Introduction
In the case in question, the a2MC corporation has difficulties in maintaining a competitive advantage in its market segment, which is caused by the entry of the other major participant. In addition, the organisational structure and objectivity of the expansion strategy used deserve particular attention as areas where potential changes are needed. Currently, the company has faced challenges while continuing to operate in the Asian market due to the entry of Nestle, another large corporation specialising in the sale of dairy products.
The chosen expansion strategy may be erroneous since the intention to increase the supply of A1-free milk to the west is fraught with the loss of credibility in the eastern region. Despite the fact that a2MC has a wide client base, existing difficulties can affect corporate profits adversely. Several applied analysis tools presented in the Appendices, in particular, the SWOT model, the TOWS analysis, the ViPA and VRIO techniques and the PESTLE framework help justify relevant issues. In case no measures are taken to establish business activities, the corporation may lose a significant market share and give a leading position in the industry to a competitor.
As recommendations, a merger strategy with Nestle can be a successful solution, as well as changing the business development strategy and shifting the focus from long-term to short-term prospects. If the company’s management changes its course from expansion to interaction with the competitor and establishes a productive partnership, this will eliminate the threat of the loss of profit. Ongoing interventions should be aimed not at managerial changes within the corporation but at creating a sustainable leadership system to achieve intermediate goals. This approach is optimal in conditions of stock fluctuations and problems with the supply of products to the Asian market.
The A2 Milk Company Case Study
Identification of Key Strategic Issues and Problems
Despite the fact that the a2 Milk Company (a2MC) has been operating in the dairy market for twenty years, today, the corporation experiences some challenges caused by various circumstances, including external factors and internal shortcomings. In conditions of continuous production, the company management misses some significant aspects that are crucial to consider to maintain stable profits and customer recognition. As gaps and problems that affect the Australian market, one should mention such issues as difficulties in maintaining a competitive advantage, inadequate organisational control and the irrational use of expansion opportunities and innovations.
Maintaining a Competitive Advantage
The validity of the problems caused by the loss of competitive advantage is explained by the participation of other large companies, in particular, Nestle in the promotion of A1-free dairy products. According to Esty and Fisher (2019, p. 1), in 2017, after the Swiss corporation directed its activities to the Asian market, the price of a2MC’ shares fell 10%, which damaged its reputation severely. One should note that, in the same year, the Asia-Pacific region was a key target area of product promotion for a2MC, and in Figure 1, its market share is presented (A2MC market share, 2019). As a result, the company was in a dangerous situation that could lead to the loss of the target audience and a decrease in investors’ confidence, which, in turn, was fraught with significant financial problems.
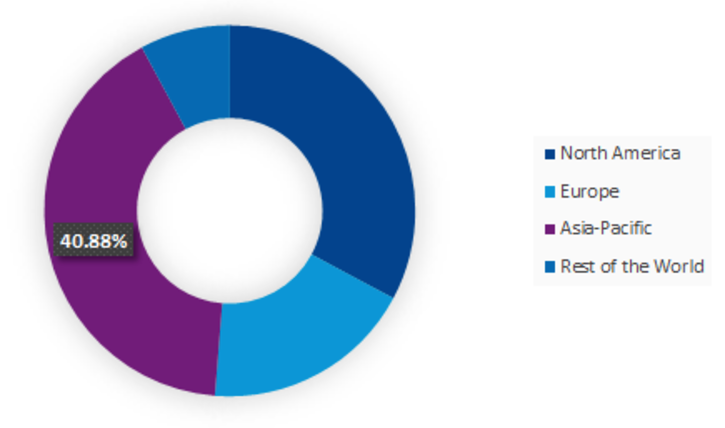
In the context of new circumstances, a2MC faced the problem of maintaining a competitive advantage in the target region since this aspect of activity became one of the main weaknesses. The SWOT analysis confirms that Nestle’s entry posed a threat to the business of the corporation in question (see Appendix A). This outcome became an incentive for a2MC management to create business solutions and look for ways to market products not only in Asia but also in the UK and the USA by involving available resources.
However, as Esty and Fisher (2019, p. 7) note, in 2018, 80% of products were still sold in New Zealand and Australia. As a result, despite its obvious dominance, a2MC has faced the challenge of maintaining leadership positions. According to Rothaermel (2018), competitive forces are formed in a dynamic entrepreneurial environment in which the emergence of new participants is a driver for innovation and technological implementation. Since Nestle is a recognised global brand with a wide target audience, its entry has indicated the need for significant changes in a2MC’s internal policy. Therefore, the reorganisation of market activity is a significant issue for the corporation.
Inadequate Organisational Control
One of the significant problems a2MC faced was the inadequately organised process of cost control and acquisitions. Esty and Fisher (2019) note that Geoffrey Babidge, who had been CEO of the corporation until 2018, sold almost half of the company’s shares, which reflected the leadership’s uncertainty about a2MC’s financial sustainability. This approach was unexpected for many market participants because, based on the professional experience of Mr Babidge, he previously held leading positions in several organisations and acted as a financial consultant (Geoffrey Babidge, 2020).
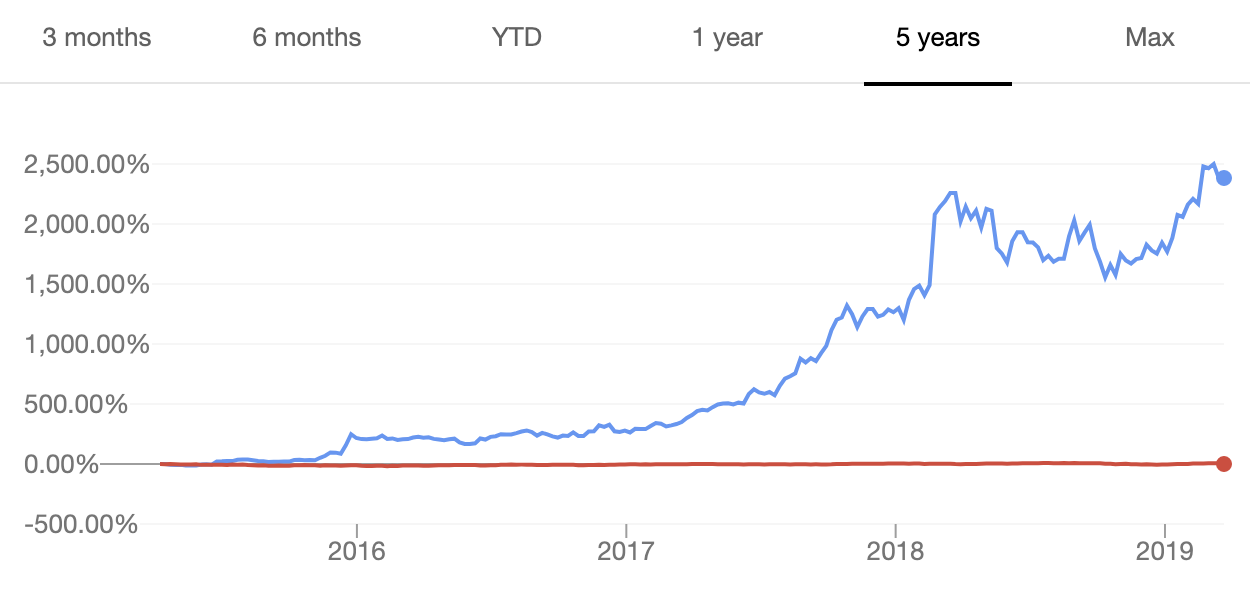
The sale of shares meant the company recognised the threat of suppression by competitors, which weakened the stability of a2MC. Stock price fluctuations shown in Figure 2 indicate the management’s inability to ensure a stable practice of interaction with investors and shareholders (A2MC share prices, 2019). As a result, the acquisitions of the corporation were threatened by the lack of demand in the market and could cause losses associated with the biased organisation of financial and control practices.
Irrational Use of Expansion Opportunities and Innovations
Marketing tactical decisions made by a2MC at the stage of its formation as a global corporation were effective and brought significant results. For instance, based on the progress report, the programme called “Thank you, A2” increased sales in Australia by more than 90% over two years (Thank you, A2, 2015, p. 6). However, with regard to expanding the business beyond New Zealand and Australia, a number of problems have arisen in planning and creating a sustainable implementation strategy.
Nestle’s entry into the Asian market has proven that the success of a2MC is not sustainable to counter the other major player. Despite the capitalisation of profits before 2018, Nestle’s emergence in China was one of the key problems that entailed associated challenges, and in Figure 3 proposed by Esty and Fisher (2019), the situation is reflected. In addition, the innovative technologies used by a2MC are expensive, which prompts the management to determine product prices above the market average.
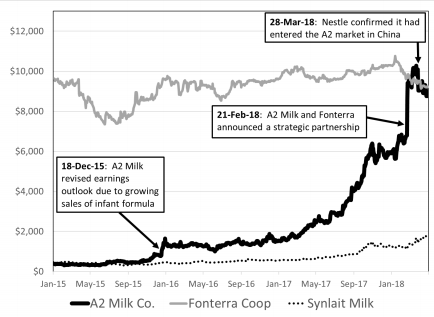
According to Esty and Fisher (2019, p. 8), while the company in question offers a litre of A1-free milk for A$2.4, the cost of the same products from manufacturers with a lesser-known brand does not exceed A$2.1. The company’s business expansion to the west distracts a2MC from upholding its leading position in the Asian region. Moreover, the concept of market culture proposed by Rothaermel (2018) implies an emphasis on the individual conditions of entrepreneurship in each competitive environment.
For the western and eastern regions, identical principles of supply and interaction with the target audience are applied, which is unacceptable in terms of organisational design. In addition, profit capitalisation would be possible if appropriate innovations were implemented competently, for instance, unique digital control methods or other new items in the logistics market. However, the leadership of a2MC do not focus on the technological upgrade of the material base, explaining this by high demand for products and well-deserved authority in its market segment. As a result, these challenges make it difficult to maintain stable profits and serve as constraints to the steady growth of capital.
Diagnosis: Analysis and Evaluation
Since the competitive advantage of a2MC is a key issue for the development of the company’s business and is associated with other challenges, the assessment of this topic is of the greatest importance. In Appendix B, the TOWS analysis is presented, which shows how the corporation can use specific factors to strengthen its position. In Appendix C, the ViPA and VRIO analyses are given, which reflect the quality of market engagement and the uniqueness of the competition strategy, respectively. Finally, in Appendix C, the relevant information is provided on external factors affecting a2MC’s business. However, in the context of gaps and difficulties, the application of Porter’s Five Forces technique may be essential to assess which strategies for optimising the corporation’s activities can be useful in the current competition conditions.
Porter’s Five Forces
Since the dairy sector is a competitive environment, the use of the Porter’s Five Forces framework is a convenient mechanism for assessing the impact of specific factors on companies’ ability to resist other participants’ business expansion. Savytska, Chmil and Redka (2018) consider this tool as a strategy that describes the roles and functions of competitors, new entrants, suppliers, consumers and substitute products. All of these factors can influence profitability, and in the context of a2MC’s problems, the use of this evaluation mechanism is reasonable.
Before Nestle entered the Asian market, a2MC had favourable prospects for expanding its business. However, the activities of the main competitor created obstacles for successful brand promotion. New entrants are unlikely to pose a severe threat to a2MC since the corporation is one of the leaders in the supply of A1-free dairy products. The role of consumers is of high importance because the dynamics of demand depends directly on this indicator. Suppliers, in turn, have no effect on the company’s business since a2MC owns its own dairy farms, including those for delivery to Europe. Bodnár et al. (2018) note that in 2014, the company used the power of twenty farms to supply milk to the UK. Substitute products are also unlikely to affect the corporation because a significant part of the patents for the production of milk based on A2 protein belongs to it (Esty and Fisher, 2019).
This achievement has allowed the corporation to partially protect its intellectual property and ensure the uniqueness of the technologies used. Therefore, the influences of competitors and customer power on a2MC’s business are dominant and require appropriate actions.
Organisational Performance
The activities of the current management board of a2MC are not effective and well-grounded in the context of the challenges encountered. In particular, the speed of the previous CEO’s decision-making in relation to selling shares proves that the company did not have a well-defined strategy for overcoming the competitive barrier and was afraid of losing its market recognition. Nevertheless, as Esty and Fisher (2019) note, the current CEO, who came to a2MC from the aviation industry, cannot maintain the same development indicators that Mr Babidge achieved. In this regard, the board of directors of the company probably makes a mistake when planning the new CEO as a manager on a long-term basis. The current conditions of high competition require adaptation and flexibility. In addition, as Rothaermel (2018) argues, internal analysis should be applied in case of crucial changes in the course of the development of business companies. Otherwise, a straightforward approach to organising control may be ineffective due to the misunderstanding of upcoming changes. Therefore, in the context of organisational effectiveness, the long-term planning of a managerial position is not an optimal solution.
Mistakes in the Expansion Strategy
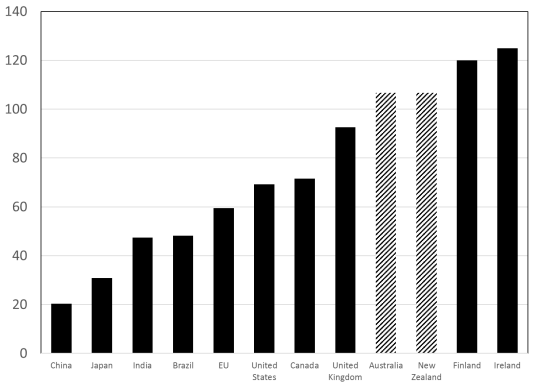
The expansion strategy, in particular, the shift in emphasis from the Asian market to the European one, is caused not only by the project of business globalisation but also by additional factors. In particular, Esty and Fisher (2019) provide statistics for 2016, which reflect the share of milk consumption in individual countries, and this graph is shown in Figure 4. However, a2MC management might not have taken into account that, for instance, the US market was oversaturated with local milk, and supplies from Australia and New Zealand could not be beneficial to the US economy. Despite the relevance of a2MC’s products and their popularity among the population, reducing the share of sales in China caused by fears of Nestle’s activities was a mistake. This gap can lead to the loss of this target market if appropriate measures are not taken. Moreover, while taking into account the business potential of the main competitor, ignoring these problems is fraught with the loss of regular customers’ trust. In the current conditions, any intervention may become critical, and assessing the prospects for market dynamics is an integral element of analysing the corporation’s expansion strategy.
Recommendations
Despite the fact that Nestle is a larger player in the dairy market, a2MC is also recognised by a wide range of consumers. In this regard, to address the problem of competitive advantage, the company management needs to establish contact with the Swiss corporation and create a single supply and sales mechanism. A merger is a possible mechanism that may be achieved through the acquisition by Nestle of a larger share of a2MC’s shares. The board of directors of the New Zealand organisation should weigh the pros and cons and draw conclusions based on real profit indicators over the past months. According to the official report of 2019, the Chinese infant food market is only 6.4% covered by a2MC products, which is the highest rate ever (The a2 Milk Company, 2019, p. 8).
The merger with Nestle may provide an opportunity to increase sales and, at the same time, preserve a significant part of assets. Today, acquiring one business by another is not shameful and is a common practice. Therefore, a2MC can ensure successful sales in China through a competent partnership with the major competitor.
The value of the merger approach can also be justified due to the principle of expanding the sphere of influence with the help of Nestle’s authority. Esty and Fisher (2019) note that the business of a2MC in western regions is not sufficiently stable to promote products with big profits. However, if the partnership with the main competitor is established, this will make it possible to deliver products globally and more successfully. Since Nestle has been operating in its market segment for a long time, the corporation has a large client base that is growing regularly. Effective advertising by such a large company can be an effective tool to stimulate consumer interest in a2MC’s products. In addition, through joint business management, more new regions can be covered, which is one of the priority development objectives. Therefore, the validity of the merger strategy is explained by the prospects for business growth and the expansion of the target audience.
In relation to the issues associated with an underperforming organisational structure and, consequently, potentially lower productivity, the a2MC board needs to review its CEO position. It is possible that the new leader is experienced in the control of business organisations and can establish sustainable monitoring. Nonetheless, in the current conditions, the company needs to plan a temporary development perspective but not long-term strategies.
As Ang, Benischke and Hooi (2018) state, for multinational corporations, such short-term planning is a common approach in the context of promoting expansion modes. In other words, for a2MC, it is logical to adhere to a strategy that can allow achieving sustainable sales in the Asian region, despite Nestle’s entry, without being distracted by additional organisational nuances. Therefore, the existing corporate strategy should not undergo significant managerial fluctuations in the face of increased competition and the perspective to maintain market relations with China.
The existing gaps in maintaining effective expansion tactics require changes in the business model. In particular, one of the weaknesses of a2MC identified during the SWOT analysis is the high cost of increasing the business share (see Appendix A). In order to avoid high costs and preserve financial assets, Bijman (2018) suggests paying attention to the cooperative model as a mechanism that can minimise the expenses associated with logistics and delivery. In particular, the author notes that the European experience of dairy farms confirms the relevance of such a development methodology, which is widespread in the industry in question due to increased competition (Bijman, 2018).
The need to optimise internal organisational processes justifies the transition to this mechanism. In addition, performance indicators may increase if the company adheres to this model since financing from various entities can help strengthen production and introduce innovative technologies. This approach is potentially valuable as a project to attract additional capital and interact with different market participants.
Raising capital as an aid to the development of productive activities is of great importance for a2MC. As Esty and Fisher (2019) argue, the corporation that has experienced significant stock prices fluctuations and the threat of losing market share needs financial support to spend on streamlining workflows and overcoming the competitive barrier. However, in case of receiving appropriate sponsorship, according to Rothaermel (2018), any company has certain obligations to the party providing such assistance.
As this aid, Nestle’s assets may be used wisely if a2MC management follows a merger strategy. Both companies have a large market influence, but the activities of the New Zealand corporation are complicated by the attendant difficulties, in particular, organisational issues. Moreover, sales are not stable in all regions, which is also a challenge. Provided that the partnership is established, a2MC will be able to realise its short-term goals successfully, thereby preserving the market credibility and comsumer interest.
Finally, to address the issue of innovations, the strengthening of the technological base can be realised by updating outdated equipment and introducing additional tools to improve supply chains. According to Bodnár et al. (2018), the absence of the need for changes in the technical base is the strength of companies involved in the dairy industry. For a2MC, the reorganisation may be relevant in order to eliminate errors and delays in deliveries and follow the standards of storage and transportation of its products. In case of successful changes, the corporation will be able to count on positive feedback from the target audience and, consequently, increase the customer loyalty indicator.
Conclusion
Throughout its market activity, a2MC has demonstrated high results in expanding the business and working successfully to promote its unique products. However, after Nestle’s entry into the Asian market, the corporation in question faced the challenge of overcoming the competitive barrier. In addition, the issues of expansion, organisational structure and innovation have arisen. The analysis using relevant concepts and techniques allows identifying the key gaps and providing the necessary recommendations regarding the company’s business optimisation.
Reference List
A2MC market share. (2019). Web.
A2MC share prices. (2019). Web.
The a2 Milk Company (2019) ‘Stepping it up’. Web.
Ang, S. H., Benischke, M. H. and Hooi, A. W. L. (2018) ‘Frequency of international expansion through high control market expansion modes and interlocked directorships’, Journal of World Business, 53(4), pp. 493-503.
Bijman, J. (2018) ‘Exploring the sustainability of the cooperative model in dairy: the case of The Netherlands’, Sustainability, 10(7), p. 2498.
Bodnár, Á. et al. (2018) ‘A2 milk and its importance in dairy production and global market’, Animal Welfare, Etológia és Tartástechnológia, 14(1), pp. 1-7.
Esty, B. and Fisher, D. (2019) ‘The a2 Milk Company’, Harvard Business School Strategy Case No. 719-424.
Geoffrey Babidge (2020). Web.
Rothaermel, F. T. (2018) Strategic management. 4th edn. New York: Mc-Graw-Hill.
Savytska, N. L., Chmil, H. L. and Redka, M. V. (2018) ‘Marketing study in the competitive positions of dairy industry enterprises’.
Thank you, A2. (2015). Web.
