Introduction
Human resources (HR) management plays an essential part in the general field of business administration, and there have been several significant changes in the industry recently. One of them is the continually increased necessity of retraining and reclassification of personnel. Digitalization, globalization, the prevalence of automated processes, and the consequences of the COVID-19 pandemic have transformed the approach to business administration. As a result, the managers need to ensure that all employees are appropriately trained and educated regarding innovative technologies and remote work. Ultimately, the current essay thoroughly analyzes digitalization and COVID-19 consequences that led to the increased need for retraining in recent years.
Work in Digital Age
The first reason for the necessity of retraining is the continual development of innovative technologies and the implementation of digital alternatives. The recent research demonstrates that approximately 14% of workers globally will have to switch occupations or even industries due to the process of digitalization by 2030 (Illanes et al., 2018). A large number of manual labor jobs are being substituted with technological analogs, and people have to either adapt and relearn or change occupations. The problem is further complicated by the aging population and a large number of people not wanting to acquire new skillsets. The experts compare the current situation with the shift from agriculture to manufacturing at the beginning of the 20th century; however, the complexity of required competencies has increased (Illanes et al., 2018). Unlike relatively straightforward manufacturing, digital solutions require comprehensive education and additional training for employees to adapt to the current technologies. Therefore, the problem of retraining and reclassification is more relevant today than it has been over the last century.
From these considerations, the problem of necessary retraining has emerged, which is crucial to the general field of business administration. The executives of private sector organizations in the United States and Europe acknowledge the problem and consider retraining an organizational priority (Illanes et al., 2018). Figure 1 below demonstrates the overall response of managers and analysts to the issue:
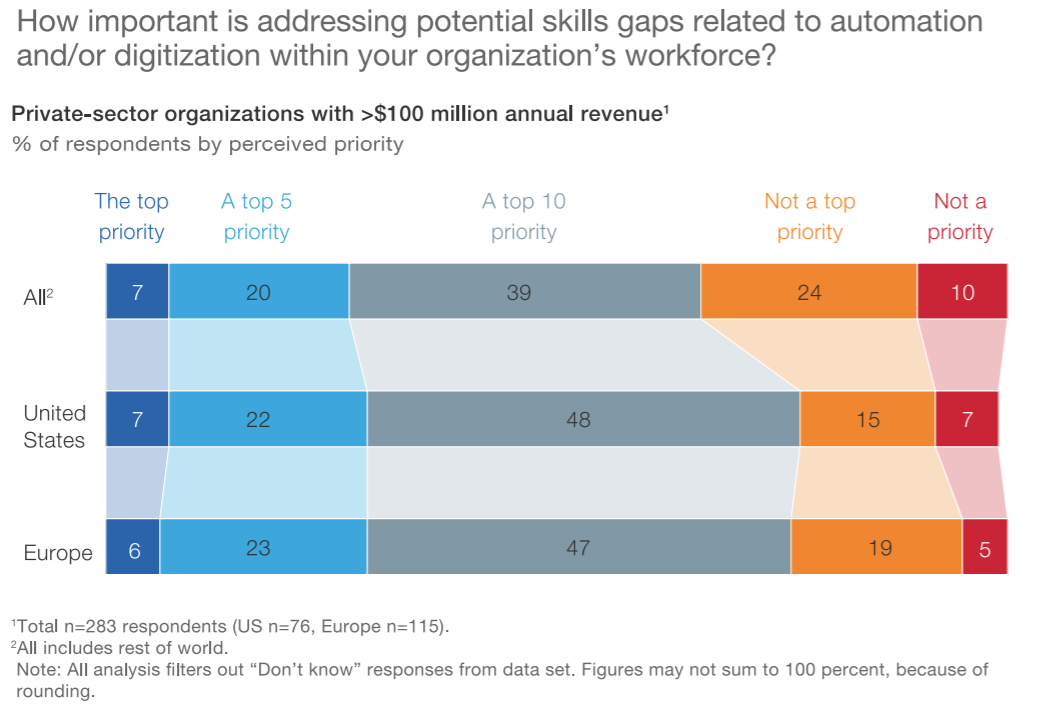
Furthermore, the research reveals that almost two-thirds of managers consider retraining or replacing some of their employees by 2023 due to digitalization (Illanes et al., 2018). Consequently, the problem is complicated by the low levels of preparation in most organizations. Regardless of benefits, automation of operational processes is a highly complex approach, and only 16% of companies state that they are ready to retrain their personnel to meet the required competencies (Illanes et al., 2018). In other words, the increased need for retraining is one of the most relevant changes in recent years, which requires the cooperation of managers and researchers to solve the problem.
The Consequences of COVID-19
The second significant cause is the disruption of traditional operations by the COVID-19 pandemic. The spread of the disease and contamination risks forced many companies to adjust their processes to remote work (Henry et al., 2020). Evidently, this change requires the employees to acquire new competencies, which might pose many difficulties for aging workers (Henry et al., 2020). Furthermore, the experts agree that the adjustments made due to the pandemic would not be reverted even after the global vaccination (Lund et al., 2021). Therefore, most companies will retain remote and automated processes, which would create the increasing necessity for retraining. Consumers will also shift to e-commerce and digital solutions, which would increase the demand for competent professionals in most industries (Lund et al., 2021). For instance, the current growth of e-commerce is approximately two to five times faster than before the COVID-19 pandemic (Lund et al., 2021). Ultimately, the analyzed changes enforce the need for competent experts and, thus, the necessity of retraining.
Consequently, the COVID-19 pandemic has had an immense impact on global health, national economies, supply chains, and resource management. All the consequences change the daily lives of most people and disrupt conventional work operations (Zou et al., 2020). From these considerations, effective management with a focus on retraining personnel rather than searching for new talents is highly relevant (Zou et al., 2020). Most companies, specifically small- to medium-sized organizations, experienced an economic downfall due to COVID-19 and might have insufficient funds to hire competent professionals (Zou et al., 2020). Therefore, the economic disruption due to the pandemic also stimulates managers to find solutions concerning personnel retraining and reclassification.
Conclusion
Digitalization and a more recent occurrence of COVID-19 have significantly changed the approach to HR management and retraining of personnel. The said causes require employees to receive comprehensive education concerning innovative technologies, methods of remote work, and even new ways of social interaction. However, a large number of people are unwilling to retrain and might have to change occupations to less automated industries. As a result, the necessity of retraining caused by digitalization and COVID-19 is one of the most relevant changes in business administration in recent years. Therefore, the researchers and managers will need to cooperate to find the most appropriate solution to the problem and create innovative programs of personnel retraining.
References
Henry, M. S., Bazilian, M. D., & Markuson, C. (2020). Just transitions: Histories and futures in a post-COVID world. Energy Research & Social Science, 68.
Illanes, P., Lund, S., Mourshed, M., Rutherford, S., & Tyreman, M. (2018). Retraining and reskilling workers in the age of automation. McKinsey Global Institute. Web.
Lund, S., Madgavkar, A., Mischke, J., & Remes, J. (2021). What’s next for consumers, workers, and companies in the post-COVID-19 recovery. McKinsey & Company.
Zou, C., Zhao, W., & Siau, K. (2020). COVID-19 calls for remote reskilling and retraining. Cutter Business Technology Journal, 33(7), 21-25.
