Abstract
The concept of leadership has attracted attention of scholars over the recent past as companies struggle to manage stiff competition in the local and international markets. The aim of this systematic review is to critically synthesize the relationship between employee leadership and work environment happiness within the theoretical paradigm of the contemporary academic literature. Primary data was obtained through semi-structured interviews with.
Secondary data was collected from 21 scholarly sources, including books and journal articles on the subject matter, and further analyzed with the help of mixed quantitative-qualitative methods to answer seven predefined research questions, investigating the role of work environment. Results of the systematic review showed that happiness in the workplace directly influences the ability of employees to ascend to top management positions. The study has identified five independent variables that directly affect the ability of to become leaders: 1) job satisfaction, 2) employee engagement, 3) workplace safety, 4) valued social position, and 5) support from friends. Findings provide a foundation for further educational research with potential recommendations for employers. Potential limitations include judgmental sampling and failure to incorporate socioeconomic variables, sensitive to culture.
Keywords: Employee engagement, job satisfaction, happiness, workplace environment, safety, social support, leadership
Introduction
Happiness in the workplace is one of the major concerns that many organizations are trying to address as a way of enhancing productivity and leadership. According to Al-Emrana, Mezhuyeva, Kamaludina, and Shaalan (2018), in the current society, the majority of adults spend most of their time in the workplace. The tough economic times have forced many people to take two or three jobs just to ensure that they can earn enough income to meet their personal needs. Others work overtime to increase their earning. It means that they have very little time to spend with family and friends. The nature of the workplace environment, especially in terms of satisfaction that workers get, significantly affects their lives. As Tasnim (2016) observes, it is important to ensure that the workplace environment is conducive to enhance the performance of the employees by making them feel valued, respected, and trusted with tasks assigned to them. Such employees would feel indebted to the firm, and as such, would be willing to sacrifice their time to ensure that they deliver on every assignment given to them.
Scholars have been interested in investigating how different factors affect employee’s happiness in the workplace. They have also developed models that explain how happiness of workers influences performance, and its subsequent relationship with leadership, especially among women. Studies have shown that women thrive in an environment that is supportive. Organizations that have created a happy workplace environment tend to have a higher number of women in top leadership positions than those with high levels of stress. Women tend to be more sensitive to criticism, especially when they are trying to climb the career ladder. When they feel that they lack the support they need, they will avoid pursuing promotions for fear of making mistakes that would lead to further criticism. In this paper, the researcher seeks to investigate the effect of happiness in the workplace environment on employee performance and satisfaction, and its relationship with leadership, especially among women.
Research Questions
It is important to define a specific question that will guide the entire process of collecting and analyzing primary data from various sources. As explained in the introduction, the study seeks to investigate the relationship between happiness at the workplace and employees’ performance/satisfaction. As such, the following research question was formulated to help in the process of collecting primary data from respondents:
- RQ1. What are the factors that affect happiness at work, and how do they influence employees’ performance and leadership?
- The following are the supportive research questions that will help in the data collection process:
- RQ2. What are the factors affecting work environment?
- RQ3. How can organizations design a healthy work environment?
- RQ4. How do work environment help in supporting women leader?
- RQ5. How do work environment affect employee performance?
- RQ6. How does employee performance affect employee satisfaction?
- RQ7. How does employee satisfaction affect employee leadership?
Research Objectives
Employees’ satisfaction, performance, and happiness are some of the widely researched areas of study because of their significance in the current workplace environment. Isa, Tenah, Atim, and Jam (2019) also explain that women leadership and how it can be motivated have also attracted a significant number of scholars over the recent past. Osborne and Hammoud (2017) explain that objectives help a researcher to define the specific data that should be collected from primary and secondary sources. The following are the specific research objectives that guided the process of collecting and analyzing data from various sources.
- To identify factors that influence employee’s happiness in the workplace environment.
- To establish the relationship between happiness in the workplace environment and employees’ satisfaction and performance.
- To establish the relationship between employees’ satisfaction/performance and employee leadership.
- To discuss how organizations can create an environment where women can flourish in their careers to become successful leaders.
Research Importance
The United Arab Emirates is one of the fastest developing economies in the Middle East and North Africa (MENA) region (Al-Hammadi, Al-Hammadi, & Ahmad, 2018). The government has invested a lot of resources to empower its workforce to ensure that they can participate actively in the economic progress in various sectors. Access to education has been made easier and more affordable to all citizens than it has ever been. A new trend has emerged in the region where women are getting empowered through education so that they can be engaged actively in different sectors of the economy. Cunningham (2016) argues that studies have proven that women have a lot to offer when they are put in managerial positions. Academic empowerment is one of the ways of ensuring that women are offered the opportunity to get into positions of leadership. However, Salas-Vallina, Alegre, and Guerrero (2018) believe that academics alone cannot help women assume leadership in the private sector and public entities.
The workplace environment is changing with the changing trends, beliefs, and practices in the global society. During the Industrial Revolution in Europe, employees ruled with iron fist, using various ways to punish employees whenever they felt that they were underperforming (Elmasry, Benni, Patel, and Moore (2016). This dictatorial approach of leadership remained popular for decades as it made it easy for managers to force workers to meet specific targets. However, such leadership approaches are no longer effective. Employers have learned the benefit of working with highly motivated employees who feel valued and respected instead of feeling threatened. Instead of using threat, it has emerged that using incentives and promoting happiness in the workplace is a better way of improving the performance of employees. Moreover, some workers would prefer leaving their current job for another when they feel unhappy with their workplace environment (World Economic Forum, 2020). As such, promoting happiness has become one of the ways through which organizations can improve their overall performance.
The research is important because it identifies ways in which local firms can promote happiness in the workplace as a way of promoting employees’ satisfaction, performance, and effective career development, especially among women. The government has created an environment where women are academically empowered. It is the responsibility of private and public entities to ensure that they help them to ascend to top leadership positions. This study explains the kind of environment that women need to help them prosper in their careers. The document will help senior managers within the country to understand the value of creating a happy workplace environment and how that can be achieved by engaging all stakeholders, including junior employees, when making policies that govern their organizations.
Literature
The performance of employees has always been linked with their level of satisfaction at work. In a society where coercive approach to management is becoming less effective and undesirable, managers are redefining their approach to enhancing the productivity of their workers (Sandhu, 2020). In order to answer clearly formulated research questions, responding to the objectives of this study, a systematic review is utilized. With systematic and reproducible methods to determine, choose, and evaluate the relevant research, this type of literature review proves to be most efficient in collecting and analyzing data included. Findings made by other scholars will help in identifying factors that affect happiness in the workplace, which in turn influences job satisfaction, and the ability of women to rise to top managerial positions. In this section, the researcher has identified five independent variables that directly affect the dependent variable.
Independent Variable 1: Employee Engagements
Employee engagement, according to Serrat (2017), refers to a concept that focuses on the nature of the relationship between a given entity and its employees. Many firms have realized that the best way of empowering their workers is through employee engagement. Scholars have developed different ways of promoting employee engagement within an organizational setting. Figure 1 below identifies various opportunities that a firm can use to improve employee engagement as a way of enhancing their productivity.

As shown in the figure above, one of the ways of promoting employee engagement is to encourage personal growth. A firm should create an environment where workers can experience personal growth at work. It is also important to ensure that there is happiness in the workplace. Factors that may cause confrontation or undesirable arguments among workers should be eliminated. The model identifies ambassadorship as another approach of promoting employee engagement. In this case, a firm will encourage its workers to represent it in various contexts as a way of promoting the brand. Effective representation of the brand would help to strengthen the firm’s position in the market. A firm should find ways of enabling employees to strengthen their relationship to peers. Workers should be willing and capable of helping their colleagues to achieve career growth. Relationship with managers is equally important (Pisano, 2017). The relationship can be strengthened by having an effective vertical communication system within the company.
Recognition should not be underestimated when promoting employee engagement. King (2019) argues that it is crucial to acknowledge the excellent work that employees do in their respective areas of work. The model also identifies an effective feedback system as a way of promoting employee engagement. The feedback helps them to identify their strengths and weaknesses. It makes it possible for these workers to have a continuous improvement program as they climb the career ladder. Wellness is another major factor. Issues such as occupational health and safety, and emotional wellness of workers should be taken seriously by the management. Alignment is the ninth factor as shown in the figure above. The human resource (HR) department should ensure that skills and experience of workers is aligned with responsibilities assigned to them. The last factor is compensation based on the job that an employee is assigned. Kane (2019) believes that it is crucial for the management to ensure that employees feel adequately compensated. When each of these factors is taken care of within an organization, employees will be satisfied with their work and their performance will ultimately improve. Such an environment will also be conducive for women to achieve career growth. The following questions will need to be addressed:
- What are the factors that promote employee engagement in the workplace?
- What are the benefits of employee engagement to an organization?
Independent Variable 2: Job Satisfaction
Job satisfaction is another major factor that defines the environment under which an employee works. Pauleen (2016) defines job satisfaction as the extent to which a given worker feels contented and self-motivated with their job. When an individual feels satisfied with their work, there is always the desire to register a better performance because they feel they are getting as much as they give. Figure 2 below identifies factors that define whether an employee would feel satisfied with their job.
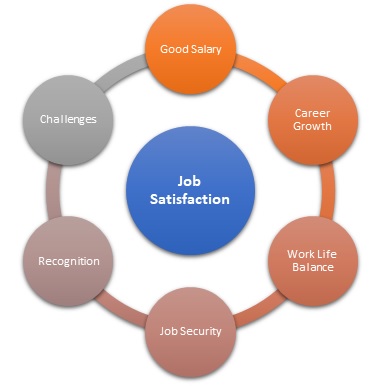
Good salary is one of the main factors that define job satisfaction. Bratianu (2018) explains that employees tend to move from one company to another in search of good remuneration. Higher salaries enable them to meet their financial obligations, making them satisfied with what they do. Career growth is another major factor. An overwhelming majority of workers often desire to climb the career ladder (Dam, 2018). As such, firms should have systems that assure its workers of career growth depending on the time they have worked for the company and their productivity. The process should be seen to be fair and based on specific criterion that is meaningful to stakeholders involved.
Having a work-life balance is critical in enhancing job satisfaction within an organization. As employees focus on spending a lot of time at work to increase their income and enhance their career growth, their private life should not be compromised (Pauleen, 2016). The management should ensure that these workers have enough time to spend with their friends and family to help fight burnout. The model also emphasizes the need to have job security. Workers should not feel that their job will be threatened when they make a mistake or in instances when the firm is going through economic challenges. Just like the case of employee engagement, job satisfaction also champions for recognition of employees when they register exemplary performance. Challenges also define the experience of workers within a firm. Sandhu (2020) explains that it is often advisable to subject workers to meaningful challenges in their assignment that motivates critical thinking and creativity. When they overcome these challenges, especially through the use of new skills and practices, these employees will be more satisfied with their work. The following questions will need to be addressed:
- What are the factors that affect workplace environment?
- How does employee’ performance affects employee satisfaction?
Independent Variable 3: Workplace Safety
Health, safety, and wellbeing of the workers is another independent variable that cannot be ignored when discussing about employees’ satisfaction, performance, and the ability to promote leadership, especially among female workers. As Pisano (2017) observes, workers want to feel safe in their places of work. Many companies in Chinese Hubei province have currently opted to have their employees work from home because of the fear of corona virus infection. These companies understand the need to protect the health of their workers and are committed to embracing policies that would limit the spread of the disease to their workers.
Occupational safety is another factor that is clearly defined in various laws, especially those enacted by the International Labor Organization (ILO). Companies are expected to have internal policies that enhance safety of all workers and visitors who come to the premise. It is necessary to ensure that various hazards are eliminated for the benefit of workers. According to King (2019), it is equally important to ensure that employees are educated on issues relating to their safety when they are in their respective workplaces. Providing them with the right protective gear may not be enough if they do not understand and appreciate the need to use them.
The well-being of the employees is another factor that defines workplace safety (Serrat, 2017). Sometimes an employee may be suffering from emotional instability caused by issues in their private lives. It is dangerous to ignore emotionally distraught employees because they not only expose themselves to danger but can also be a major threat to safety of others (Pisano, 2017). It is necessary to have a system that can help such traumatized individuals as soon as it becomes apparent that they are emotionally unstable. Workplace safety defines employee’s satisfaction and their performance at work. The following questions will need to be addressed:
- How can an organization design a healthy workplace environment?
- How does an enabling work environment help in supporting women leadership?
Independent Variable 4: Valued Social Position
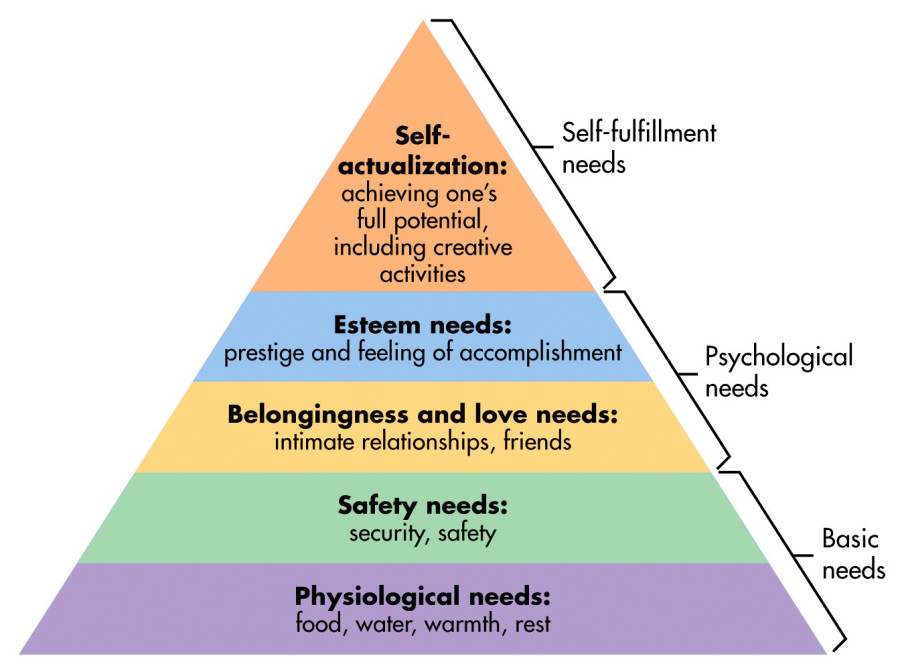
The need to have an environment where employees feel valued at the workplace is also important when promoting employee satisfaction and an environment where workers feel valued. According to Bratianu (2018), it is normal for people to demand respect for those they work with. It is also important to ensure that they are given valued social position based on the time they have been working for the organization and their performance. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs model, shown in figure 3 below, can help explain this concept. At the bottom of the pyramid are psychological needs. When an employee is newly recruited within a firm, they will only have basic needs (Pisano, 2017). The most important thing to such employees is the fact that they have a job and can afford to pay their bills.
When such an employee has spent a year or two at the firm, they will graduate from basic needs to the second level of safety needs. They will demand to have a workplace environment where their safety and security is not compromised. They will be interested in ensuring that the organization abides by ILO laws and other legal requirements within the country meant to protect their interest (Tasnim, 2016). When the employee has taken more than five years at a given organization, belongingness and love needs would set emerge. They would expect respect based on their position, age, and the time the time they have spent in the firm.
Esteem needs is the second highest level in this model, as shown in the figure below. In most of the cases, such an employee would be in the mid to senior managerial levels. They are often heads of department who are expected to make critical decisions that would enhance the overall performance of the organization. They expect their position to be accompanied with appropriate remuneration and other benefits. At the apex of this model are the self-actualization needs (Bratianu, 2018). Most of those with these needs are chief executive officers or individuals holding top managerial positions. When one’s social position within the firm is valued, they will feel contented and committed to achieving a career growth.
The following questions will need to be addressed:
- What are the factors that affect workplace environment?
- How does work environment affect employee performance?
Independent Variable 5: Friends’ Support and Work-Life Conciliation
The support that one gets from friends and coworkers also define their job satisfaction and the ability to become leaders in their organizations. According to Pisano (2017), people often want reassurance from their peers to pursue top leadership positions. Being a leader is often characterized by numerous challenges and there is always the fear that one might fail. As such, it is often helpful if one gets the support of their friends who will assure them that they can make it in leadership positions. Women tend to require regular assurance than men whenever they consider pursuing a higher office. Kane (2019) explains that one of the main reasons why some people, especially women, avoid higher offices is the problem of criticism.
It is important for an organization to promote a culture where workers learn to support their colleagues instead of engaging in criticism. As Sandhu (2020) states, positive criticism is constructive because it involves pointing out both strengths and weaknesses and explaining how one can use unique skills and capabilities to overcome weaknesses and achieve success. Employees should focus on peer reviews as an effective way of promoting growth based on merits. Of interest in such reviews should be to improve the overall performance of colleagues without making them feel less valued. It is the responsibility of an individual employee to associate with positive people outside their workplace environment (King, 2019). They should associate with people who believe in their capacity to be successful leaders. These five independent variables directly affect the following dependent variable. The following questions will need to be addressed:
- How does work environment affect employee performance?
- How does employee satisfaction affect employee leadership?
Dependent Variable 1: Employee (Women) Leadership
The concept of leadership has attracted the attention of leaders over the past several decades because of the changes in the socio-economic and political environment. Approaches of leadership that were used prior to the twenty-first century are no longer effective. Dam (2018) explains that highly successful companies such as Google Inc., Apple, and Microsoft have learned the importance of embracing the right leadership approaches that emphasize the need to motivate workers instead of coercing them to undertake a given responsibility. It has also become apparent that women play a critical role in the management of organizations irrespective of their size (Budhwar & Mellahi, 2016). Some of the qualities unique to women such as compassion and the ability to multitask make them good leaders, especially when handling young workers. Companies are currently committed to promoting their workers to higher managerial positions based on their competency, regardless of their gender.
In the context of this study, the ability of female employees to rise to the rank of senior leadership positions is considered a dependent variable. According to Pauleen (2016), the global society, including the United Arab Emirates, has come to realize the importance of having women in managerial positions. However, it takes individual commitment among female employees for them to rise to the position of top management. The five variables discussed above, which include employee engagement, job satisfaction, workplace safety, valued social position, and friends support all have a direct influence on the ability of women to get into managerial positions (Dam, 2018). They define the environment under which these employees work and the ease with which they can rise to higher managerial positions. Having the right policies both in private and public entities would help create an environment that can nurture women to become successful corporate leaders in the country.
- What are the factors that promote women leadership in local organizations?
- How can an organization promote career growth among employees?
Research Model
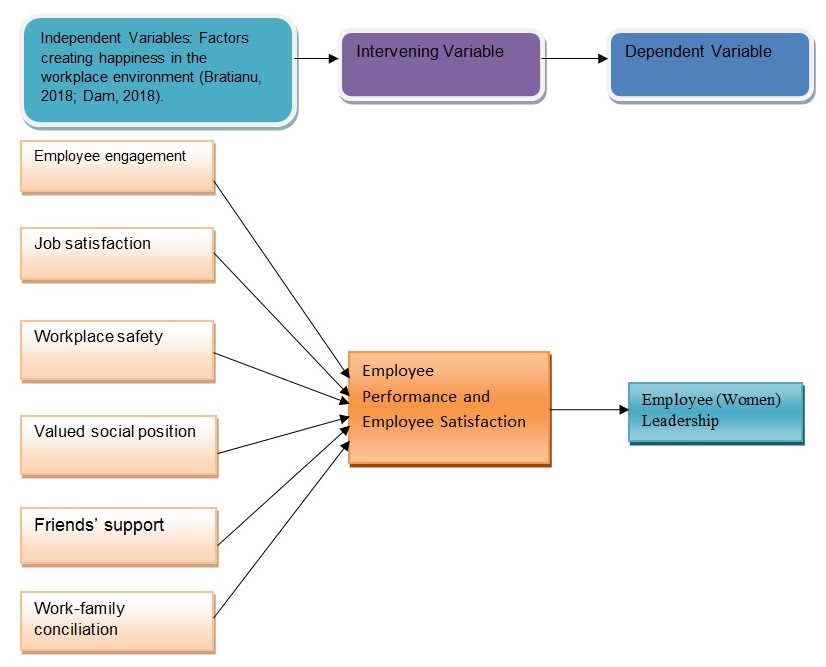
It is necessary to develop a research model that helps in explaining how independent variables relate with the independent variables in a given study (Serrat, 2017). As shown in figure 4 below, there are five independent variables. Employee engagement, job satisfaction, workplace safety, valued social position, friends’ support, and work-family conciliation all affect employee performance and employee satisfaction. Pawirosumarto, Sarjana, and Gunawan (2017) believe that employee satisfaction and performance significantly influences their chances of becoming leaders in their organization. It means that chances of female employees rising to positions of management depend on how the independent variables influence the intermediate variables, which in turn, influences the dependent variable. The model below summarizes the relationship.
Research Hypotheses
It was important to develop hypotheses based on the primary research question and the objectives of the study. The hypotheses would be rejected or confirmed based on the findings that will be made from the analysis of primary data. The following are the hypotheses that were developed for the study:
- H1o. There is no direct relationship between happiness in the workplace environment and employees’ satisfaction and performance.
- H1a. There is a direct relationship between happiness in the workplace environment and employees’ satisfaction and performance.
- H2o. There is no direct relationship between employees’ satisfaction/performance and employee leadership.
- H2a. There is a direct relationship between employees’ satisfaction/performance and employee leadership.
- H3o. Women do not flourish in their careers to become successful leaders when they have a happy workplace environment.
- H3a. Women tend to flourish in their careers to become successful leaders when they have a happy workplace environment.
Methodology
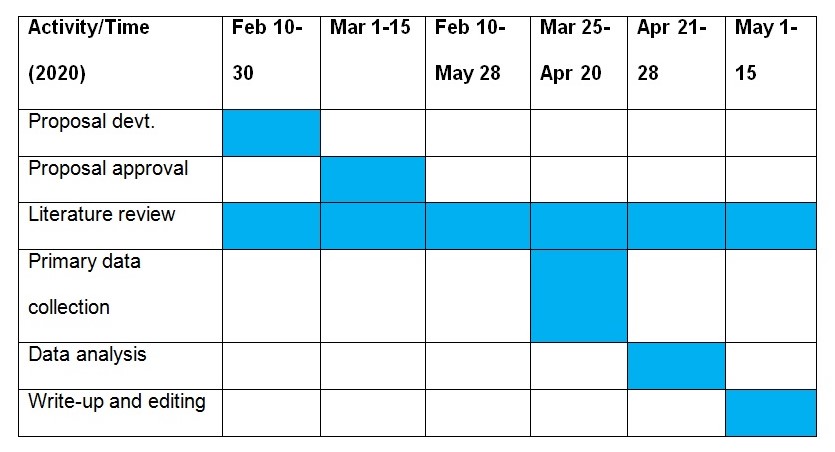
To the best of the researcher’s knowledge, the most effective approach to this study would be a combination of qualitative and quantitative methods. After reviewing the relevant literature, the researcher will focus on the collection of primary data from a sample of respondents. The primary data will help in answering the set research questions. Table 1 below is the proposed timeline of the activities that will be conducted to obtain data from a sample of respondents.
Table 1: Gantt chart
According to Ravitch and Riggan (2017), when planning to collect primary data from specific individuals, it is often important to define the criteria that would be used in selecting participants. The inclusion/exclusion criteria help in ensuring that those who are selected to take part in the investigation have the right skills that can enable the researcher to collect the right information. Table 2 below shows the inclusion/exclusion criteria.
Table 2: Inclusion/exclusion criteria
In this study, judgmental sampling will be appropriate to ensure that individuals with specific qualities are selected to participate in the study (Boeren, 2018). The researcher will develop a questionnaire that will be used to collect data from the selected participants. A face to face interview will be conducted with the respondents to collect primary data. Once the data is collected, the researcher will use mixed method to conduct the analysis. Table 3 below shows keyword searches used to identify online secondary data
Table 3: Keyword search
Table 4 below shows the databases where online secondary data was obtained and their search frequency.
Table 4: Databases frequencies
Figure 5 below shows how digital data (online journal articles and books) were identified and included in this study. The same process will be used when conducting the study:
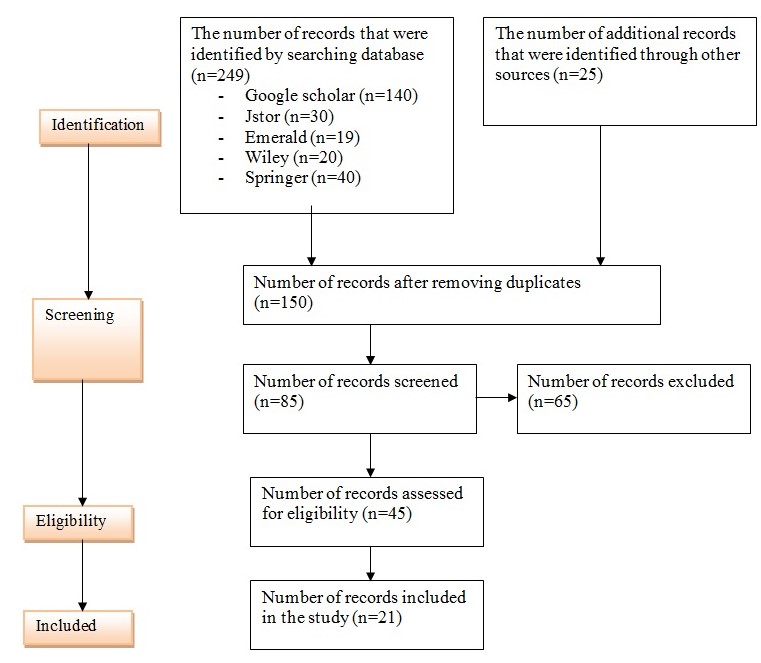
The quality assessment criteria, shown in table 5 below, were used to appraise articles and books to determine their relevance for the study. Of interest was to ensure that these secondary sources could provide adequate knowledge about factors that promote happiness and satisfaction in the workplace, and how these two factors promote leadership among women.
Table 5: Quality assessment checklist
It was necessary to conduct a quality assessment for each study to determine if they meet the criteria set in table 5 above. The results are shown in table 6 below, which indicates that the 21 sources used meet the criteria.
Table 6: Quality assessment results
Discussion
Results of the study showed that worker’s satisfaction is positively correlated with the employee performance at a workplace. The main purpose of this review study is to systematically synthesize the research on the subject matter to increase the understanding of concomitant factors, contributing to the employee’s happiness. Table 6 shows the categorical classification of components included in the concept of work satisfaction, as per 21 studies. The derived variables are as follows: employee engagement, job satisfaction, workplace safety, valued social position, friends’ support, and work-family conciliation. One third of researchers (7) identified employee engagement as a primary factor of satisfaction at a workplace. Five articles focused on the significance of job satisfaction and valued social position in the formation of positive attitudes toward one’s work environment. Four studies discussed the role of friends’ support, while three researchers emphasized the importance of workplace safety and work-family conciliation. The majority of the authors included two or more factors in their work, which signifies the need for comprehensive assessment of the issue.
Table 7 provides a brief analysis of studies on factors creating happiness in the workplace environment. When reviewing the current research, it is essential to take into consideration cultural background. Studies conducted in Middle Eastern countries consistently showed more emphasis on the opinions of friends and family, while western nations, like US or Canada, stressed the importance of work security and employee engagement. Such findings demonstrate that the perception of employee happiness differs depending on the individualistic or collective type of culture.
Conclusion
This systematic review investigates the relationship between employee leadership and happiness in the work environment. The analysis of secondary and primary data shows that there are five variables, contributing to the level of the worker’s satisfaction at workplace, such as employee engagement, job satisfaction, workplace safety, valued social position, friends’ support, and work-family conciliation. The degree to which the aforementioned aspects matter to the worker depends on the gender, culture, and individual perceptions.
References
Al-Emrana, M., Mezhuyeva, V., Kamaludina, A., & Shaalan, K. (2018). The impact of knowledge management processes on information systems: A systematic review. International Journal of Information Management, 43(1), 173-187.
Al-Hammadi, A. H., Al-Hammadi, A. Y., & Ahmad, A. R. (2018). Leadership, strategic planning, organizational performance and innovation: A case of Dubai/ UAE public sector. International Journal of Management and Information Technology, 3(1), 3179-3186.
Boeren, E. (2018). The methodological underdog: A review of quantitative research in the key adult education journals. Adult Education Quarterly, 68(1), 63–79.
Bratianu, C. (2018). Organizational learning and the learning organization. ResearchGate, 5(1), 1-20.
Budhwar, P. S., & Mellahi, K. (2016). Handbook of human resource management in the Middle East. Northampton, MA: Edward Elgar Publishers.
Cunningham, J. B. (2016). Strategic human resource management in the public arena: A managerial perspective. London, UK: Palgrave Macmillan.
Dam, N. (2018). Elevating learning & development: Insights and practical guidance from the field. New York, NY: McKinsey & Company.
Elmasry, T., Benni, E., Patel, J., & Moore, J. (2016). Digital Middle East: Transforming the region into a leading digital economy. New York, NY: Digital McKinsey.
Isa, K., Tenah, S. S., Atim, A., & Jam, N. M. (2019). Leading happiness: Leadership and happiness at a workplace. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering, 8(3), 2277-3878.
Kane, G. C. (2019). The technology fallacy: How people are the real key to digital transformation. Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
King, P. (2019). Persuasion tactics (without manipulation): Covert psychology strategies to influence, persuade, & get your way. London, UK: Publish Drive.
Osborne, S., & Hammoud, M. S. (2017). Effective employee engagement in the workplace. International Journal of Applied Management and Technology, 16(1), 50-67.
Pauleen, D. J. (2016). Personal knowledge management: Individual, organizational and social perspective. New York, NY: Routledge.
Pawirosumarto, S., Sarjana, P., & Gunawan, R. (2017). The effect of work environment, leadership style, and organizational culture towards job satisfaction and its implication towards employee performance in Parador Hotels and Resorts, Indonesia. International Journal of Law and Management, 59(6), 1337-1358.
Pisano, G. P. (2017). Toward a prescriptive theory of dynamic capabilities: Connecting strategic choice, learning, and competition. Industrial and Corporate Change, 26(5), 747-762.
Ravitch, S. M., & Riggan, M. (2017). Reason & rigor: How conceptual frameworks guide research (2nd ed.). New York, NY: SAGE Publications.
Salas-Vallina, A., Alegre, J., & Guerrero, R. F. (2018). Happiness at work in knowledge-intensive contexts: Opening the research agenda. European Research on Management and Business Economics, 24(3), 149-159.
Sandhu, K. (2020). Leadership, management, and adoption techniques for digital service innovation. Hershey, PA: IGI Global.
Serrat, O. (2017). Knowledge solutions: Building a learning organization. Singapore, Singapore: Springer.
Tasnim, Z. (2016). Happiness at workplace: Building a conceptual framework. World Journal of Social Sciences, 6(2), 62-70.
World Economic Forum. (2020). Inclusive deployment of block-chain: Case studies and learning from the United Arab Emirates. White Paper, 91(93), 1-25.
