Introduction
Background information
The current change in the world economy due to the prevalent high rate of globalisation is exposing companies to exchange-rate risk exposure (Goldberg & Drogt 2009, p. 49). Organisations may undertake activities involving foreign currencies through two main avenues, viz. undertaking transactions in foreign currencies or being involved in foreign operations. Exchange-rate exposure is one of the main sources of risk that multinational companies experience (Siddaiah 2010).
The Coca Cola Company operates as a multinational company (MNCs) with its headquarters situated in Atlanta, Georgia. As a multinational company, the Coca Cola Company earns its revenues, purchases assets, and settles its liabilities and other operational expenses using currencies of the host country such as the Euro, the Mexican Peso, the Japanese Yen, and the Brazilian Real among others. In 2009, the company used 71 different functional currencies, which generated 74 per cent of its total operating revenue from its multi-national operations. Consequently, the Coca Cola company is exposed to three main types of foreign exchange risk, which include economic exposure, translation exposure, and transaction exposure.
Multinational corporations have to create their financial statements by consolidating the financial statements of respective subsidiary firms (Madura 2011). Therefore, when preparing its consolidated financial statements, the Coca Cola Company has to translate its assets, liabilities, earnings, and expenses to the US dollars using the prevailing exchange rates. Thus, fluctuations in the exchange rate of the US dollar against the currency of the host countries affect the value of its operating revenue, assets, liabilities, and operating income (United States Securities and Exchange Commission 2009).
Aim and scope
In a bid to survive as an ongoing entity as a multinational company, the management team of the Coca Cola Company must understand how exchange rate fluctuations affect its performance. This report aim at illustrating how the Coca Cola Company has been affected by exchange rate fluctuations with specific reference to contract settlement, cash flows, and market value. The report specifically focuses on the financial aspect of foreign exchange rate movement on Multinational Corporations. Specific reference goes to cash flows, market value, and contract settlements. This paper does not evaluate other operational aspects that are affected by exchange rate movements.
Analysis
Impact of exchange rate fluctuations on the company’s cash flows
Management teams of multinational companies carry the responsibility of making effective decisions regarding their foreign operations. One aspect that should come into play is the effect of foreign exchange fluctuation on the company’s cash flow performance. Multinational corporations exceedingly volatile to foreign exchange rate movements compared to firms that are only involved in domestic operations (Doukas, Hall, & Lang 2003, p. 296).
The volume of accumulated foreign exchange rate also determines the extent to which a company’s operations are subject to exchange rate fluctuations. Firms with higher volume of foreign exchange reserves are highly volatile compared to those with a low volume. Additionally, firms with extensive multinational operations are also highly volatile to exchange rate movements (Doukas, Hall, & Lang 2003, p. 296).
Cash flow information is very important because it enables firms’ management teams to formulate effective operational models. Firms can achieve this goal by being in a position to compare the present values of future cash flows. Additionally, cash flow analysis enables organisations to assess their ability to generate more cash and cash equivalents. Considering the fact that exchange rate has a significant effect on the cash flows of multinational companies, it is paramount for management teams of these firms to develop a comprehensive understanding of how cash and cash equivalents are affected by exchange rate fluctuations. An indirect relationship exists between exchange rate movements and a company’s cash flows (Madura 2011).
Therefore, if the US dollar depreciates against a particular foreign currency, the multinational companies with their parent company based in the US will experience a reduction in cash flows despite making higher revenue in the host country. When the earnings are translated into the US dollar, the cash flow reduces significantly.
In the 21st century, the global market has increasingly become very volatile. As a result, the severity and frequency of exchange rate fluctuations across the globe have increased significantly. Consequently, the Coca Cola Company has been experiencing significant fluctuations in its cash flows. One of the company’s cash flow items that have adversely been affected is the cash and cash equivalent. Companies hold cash equivalents to assist them in meeting short-term cash requirements. For a particular asset to qualify as a cash equivalent, it must have a high degree of liquidity. Additionally, minimal probability of changing due to prevailing risk must also characterise the value of an asset. Consequently, a particular investment qualifies as a cash equivalent if it has short maturity duration, for example 3 months.
Over the past few years, the Coca Cola Company has been experiencing a challenging global business environment. One the major sources of these fluctuations touches on changes in the global economic environment. Due to the global economic recession that started in 2007, the company experienced a significant reduction in its cash flow in 2007. This scenario arose from the depreciation that the dollar went through compared to other major currencies. Consequently, the company’s cash flow reduced by $ (615) million in 2008 due to its multinational operation while its total cash flow during the preceding year reduced by a relatively lower margin of $249 million.
Reduction in the company’s cash flow emanated from the fact that the value of the dollar against other major currencies depreciated. Despite leading to an increment in company’s sales in the international market, the depreciation affected the earnings when they were translated into the US dollar (Stock Analysis on Net 2012). In 2009, the company’s cash flows increased significantly with a margin of $576 million.
In line with the US government commitment to restore the country’s economic growth, the Federal Reserve lowered the federal fund rate (FFF) in 2009.This decision adversely affected the value of the dollar against most major currencies such as the Euro. Consequently, the Coca Cola Company experienced a minimal increment in the size of its cash and cash equivalent in 2010, which was only $ 166 million.
Figure 1: Table showing changes in the Coca Cola Company cash flow due to exchange rate fluctuations.
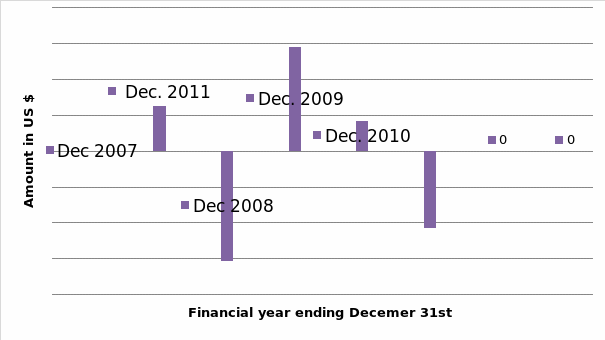
From the graph above, it is evident that the Coca Cola Company has been experiencing a significant reduction in its cash and cash equivalent. The negative effects of exchange rate fluctuation have been persistent from 2011, as illustrated by its financial performance over the past few months. The firm’s cash flow statement for the first six months ending June 29, 2012 revealed that its cash and cash equivalents reduced by $ (3,466) million while that of its first half in 2011 increased by $ 1, 649. Therefore, the company experienced a significant reduction in its cash and cash equivalent in 2012 compared to 2011(Thomson Reuters 2012, p.8).
Nevertheless, the recent fluctuations in the exchange rate have also led to a reduction in the company’s cash and cash equivalent balance. By the beginning of 2012, the company’s total cash and cash equivalent balance was $12,803 million. Due to the exchange rate fluctuation, the balance dipped to $9,337 million, which is relatively low as compared to the cash and cash equivalent value at July 1, 2011, which amounted to $10,166 million (Thomson Reuters 2012, p.8). This scenario clearly illustrates that exchange rate fluctuations adversely affect a company’s cash flow.
Analysis of the effects of foreign exchange rate fluctuation on its cash flows will help the Coca Cola Company to evaluate how the changes are affecting the entity’s operations. Thus, the company will be in a position to make possible adjustments that will enhance its ability to adapt to the changing business environment. Additionally, understanding the effects of foreign exchange rate fluctuations will enable the company to exploit other available market opportunities (Doukas, Hall, & Lang 2003, p. 296).
As the leading multinational corporation within the global soft drink industry, the Coca Cola Company can be in a position to shift its foreign operations from a country whose currency is characterised by high fluctuations against the US dollar to one whose currency experiences minimal fluctuations against the US dollar.
Effect of exchange rate fluctuation on company’s market value
The stock markets underscore one of the sources of information that investors can rely on when making decisions on the company to invest in (Hamrita & Trifi 2011). One of the aspects that investors take into account is the market value. From the stock market, investors can acquire information regarding a company’s market value. A company’s market value is an indicator of its market size. The stock price of a company is one of the indicators of its market value (Krantz 2010, p. 178). The stock price indicates the value that investors have attached on a particular company. The market value of a company is determined by multiplying the price of its share with the number of its outstanding shares (Wang n.d). High stock price tends to attract both domestic and international investors. This element arises from the fact that investors develop a perception that they will be in a position to maximise their wealth (Chen 2011).
Exchange rate exposure experienced by multinational corporations results in reduction in the value of their returns. Consequently, the profitability of the firm is negatively impacted, which is consequently reflected in the company’s share price. Previous studies conducted on the subject reveal that there is a dual causal relationship between exchange rate and share prices in the short run. However, this relationship does not exist in the long run. Depreciation in the value of domestic currency against major foreign currencies results in a decline in share price of companies and hence their market value.
Over the past few years, the Coca Cola Company has been experiencing a significant reduction in its market value. One of the factors that have contributed to this trend is depreciation of the dollar against major currencies as aforementioned. A report released by the Federal Reserve showed that the US dollar has come under pressure from most major currencies. This element has adversely affected the market capitalisation of most multinational currencies over the past few years. A company’s market capitalisation is one of the elements that investors can use to measure the market value of a company. From 2010, the Coca Cola Company’s market capitalisation has been on an upward trend, which can be attributed to the appreciation experienced by the dollar due to the numerous economic stimulus packages that the government put in place in an effort to restore the country’s economic growth.
Table 1: Coca Cola Company market capitalisation. Source: Ycharts 2012.
However, this trend has been on the reverse in 2012. Over the past few months, the US dollar has depreciated significantly. This element has led to a decline in the value of Coca Cola shares in most stock exchange markets. The chart below illustrates the trend in the company’s share price during the month of November 2012.
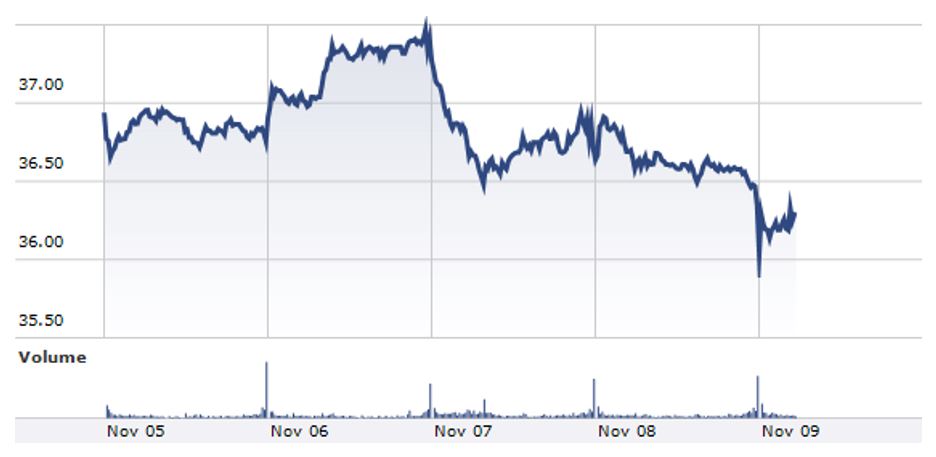
From the chart, it is evident that during the period ranging from 5 November 2012 to 7 November 2012, the company’s share price was on an upward trend. Nevertheless, this trend has been reversed during the last few days. By November 09, the price of each share of the Coca Cola Company was $ 36. During the month of November 2012, the company’s market capitalisation is $163.33 billion. Consequently, the descent in the price of the share means that the Coca Cola Company’s market value was adversely affected, for to obtain the market value of the company, the total outstanding shares would be multiplied with a lesser figure.
Effect of exchange rate movement on contract settlement
In its operation, the Coca Cola Company is involved in a number of contracts. These contracts emanate from the company’s integration of diverse derivative instruments such as forward contracts, collar and swaps, option contracts, and commodity future contracts. Commodity futures and forward contracts are constituted of agreements between the company and other parties to purchase or sell a specific amount of commodity or foreign currency at a specific preset future date. Additionally, the price or rate of the contract is also predetermined.
On the other hand, option contracts include agreements, which give a particular party the right to purchase or trade a preset amount of foreign currency at a specific future date However; the contract does not stipulate that the party must purchase the currency or commodity. Considering the fact that these contracts entail usage of foreign currency in most cases, they are subject to exchange rate fluctuations (Madura 2011). This observation means that either party to the contract may lose or gain.
Exchange rate fluctuations may lead to a significant alteration in the fair value of the contract despite factoring in a probable change in the exchange rate. When determining the fair values of such contracts, companies use the prevailing market rates and prices. In its operation, the Coca Cola Company enters into a number of forward exchange contracts. These contracts aim at enabling a firm to counterbalance the negative effects of its earnings due to exchange rate volatility.
Consequently, the company stands a chance to safeguard itself against significant negative changes in the value of its assets and liabilities. In addition, entering into such contracts also aim at hedging the company’s net investments from adverse effects of exchange rate movement. Its forward contracts are mostly denominated in major currencies such as the Euro, the US dollar, and the Japanese Yen (The United States Securities and Exchange Commission 2009).
Conclusion
Exchange rate movement is one of the major risks that multinational companies face. This aspect arises from the fact that these companies have to translate the earnings of their foreign subsidiary firms to domestic currency when preparing their consolidated financial statements. Consequently, multinational corporations such as the Coca Cola face an enormous challenge of dealing with exchange rate fluctuations. Some of the financial elements that are directly affected by exchange rate fluctuations include the cash flows, market value, and contract settlement. Fluctuations in the exchange rate of the dollar against major currencies such as the Euro have led to the Coca Cola Company experiencing a significant decline in its cash flows over the past few years.
Secondly, exchange rate movements have also adversely affected the company’s market value. The recent depreciation of the dollar has led to a significant decline in the share price of the Coca Cola Company. Consequently, the firm’s market capitalisation has reduced significantly. The value of the company’s share has undergone a decline with a margin of more than $2. This element has adversely affected the market value of the firm and hence its attractiveness. Additionally, the Coca Cola Company’s contract settlement has also been affected, which has arisen from depreciation of the major currencies that it uses in hedging itself against risks. This observation well illustrates that exchange rate movements significantly affect multinational companies in their operation compared to domestic company.
Recommendations
Considering the dynamic nature of the business environment, it is paramount for multinational companies to take into account the following measures:
- In a bid to survive in the foreign market, management teams of multinational corporations such as the Coca Cola Company must understand how exchange rate movements affect their operations. This move will aid in formulating effective operational strategies. For example, in countries with huge exchange movement, a firm may consider the probability of advertising its operations because of the high degree of exchange rate exposure.
- Multinational companies should also incorporate effective foreign currency management strategies. This move will aid in safeguarding the firm against significant foreign exchange rate risk.
- Multinational corporations should also evaluate their contracts constantly involving foreign currencies. This step will enable firms to determine how exchange rate movements will affect their contracts. Consequently, they will be in a position to implement strategies to caution themselves from potential losses.
Reference List
Chen, A. 2011. Research in finance, JAI Press, Greenwich.
Doukas, J, Hall, P & Lang, L. 2003. ‘Exchange rate exposure at all the firm and industry level’, Financial Markets, Institutions and Instruments, vol. 1 no. 5, pp. 291-343.
Goldberg, S & Drogt, E. 2009. Managing foreign exchange risk, Wiley Periodicals Incorporation, New York.
Hamrita, M & Trifi, A. 2011. ‘The relationship between interest rate, exchange rate and stock price; a wavelet analysis’, International Journal of Economic and Financial Issues, vol. 1 no. 4, pp. 220-228.
Krantz, M. 2010. Fundamental analysis for dummies, Wiley Publishers, New Jersey.
Madura, J. 2011. International financial management, South-Western Cengage, Mason.
Morningstar Premium: Coca Cola. 2012. Web.
Siddaiah, T. 2010. International financial management, Pearson: Upper Saddle.
Stock Analysis on net: Coca Cola Company; statement of cash flows. 2012. Web.
Thomson Reuters: Coca Cola Company- United States Securities and Exchange Commission 2012. Web.
United States Securities and Exchange Commission: The Coca Cola Company 2009. Web.
Wang, Y n.d, Fluctuations of exchange rate on the valuation of multinational corporations as Taiwan’s samples. n. d. Web.
YCharts: The Coca Cola Company market capitalisation 2012. Web.

