Introduction
The 21st century can be characterized by the increasing complexity of the business environment. The rapid technological progress introduces new advancements at a quick pace, adding new dimensions to existing practices. At the same time, the prevalence of globalization alters the entrepreneurial landscape across the world. Successful companies, which dominate their domestic markets, eventually come to a decision to expand their operations to new locations. Meanwhile, local organizations face an increasing level of competition conditioned by the emergence of international players. In this regard, the images of industries remain subject to changeability, as new variables are introduced in the global equation.
Challenges are constant within the contemporary environment, and companies are expected to adjust their operations accordingly in order to ensure survival and development. The in-depth examination of practical examples of organizations, which manage to overcome the challenges imposed by the business landscape enables a better understanding of today’s most effective strategies.
The present case study focuses on ANI Technologies Private Limited operating under the trademark of Ola Cabs Company. The primary focus of its business activities is online transportation networking. This sphere is highly prominent in today’s technologically advanced environment. In the case of transportation, Pandya et al. (2017) distinguish between two major types of online networking. First, there are car-sharing services, allowing individuals to pick up passengers who travel in a similar direction. This group of networks is represented in India by the Bla Bla company.
Such a model of traveling is popular across the globe, and it is mostly applicable in mid-to-long-distance traveling between cities. Ola Cabs follows a different, even more, popular model of transportation networking in the 21st century, which is a taxi marketplace/aggregator model (Pandya et al., 2017). This framework has been conceptualized and redefined by major international players, such as Uber. The latter is present globally, uniting drivers and passengers across all continents (Uber, 2021).
Nevertheless, despite the global presence and reputation of Uber, Ola Cabs managed to emerge and effectively develop its operations throughout India and even abroad. Accordingly, one can infer that the market of online taxi aggregator networking has a vast potential, which is yet to be fulfilled, making it a valuable industry in terms of examination.
Ola Cabs Company
Overview
Ola Cabs is an excellent example of an organization, which has utilized the potential of an emerging market and withstood the competition from a giant in its industry. According to the company’s website, Ola is the largest ride-hailing platform in India, meaning that it effectively occupies the same niche as Uber (Ola, n.d.). The operations of the company are based online, dwelling on the immense potential of the Internet. This way, Ola is capable of providing its customers with convenient, available services while optimizing the use of its resources.
Ola provides a range of transportation opportunities, including regular automobiles, electric vehicles, auto-rickshaws, and metered taxis (Ola, n.d.). The broad selection of services is expected to appease a broad, diverse audience of Indian people, ensuring the competitive advantage of the company. Pandya et al. (2017) state that, historically, the Indian taxi market was dominated by unorganized drivers, which prevented its quality development. The emergence of Ola Cabs, as a well-structured, convenient company with a clear vision, entailed a further re-organization of the Indian taxi market, positively contributing to the passenger service quality.
History and International Development
The sustained growth of the Ola Cabs company speaks of its timely emergency in the market. India became the home country for the organization, which became another important component of its success. It is a vast, developing economy with incredible opportunities and immense potential. From the organizational standpoint, Ola Cabs became a start-up, which managed to seize the emerging opportunities and conquer a considerable portion of the Indian market at a rapid pace.
The foundation of the company dates back to the year 2010, which marked the beginning of a new era of transportation networks in the area. In the following decade, Ola Cabs’ business model proved effective across hundreds of Indian cities, and the number of its passengers exceeded several hundreds of millions. Finally, the company has accumulated sufficient resources to extend its operations to a new market, following the path of Uber. As of 2021, besides India, Ola Cabs is present in New Zealand, Australia, and the United Kingdom. Accordingly, the company has acquired an international status, which reflects the effectiveness of its strategy.
Management and Key Figures
The history of a prosperous company is usually inseparable from the strong personalities behind its creation and development. Organizations do not exist autonomously, and the lack of proper strategic vision and management can prevent a company from growing even when the business environment is nearly perfect for it. Panigrahi et al. (2018) state that “start-ups do not die – they commit suicide” (p. 30). In other words, failures of emerging companies are usually conditioned by incorrect decisions of the management, trying to extend beyond the current potential of an organization.
An opposite situation is equally possible when the need for development is not met and a company falls into stagnation. In this regard, Ola owes a considerable portion of its success to Bhavish Aggarwal and Ankit Bhati, the co-founders of the cab aggregator service (Ola, n.d.). The former was able to utilize his experience from working with Microsoft Research, whereas the latter added his technological expertise to the equation. The partnership between Aggarwal and Bhati became highly fruitful, resulting in the development of India’s most popular cab aggregator platform. Following a decade of positive development, the co-founders retain Ola’s leadership, working on its further development, including in the international arena.
Company’s Performance
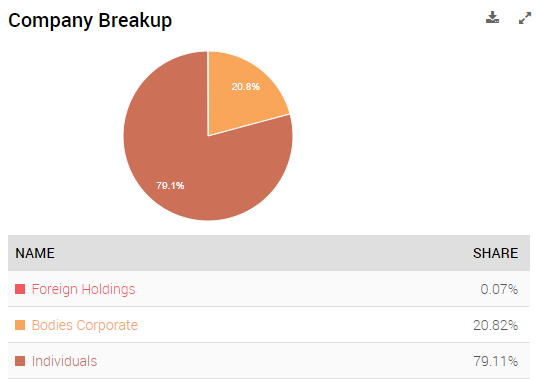
As established earlier, Ola has managed to retain an impressive growth rate throughout the decade. From a financial standpoint, the company has relied mostly on individual investors, as presented in Figure 1. Nevertheless, later in March 2021, Ola plans to hold an IPO in order to extend its financial capability and enable further growth (Reuters, 2021). In its most recent financial statement, Ola “reported a 16% rise in revenue at Rs 2,155 crore ($300.96 million), while its net loss of Rs 1,160 was almost 60% smaller than the year-earlier” (Reuters, 2021, para. 10). Therefore, even amid a global, pandemic-induced crisis, the company managed to perform above par.
As of now, Ola serves over 250 cities in India, Australia, New Zealand, and the U.K., organizing over one billion rides annually. The number of partner drivers registered in Ola’s product networks exceeds 1.5 million, whereas the list of its current employees has over 7.000 entries (Ola, n.d.). However, the company openly speaks of its plans to optimize the staff and reduce it by 500-1000 people (Reuters, 2021). Overall, Ola remains a highly profitable company with a vast potential capable of challenging the leaders of the industry in the global arena.
Ola Cabs Company and Internationalization
Internationalization has become a norm in the current business environment where globalization dominates the landscape. In a way, global presence and international operations have become a common stage of development for thriving businesses. At some point, a company is bound to transcend the limits of its internal market and aim at a higher status. Modern opportunities enabled by globalization allow organizations to plan such expansions realistically. While this stage of development may become highly promising for a company, it is traditionally associated with considerable challenges.
The expansion is to be planned with accuracy and caution, as it involves the choice of destination per se combined with the necessity to select the fitting internationalization mode. If the management fails to assess the situation correctly, the expansion will be a waste of time and resources. An additional challenge in terms of internationalization is related to global competition. If a company is to initiate new operations abroad, it will have to face new rivals in the form of organizations, which have already completed this procedure with success.
Foreign Markets
In the case of the Ola Cabs company, internationalization became a natural evolution stage for the organization. Over the course of the previous decade, the company has achieved resounding success in the Indian market. Its stable financial performance, combined with a steady growth of assets, enabled a feasible transition to the status of an international company. As of 2021, Ola (n.d.) is present in several countries of the Commonwealth, namely New Zealand, Australia, and the United Kingdom. The emergence of the new player was well-received by the local population, resulting in hundreds of thousands of new clients for Ola (Salman, 2020).
With this recent expansion, the company began a new era of international competition against the most famous cab-hailing company in the world. From one perspective, the local expertise allowed it to withstand the competition from Uber in India. On the other hand, these other nations of the Commonwealth pose new challenges, which may be even more difficult to overcome.
The Course of Internationalization
As established by the prior discussion, internationalization is a long, demanding process requiring thoughtful analysis and effective performance at all stages. Whenever further expansion is planned, it is essential to select the correct mode of entry to the new market and optimize the use of resources. According to Reuters (2021), Ola has the support of SoftBank, a Japanese financial organization, which infuses additional funds into the company’s structure prior to its IPO (Kapur, 2019a). This partnership positively affects the financial stability of the organization in focus. Furthermore, previous sections have presented the information regarding the impressive performance of Ola Cabs, in general. The revenue stream is considerable, which, combined with the investors’ support, positively affects the international capabilities of the company.
Ola Cabs often works through the acquisition of local companies, which allows it to build upon the existing infrastructure, accelerating the entrance to the new market (Kapur, 2019b). The expansion occurs gradually, as the choice of new locations appears thoughtful and precise. Evidently, Ola proceeds with caution, conducting thorough research prior to engaging in new operations. This approach to internationalization has become of the primary enablers of the company’s success.
Enablers of Internationalization
Internationalization is a rather long, challenging, and multifaceted process, which cannot be deemed inherently good or bad. Each particular company usually finds itself in a complex situation in which multiple factors are to be considered. Their in-depth analysis has the potential to reveal positive aspects, which may be utilized by the management of the company. In the case of Ola, a considerable portion of its domestic success was enabled by the technological expertise of the company. Ankit Bhati “has played a lead role in pioneering technologies such as mapping innovations, the world’s first connected car platform, and offline bookings that made Ola accessible for a large segment of the population” (Ola, n.d., para. 7).
These advancements have considerable international potential, as the world of the 21st century speaks the same language of technology. In fact, high-tech solutions can be expected to form the core of a modern company’s competitive advantage. For Ola, the new factor of technological superiority combined with the traditional aspect of sufficient financing served as the primary enabler of internationalization.
Barriers to Internationalization
At the same time, certain elements of internationalization may become considerable impediments preventing a company from reaching its full potential in a globalized society. Evidently, the range of players, who envision a global presence, is broad and it continues to become larger. In this regard, the competition is growing across the globe, posing new challenges for developing organizations. Therefore, internationalization is a highly competitive process, which requires dedication and precision on behalf of the entire company.
Cultural competence is one of the key issues faced during the new market entry. The lack thereof entails the incorrect evaluation of the location and its attributes, which, in turn, causes ineffective marketing strategies. Ola Cabs built its foundation in India, which, despite its common historical heritage, is rather distant from other Commonwealth nations in terms of culture. Aspects valued by Indian people may be neglected by the residents of Australia and the U.K or vice versa.
All things considered, the primary barrier to internationalization lies in the area of intense competition. The presence of a well-established leader in the industry on an international level may prevent new players from reaching their potential. For example, fast-food burger companies would struggle to beat McDonald’s internationally, which is equally true for the car-hailing industry in the age of Uber. Apparently, the management of Ola Cabs has considered this barrier and utilized a thoughtful, pointed model of international expansion limited to several Commonwealth markets so far.
Internationalization Model Experience
The contemporary environment possesses numerous examples of both successful and failed attempts at the internationalization of the business. The names of renowned industry leaders are known across the globe as they conquer the markets of new countries. In the case of the fast-food area, McDonald’s, Kentucky Fried Chicken, and Burger King have been actively developing their assets across all continents. These companies utilize the franchising entry mode, allowing them to combine their history and reputation with local entrepreneurs’ expertise and funds. At the same time, giants of the automobile industry, for example, acquire entire factories in new countries, which allows them to produce their vehicles abroad under their trademark.
The case of Ola and the car-hailing industry appears to be located in between these two strategies. Its distinct feature consists of the Internet-based nature of Ola’s operations. It does not need to introduce anything new physically, as such notions as cars, drivers, and taxi services exist in virtually all countries. All that is required from Ola is to introduce a new framework, which would unite drivers and passengers via the online space.
In the context of the car-hailing service industry, Uber serves as the most vivid example of successful internationalization. This company essentially became the pioneer of ride-hailing across the globe, earning the status of disruptive innovation (Dudley et al., 2017). The company’s management has been able to utilize the emerging concept of the “sharing economy,” the importance of which has been growing worldwide.
Dudley et al. (2017) write that, in order to retain the pace of its growth, Uber had to continue its expansionary business model development, rapidly entering new markets. Its technology is not unique, and local competitors could have been the first to occupy some markets, which was the case with Ola and India. In order to maintain the desired expansion rate, Uber has been actively cooperating with local ride-hailing services. This way, one party profited from the reputation of the other, whereas Uber was able to keep its global presence.
Ola Cabs Expansion Opportunities
As Ola Cabs positions itself as one of the leading competitors of Uber in the global arena, further expansion appears inevitable in the following post-pandemic years. So far, the company has been able to demonstrate a thoughtful approach to internationalization. In this regard, considering the stable financial performance of Ola Cabs, it is not desirable to change the pattern and resort to aggressive, Uber-style expansion. The company should begin by outlining the opportunities in terms of its international growth.
It is useful to investigate the potential of the world’s leading markets, such as the United States and China. However, as of now, Ola Cabs does not appear prepared for entering there due to the process requiring excessive resources while the results are not guaranteed. As of now, Ola has successfully entered three developed markets of the Commonwealth. This situation implies that the company is proficient in understanding these countries and their residents. Accordingly, it is advisable to expand to similar regions next, and Canada appears to be a viable option. It shares a similar heritage with Ola’s markets, as well as modern democratic values. In addition, Canada can become a useful starting point for potential expansion into the United States.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the case of Ola Cabs is representative of the modern internationalization demands. The expansion is conditioned by several major factors, including the rapid technological development of the human civilization, which, in turn, enables the globalization processes. Ola Cabs became an important example of a successful start-up, which was able to withhold its ambitions until the point where it was capable of truly reaching its potential. The company’s exceptional leadership has enabled stable growth in a difficult business environment of a large emerging economy. In addition, it has faced intense competition on behalf of Uber, the world’s leader in this industry.
The thoughtful assessment of the global market opportunities, combined with a precise allocation of resources, has allowed Ola to begin its internationalization in an effective way. Having established subsidiaries in Australia, New Zealand, and the U.K., the company is ready for the next stage, and Canada appears to be a fitting destination.
References
ANI Technologies Pvt Ltd. (2021). Autolytic. Web.
Dudley, G., Banister, D., & Schwanen, T. (2017). The rise of Uber and regulating the disruptive innovator. The Political Quarterly, 88(3), 492–499. Web.
Kapur N. (2019a). SoftBank fires up Ola Electric with a $250 mn capital infusion. VC Circle. Web.
Kapur N. (2019b). Ola acqui-hires AI start-up Pikup.ai to beef up deep-tech skills. VC Circle. Web.
Ola. (n.d.). About us. Web.
Pandya, U., Rungta, R., & Iyer, G. (2017). Impact of the use of mobile apps of Ola Cabs and Taxi for Sure on yellow and black cabs. Pacific Business Review International, 9(9), 91–105.
Panigrahi, A., Shahi, S., & Rathore, A. (2018). The success story of a start-up – A case study of Ola Cabs. IOSR Journal of Business and Management, 20(2), 30–37. Web.
Reuters. (2019). Ola may lay off 225 employees as SoftBank-backed firm gears up for IPO. VC Circle. Web.
Salman, S. N. (2020). Ola expands corporate travel service to international markets. Mint. Web.
Uber. (2021). About us. Web.
Zucchella, A., Hagen, B., & Serapio, M. G. (2018). International Entrepreneurship. Edward Elgar.

