Apple Inc. (simply known as Apple) is a United States technology company, best known for its personal electronic devices under the brand names iPhone, iPad, iWatch, iMac, Airpods, and a few others. It is one of the largest technology and overall firms in the world and one of the few that directly sells consumer products. The company is reputable for its quality of products and services and as one of the leaders of innovation in consumer electronics. The current CEO is Tim Cook. Apple has over 147,000 employees and remains the largest technology company by revenue, equaling a record-breaking $274.5 billion in 2020. Overall, the company offers and consistently expands the range of products and services within its closed ecosystem and proprietary operating system (Business Standard, 2020)
History
Apple was founded in 1976 in Los Altos, California, a suburbia of San Francisco, by Stephen Wozniak and Steve Jobs. Inspired by the first commercial microcomputer, the two decided to create their microcomputer that was accessible to everyday users through the use of a display. Wozniak was known for the engineering element of the company, while Jobs was the entrepreneur and businessman.
By 1977, the company secured investors and funding and produced the Apple II, a commercial hit which allowed users and amateur programs to store and manipulate data. The company grew at unprecedented levels, beginning to challenge the industry leaders such as IBM. Jobs had conflict visions with Apple’s board members, seeking to create the best and perfection, and was eventually ousted from the company in 1985, after which Apple began a long decline (Levy, 2021).
In 1997, Jobs returned to the company as undisputed leader and CEO. He quickly revitalized the company, streamlining products and inviting designers such as Johnny Ive to create appealing concepts. In 1998, Apple released the iMac, a simple but effective computer which greatly attracted consumer and educational markets, lifting Apple’s market share. In 2001, Apple entered the music business, presenting a digital mp3 player, the iPod which went on to revolutionize the music industry, and a program iTunes which had to be used to buy and load songs unto all of Apple devices from then on. In 2007, Jobs presented the first iPhone, the first of its kind ‘smartphone’ that began the modern revolution of technology and smartphones known today.
Over the years, Apple has continued to release multiple products, continuing its iMac home computer line and portable laptops, as well as new devices such as smart watches, tablets, wireless headphones, and others, with new models released every year or two (depending on device). Steve Jobs was diagnosed with cancer in 2003, which he was able to fight until his death in 2011 (Levy, 2021). In the last years of his life, Jobs was gradually transitioning the CEO position to his friend and COO of the company, Tim Cook, a position he successfully holds to this day, with Apple climbing in practically every aspect of financial and marketing indicators yearly.
Industry Type
Apple operates in the technology and consumer electronics business. It designs, manufactures (by outsourcing), and sells a range of devices, with iPhones being its primary revenue sources at approximately 48-52% annually. Apple maintains a closed ecosystem where its devices can interact with each other and use proprietary programming known as either iOS for mobile devices or MacOS for its computers. Therefore, Apple is in the programming industry and creating digital applications and services for its users. It has also entered the digital entertainment and media industry with services targeted at its consumers such as music and video streaming.
Apple’s competitors design and produce their consumer electronic devices, license an external operating system such as Android for mobile and Windows for PC, and typically rely on third-party software and services for the majority of functions, applications, and media. Meanwhile, Apple is unique in that it creates everything itself within its system, relying on 3rd parties only for applications in its App Store or some of the content in its media services.
Position with-in Industry
Due to the complexity of modern technology companies, it is difficult to track position in the industry. By revenue, Apple is the sole leader as of 2020 in technology companies including both producers, manufacturers, and software developers. The company is also worth $2 trillion, the first U.S. company to reach that mark, and holds the position as the most valuable company in the world. By smartphone sales, Apple is third on the global market with approximately 14% market share, behind Samsung (21%) and Xiaomi (15%) respectively. However, in the premium segment, which makes up 95% of Apple’s line-up, the company holds a 57% market share (Stanton & Peng, 2021).
In PC, Apple holds approximately 15% of the market, with 8.8% of the world using MacOS, but the majority of computers are dominated by Windows which all other manufacturers use. However, in wearable electronic devices (smart watches and headphones), Apple holds a strong lead with 34.1%, with nearest competitor Xiaomi being at 11.8% market share (Vailshery, 2021).
Legal Structure
Apple Inc. is a corporation, being incorporated soon after its founding in 1976. It is a C type corporation as under U.S. tax law, any corporation that is taxed separately from its owners, and applies to most publicly traded firms. A corporation is defined as business entity that is legally separate from its owners, known as shareholders. It can be owned by both individuals or entities, with ownership transferable via buying and selling of stock. The corporation is governed by a board of directors chosen by its shareholders. This entity is often chosen by entrepreneurs that need a more formal business structure, since an LLC cannot have shareholders (Schooley, 2020). The corporation structure is beneficial when taking on rounds of funding, rapid growth of business, and plans to eventually have an IPO for a company.
One of the primary benefits for a corporation is that it is a completely separate entity from its shareholders, meaning that they are protected from personal liability, and the company enters litigation and contracts on its own as an entity. The ease of transferring ownership via stock offers flexibility from a business security perspective and ensure perpetuaty of the business, such as when Jobs and Wozniack left Apple in 1985 but the company continued to exist. The corporation form allows much greater access to capital, such as raising funding through selling stock through private investor rounds or public offerings, a form of funding that other legal entities do not have.
In terms of disadvantages, corporations are highly expensive to form and operate, with the process being rigorous and tediuous, as well as expensive to maintain at the organizational and legal level, so only businesses that are growing at a rapid pace or have high earnings should consider this form. Finally, for C-corporations there is the disadvantage of double taxation, where the firm is taxed as an independent entity, meanwhile shareholders are taxed as individuals for any profits and individual income made off their shares (Schooley, 2020).
Management
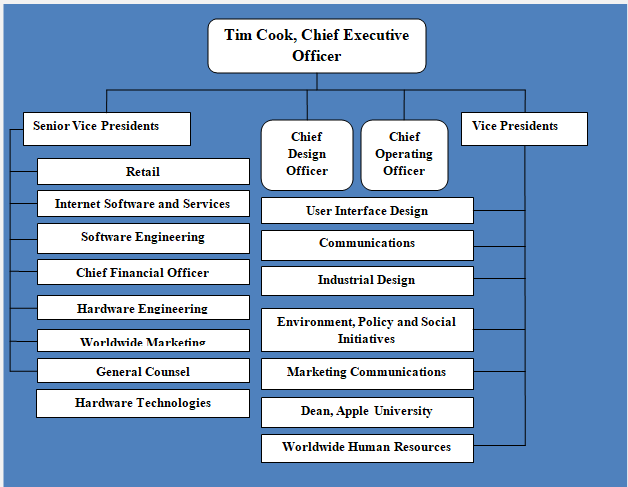
When Jobs returned to Apple in 1997, it had the traditional divisional hierarchical structure for a business of its size, with each business unit having its own general managers and P&L responsibilities. Jobs believed this bureaucracy stifled innovation, so he brough all the business units together under one functional leadership and organization and P&L. While departments still had managers, the organization functioned as a whole with each department closely interacting and interconnected with each other.
This structure is common for small startups where efficiency is both motivated and financially required, but Apple has now 40 times as much more revenue and the organization has grown to be incredibly complex, but it retains the structure. Senior vice presidents are in charge of functions, not products, such as design, operations, marketing, engineering, retail, and others. The company has no conventional general managers, other than the CEO, where all the function departments meet (Podolny & Hansen, 2020).
Conventionally, as organizations grow in size and complexity, they shift to the multidivisional structure to align control and prevent congestion of decision-making flowing up the organizational chart, with general managers make the priority decisions, with the CEO only seeing the most critical strategic decisions. However, Apple is unique and utilizes the structure to fuel innovation (Podolny & Hansen, 2020). Apple develop products and product categories which are continuously improving. For example, the iPhone camera went from being a simple camera to virtually the leading mobile camera ever due to innovational improvements over the years.
In order to do that, the company relies on functional expertise in their respective elements, such as when Apple introduce the dual lens camera, it was risky but implemented by staff who worked with Apple’s camera system from the start. Furthermore, the functional structure enables collaboration, such as the camera system in Apple products is so successful not only due to engineering, but the incredible software which utilizes every last aspect of the hardware’s potential, creating a tightly integrated and quality product in the end.
Organizational Culture
The organizational culture is highly motivational and inspirational, there is much emphasis on collaboration, but the organization is also highly secretive about its inside operations. In general, the culture promotes the premise that one is a part much bigger than yourself, and one is making a significant contribution which should satisfy one’s professional and personal ego. The Apple Campus where the majority of employees work is a significant piece of engineering and urban infrastructure, holds not only specifically designed spaces for collaborative and open work, but also has a number of perks for employees.
Unlike at other companies where one reports to a manager, the majority of work is peer vetted, and feedback is offered constructively. At the same time, Apple holds high expectations from its employees to maintain the quality and ‘perfection’ of the Apple brand, meaning that long hours, constant tension, and sometimes disrespectful management is present. The secrecy of Apple attempting to keep leaks at bay and maintain its numerous projects secret has led to accounts to employees being terrified into absolute secrecy (Edwards, 2013). Therefore, Apple is both a mix of healthy vibrant start-up vibe culture and the negative corporate nuances that can be expected from a company of this size and position.
Management Style
Former CEO Steve Jobs was known for his highly autocratic, almost ruthless leadership style which pushed many of his employees to the brink but also produced tremendous breakthroughs in technological innovation. His successor, Tim Cook is best known for a democratic leadership style. Cook is described as highly charismatic, and that serves to inspire employees as he dedicates his strengths towards existing products and fostering employee relationships. He utilized the framework built by Jobs and used his strengths as a democratic leader to advance collaboration among highly talented Apple employees and departments. His leadership style focuses on consensus building and mutual decision-making (Schmitt, 2021).
However, one element that Cook adopted from Jobs was tremendous attention to detail, which is required in the functional organizational structure. Apple is a company where experts lead experts, and in order to expedite decision-making and collaborative work in this vertical structure, vice presidents of the departments and Tim Cook himself are expected to have the deep expertise and intense attention to the smallest details, with the principle “Leaders should know the details of their organization three levels down” (Podolny & Hansen, 2020). The managers are familiar with the project spreadsheets, lines of code, or product test results, with few other organizations outside of Apple maintaining such high level of standards.
Mission
Apple’s mission statement is, ““To bringing the best user experience to customers through innovative hardware, software, and services” (Rowland, 2020). The mission statement recognizes the uses of consumers electronics devices across a spectrum of industries and applications as well as the trends and changes to the market and industry environment. The company focuses on computing products, not just in the forms of hardware, but software and services based on the technology to enhance quality and experiences of consumers across all market segments globally.
Vision
The corporate vision for Apple is, “To make the best products on earth and to leave the world better than we found it “(Rowland, 2020). This vision statement guides Apple’s strategic decision-making, management, and operations. It emphasizes the strive for leadership in product design and quality to creating the best products, but also a recognition of the impact it has both socially and environmentally. Apple seeks to be fully carbon neutral by 2030 and hopes its technology and solutions can be used for a sustainable future for human society.
Core Competency
For the longest time, the defining core competency of Apple was innovation, with its ability to push the industry forward with new technologies and product categories. That remains to an extent but has slowed down significantly as both part of the general trend in the industry and the result of Tim Cook’s management which is more business oriented compared to his predecessor’s desire for pure innovation. The current core competency of Apple can be described as the strategic integration of hardware, software, and services to create a fully interconnected but at the same time isolated ecosystem. Despite many attempts, no one competitor such as Google or Samsung can achieve this level of integration (Bajarin, 2011).
Apple customers own Apple hardware, that runs Apple software, that utilizes Apple services or downloads applications through the Apple App Store, which the company fully controls. Apple users can seamlessly switch between devices, and the software will understand switch everything over with them, such as Airpods connecting from the smartphone to the laptop or answering the call from the Apple Watch and deciding to switch to one’s phone. Users typically do not need to do anything as the technology recognizes the switch itself, it is an unprecedented level of integration within the ecosystem.
PESTLE
- Political – As a multinational corporation, Apple is strongly affected by political factors, particularly trade and business policy. The company is interested in pro-business policy, lesser corporate tax, and enticing free trade across borders to lower tariffs for its supply chain activities. One political relationship that is critical to Apple is the one between U.S. and China as the significant majority of Apple products are manufactured in China by its partner Foxconn, so the flow of trade and non-sanctioned diplomatic relationships are important (Leswing, 2019). Another political aspect to consider is regulatory legislation around the world that oversees the hardware and software use by Apple, as for example a recent EU decision is mandating that Apple integrate the common standard USB-C charging ports into its iPhones (Peltier, 2021).
- Economic – As a commercial company, Apple is interested in economic growth of the U.S. and other developed countries. Economic crises typically result in less disposable income and consumers are less willing to purchase non-critical electronic devices and digital services, especially with Apple products which have long operational lifetime due to quality (Bary, 2021). Another economic factor affecting Apple are inflation and currency fluctuations, as Apple sells its products globally, prices may vary significantly due to changes in currency value and local import taxes as well.
- Social – There is an increased dependence on digital systems and services, which presents an opportunity for Apple to grow, and the predominant use of mobile and wearable technologies and society is considerably beneficial. Apple sales are driven strongly by brand loyalty and perception, so the company must maintain a positive social image and practice corporate social responsibility. There is some mistrust that Apple violates privacy and will offer data to governments if legally forced to do so, the company must address this social fear.
- Technological – As a technology firm, Apple strongly depends on shifting technological factors. Some examples such as growth of cloud computing, artificial intelligence, and general integration of technology in business and society ultimately benefits Apple as it serves as opportunity to sell its products and services. At the same time, rapid technological breakthroughs could create new areas of commercialization where Apple does not operate or has fallen behind competitors. There are also technological limitations, such as Moore’s law as microprocessors are arriving at a point where it will be physically impossible to stack more transistors, potentially causing a temporary stagnation in the industry (Robinson, 2017).
- Environmental – Apple has voiced its support for environment sustainability, promising to achieve carbon net neutrality by 2030 in all areas of the company, from beginning of the product design cycle to the end. Apple attempts to recycle materials, reutilize components, and refurbish devices for secondary use whenever possible. External environmental factors can impact Apple by severely disrupting supply chains due to climate change. There are limited resources of certain materials used in production, such as rare metals, which all electronics contain.
- Legal – Due to the size and strategic practices of Apple to maintain a closed-off ecosystem, it consistently faces lawsuits from users, app developers, and governments on some aspect related to the way the ecosystem operates. Apple has also faced a number of anti-trust legal investigations as well as lawsuits over its ties with abusive labor conditions in China and Asian manufacturing facilities where it contracts production.
Financial Analysis
Apple is seeing rather consistent growth over the last several years, except for a slight drop from 2018 to 2019. This was attributed to stagnating iPhone sales and lack of refreshing new features. However, in the last fiscal year, Apple has demonstrated record-breaking revenue, both due to high demands for consumer electronic devices during the Covid-19 lockdowns, as well as a new form factor and functionalities introduced with iPhone 12.
Operational Expenses
As expected, the company’s operational expenses grow annually, at a rather consistent pace over the last years. This is due to inflation, rising costs, and natural growth of the company, this indicator will expand. Research and development is included as an operational expenses, accounting for approximately 60% of the costs, while the rest are general, sales, and administrative costs.
Profit Margin
Apple’s net profit margin remains consistently the same year over year of around 21%. This past year saw an increase to almost 26%, it is yet unclear if this will persist. Overall, such profit margins are excellent in the technology field while still demonstrating successful growth and sales in numbers. As a premium product, Apple has always sought to extend its margins
Stock Performance
Apple’s stock price has grown consistently and exponentially over the years, ever since the release of the first iPhone which propelled it into international success. Apple is considered one of the safest and most reliable stocks to invest in, and as the company continues to introduce new products and services, with record-breaking revenues, the stock price will continue to climb. With the advent of retail investing, Apple is one of the most popular and recognizable stocks, so it will likely see further rise as investor confidence in the company continues.
Latest Market Value
Apple is the first company to reach a 2 trillion dollar mark, and will likely soon reach a $3 trillion evaluation. The market value growth is due to the success of the stock market price discussed above and a greater number of investors purchasing shares further inflating the company’s value. However, it seems that the value is justified based on their financial indicators, and it is not a bubble that will burst, because Apple have a variety of mechanisms to supports its company market value.
Debt
Apple has been increasing its debt obligations gradually, with the majority of debt being long-term debt. That is appropriate for a company of Apple’s size to borrow in order to finance its operations. Companies do so in order to invest in operations, and increasing their leverage without increasing their equity. By borrowing against value of assets and investments, companies avoid the capital gains tax bill that would be charged if equity was sold for cash.
Cash Position
Apple maintains a strong cash balance from years of successful sales. The balance remains largely as reserves, and the majority is in offshore accounts as it would be heavily taxed if brought into the U.S. The company supposedly cannot get rid of the cash fast enough. Apple is #1 by rank based on cash on hand. The criticism is that the opportunity cost of holding that much money is tremendous, essentially lost to inflation. Apple has invested some into treasuries and bonds, but those have low yields, so there is much call for Apple to use the money for dividends and stock buybacks as well as investment into more profitable ventures (Krantz, 2021).
Liquidity Measurement Ratios
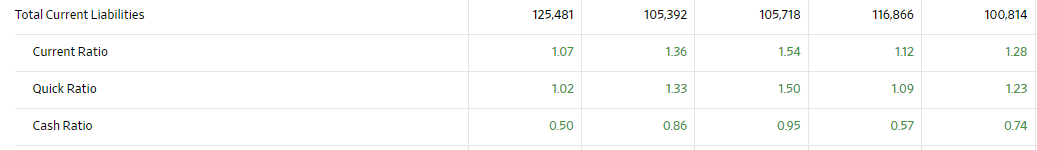
In general, the ratios demonstrate the Apple is a healthy business that is able to pay its liabilities. The current ratio is slightly below the preferred 1.5-3 range, but it remains above 1 so the company does have enough liquid assets to cover short-term liabilities. The quick and cash ratios are within healthy ranges, so there is no indication that Apple is any financial turmoil.
Marketing
Apple offers 5 major lines of product offerings or services.
- iPhone – the core product (see below), with models both new and old ranked consistently as the best smartphones in the world since 2009. Serves as the primary consumer and marketing tool for the company.
- Services – a developing line of offerings, with a 63.7% profit margin, it is a lucrative sector. Apple users sign up for services through a subscription-based format and enjoy elements of streaming music, films, and recently more interactive formats such as fitness tracking. Significant opportunity for growth in this segment.
- Mac – Apple remains a relatively strong player in the personal computer segment, despite having a small market share. PCs accounted for 11% of Apple’s revenue and remain popular in certain segments such as education and creative disciplines. Apple has recently invested heavily into new processing power for its computers which have received critical praise from professionals, potentially increasing sales.
- iPad – Apple essentially introduced this category to consumer electronics with the release of the iPad in 2010. It became a commercial success and is now used as a tablet computer for a wide variety of purposes. The iPad holds a 36.5% share of the global tablet market, similarly to iPhones, aimed largely at premium.
- Wearables and accessories – in recent years Apple have begun to offer wearable smart devices which are greatly improving in functionality with passing years. The Apple Watch is an excellent side companion to the iPhone, while Airpods in their different versions are the most popular wireless headphones in the world (Delventhal, 2021).
Core Products
Apple’s core product is the iPhone. Out of the $365 billion in revenue in 2020, 52% came from iPhone sales (Delventhal, 2021). The iPhone remains the company’s flagship product, and the one that drives sales to all other departments. For example, services and app downloads are meant to be used with the iPhone, generating more revenue. Wearables such as the Apple Watch and Airpods cannot function without an iPhone connection. It is the iPhone that brought the Apple brand to international spotlights and remains the device that many around the world would like to purchase and use.
Distribution Method/Strategy
Apple distributes its hardware products directly through its famed retail stores or online sales. In countries where Apple does not have retail stores, it commonly has an official partner retailer. However, it also sells the products to wholesalers that can also sell it via retail or online. So, Apple products can be found virtually in any location that sells electronics. Therefore, the distribution channel is mixed, using a direct and indirect approaches. At the same time, all of its non-hardware products such as software and services can only be purchased on and used on exclusively Apple devices.
Target Audience
Apple’s target audience from a demographic perspective is young (ages 25-44), ‘hip’, creative, lifestyle-oriented, middle-class and above. In recent years, the company has been expanding its target audience, attempting to capture more people within its ecosystem. Apple products have grown more appealing to older adults as well, with some functionalities such as health tracking/ECG, aimed towards them. iPhones for younger generations are popular as well, getting the individual into the Apple ecosystem from an early age.
Main Competitors
Apple’s primary competitors are other firms specializing in consumer electronics across a variety of segments, but particularly in smartphones and related accessories as this is Apple’s most profitable category. On a global scale, Apple competes with its main rival Samsung Electronics from South Korea. Samsung sells a wide range of devices globally running on the operating system Android, including in the low-budget and medium-budget segments which Apple does not target. However, Samsung produces ultra-expensive premium phones in its Samsung Galaxy line, matching the iPhones in power and capabilities.
Samsung also has a range of other income sources as it sells household electronics and manufactures microprocessors as well as being the leader in screen technology, actually producing the screens seen in most modern iPhones. Other rivals to Apple include rapidly rising firms from China such as Xiaomi, and until recently Huawei (sanctioned by U.S. government, losing the majority of international business. These firms are similar to Samsung, relying heavily on the budget segments, but have begun to enter premium segments, undercutting competitors by selling devices at a loss or with extremely low margins.
Geographic Reach
Apple has extensive geographic reach as its hardware products (especially the iPhone lineup) are sold in virtually every global market. For its less popular product lines and services, Apple offers them selectively based on country and market. The company has more than 500 official retail stores worldwide in 25 countries, and an online presence in over 100 different countries. The App Store support is available in 175 countries and regions, indicating that Apple products are sold there in some capacity (Apple, 2020).
Advertising and Promotion Strategy (IMC)
Apple’s advertising strategy is unique but extremely efficient and potent. The company brand is highly critical to the success, so promotion focuses on upkeeping a certain image and perception of the brand name. Unlike other brands focusing on spamming adverts, Apple’s promotion relies on strategies of product placement and buzz created by positive media reviews. Apple does not attempt to undercut competitors, pricing, or anything else. All of Apple’s advertising focuses on one thing, which is Apple and its product. Apple knows its unique value proposition and it maintains it. If product placement is used with celebrities and influencers, it is done in a classy, natural way.
Most of Apple’s marketing is simple and intriguing, with advertisements being modern, diversified, and focusing on one product or even just a feature of a product. Simplicity with premium quality is Apple’s brand image, and it can be seen through its advertising. Through its history, the company has had a slogan to rally consumers, under Jobs, it was “think different” and now it uses “introducing [device name]” and showing off its basic features in a video vignette. To emphasize simplicity and understanding the audience, Apple never mentions technical specifications or numbers, but reliably shows the product images and short copy highlighting the benefits (Patel, n.d.). Apple’s marketing is emotional, it triggers feelings and awe at the power and beauty of its products which are all interconnected in design and functionality.
Pricing Method and Strategy
Apple maintains a premium pricing strategy, with the objective as told by Tim Cook, “not to sell a low-cost phone. Our primary objective is to sell a great phone and provide a great experience, and we figured out a way to do it at a lower cost” (Nielson, 2020). Apple focuses on customers that are willing to pay more and premium price for innovative and high-quality products. The pricing add exclusivity to Apple products, therefore, drawing demand and desire for them.
Apple’s products are premium and expensive, but just enough to be ‘within reach’ and affordable to the middle-class consumers. Apple employs a minimum advertised price (MAP) retail approach, essentially legally forbidding them to sell the product below an established minimum price but provides some marketing subsidies to its resellers (Nielson, 2020). The company strongly regulates prices and enforces this premium policy, which is why even older iPhone models are relatively expensive.
Positioning Strategy
Apple has always sought to position itself as a premium, almost luxury brand, with products and services that can match that level of quality and customer experience. The strategy has revolved around four pillars, established by Steve Jobs. First, Apple will offer a small number of products, in which it specializes and can produce the best in that respective category. Although Apple has expanded its offerings, in terms of hardware, Apple’s smartphone, tablet, smart watch, and wireless headphones are arguably the best or at least at the top of the category compared to competitors. The second pillar is focusing on the high-end, emphasizing the premium feel, materials, and functionality of each device.
The third pillar is to give priority to profits over market share. Apple has never chased market share, it sold its devices and by producing quality, it generated sales that expanded the market share naturally. Finally, the fourth pillar is to create an effect that makes people want and eager for more Apple products, referring to the promotion aspect, with Apple products drawing people in, even if one is not an Apple fan.
Value Proposition
Apple understands that the smart device market is oversaturated, and most of the competitors share identical or similar features, designs decisions, and capabilities of the devices. However, Apple offers the value proposition that its competitors cannot offer, which is the seamless integration within its ecosystem and customer experience of using an Apple device. As discussed previously, the Apple ecosystem is closed off but allows for ease of use and sharing between the company’s products to make the consumer experience hands free, simple, and intuitive. Apple pays attention to the smallest details of industrial design and software development to ensure these capabilities and compatibility among devices.
Differentiation Strategy
Apple differentiates its product in marketing by pricing them higher than the competition and positioning them as premium devices. The whole brand is based on luxury and quality of products, justifying the pricing point alongside the flagship level features that these devices offer (processing speed, camera, etc.). Alongside other benefits described such as the integrated ecosystem, services, excellent customer support, Apple differentiates itself and has gained a competitive advantage through its premium pricing and positioning.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Apple is well-known for its company positioning and ethos, but one of the ‘behind the scenes’ reasons to its success is excellent CRM strategy. Apple famously does not conduct any serious market research nor does it have any loyalty programs to keep customers enticed, but it has one of the most loyal followings in all of corporate history. One of the primary principles behind this was voiced by Steve Jobs, “You’ve gotta start with the customer experience, and work backwards to the technology” (Binns, 2021).
Apple knows its customers and recognizes their needs. Every year, its software and hardware is updated to enhance the customer experience, but notably, even if one has an older device, the majority of the features can be experienced. Apple maintains uniformity and treats all customers with equal respect, no matter if they bought the latest models or own a five-year old model. Apple combines the need to innovate with perfection for the customer experience. For example, they could have added the second and third cameras at the same time as their competitors, but they did not do so until almost 2-3 years later to ensure that the quality of images stemming from the other cameras met the high standards that Apple has established with its primary sensor and software assistance.
Virtually every aspect of Apple’s interaction with customers focuses on the customer experience, ranging from the unique experience shopping in official Apple stores to the experience opening the device for the first time. Apple has built up an impeccable brand, that is appealing, that is iconic and recognizable, that draws interest around the world and media every time a new device is about to be unveiled. The brand has also successfully appealed to millennials, with Apple being one of the few brands that Generation Y and X are most emotionally attached to. The customer is central to Apple’s strategy and that is a strong contributor to why brand loyalty for the company is consistently at 90% and above, with few ever leaving the iOS ecosystem for their competitors (Binns, 2021).
SWOT Analysis
Conclusion
Apple is a multinational technology corporation that has become one of the leading consumer electronics producers in the last 15 years. Known for its high-quality premium products, innovation and leading the industry in many elements, and impeccable strategic marketing, Apple is now the most valuable and one of the most profitable corporations in the world.
Part of it stems from its rich, industry-changing culture and organizational structure that has been created by its late founder Steve Jobs, while other successes are attributed to modern management, its tremendous marketing potential, and strategic approaches to sales. The corporation has achieved significant popularity, especially in developed countries, and continues to draw people into its ecosystem, ensuring continuous streams of revenue. The financial health and cash resources of the company have ensured that it will continue to be around for decades to come, creating new innovations and legacy for the famed Apple brand.
References
Apple. (2020). Apple Services now available in more countries around the world. Web.
Bajarin, B. (2011). Why competing with Apple is so difficult?. Time. Web.
Bary, E. (2021). The pandemic may have permanently altered Apple’s path. MarketWatch. Web.
Binns, R. (2021). Apple CRM case study. Web.
Business Standard. (n.d.). Apple Inc. Web.
Delventhal, S. (2021). Apple’s 5 most profitable lines of business. Web.
Edwards, J. (2013). What apple employees say about the company’s internal corporate culture. Business Insider. Web.
Krantz, M. (2021). Apple’s got a $204 billion ‘problem’ that’s costing it a fortune. Investor’s Business Daily. Web.
Leswing, K. (2019). Here’s why Apple is so vulnerable to a trade war with China. CNBC. Web.
Levy, S. (2021). Apple Inc. Web.
Liu, X. (2013). Multi-divisional structure and matrix structure. Web.
Nielson, S. (2020). Apple’s premium pricing strategy, product differentiation. Web.
Patel, N. (n.d.). 7 key strategies that you must learn from Apple’s marketing. Web.
Peltier, E. (2021). In a setback for Apple, the European Union seeks a common charger for all phones. The New York Times. Web.
Podolny, J.M., & Hansen, M.T. (2020). How Apple is organized for innovation. Harvard Business Review. Web.
Robinson, D. (2017). Moore’s Law is running out – but don’t panic. Web.
Rowland, C. (2020). Apple Inc.’s mission statement and vision statement (an analysis). Web.
Schooley, S. (2020). Pros and cons of forming a corporation. Business News Daily. Web.
Stanton, B., & Peng, N. (2021). Apple retakes second place with strong iPhone 13 sales. Canalys. Web.
Vailshery, L.S. (2021). Wearables shipments worldwide market share 2014-2021, by vendor. Statista. Web.
Wall Street Journal. (2021). Apple Inc. Web.
