Members of any organization always have different views about how to solve a particular issue and as a result, members involved in the decision-making process negotiate and agree on one issue. It involves bargaining and debating on the best choice. This model is unbiased and the alternative selected depends on the power and favors of the members involved. Powerful people support a particular alternative then the rest of the group backs them up. Individuals involved in decision-making and implementation may not actually be there in the bargaining process.
A good scenario for application of the decision-making is in the Barclays Bank where the administrative model has been implemented to make decisions. In the bank, the management of the banking group make decisions partially rationally and administrative. The model was chosen in the firm since it experiences situations when timing of decision is more critical than its outcome and hence a section of all the members used in decision-making is chosen to make decision within a given time period. However, the model has results to slow decision making since the decision makers do not have full mandate in the decision making process and a series of hierarchies and protocol have to be followed.
Bibliography
Data Protection Act, Changes to United Kingdom Legislation, 1998. Web.
Powell, T & S Steel, ‘Collection Evaluation of Data: An overview of sources and methods’, Program Development and Evaluation, 1996. Web.
Zhibin, W & X Jiuping, ‘A consistency and consensus based decision support model for group decision making with multiplicative preference relations’, Decision Support Systems, vol. 52, 2012, pp. 757–767.
Zins, C, ‘Conceptual Approaches for Defining Data, Information and Knowledge’, Journal of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, vol. 58, no. 4, 2007, pp. 479–493.
