According to the National Bureau of Statistics of China (2008), China has gained a GDP growth of 10.2% at the end of the financial year 2007 with an average annual growth rate of Foreign Direct Investments (FDI) of 9.1% and an export growth rate of 25.4%. With such tremendous growth, China becomes one of the most impressive economies in the world. Due to the practice of dual policy of capitalism and socialism, as well as to liberalization of its economic aspects, China has turned into a more attractive place for Foreign Direct Investment. The foreign companies, however, are facing some threats here.
The Chinese government, in its turn, is also trying to minimize the threats for these companies. This paper aims to identify the threats, which foreign companies in China face, and to outline the preventive measures taken by the authorities to deal with these threats.
Overview of the Present Chinese Economy
The CIA fact sheet (2009) has registered dramatic changes in China over the past 30 years. The country has moved from the centrally planned system to a mixed economy of public and private practice simultaneously. Earlier, the internal market of China kept closed for international trade, but now its orientation has changed towards a market-based open economy. The private sector has been developing extensively; owing to the reforms of the 1970s, it started playing a major role in not only the local but also in the international market. The previous economy of the country focused on the collectivized agricultural system; it, however, has collapsed with time.
Afterward, liberalization and decentralization took place. This has significantly reduced the prices, increased fiscal policies, as well as autonomy for state business entities; in addition, liberalization and decentralization structured the banking system with high diversification, contributed to the development of stock markets and rapid growth of the private sector and made the market open for international trade and investment. The gradual introduction of the reforms into the economy of China has tangibly improved its economic performance. The following table presents the growth of the FDI over the past two years:
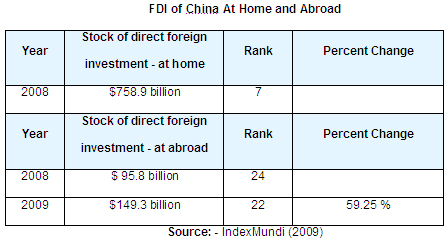
This table allows tracing a significant increase in FDI in China. Thus, in 2008, the stock of direct foreign investment constituted $95.5 billion, while already in a year it increased by $53.5 billion. This means that economic reforms in China were quite successful.
Threats Faced by the Foreign Companies
Some of the foreign investors refuse to invest in China due to certain threats that they may face. These threats are as follows:
Intellectual property rights
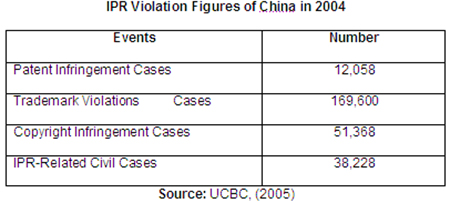
Though certain legislation concerning the protection of intellectual property rights exists in China, the government still does not pay sufficient attention to this issue. Here are some data demonstrating the present status of IPR (Intellectual Property Rights) in China:
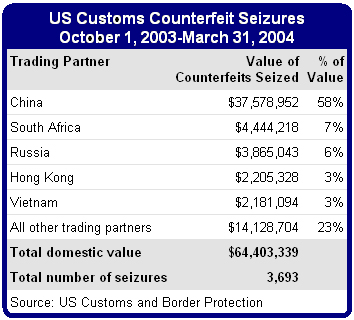
Several countries, the USA in particular, aim to fight IPR infringement. The following figure demonstrates that the value of counterfeits seized by the US customers in China is the highest, which means that the IPR infringement rates in this country are also rather high:
Thus, the cases of IPR infringement in China are numerous, which often serves as a sufficient ground for foreign investors to invest in other countries (Yu, 2007). This, however, is only one of the threats that foreign investors may face in China.
Corruption
The Chinese government has more than 1200 laws and directives against corruption. Most of them rarely find any implementation this is why the corruption rates in the country are ever-increasing. Already in the 1980s corruption affected foreign investment rates in China by striking the country’s infrastructure, real estate, procurement, and financial services. A foreign company had to pay a huge amount of money illegally to the corrupted officers before starting the business. At present, the direct costs of corruption are almost 86 billion USD per annum. Foreign investors are losing many of their strengths to maintain the monetary demands of the corrupted officers. They have to face efficiency losses for bribing and disturbance in set up; their operations are not concerning the environment or the people of the country.
Besides, the local business entities also practice corruption, which made it almost impossible for foreign investors to compete with them. Therefore, the economic reforms carried out in the country some time ago are to blame for the high rates of corruption at present and, correspondingly, for the mistrust of foreign investors (Chow, 2005). This table shows the growth of the corruption rates in the country over the past two decades:
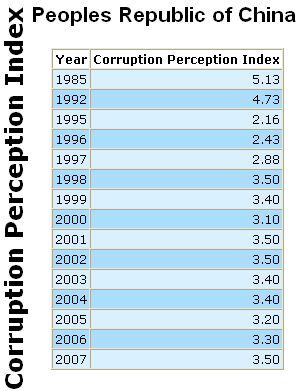
As reported by China Digital Times (2006), the sixteenth Congress of the CCP (Chinese Communist Party) has sentenced about 100 ministers and high-level officials for corruption; the total number of punished officials was 47,306. This shows that the country is trying to fight corruption, though the present high rates of it still deter the flow of foreign investments into the country.
Local competitors
In addition to the abovementioned problems, foreign investors also face high competition on the part of Chinese businesses. After entering into the free economy, the local companies acquired great autonomy, which implies that now they design their operational strategies according to their own needs. Moreover, Chinese people prefer Chinese products to international ones, which results in lower demand for these products.
Besides, there are several successful companies in China. For instance, Motorola has started its Chinese operation in 1998 and now it has to combat the China Local vendor of telecommunication products; at the same time, Motorola has to face the global major mobile phone manufacturers like Nokia, Samsung, Sony Eriksson, and LG working in China (China Contact, 2000).
Foreign competitors
All foreign companies are facing the same problems and prospects in China, but the competition among the foreign companies themselves is not the same. Some multinational companies are coming with huge investments and the operation of most of them is quite profitable. In 2006 about 81% of the total foreign companies gained satisfactory profit. Many foreign companies have marketed their products or services that may be considered national. China has now implemented the major views of WTO, which also pressurizes the competition within the foreign investors. The foreign companies face competition mainly in the case of having skilled laborers as the Chinese people prefer the local companies, rather than the foreign ones (The US China Business council, 2007).
Protectionism
Johnson (2009) argued that protectionism is a new stimulus program of the Chinese government, which is discriminating against the non-Chinese companies in China. In this program, maximum business leaders are trying to channel stimulus money nationally to national policies, which is beneficial for the local companies. Chinese authorities are also realizing that protectionism is worsening the business environment in China. Before the country entered the WTO in 2001, its export was experiencing growth, there was trade surplus, and China gained highest foreign reserve of 1.9 trillion. India announced a ban on toy imports from China. The USA is planning to get a protectionism plan against China. Thus, different companies willing to invest in China do not have government permission (Moore 2009).
Chinese Authorities and Their Attempts to Combat the Threats
The different Chinese authorities have been concerned with the threats faced by foreign companies. Numerous attempts to deal with this issue have been taken by the authorities. Here is how the central government attempts to clarify some dilemmas concerning the threats foreign investors face in China:
- Taking into account the continuous failure of matching the domestic savings and domestic demand, which leads to the decrease of social safety net comprising pension and healthcare systems, China needs high domestic savings, but it has low domestic demand.
- An increasing number of migrants face problems as they also strive to achieve jobs. This led to sustaining the job growth through welcoming the new entrants; however, this tendency is failing because of the worker layoff in the state-owned firms.
- Increasing corruption in almost every level of the business and government, all relevant entities will have to invest heavily to prevent corruption.
- The rapid transformation of the economy towards industrialization increased the destructive effects on the overall environment. These also affect the social structure of China.
Attempts took by the Chinese government to help the foreign investment are:
- Relevant legislation: The government of China takes many legislative actions to unify the internal system and some of these are:
Financial sector:
- Made open to foreign investments in future companies but restricting it with some bindings
- Extra investment allowances for security companies
Mineral resource:
China recently made some of its minerals open, which was forbidden before. Some of these are antimony, tin, molybdenum, and fluorite. Phosphorus is now in the encouraged category; the same goes for some other minerals that used to be restricted.
The other two sectors are real estate and power which are also becoming open by legislation for foreign investment. (Gump, Hauer & Feld, 2007)
- Importance of bilateral organizations: Chinese government is trying to reduce the threats by increasing the number of bilateral organizations. The countries that are practicing protectionism against China are the main targets. Recently the President of the USA Barrack Obama visited China and participated in many business dialogues. American Chamber of Commerce in China and the American Chamber of Commerce of Europe in China also sign several agreements bilaterally.
- Multilateral organizations: China has a bilateral agreement with ASEAN, which is an association of southeastern countries of Asia, through which it is trying to reduce the threats. Through ACFTA, it is also beneficial for China to invest in the ASEAN countries, which can attract investment from other countries (Rajan).
It is rather difficult to predict whether the Chinless economy would continue at the same rate of this decay because error or omission in forecasting can be more dangerous than no prediction. This paper considers that there is an exceptional prospect of the Chinese economy to continue speedy growth in future decays by conducting the Risk Assessment with the following parameters:
- Human Capital: The most significant reason for China to have continuous growth is the high amount of hard-working human capital that would work for the low wages. China possesses a skilled and entrepreneurial labor force, which is unquestionably the most valuable determinant of economic growth and a competitive advantage for China that no other country has.
- Rapid boost of Chinese Domestic Savings: Malkiel, Mei & Yang (2005) argued that domestic savings are increasing and the deposit rates are reducing, which minimizes the risk of liquidity.
- Strategies for Investing in China: China has designed lucrative investment strategies for the U.S. investors who would benefit from the sustained fast growth of the Chinese economy with such schemes as Open-End US Mutual Funds, Closed-end Investment Company Shares, and Investing through Hong Kong, Taiwan, Japan, and U.S. Companies. It also includes Direct Investment in Chinese Companies Listed Overseas, Closed-end Investment Companies Selling at Deep Discounts, Investing in Chinese Real Estate, and Investing in Natural Resources.
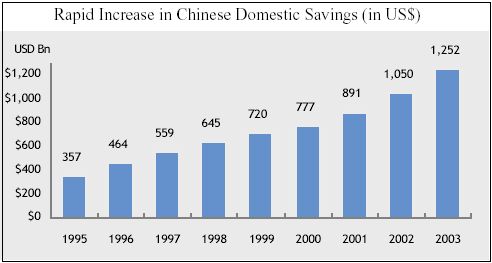
- Potential Currency Gratitude: Malkiel et al (2005) point out that investing in China may prove to be beneficial for the investors in the future because it is likely to lead to the fast growth of trade and high savings rates, which will further result in huge trade surplus and foreign currency reserve.
Current Economic Situation in China
Library of Congress (2006) argued that China’s financial system during the past 30 years has changed due to the development of agricultural sectors, rapidly growing private sector, fiscal decentralization, labor forces, GDP, FDI, improved autonomy for state enterprises, the establishment of a diversified banking system, the progress of stock markets, as well as fiscal and monetary policy. According to the Indexmundi (2009), China’s total export in 2009 is $1.435 trillion and it was $1.220 trillion in 2008. On the other hand, its total import in 2009 is $1.074 trillion and it was $904.6 billion in 2008. According to the Library of Congress (2006), the main exports products are electrical and machinery products including data processing equipment, textiles, food, seed, cars, iron, steel, and other products; key imports products are oil and mineral fuels, optical and medical equipment, metal ores, plastics, and organic chemicals and so on. The following figures show the continuing development in all sectors of its economy:
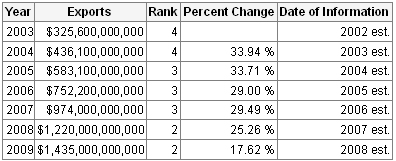
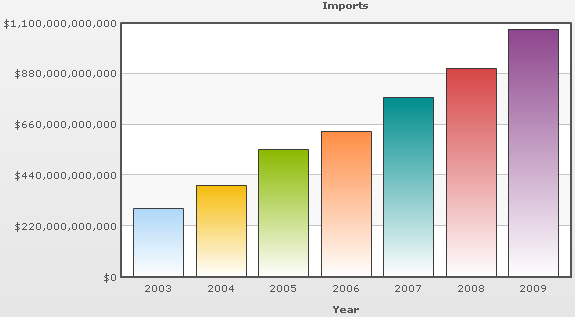
If Purchasing Power Parity of the country is taken in account, it appears to be the second prime and the hastiest growing economy internationally. The per capita income and the average annual rate is more than 8%, which is very accommodating to reduce poverty and trim down income inequalities. The per capita income of China’s people is calculated from the lower middle category, which was $3,180 USD in 2008.
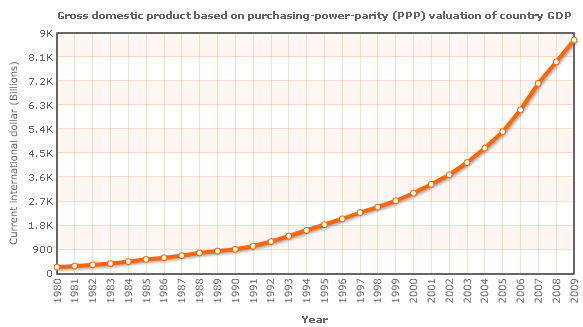
Evidence Related to Current Economic Condition of China
As per the WTO, China’s trade and economic performance has significantly improved concerning governmental and world standard policies. These policies are bringing changes from limited opening until a regional field of industries and foreign trade under the legal framework of the government of China. China’s trade opening processes have changed from one way opening to a two-sided aperture between China and WTO members that now can take part in the international market with acceptance of trade rules in a passive manner. Since China has a bilateral and multilateral situation with other countries, it has brought changes in economic and trade relations with other countries to remove disputes between them in trade actions.
These changes are very few but they still have a great impact on the future by providing new opportunities for FDI. China has become a member of WTO to fulfill the commitment of earnest and responsible changes in its economic performance. According to 2,300 laws and regulations of the government of China, it is removing tariff barriers by lowering tariff level in economic level and foreign trade, which will bring a positive outcome for its economic development (United Nations 2009).
Political Evaluation
- Currency: China is restricting the value of the Yuan about the value of the Dollar. President Barack Obama also argued to raise the value of China, but the government of China ignores it. Even the director of the International Monetary Fund suggests to keep Yuan as a stronger currency, but the government of China is raising it only by 21% against the Dollar ignoring foreign pressure (The Economist 2009)
- Importance of Bilateral Relationship: China is in the most critical position of the bilateral relationship with other regions. This approach is friendly and emphasizing more power to China. For example, for the reunification of Korea, China may deprive of South Korean investment
Economic Situation
- Stock Value: Chinese Shares are closing up 1.61%, which is slightly lower than Hong Kong. The price of the stock values of the industries is also higher in comparison with other regions.
- Funds: The funds of China’s economic market have needed to improve in terms of customers’ services. China’s funds have focused on fidelity and the raising of funds regains momentum and rebound. It is also setting up $1.32 billion for technological development.
Social Condition
- Fluctuation of Commodity Price: China is always focusing on the commodities in big cities, their properties, stock markets, etc. However, the unlikely-targeted people of China were ignoring the value of common products. Now, the foreign currency transfer has been controlled into the country for targeting them and lowering prices of these products. (The Economist 2009)
- Decreasing Public Savings: Chinese consumers are not spending too much money on commodity products, but they are buying more on their credit cards. According to the global economy, Chinese people are buying more and saving less. (Moore, 2009)
Technological Advancement
- Production of Wind Power: At present, China is the biggest producer of wind power. This wind power is now bought and sold at fixed prices as a source of electricity for the state government. (The Economist, 2009)
- Sales of Cars: The demand for passenger cars is increasing in the USA; the sales growth by 45% has been registered in 2008. Earlier, the reduction in sales could be observed due to the increasing prices of petrol. At present, however, the number of passenger cars bought is so great, that any fluctuations in sales are hard to identify (The Economist, 2009)
- Sales of iPhone in China: The sales of the Apple iPhone in China have significantly increased over the past several years. This also has a considerable effect on the development of China’s economy (The Economist 2009)
Future Prospects of China’s Economic Development
Future economic development is important in terms of growth of productivity according to long-term living standards of capital and labor improvements. Productivity growth is rather low now, but it can be improved by labor productivity which is rising by 7-8%. Within 22 years of China’s economic development, potentiality and living standards are fairly lower in economic society. However, in the 21st century, it has improved and strengthened macroeconomic conditions (The Economist 2009). To hold the development of this economy in long-term, China is adopting 10 years plan strategy from 2001 to 2010 which is targeting the following aspects:
- To sustain the rapid growth of strategic restructuring and improving quality of economic growth by increasing GDP from 2000 to 2010;
- To perfect socialist market economy and put stated enterprises according to international cooperation and competition;
- To improve the standard of life with 5% annually in disposable income of urban residents and rural residents;
- To maintain stable prices balancing international revenues and expenditures.
- To upgrade industrial structure according to the competitive edge;
- To increase urbanization;
- To develop disparity between regions with effective control.
These targets have been fulfilled according to the schedule in 2005. In addition, these plans are used as a basis for the future 2006-2010 plans which are currently under development (United Nations 2009)
China is maintaining high economic growth rates and is predicted to become the world’s largest FDI by 2010. Urbanization, technological prospects, current economic conditions have a considerable impact on its future growth. These growths are important for the aging population and costs of environmental damages with the global financial crisis in 2008-2009. Therefore, China has to focus on increasing housing, restricting credit eating, lowering taxes, increasing public investments, etc.
It has been evidenced that after long criticism for the last three decades China has turned the global economic superpower. Therefore, if the Chinese government leads its economy according to its policy, rather than according to those of the IMF or the World Bank, it is likely to meet its long-term goals for economic development.
Reference List
China Contact 2000. Wireless Application Protocol (Wap) In China: A Market Analysis. Web.
Chinalist 2009. Corruption Perception Index: China. Web.
China Digital Times 2006. Figures of China Corruption – People Net. Web.
CIA. 2009. The world fact book- China. Web.
Chow, G C. 2005. Corruption and China’s Economic Reform in the Early 21st Century. Web.
IndexMundi. 2009. Exports, Import& GDP of China. Web.
Gump, A, Hauer, S & Feld, A. 2007. China Alert. Web.
Johnson, I. 2009. Foreign Businesses Say China Is Growing More Protectionist. Web.
Library of Congress 2006. Country Profile: China. Web.
Moore, M. China leads the way in protectionism. Web.
Moore, M 2009. If Chinese consumers aren’t spending, why do they have unpaid credit card bills?. Web.
Malkiel, BG. Mei, J & Yang, R 2005, Investment Strategies to Exploit Economic Growth in China. Web.
National Bureau of Statistics of China, 2008, Principal Aggregate Indicators on National Economic and Social Development and Growth Rates. Web.
Rajan, R. n.d. What Does The Economic Ascendancy Of China Imply For Asean? Web.
The Economist 2009. Investors are breathless over China’s biggest developer of wind farms. Web.
The Economist 2009. Car sales up, petrol sales flat: stockpiling, fuel-efficiency, or simply lousy data?. Web.
The Economist 2009. Chinese firms are making and exporting ever more suspect phones. Web.
The Economist 2009. The price also stinks. Web.
The Economist 2009. Why China resists foreign demands to revalue its currency. Web.
The Economist 2009. The president pays Asia the compliment of courtesy; rewards are not immediate. Web.
The Economist 2009. China’s rapid growth is due not just to heavy investment, but also to the world’s fastest productivity gains. Web.
The US China Business Council 2007. Foreign Investment in China. Web.
United Nations 2009. China’s Economic Development. Web.
United Nations 2004. Minister: Five Positive Changes for China’s Opening to Outside World. Web.
UCBC 2005. Intellectual Property Rights in China: Background and Figures. Web.
Yu, P 2007. Intellectual Property, Foreign Direct Investment and the China Exception. Web.

