Summary
This paper explores the topic of process improvement via total quality management (TQM). To achieve the stated objective, the paper explores the various tools that are currently being applied by businesses to improve their overall performance. Contemporary organizations deploy TQM tools to improve their processes to maximize their overall turnover and to increase their market shares. This paper explores three major tools that firms in the UAE use to boost their productivity.
The three tools are Six Sigma, lean manufacturing, and dashboards. The choice of UAE firms is informed by the view that the currently published works of literature have not captured in detail the total quality management strategies that firms in developing countries can use to streamline their operations. The paper uses case studies of various companies in the UAE to show how the application of TQM tools has helped to boost their operations and productivity.
Introduction
The contemporary business environment is characterized by stiff competition where businesses strive to outsmart each other and/or gain a profitable market share. Consequently, firms are utilizing every tool at their disposal to gain a competitive advantage. One of the concepts that are increasingly being adopted by firms to improve their processes is total quality management (TQM). The concept refers to the process of aligning the objectives of the company with its resources. Using the concept, managers and employees work together to formulate the business goals and to develop strategies for measuring performance during different stages (Pyzdek & Keller 2014).
Various studies have established a direct connection between TQM and companies’ growth in revenue. This paper discusses the various total quality management tools that are applicable to businesses based in the United Arab Emirates (UAE). The paper specifically explores the following process improvement techniques: Six Sigma, lean manufacturing, and dashboards.
Research Questions, Aims, and Objectives
This paper aims to add to the existing literature regarding the role of TQM in process improvement. In the past, researchers have explored the topic with reference to organizations operating in developed countries while ignoring firms in developing countries. This situation has created a gap in the knowledge about the useful application of total quality management techniques to improve performance. In light of the observation, this paper explores the issue with reference to a developing country, the UAE. It is important to note that the exploration of the topic with reference to firms in developed countries may not reflect the actual situation in the upcoming states. This issue underscores the need to research the topic using firms in developing countries to have results that are more reliable. To achieve the stated objective, this paper explores the following hypotheses:
- H1: There is a direct relationship between total quality management and process improvement, customer satisfaction and the profitability of a company.
- H2: There is no direct relationship between total quality management and process improvement, customer satisfaction and the profitability of a firm.
In light of the mentioned hypotheses, this paper seeks to answer the following research question:
- Q: Why and how do firms in the UAE utilize the concepts of total quality management to streamline their processes?
Literature Review
Numerous works of literature have recently emerged regarding the topic of total quality management. Chakravarty, Grewal, and Sambamurthy (2013) propose the use of dashboards to manage quality in an organization to achieve customer satisfaction and profit growth. Generally, dashboards denote a set of equipment that facilitates the monitoring of multiple activities contemporaneously from a central location.
The dashboard technology was first introduced in the automobile industry. However, it is slowly penetrating other industries, apparently due to the need to monitor the progress of different activities from a single point. Dashboards streamline a firm’s decision-making process to improve customer experience in the backdrop of the stiffening rivalry in the international business environment. Dashboards allow communication between the various stakeholders of a company, a situation that makes things clear and easily understandable by the people concerned. According to Mello (2015), dashboards give employees freedom of speech, hence empowering them to express their views for inclusion in problem resolution processes.
The other total quality management tool that has speedily gained acceptance in the contemporary business environment is the Six Sigma. Pyzdek and Keller (2014) define the Six-Sigma concept as a total quality management methodology that is designed to help a firm to achieve customer contentment by offering first-class goods and services. The primary objective of applying this methodology is to improve the quality of the products and services to achieve customer satisfaction.
Under the concept, managers engage employees in the process of formulating business goals and the strategies to achieve them. Teamwork is considered an essential component during the process of executing the strategies. Communication between the stakeholders involved in executing the strategies is a common phenomenon (Barone & Franco 2012). Managers who embrace the Six-Sigma approach often hold numerous meetings with employees. In such meetings, departmental managers report on the progress of each function. Controls are used to assess the achievement of the goals at different stages to ensure that the organization achieves the desired targets.
Other than the concepts that have been discussed above, some companies also employ the lean enterprise system to streamline their operations and to reduce the overall operations costs. According to Myerson (2012), the lean system is a total quality management methodology that seeks to eliminate all processes that do not add value to a company, although they enhance the operations costs. The primary objective of employing the strategy is to remove all undesirable costs. In other words, the lean approach seeks to not only lower the operations costs but also reduce the prices of goods. It is important to note that price is one of the determinants of the demand for a good or service. Goods that sell at a considerably low charge tend to have a higher demand compared to those that retail at higher prices.
However, although companies are compelled to sell their products at reduced prices to maximize their market shares, they have to set a good markup to remain profitable. The only way they can sell their products at lower prices without compromising profitability is by eliminating unnecessary costs. The elimination of such costs is only achievable by employing the lean enterprise system.
Case Studies
The Abu Dhabi National Oil Company is one of the leading distributors of oil in the UAE. In 2011, the company realized that the average rig move time for its fleets exceeded the maximum acceptable time of 4 days by about 25% (Al Kind & Al Lawati 2014). The extended time was largely attributed to the lack of proper quality control measures, a situation that led to the application of Six-Sigma and lean strategies. A team consisting of experts in the field of quality management was tasked with the role of implementing the mentioned techniques in the company. The team applied the DMAIC (Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve or optimize, Control) strategy to identify the processes that needed to be streamlined. Figure 1 below shows the DMAIC framework.
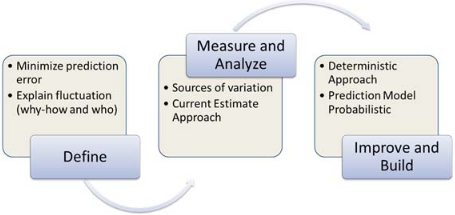
The company achieved a reduction in the rig move time from the initial 5-7 days to an average of 3.7 days. This improvement illustrates the effectiveness of the Six-Sigma and lean concepts in helping a firm to achieve savings while maintaining the original quality of its products.
The National Drilling Company is a contractor firm, which operates in the UAE. Most of its machines are procured offshore, implying that it has to maintain a warehouse to store the imported goods. In 2011, the company realized that it was not meeting its customer needs, a situation that was largely attributed to poor inventory management. For example, some of the inventory items became obsolete before the company could utilize them.
The company started employing the Six-Sigma technique to manage its inventory. The strategy greatly reduced the inventory days and the lead-time, hence illustrating the power of the stated quality management technique (Al Kindi & Al Lawati 2014). In the recent past, the company has introduced dashboard technology to monitor different activities from a central point. The technology has drastically increased the interaction between managers and employees. The approach has led to better decisions by the firm.
The function of Abu Dhabi Health Services Company (SEHA) is owning and managing the public healthcare system in UAE (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016). The government had high expectations from the hospitals which they could not always achieve. The top priorities of the healthcare system were accessibility and waiting time (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016). Hospitals could not meet the patients’ needs in many spheres, and solutions had to be sought to reach the best outcomes for the customers and healthcare providers. In 2015, lean manufacturing was employed in a government hospital in Abu Dhabi city, UAE.
The hospital’s aim was to be able to cope with a growing number of prescriptions and patients and enhance the waiting time possibilities (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016). To meet these challenges, the hospital’s authorities decided to implement lean manufacturing. The project was called “Outpatient pharmacy Kaizen project” (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016). The management team had to start by outlining the weak areas and the ones which required improvement. Figure 2 below shows the conceptual model designed for the implementation of lean manufacturing in the public hospital.
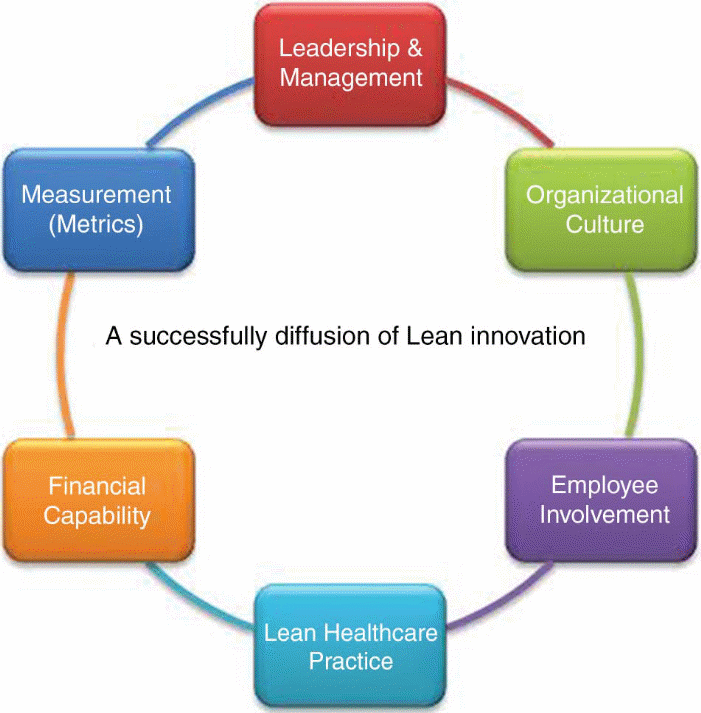
The suggested framework consisted of the following elements: leadership and management, organizational culture, employee involvement, lean healthcare practice, financial capability, and measurement (metrics) (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016). To succeed in implementing lean manufacturing, a multidisciplinary team was organized, which was responsible for creating the most productive plan of action. With the help of lean manufacturing, the team used small “Plan-Do-Check-Act” cycles, which helped to test the proposed alterations and see the outcomes at every stage (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016, p. 28).
The most significant achievement of implementing lean manufacturing was a significant reduction in patients’ waiting time. However, there were other essential changes. Lean manufacturing made it possible to empower the staff and enhance their job satisfaction and morale. Moreover, lean manufacturing developed the employees’ self-confidence and desire for innovative and creative ideas (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016).
The results of the innovations were astonishingly positive. The waiting time decreased from 45-60 minutes to 4-6 minutes. Thus, the results of the project not only reached but even surpassed the initial predictions. The role of each element of the framework was important in reaching the goals of the experiment with lean manufacturing. The role of senior management was the most responsible one, as it established the priorities, gave directions, carried out the innovative “Lean reverse pyramid” leadership model, and empowered the employees (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016, pp. 29-30).
Leadership performed such major functions as altering the organization’s culture and scheduling the setup of lean management. Next, the leadership team implemented lean manufacturing and supported it by providing the sustainability of the project. An important step in the implementation of the project was arranging a favorable organizational culture at the hospital (Abuhejleh, Dulaimi & Ellahham 2016). With that aim, the management team empowered the employees, initiated their participation in the decision-making process, encouraged them to work in a team, and, most of all, inspired the staff to realize that patients’ needs were their first concern.
As a result, lean manufacturing has proved to be an extremely successful innovation. It helped to decrease the patients’ waiting time and empower the caregivers. Profitable implementation of lean necessitated a combination of the endeavors of the staff and the leadership team.
Discussion/Conclusion
The literature review has unraveled the total quality management techniques employed by major companies operating in the UAEs. The results indicate three major total quality management techniques that are used by firms in the region to maximize their market shares and to make favorable profits. The discussed strategies, namely, Six-Sigma, lean manufacturing, and dashboards, are all designed to improve companies’ performance. The first one, Six-Sigma, is designed to help a firm in gaining a competitive advantage by producing high-quality goods and services. The technique is applicable to any company.
It is largely based on the concept of customer-centered goods and services. Each employee of the firm has a role to play to ensure that the firm achieves its primary goal of maximizing the quality of goods and services offered. Managers who uphold the Six-Sigma approach regularly communicate with employees to establish business goals and to track the achievement of the goals at different stages.
The second technique, lean enterprise system, refers to a total quality management technique whose target is to eliminate all the unnecessary activities in a production system. Based on the literature review, the concept is based on the assumption that low-priced goods are more attractive to customers, as opposed to the highly-priced ones. The concept is crucial to modern firms, which operate in an environment that is characterized by stiff rivalry. Lastly, the study found that companies also utilize dashboards to increase the quality of their products and services. Dashboards are technologically designed to facilitate the contemporaneous monitoring of several activities from a central point. Organizations, which use dashboards to manage their activities, are usually successful since all activities are tracked at different stages to mitigate any deviations.
Recommendations
Al Ghurair Group is an investment company whose main offices are located in Dubai. The company engages in three types of businesses, namely, manufacturing, real estate, and investments. In the past, the company has experienced problems in its decision-making, a situation that has led to slowed task execution processes. This issue may be harmful to the organization’s performance. This paper proposes the implementation of the dashboard and the Six-Sigma technologies in the company to fasten its decision-making. If implemented, the dashboard technology and the Six-Sigma techniques will increase interaction between the firm’s managers and employees. If the company introduces dashboard technology, employees will be able to air out their views on how best the organization must be run for it to achieve the set goals.
The TQM tools will largely contribute to a greater performance of the organization both in the short and long term. Employee involvement in the decision-making process is essential since it introduces a wide variety of ideas that may be helpful in assisting managers in making informed decisions (Barone & Franco 2012).
Additionally, according to Chakravarty, Grewal, and Sambamurthy (2013), employees are more motivated to work hard to achieve goals, which they formulate by themselves, as opposed to those imposed on them by the management. This finding underscores the need for the implementation of both the dashboard and the Six-Sigma techniques in the company to improve its performance. However, the company may also utilize a lean enterprise strategy to maximize its profits without compromising the quality of the goods. Under the strategy, through consultation with the functional managers and the employees, the company should identify all the functions that are not directly associated with production. Such activities should be scrapped to lower the operations cost to facilitate the execution of the low pricing strategy.
Reference List
Abuhejleh, A, Dulaimi, M & Ellahham, S. 2016, ‘Using Lean management to leverage innovation in healthcare projects: case study of a public hospital in the UAE’, BMJ Innovations, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 22-32.
Al Kindi, M & Al Lawati, M. 2014. Framework to implement six-sigma methodology to oil and gas drilling budget estimation. Web.
Barone, S & Franco, E. 2012. ‘Six sigma methodology,’ Statistical and Managerial Techniques for Six Sigma Methodology: Theory and Application, vol. 5, no. 7, pp.1-21.
Chakravarty, A, Grewal, R & Sambamurthy, V. 2013. ‘Information technology competencies, organizational agility, and firm performance: enabling and facilitating roles’. Information Systems Research, vol. 24, no. 4, pp. 976-997.
Mello, J. 2015. Strategic human resource management, Cengage, Boston.
Myerson, P. 2012. Lean supply chain and logistics management, McGraw-Hill Education, New York City.
Pyzdek, T & Keller, PA. 2014. The six sigma handbook, McGraw-Hill Education, New York City.
