Location
Selecting the right location is one of the central decisions for a small business owner. Several factors affect the choice of location for a start-up, such as the market health, the specifics of a business, loan opportunities, price of the property and rent, and access to talents. D’Angelo (2020) argues that price and loan opportunities are the central factors that usually affect the choice of location. This especially applies to businesses that do not require on-foot traffic, such as restaurants and retail (D’Angelo, 2020). However, all business needs to be considered, such as proximity to major suppliers and access to other business needs, such as availability of storage space, supply deliveries, and client meetings space (D’Angelo, 2020). Thus, a careful analysis of a business model is required to make the correct decision.
After considering the specifics of the virtual business, it was decided to settle near Amazon’s headquarters in Seattle, as it can provide the company with access to its talent pool. The virtual business does not require on-foot traffic, as the majority of business will be done online. The central factor that contributes to the selection of the location of our business was the availability of storage space and access to delivery services. Brief market research demonstrated that the warehousing and delivery markets in Seattle are booming due to the presence of Amazon in the area and the impact of the COVID-19 pandemic (the market research is not included in the present report to avoid overloading with information). Additionally, since Copious.com is expected to emulate the growth model of Amazon, it is crucial to have access to the talents.
Technology Plan
The present section outlines all the types of technologies needed to run an E-business. Technologies required for running an E-business include mobile commerce, electronic funds transfer, supply chain management, Internet marketing, online transaction processing, electronic data interchange, inventory management systems, and automated data collection systems (Rahman, 2014). Additionally, E-business uses common technology, such as e-mail, mobile devices, social media, and telephones (Rahman, 2014). The technology plan is split into several sections that group the required technologies into clusters.
Website development (Hasan, 2017):
- Web Server;
- Server Software;
- Web Tools;
- Database System;
- Networking System;
- Browser Compatibility;
- Ports.
Money transactions:
- Electronic funds transfers;
- Online banking;
- Digital payment processing system.
Communication systems:
- Customer relation management system (CRM);
- Social media access;
- Messenger access;
- Telephone;
- E-mail.
Other:
- Mobile application development;
- Automated data collection;
- Data analysis systems;
- Inventory management systems;
- email marketing platforms and print marketing;
- Shipping service integrations;
- Social media management solutions.
Required Tools and Equipment
Today’s technology does not require significant investments in equipment due to the nature of the business. Such costly pieces of equipment like servers and network equipment are not needed for small-scale E-businesses, as the equipment can be rented using clod services. Below is a list of equipment that covers the basic needs of starting a virtual business that distributes part equipment. The list was created considering all the suggestions provided by Belew and Elad (n.d.).
- Computers. Approximate cost: $1000 per employee. Personal computers are crucial pieces of equipment that help to run a business. Investing in up-to-date computers is crucial, as they improve the efficiency of operations. While the cost of the computers may differ depending on the employee’s specialization (website developers may need faster computers than the customer support team), it is still considered desirable to have up-to-date equipment.
- All-in-one printer. Approximate cost: $500. Even though the majority of correspondence will be electronic, invoices, offline marketing materials, and printouts will still be needed. Additionally, such printers can cover the basic needs of copying and scanning documents or materials. While online services can be used for such needs, investing in an all-in-one printer may be rational for flexibility purposes.
- Routers, cables, repeaters. Approximate cost: $200. These basic pieces of equipment are required to connect all the computers in one network to share the data quickly.
- Business communications. Approximate cost $1000. Business communications may include mobile phones, land phones, and faxing equipment. While all of these types of equipment can be replaced with online communication services, such as IP telephones and emails, a mix of business communication devices may still be needed.
Milestones and Measures of Success
The present section provides an outline of milestones that are crucial for measuring the success of the timeliness of business development. The list below provides the names of crucial events, approximate dates in days from the start of the project, and a description of a measure of success.
- Official project start (Day 1). The project starts off with the meeting of all the stakeholders, where it is declared open.
- Preparation stage starts (Day 2). This milestone declares the start of the preparation stage for starting the business.
- Office prepared (Day 6). By this milestone, an office is selected, all the equipment is purchased and installed, and all the office-related contracts are negotiated and signed.
- Staff hired (Day 11). All the staff required to start the project is hired by this date, including the developers, a marketing specialist, a contract manager, a financial manager, and a customer support specialist. Moreover, all the outsourcing contracts, such as accounting and legal services, should be negotiated and signed.
- Website developed (Day 30). By this date, the website is to be ready to accept orders from customers.
- The preparation stage ends (Day 31). By this date, the preparation stage is to be completed.
- Sales start (Day 35). By this date, the sales should officially start. This also includes that the marketing campaign should be properly set up and all the staff should be ready to operate.
Required Legal Actions
There are at least nine legal actions that should be made before starting an online store. A list provided below provides brief descriptions and rationale for conducting these actions. The list was developed based on the recommendations provided by Pruet (2019).
- Register a trademark. Registering a trademark before starting a business may be a costly endeavor; however, it is crucial for avoiding any problems in the future with legal liabilities in the future. Currently, Copious is an available trademark name in the US.
- Create a business entity. This step requires selecting the business structure and completing all the legal proceedings accordingly. For Copious, LLC or corporation structure seem the most appropriate.
- Acquire business licenses. It is crucial to acquire the required business licenses before starting operations if they are required. The eligibility for business licenses may differ depending on the state.
- Register for “safe harbor” protection. This step will protect the company from being legally prosecuted if any website user posts information they do not have copyrights for.
- Develop terms and conditions. This document is crucial for setting up a legal relationship with customers.
- Develop a privacy policy. This document will establish the measures utilized for protecting private data.
- Obtain a FEIN. Acquiring Federal Employee Identification Number (FEIN) from the IRS is absolutely free and skipping this step is impossible for legally running a business that hires employees.
- Open a business bank account. It is a legal requirement to have an official bank account and gives the IRS a notice that the new website is a business rather than a hobby.
- Check for copyright everything included in the website. This step saves the business from possible lawsuits in the future. It should be repeated frequently to maximize the effect.
Risk Management
Risk management is a crucial part of any project, as it helps to create contingency plans for possible adverse events. Risk is identified as a possibility of harm or loss (Meredith & Mantel, 2011). Risk management is divided into three different sets of activities, including identification, quantification and mitigation (Maylor, 2010). The risk management framework is provided in Figure 1 below.
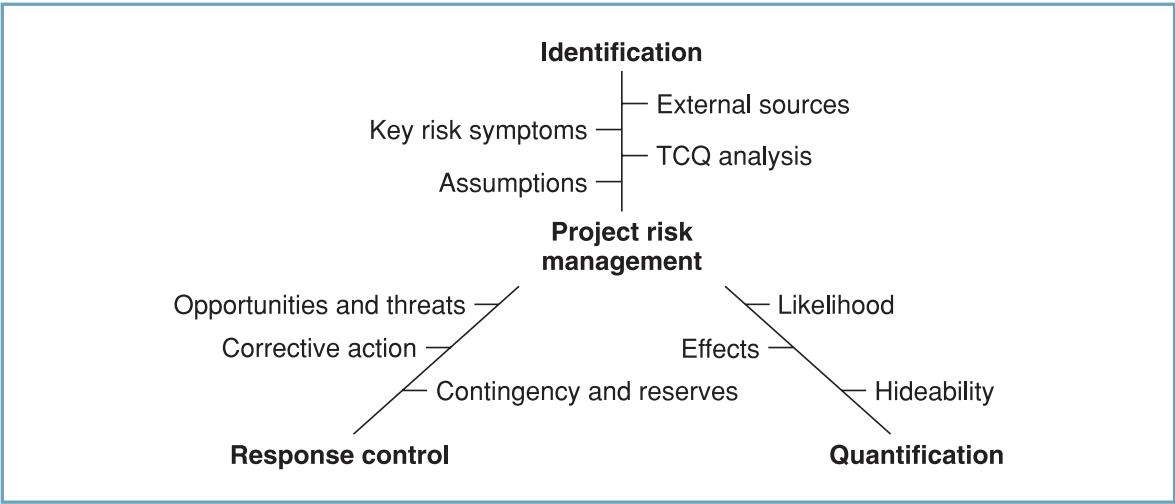
Table 1 below demonstrates identified risks, their impacts, and associated mitigation plans. The risks are also ranked in terms of their probability, impact, and priority on a five-point scale. The final score demonstrated in the sixth column (Score) is calculated by multiplying three other scores. The analysis revealed that lack of demand due to the pandemic and inability to overcome competition in the sector is the most dangerous risks associated with the project. Thus, it is crucial to implement mitigation plans before possible problems appear.
Financial Projections
Cashflow Statement
Profit/Loss Statement
Balance Sheet after 12 Months of Operations
Breakeven Analysis
Breakeven analysis requires defining the variable cost per unit and revenue per unit. Since the company will be selling three products, including eco balloons, floating lanterns, dog party supply packages, and custom supply packages, the average cost per unit and average revenue per unit were used for breakeven analysis. Table 2 below demonstrates the list of assumptions made for the analysis. Figure 2 visualizes the breakeven analysis using appropriate graphs.
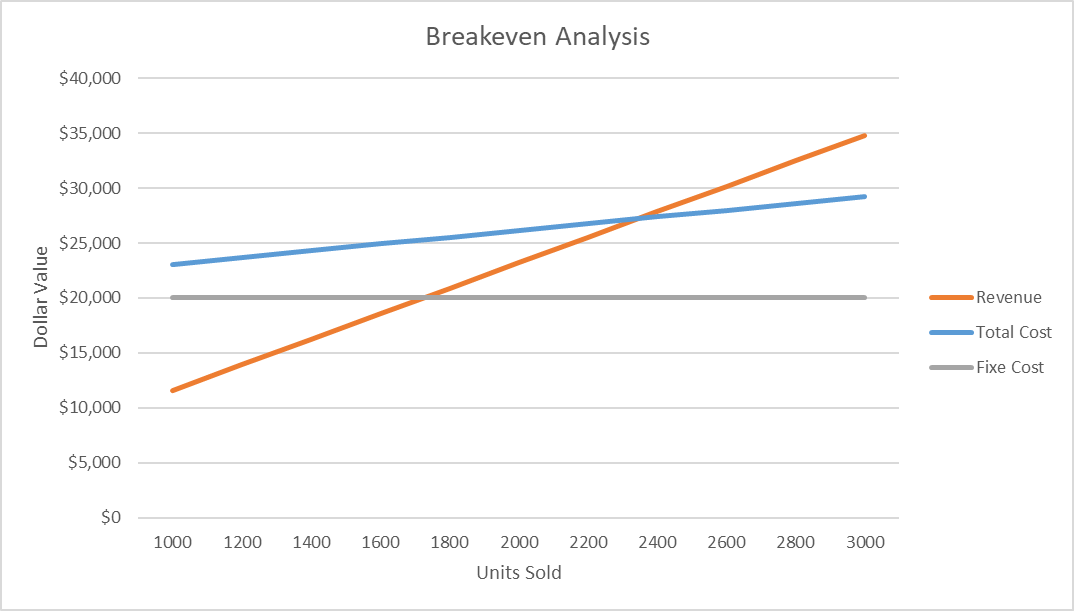
Using the following calculations, the breakeven point was established at 2,345 units.
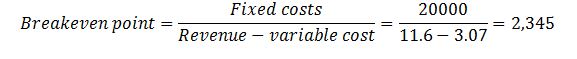
References
Belew, S., & Elad, J. (n.d.). Must-have equipment for starting an online business. Dummies.Web.
D’Angelo, M. (2020). Tips on choosing the right location for your business. Web.
Hasan, A. (2017). What technologies are needed to build an E-commerce website? Arpatech. Web.
Maylor, H. (2010). Project management (4th Ed.). Pearson.
Meredith, J. R., & Mantel S. J. (2011) Project management: a managerial approach (8th Ed.). Wiley.
Pruet, M. (2019). Important legal considerations to make before starting an online store. Volusion. Web.
Rahman, S. (2014). Introduction to E-commerce technology in business. Grin. Web.
