Introduction
Human resources management requires not only following appropriate algorithms for controlling employees’ activities but also maintaining objective and adequate recruitment mechanisms. Hiring staff is a crucial task because, in addition to assessing the professional abilities of applicants, HR specialists are obliged to determine the individual traits of future employees. In addition, due to a variety of tools and practices used in this field of activity, specific recruitment principles promoted in a particular company may not meet the current development goals and can be ineffective. In this regard, it becomes necessary to identify the key weaknesses of the current recruitment strategy used in the organization and draw conclusions concerning the opportunities for improving this industry through effective intervention strategies.
An opportunity to strengthen recruitment practices through specific change steps is a significant objective in the context of the current gaps. According to CIPD (2017), most private organizations seek to devote more budget funds to develop strategies for hiring talented and promising employees. At the same time, the use of modern resources as tools for recruitment is a potentially productive activity.
One of the possibilities is to hire staff through social networks and other digital platforms. As Bagheri Rad, Valmohammadi, and Shayan (2020, p. 517) note, in their study, about 75% of the companies surveyed utilize social networks as a source of interaction with applicants. This result proves that applying for the capabilities of digital technologies can help expand the quality of tactical recruitment solutions and attract more active potential employees.
As a result, the purpose of this report is to identify how modern tools for recruitment may be used by the HR department of the organization. A set of objectives is planned: a literature review will be conducted to review the existing findings in relevant sources, ways to optimize recruitment policies will be assessed, and recommendations to stakeholders will be offered. As interested parties, line managers, HR specialists of the department, IT employees, and senior managers will be involved. An adequately organized online recruitment policy using the appropriate principles of personnel selection is a valuable tool for ensuring the stable operation of the company with the involvement of competent and talented specialists.
Literature Review
The predominant number of selected academic sources for review considers modern recruitment strategies through digital technologies and, in particular, social media as convenient platforms for interacting with candidates. Bagheri Rad, Valmohammadi, and Shayan (2020) analyze such activities as a process that is characterized by low costs and quick communication with applicants due to the ubiquity of virtual interaction. The key emphasis is on online solutions with the involvement of social media.
The authors consider traditional recruitment mechanisms, which makes their results credible and allows comparing individual criteria regarding the selected variables, in particular, education, gender, behavior, and other personal characteristics (Bagheri Rad, Valmohammadi, and Shayan, 2020). As a conclusion, ideas are suggested about the value of communication through online platforms, and the initial hypotheses about the productivity of social media recruitment are proved by using numeric data.
In the study by Chang and Chin (2018), the authors focus on the perceptions of HR employees and job applicants of the existing recruitment practices and draw attention to job applicants’ expectations. In particular, the researchers evaluate what factors are significant for both categories involved and assess the interaction between HR commitment as a valuable feature with the indicators of future employees’ satisfaction (Chang and Chin, 2018).
However, despite detailed charts and statistical correlations, the results of the assessment are not complete. For instance, in Figure 1, a detailed employee selection process is described, which includes all the stages of interaction with applicants (Employee selection process, 2015). Chang and Chin (2018) use only a few criteria, which is a limitation and does not allow evaluating all the steps of interaction with job seekers based on satisfaction with the proposed conditions. As a result, the outcomes of the study are limited by individual criteria, in particular, HR commitment as one of the main evaluated variables.
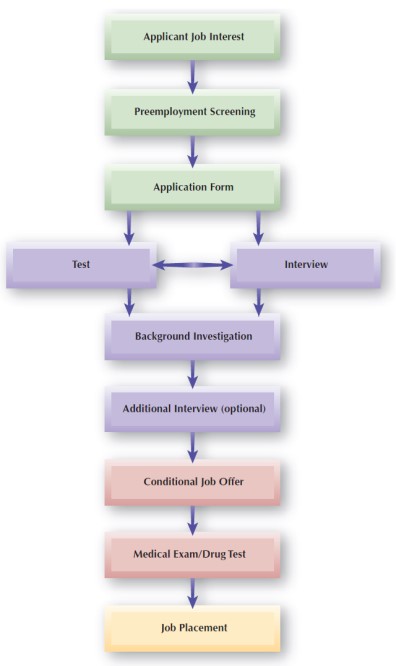
Individual academic resources consider recruitment in the context of the practice that is important from the perspective of the tools used but not a program as a whole. In particular, Gravili and Fait (2017) evaluate this practice based on strategies for building relationships between HRs and job applicants and tracking interactions among many variables.
This source is credible and valid since, in addition to analyzing the existing approaches, the authors draw attention to the manifestations of individual communication mechanisms and their impact on staff performance (Gravili and Fait, 2017). As additional justification elements, numeric formulas are utilized to calculate possible correlations and find out how hiring can take place under different circumstances and strategies.
In order to assess various manifestations of recruitment and its role in the work process, comparing individual practices from different work environments is a valuable activity that allows evaluating the implications of relevant approaches to hiring personnel. Peltokorpi and Jintae Froese (2015) focus on the Japanese labor market as a sphere that is relatively equidistant from European and American work trends. The results of the analysis are non-standard: about 90% of local companies rely on college recruitment as one of the main tools for finding future employees (Peltokorpi and Jintae Froese, 2015, p. 427).
Given that the digital base is significantly developed in the country, this figure is unique. At the same time, foreign companies operating in the state vary their recruitment strategies, although Peltokorpi and Jintae Froese (2015) do not provide specific comparative data. The value of this study is its ability to assess differences in the approach to the recruitment mechanism in distinctive work environments.
The global context of recruitment as an approach to the selection of talented employees is a significant area of research, and Banks et al. (2018) focus on the analysis of multinational companies’ techniques. According to the results of evaluating and obtaining empirical data, more than 98% of employees of various corporations used the websites of their companies as job search sites (Banks et al., 2018, p. 480).
One of the limitations of this study is that countries with successful economies and large GDPs are assessed – the USA, Canada, the UK, and some other developed states. However, based on the topic of the article, analyzing the manifestations of unique recruitment practices is a valuable way to determine what common and distinctive features exist. According to the results, the use of the Internet as a recruitment tool is a widespread and potentially effective practice.
Gelinas et al. (2017) focus on the growing role of social media as platforms that are utilized for recruitment purposes. The authors consider this practice from an ethical point of view and note that today, there are gaps in the regulation of approaches to this principle of personnel selection (Gelinas et al., 2017). In particular, the management of online communication of HR specialists with applicants should be maintained within a special framework that meets the criteria of business interaction.
This is not always easy to ensure due to a small experience of individual enterprises in conducting such activities, although the growing interest in social media from the perspective of recruitment is proved. As an omission, one can note an insufficient number of real examples and the use of abstract situations that simulate the conditions of utilizing social media in recruitment. For instance, in Figure 2, relevant statistical data are provided, which highlights the significance of virtual interaction in different companies’ hiring policies (Social media usage in recruitment, 2017).

The dynamism of the recruitment process is the main topic discussed in the article by El Ouirdi et al. (2016). The researchers pay particular attention to the virtual communication of HR specialists with job seekers and state that there is a lack of information on the value of this approach (El Ouirdi et al., 2016).
Although many criteria and factors are mentioned, for instance, personal characteristics, there are no examples of specific companies, which would be logical in such a study. Basic comparisons across countries are carried out, which allows assessing the prevalence of online recruitment practices. From a managerial perspective, this study can be of practical use due to a detailed algorithm for analyzing specific conditions that are necessary for hiring personnel via the Internet.
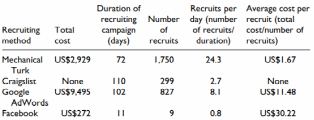
Finally, as examples of real companies using recruitment through social media, Antoun et al. (2015) propose to consider the practices of individual organizations. The authors provide the statistics on the funds spent on this work and compare the number of applicants who have applied, and in Figure 3, these data are presented (Antoun et al., 2015). This study proves that applying this recruitment principle is a common practice among large companies and can be used as a key recruitment strategy.
Stages of the Research Process and Primary Research Approaches
Any research work requires complying with a special algorithm that allows not only adhering to the chosen work strategy but also implementing renewed programs or concepts by ethical, business, and other standards. In particular, the activity of introducing changes or studying individual techniques may be divided into the eight most significant steps. About primary research approaches, interviews and surveys should be identified.
Stages of Research
To begin with, the problem is identified, and stakeholders as initiators of the study are defined, for instance, the CEO of the company or the analytical department. Further, the evidence base is collected and considered, which corresponds to the standard principle of a literary review. After that, the issue is explained based on the findings obtained from credible sources. Key objectives are set, and tasks are planned based on these goals. As a subject of research, a corresponding category of the population is selected as a sample. The data obtained are analyzed by using suitable data collection tools. Specific results are made, which prove or disprove the original hypotheses. Finally, an evaluation algorithm is proposed in order to monitor a specific area after the research and obtain data on the validity of the work performed.
Primary Research Approaches
Among a variety of approaches to data collection, primary methods are an individual area that involves direct interaction with the target audience to obtain objective and reliable data. As such tools, interviews and surveys are the most commonly used practices. Interviews provide an opportunity to review the information that reveals respondents’ specific attitudes towards a particular phenomenon or topic. The advantage of this method lies in the possibility of direct interaction, which increases the reliability of data acquisition. However, results may be biased due to respondents’ personal beliefs.
Surveys, in turn, are a more general principle of analysis and help compile the results of studies based on the analysis of the total number of respondents’ opinions. They help carry out large-scale research and get a wide range of opinions, but in order to obtain the most accurate data, clearly structured evaluation mechanisms are required. Both practices may be applied to qualitative and quantitative studies successfully. The difference is that in the first case, the responses of the target audience are the main assessment tool, and in the second one, statistical correlations in accordance with the analysis are compiled and reviewed.
Summary of the Findings and Recommendations
Based on the review of suitable academic literature, relevant conclusions may be drawn, and recommendations can be made to interested parties. Firstly, using social media as a tool for recruitment is becoming an increasingly common practice that should not be avoided. However, effective hiring mechanisms should be designed to eliminate errors and maximize productive engagement with job seekers. Secondly, the parties involved, in particular, HR specialists, should have an idea of the features of online business communication in order to use available resources competently. Regarding costs, significant expenses are not required to establish an effective system of interaction with future employees.
Most company websites have appropriate forms to fill out, which can be modified to create robust response programs for job seekers. While taking into account the remote nature of communication, a detailed assessment system should be developed to make the selection regime as correct and ethically sound as possible. Otherwise, errors can be made, which may affect the organization’s performance outcomes.
The review proves that many modern companies are ready to implement the online recruitment methodology, including large global corporations. Moreover, statistical reports confirm the convenience of such an algorithm and relatively low costs compared to complex hiring practices. The entire development and implementation process, including the creation of a digital platform and interaction with applicants, can take about two months since testing is to be conducted.
Interested parties, in particular, line managers, HR specialists, IT employees, and senior managers, can evaluate the capabilities of the online method through a presentation designed specifically to demonstrate the work of the project. Based on questions and clarifications from the parties involved, appropriate corrections and optimization solutions may be proposed to improve the potential of the system.
Business Report Formulation
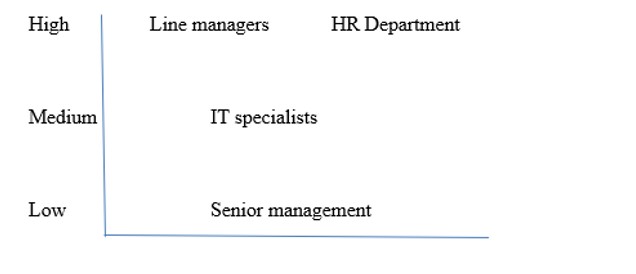
In order to present the business report to interested parties, in the presentation, an appropriate justification should be offered. In this project, real indicators of individual companies can be given, for instance, the data from Google and other large corporations, as well as the prospects for introducing an updated recruitment program. For this purpose, the project control mode and degree of responsibility may be displayed in the corresponding scheme to determine how the optimization project will be monitored. In Figure 4, an appropriate algorithm is presented, which shows how the stakeholders can be involved and what degree of responsibilities they have.
Conclusion
Applying a formulated and designed online recruitment practice is a valuable methodology for engaging active and talented professionals. The analysis proves that many modern companies implement the possibilities of this hiring policy successfully. Due to the conducted literature review, relevant recommendations may be given to interested parties, including line managers, IT employees, HR specialists, and senior managers. In particular, the degree of responsibility for specific intervention procedures should be determined in advance, and a clear evidence base is to be prepared.
All the parties involved need to be aware of the importance of the optimization program to follow the plan effectively and use their professional potential adequately. Assessing the stages of the research process and primary research methods is a useful activity that helps determine how changes occur in organizations and what tools of interaction with the target audience can be utilized.
Reference List
- Antoun, C. et al. (2015) ‘Comparisons of online recruitment strategies for convenience samples: Craigslist, Google AdWords, Facebook, and Amazon Mechanical Turk’, Field Methods, 28(3), pp. 231-246.
- Bagheri Rad, M., Valmohammadi, C. and Shayan, A. (2020) ‘An empirical investigation of the factors affecting the use of social networks in human resources recruitment’, International Journal of Public Administration, 43(6), pp. 517-526.
- Banks, G. C. et al. (2018) ‘Strategic recruitment across borders: an investigation of multinational enterprises’, Journal of Management, 45(2), pp. 476-509.
- Chang, E. and Chin, H. (2018) ‘Signaling or experiencing: commitment HRM effects on recruitment and employees’ online ratings’, Journal of Business Research, 84, 175-185.
- CIPD (2017) Resourcing and talent planning. Web.
- El Ouirdi, M. et al. (2016) ‘Technology adoption in employee recruitment: the case of social media in Central and Eastern Europe’, Computers in Human Behavior, 57, pp. 240-249.
- Employee selection process (2015).
- Gelinas, L. et al. (2017) ‘Using social media as a research recruitment tool: ethical issues and recommendations’, The American Journal of Bioethics, 17(3), pp. 3-14.
- Gravili, G. and Fait, M. (2017) Social recruitment in HRM: a theoretical approach and empirical analysis. Bingley: Emerald Group Publishing.
- Peltokorpi, V. and Jintae Froese, F. (2015) ‘Recruitment source practices in foreign and local firms: a comparative study in Japan’, Asia Pacific Journal of Human Resources, 54(4), pp. 421-444.
- Social media usage in recruitment. (2017) Web.
