‘Mobile marketing’ has several definitions and meanings, and specific views regarding its role, meaning, and functions in the modern world. According to the definition of the Mobile Marketing Association, mobile marketing is a set of practical elements and rules aimed at communicating, contacting, and interacting with the audience through the Internet and mobile devices (Oscar et al., 2017). In contrast, the scholars Shankar and Balasubramanian give this phrase a different meaning (Oscar et al., 2017).
As reported by them, mobile marketing is the interaction of several pathways between a company and its customers using mobile technologies and information carriers. In addition, Scharl, Dickinger, and Murphy call this process to promote a product, service, or idea to interested parties using wireless communications (Oscar et al., 2017). Therefore, this marketing concept consists of synthesis with mobile devices, wireless means, and advertising.
It is not easy to imagine the contemporary world without smartphones. Armed with these ‘tiny devices,’ people can search for additional information about products and services, compare them and share opinions, and retailers have become more sophisticated in attracting customers.
For example, about 70 percent of digital purchases occurred in the second half of 2016, and sales on mobile devices in US stores increased this year by about four times compared to 2012 (Fulgoni & Lipsman, 2016). The numbers will likely continue to increase gradually; mobile marketing has radically influenced the shopping process and consumer opinion in a relatively short period. In addition, many mobile trends demonstrate that mobile devices are designed to shape retail trade today and in the coming years, unlike other platforms.
Mobile is such a powerful medium for marketing for the following reasons. Firstly, a mobile device is a fast and multifunctional tool that almost every modern person uses. People order food in restaurants and stores, read books, listen to music, watch videos, and exchange messages. Consequently, content is delivered and processed instantly, and campaigns can be cost-effective. Secondly, users can access the Internet on their mobile devices anytime and anywhere.
This situation reduces laptops’ use, and online purchases from mobile apps become more accessible and easier to make than from websites. Retailers, in turn, cover the target audience that does not have access to other devices. Thirdly, it is much easier to localize marketing and set up targeted advertising through phone geolocation and location determination. Most users believe that a mobile device is a more personal thing, and therefore they expect personalized content (Stokes, 2018). Thus, solid mobile marketing is manifested due to the speed and efficiency of data transmission on mobile devices and comprehensive audience coverage due to its characteristics – accessibility, ergonomics, and ease of use.
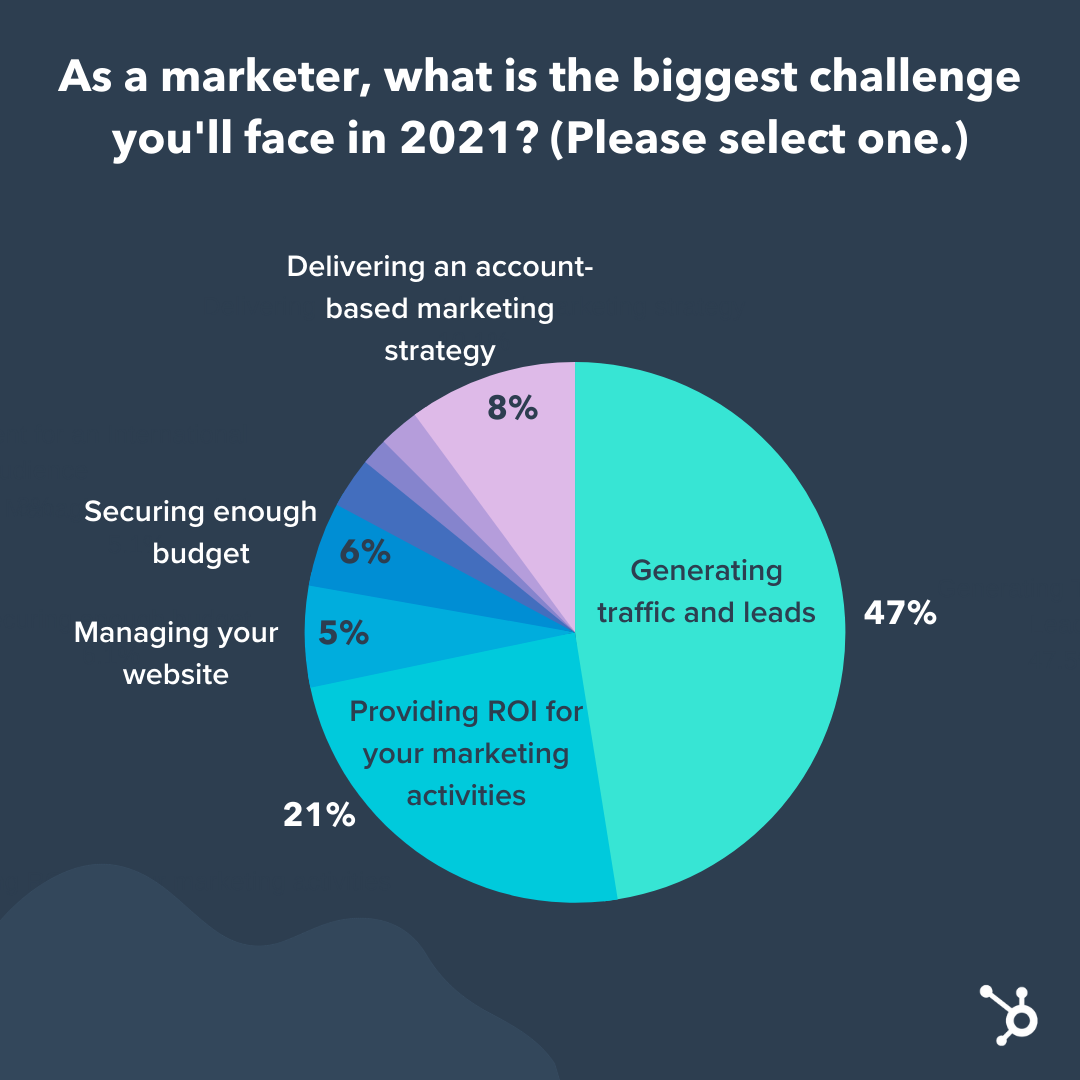
Each marketer may face problems that prevent the implementation of plans and achieving specific goals. According to recent research, three of the biggest concerns for mobile-focused marketing in 2021 are potential customer traffic, the effectiveness of marketing strategies, and a sufficient budget (Forsey, 2021). The data shows that ‘traffic’ is the most urgent problem. In this case, it is imperative to understand clients and choose the right and relevant content from mobile applications and websites (Jones, 2017). The profitability of marketing activities is an indicator of the success or failure of a specific plan (Forsey, 2021).
Undoubtedly, usability testing is the primary step to the competent implementation of the project (Jones, 2017). In addition, without a proper budget, it is not easy to create a successful marketing campaign and achieve high results. This trend is developing especially clearly after the global pandemic (Forsey, 2021). Below is a more detailed diagram illustrating the correlation of problems in mobile marketing.
Indeed, geofencing is a valuable technology that allows a point of sale to interact with potential customers. Location-based marketing has significant advantages and fantastic results for retail companies. When the client’s mobile device enters the specified area, the corresponding information is sent to the mailing service. It can be used as a trigger for automatically sending a message or as a marketing data source. Moreover, this system allows companies to focus on the consumer when conducting certain events (Statler, 2016). Consequently, the importance of geofences in marketing is to help retail chains send special offers to users using the location detection function.
If the company understands the needs of its customers and knows how to respond to them and what to offer, then, based on this situation, creating a brand app will be the best solution. In addition, it is necessary to evaluate the contribution to the creation of the ‘application software,’ determine its goals and objectives, the role in the user’s work, and what benefits it will bring to both the buyer and the company (Stokes, 2018). If all doubts about the app’s development have disappeared, then this is the best reason to start acting and creating it.
The key indicators in measuring the success of mobile marketing are the coefficient of attraction and the indicator of the involvement of active customers, as well as an increase in the average receipt, and positive sales results. Firstly, the number of visitors to the website or downloads of the app does not always give a complete picture of popularity and usefulness. It is recommended to track the sources from which new potential customers come.
Secondly, one of the most important indicators for measuring user engagement is considering their activity throughout the day and month. If the above metric criteria are growing steadily, then everything is going in the right direction. Thirdly, increasing the average check is the surest and most reliable way to compensate for the cost of attracting customers and increase the amount of profit. Its understanding allows one to evaluate pricing and marketing strategies.
References
Forsey, C. (2021). 8 of the top marketing challenges faced globally [New Data + Expert Tips]. HubSpot. Web.
Fulgoni, G. M., & Lipsman, A. (2016). The future of retail is mobile: How mobile marketing dynamics are shaping the future of retail. Journal of Advertising Research, 56(4), 346-351. Web.
Jones, R. (2017). These are the biggest challenges marketers are facing with mobile. Smart Insights. Web.
Oscar, R. P., Alexandra, M. L., & Sandra, R. B. (2017). Mobile marketing: Conceptualization and research review. Espacios, 38(61), 26. Web.
Statler, S. (2016) Geofencing: Everything you need to know. In S. Statler (Ed.), Beacon technologies (pp. 307-316). Apress, Berkeley, CA.
Stokes, R. (2018). Chapter 7: Mobile channels and apps. In R. Stokes (Ed.), eMarketing: The essential guide to marketing in a digital world (6th ed.) (pp. 153–180). The Red & Yellow Creative School of Business.
