Introduction
The car industry has both good times and bad; thus, there are booms and busts. The industry is fiercely competitive, making it difficult for new entrants and existing companies to succeed. McLaren faces many of the same entrance barriers as the rest of the mass-market automakers, but this does not mean it will negatively influence the McLaren Group’s ability to keep innovating. New entrants face significant upfront expenses, fierce rivalry, and promotion of their new businesses. Due to the difficulties faced by current and new businesses, the market is underutilized. McLaren has unquestionably surmounted the numerous market entry hurdles inherent in the mass automobile industry, evidenced by its dominance and excellent profits. Competition is a significant market entrance hurdle for the corporation, diligently identifying strategic groupings with comparable business structures and objectives in the automobile sector.
SWOT Analysis
The Group’s Progress in the Last Five Years
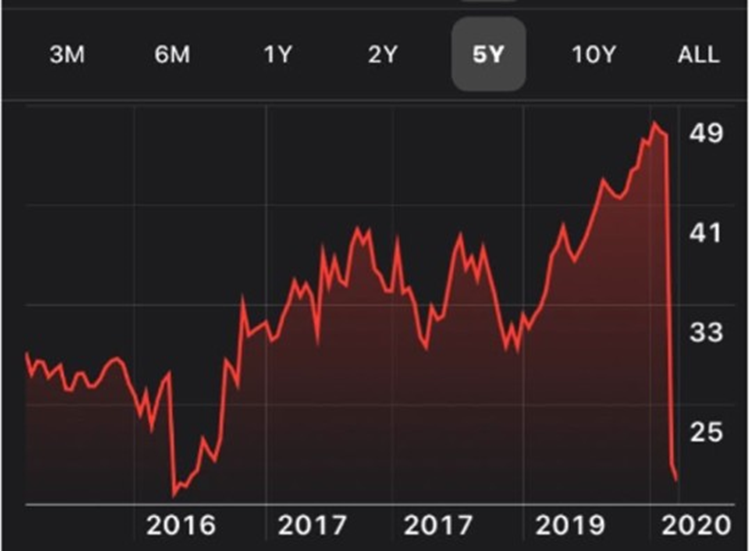
Since 2016, the stock of Formula 1 racing (McLaren is substantially involved in F1 racing) has increased significantly. The stock fell to its lowest level ever in 2020 due to the COVID-19 breakout, but it has since recovered and is anticipated to reach its peak in 2022 (Babu & Behl, 2020). A luxury brand, such as the McLaren Group, is particularly prone to such incidents, as they are not seen required (Culina, 2018). It is significantly impacted by people’s purchasing power, which is highly dependent on how well the economy performs and improves, making it risky when the economy’s position and condition are in doubt
Ansoff’s Matrix
The Ansoff matrix is used to forecast growth based on the prior variety of services offered by the business. This is accomplished by identifying specific product-market combinations to which growth strategies are then allocated. This may be summarized by evaluating why the business can expand and how it must develop (Loredana, 2017). In a two-dimensional matrix, these product-market pairings are placed against one another. One dimension is defined by established and new markets, while established and new goods define the other. This matrix generates four general product-market pairings and hence four distinct growth strategies.
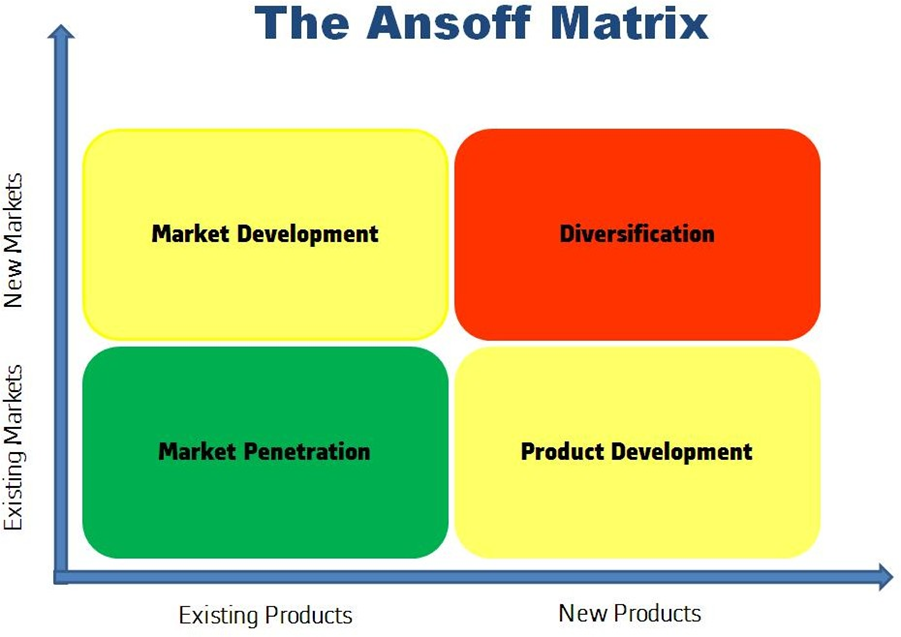
Market Penetration
In order to boost sales within the current customer base, this strategy calls for cutting expenses while also implementing a range of marketing and promotional strategies. It provides various price cuts and discounts, runs advertising campaigns regularly, and sells the product in current enticing packaging to achieve sales growth objectives as it retains the market (Rahman, 2016). With such a strategy, strong marketing is required in a highly competitive consumer market. The McLaren Group’s capability to distinguish its services while also achieving cost leadership is closely linked to market penetration as an effective strategy for rapid expansion. The mix of low-cost generic techniques and distinctiveness helps this aggressive expansion strategy succeed. The McLaren Group’s home market success depended heavily on its market penetration strategy during the initial expansion stage. Later, the company used its national standing to propel its expansion into new markets throughout the world.
Product Development
McLaren Group uses it in addition to other methods of growth. In order to appeal to the current customer base, this strategy calls for the creation of new products or the adjustment of existing product lines (Galpin, 2019). When a company’s current product line has little development potential in its existing market, such as McLaren Group, it takes this method. McLaren Group was forced to launch new products in several markets due to growing competition in recent years. It consumes considerably less time, money, and effort to sell new products to existing customers, whose brand awareness and customer loyalty have already been built up. To increase R&D investment in new product development and innovation, the company must follow this aggressive growth strategy. By utilizing a differentiated generic growth approach, the McLaren Group helps with product creation. It increases an organization’s potential to produce new or exclusive items to expand in current consumer markets.
Market Development
Ansoff’s third strategy for rapid expansion is to build the market. The major goal of this approach is to find and get into new markets. McLaren Group’s market development strategy goes hand in hand with its market penetration and product development initiatives. By using this strategy, the organization has expanded its presence to over Competitor countries across the world. In order to develop McLaren Group as a global brand, the company needed to be successful in expanding into innovative customer markets. Low prices, company identification, and flavor are the key motives for the company’s worldwide prominence. McLaren’s excellent marketing and celebrity-endorsed promotional activities have helped the firm gain new customers and position itself as a market leader in various nations outside of these reasons. The McLaren Group’s strategic goal is to enhance the value chain in support of the growth of the distribution network by implementing this strategy. This aggressive expansion strategy can only be implemented if McLaren Group keeps costs under control and maintains cost leadership positions. McLaren can invest more in new consumer markets because of the reduction in costs.
Diversification
The fourth Ansoff matrix strategy for rapid growth is diversification. This strategy calls for new goods to be introduced into existing markets in order to gain market share. Linked and disconnected diversity are two types of diversification. McLaren is able to provide a broader array of products because to a cost leadership generic growth strategy and the company’s ability to lower expenses. Because of the present architecture of the business, it is conceivable to study new product potential in emerging markets. Companies diversify by purchasing successful businesses after researching market trends and changing client expectations. Environmentalists pushed the corporation towards green business strategies and partnerships to counter revenue losses from decreasing sales, which resulted in increased investment in green business practices and partnerships. A business can achieve long-term growth goals despite turbulent markets provided the diversification development plan is strategically implemented successfully. Product diversification and portfolio management help companies hedge their risks by taking advantage of increasing trends in neighboring product categories to offset decreasing ones. This is critical.
Kotters 8 Steps
Step 1 – Create a Sense of Urgency
Educating employees on the need for and determination of change will help the management. As a result, management will garner support. The process of educating the staff member includes being candid and including an open discussion. This typically serves as a basis for convincing staff to make significant adjustments when necessary (Haas et al., 2020). The procedure is carried out by speaking and chatting about probable terrorization to obtain the necessary and effective responses. The relevant parties will need to debate and identify the looming crisis, potential emergencies, and possible possibilities. Several limitations and crises have hampered McLaren’s progress, but they have conjured the struggle and accomplished their aims. For example, McLaren has faced significant rivalry from other similar firms. Even though McLaren has undergone competition from other comparable organizations, the firm has acted prudently by establishing policies to limit competition. For instance, the company achieved success by reducing the price of its products and maximizing the use of available space.
Step 2 – Create a Guiding Coalition
To ensure organizational success, the company should frame a project team to adapt to the organizational changes being implemented. The team maintains control of any scuffles and encourages one another to work together and develop a constructive mindset. Due to the open eccentricity built into the firm, the staff may function high, allowing for staff conversion (Brock et al., 2019). To create a viable business, McLaren has assigned a team member to monitor the organization’s operations from afar. The information acquired by the team member contributes to the establishment of a successful environment since the team member can identify an organization’s vulnerability.
Step 3- Create a Vision for a Change
When it comes to cost and value, the McLaren Group takes a low-cost focus strategy and implements it by meeting the specific needs of a small market segment at the lowest possible cost, according to the company. While highlighting the flavor, size, and design of the product, the technique of concentrating on the product’s highest value is followed. Branding strategies, product design, and packaging are all constantly evolving at McLaren Group in order to meet the psychological expectations of consumers while also maximizing value for money. This is accomplished by putting a strong emphasis on the quality of the products that they manufacture.
Step 4 – Communicate the Vision
The fourth step of Kotter’s eighth phase is critical for generating support and acceptability among the employees. This, however, can only be accomplished via meaningful dialogue among staff members whenever management has the opportunity to take their sentiments, apprehensions, and worries seriously. This level of seriousness will instill a new vision in staff members, which will permeate the entire organization. Without a doubt, every move made by the McLaren group has been preceded by extensive consultation with the staff committee. Additionally, McLaren workers oversee and manage critical resources such as financial records and data to assist the firm in achieving both long and short-term goals established by the McLaren group.
Step 5- Obstacle Removal
Before recognizing change at all organizational levels, it is critical to remove and replace impediments that might destabilize its vision. Probably, stabilization must be accomplished by facilitating conversation with all staff members and making it apparent to those resisting the change. Following that will encourage staff identification of the vision, allowing staff members to benefit from their perspectives being integrated and absorbed into the transformation process. Additionally, the McLaren group stocks renewable energy equipment, a move that aids in reducing environmental impediments and therefore strengthens the company’s commitment to green energy.
Step 6 – Create short-term wins
The sixth step articulates the strategy for organizational success where organizational success is enforced by establishing short-term objectives to instill a sense of purpose in the workforce. Without a doubt, employees will be encouraged to expand and seek change after meeting the objectives. Thus, McLaren Group communicates to all employees that the company is altering the process by rewarding and recognizing staff members who are a closed part of changing and successively influencing.
Step 7 – Consolidate improvements
In the fight against organizational complacency and resistance, the continuous success of the change effort is a formidable force due to the efficient implementation of Step 7. A winning plan is hard to argue with, after all. According to John Kotter, some transformation pathways fail because success is declared prematurely. Vibrantly, transformation is a gradual process that must be integrated into the overall business culture. Probably, rapid victories are the preferred way to initiate long-term reforms. This is true for McLaren Group, which is constantly on the lookout for ways to improve.
Step 8 – Anchor the changes
In step eight, when a shifting influence has become ingrained in the business’s principles, it is said to as a fragment of the company culture. Without a doubt, values and standards must align with the new organization’s vision, with employee conduct anticipated to offer a unique match and employees expected to continue to support the transition. Additionally, discussing progress and evaluating it aids in solidifying the change. In contrast to step eight, McLaren Group maintains a highly transparent organization that enables employees to participate in an open decision-making democracy within the organizational structure.
Conclusion
McLaren Group has established itself as a global leader in the highly competitive automotive sector. This is demonstrated by its continuing development and domination in the sector. It can overcome market entrance obstacles using a variety of processes that assure its industry relevance and success. McLaren is one of the rare firms that has overcome market entrance barriers by diversifying its portfolio of enterprises. Diversification of its company activities is a significant factor in its success. McLaren has benefited from the correlation between variety and performance.
References
Babu, V. S., & Behl, M. (2020). f1tenth. dev-An Open-source ROS-based F1/10 Autonomous Racing Simulator. In 2020 IEEE 16th International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering (CASE) (pp. 1614-1620). IEEE.
Brock, J., Peak, K., & Bunch, P. (2019). Intuitively Leading Change: Completing a Kinesiology Department-to-School Transformation using Kotter’s 8-Stage Change Model. Journal of Physical Education, 6(2), 14-24.
Galpin, T. J. (2019). Strategy beyond the business unit level: corporate parenting in focus. Journal of Business Strategy.
Haas, M. R., Munzer, B. W., Santen, S. A., Hopson, L. R., Haas, N. L., Overbeek, D.,… & Huang, R. D. (2020). # DidacticsRevolution: Applying Kotter’s 8-Step Change Management Model to Residency Didactics. Western Journal of Emergency Medicine, 21(1), 65.
Loredana, E.M., (2017). The use of the Ansoff matrix in the field of business. Annals-Economy Series, 2, pp.141-149.
Rahman, K. M. (2016). Strategic Planning and Marketing Models. In Strategic Marketing Management in Asia: Case Studies and Lessons across Industries (pp. 59-110). Emerald Group Publishing Limited.
