Introduction
The global economy is in the process of emerging from a recession that hampered economic growth in most regions for the past two years or so. The recession was due to a combination of factors: runaway inflation, governments were running huge budget deficits and national debts which kept increasing, a sharp hike in the prices of raw materials raised production costs tremendously and a surge in oil prices had the result of driving energy costs out of control. As the prices of goods began to increase sharply, consumers opted to reduce any unnecessary expenditure, sticking to the purchase of necessities instead. Also due to fear of an unknown future people were opting to save instead of spend. The outcome was a rapid decrease in the gross domestic product in most countries. When consumers reduce spending to minimize their costs, it has the direct impact of lower sales for businesses. Business owners on their part react to avoid huge losses sharply reducing their costs. A reaction that eventually results in workers losing their jobs. The multiplier effect of these actions on an economy is wide-scale unemployment, lower incomes, and tightening of credit by financial institutions. The spillover effect from this situation results in recession as was experienced by the world economy in the recent past.
State of the world economy
United States
GDP
Inflation
The United States is the largest and most technologically powerful economy in the world. It has held this position since 1944 up to date. “With an income per capita GDP of $ 40,900 it is among the wealthiest nations with an equally high level of productivity per capita output” (Knoop 43). The main hallmark of the US economy is that it is a market-driven economy where individual businesses are free to make their own decisions with almost no interference from the state. The benefit of this is that it gives the businesses a level of flexibility that is not enjoyed by other business people in other countries.
The USA is also a world leader in technology with US firms being at the forefront in high technology sectors such as military equipment production, manufacturing, advanced medical research, and information technology. But this is not to say that the economy is without challenges. In 2003 the United States led a coalition into a war with Iraqi forces, to be in a position to sustain this war, government resources had to be channeled to the military. This meant that the social and development budgets had to be trimmed negatively impacting education, health, policing, and employment.
Also, high oil prices between 2008 and 2009 resulted in runaway inflation and loss of jobs, the increase in the cost of gas further served to reduce consumer spending ability (Knoop, 166). Another challenge is sizable government debt and deficit that has resulted in further cuts on social spending. By mid-2008 as a result of several factors such as the global economic downturn, collapse, and failures of banks, falling prices of homes, and the subprime mortgage crisis the United States slipped into recession (Knoop, 71). As a measure to avoid panic in the financial markets, the government set up a 700 billion dollar stimulus fund. A large part of the amount was used to purchase shares in the large financial institutions and business corporations as a way of preventing them from going under. During this period a loss of 5 million jobs was reported with overall an unemployment rate of 8.5% In January of 2009 the government provided an additional $ 787 to be spent on pump-priming to create jobs and to stimulate the recovery of the economy. While these interventions have resulted in some growth of the economy the overall level of government debt and the budget deficit is worrying to many.
Saudi Arabia
GDP
Inflation
Unemployment
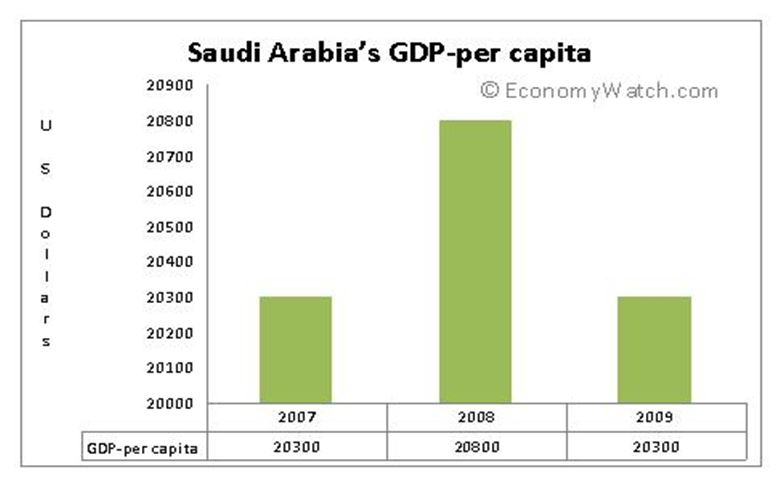
The kingdom of Saudi Arabia is the leading exporter of oil worldwide. The refinery of oil and a petrochemicals industry account for a large majority of the Kingdom’s exports and nearly 80% of all state revenue. Saudi Arabia also has about 25% of all proven oil reserves in the world. Commercial Production of oil began in the country after the Second World War. This resulted in rapid economic growth and transformation of the desert kingdom from the 1960s. “The effects of the growth have seen Saudi Arabia’s GDP per capita income grow exponentially to $ 20,300 and the country today is classified among the wealthiest in the world. More than 95% of all oil produced in Saudi Arabia is produced by giant parastatal known as Saudi ARAMCO” (Blanchard 18). This company is the largest integrated oil company in the world with expansions going on to enable the exploitation of natural gas that would feed the ancillary petrochemicals sector.
While the government controls most major economic activities in Saudi Arabia, recent efforts have been made to promote the growth of a nascent private sector as a way of diversifying the economy with the desired outcome of reducing the level of unemployment in the country. Recently the government has been investing heavily in education to improve the skills and employability of Saudi nationals as most of the people working in the country’s thriving oil and service sectors are foreign workers.
Several years of high oil prices leading up to 2008 gave the country’s government adequate financial resources to help it minimize the effects of the global economic downturn. But, a sharp decline in oil prices and the widespread recession in most of its export markets, resulted in a slowdown of economic growth in the Saudi economy. The most visible impact of this setback was that some planned development projects had to be postponed. A recent surge in oil prices has brought back optimism in the kingdom with some planned developments being restarted.
China
GDP
Inflation
Unemployment
Until the 1960s socialist China was a very poor country with an agricultural economy that was largely rural-based. During the ’70s the government started reforms initially targeting the agricultural sector. Gradually reforms extended to fiscal decentralization and price liberalization (Huw, 5). Later state-owned enterprises were granted independence significantly improving their performance. These along with other reforms targeting the banking and industrial sectors had a far-reaching impact on the Chinese economy. As the pace of economic growth began to increase, the Chinese opened up their economy to the world as a way of attracting much-needed foreign direct investment.
The result of these reforms is that China is now a huge economy that is still expanding rapidly. In terms of purchasing power parity ($8.77 trillion in 2009), its economy is currently the 2nd largest economy in the world. The rate of economic growth has been almost miraculous averaging 10% in GDP per year. This was a feat that was unimaginable only a few decades ago. However there is still a huge disparity between the poor and the rich in China and the GDP income per capita ($ 6,778) remains comparatively low ((Huw, 5).
While the country has been able to move hundreds of millions out of poverty, a large number of people especially in the rural areas remain unemployed (4.3 %) or underemployed. This problem was made worse when throughout 2008- 2009, the global economic recession significantly reduced demand for Chinese exports in its global markets. This resulted from large-scale layoffs in Chinese industries and export processing zones. Inflation also rose at a fast pace, leading to a sharp hike in food prices. For the first time in many years, economic growth in China had to slow down. In response, the Chinese government committed itself to further reforming the economy and increasing local consumption of its products as a way of making China less dependent on foreign exports to enable it to sustain growth in its GDP in the future.
Europe
Europe has about 11% of the entire world’s population living in forty-eight countries. When compared to other regions in the world, the continent has a significantly higher standard of living than most regions with its residents having a high income per capita of $ 27,383 and a comparatively high gross domestic product of $ 25,285. But there is a big difference in the size and performance of the economies of the countries within the continent. Nations located in Western Europe like France $ 36,489 Britain $ 45,731 and Germany $ 46,352 are amongst the wealthiest in the world with very high GDP, high standard of living, high per capita income, and a high purchasing power. While countries from East and Central Europe still emerging from socialism have comparatively smaller economies with a significantly lower purchasing power and GDP. These Economies are however growing at a faster rate than those in Western Europe. A major highlight of the European economy is the European Union which is a powerful and influential political, social and economic union of twenty-seven nations (Blanchard, 12). The EU as is popularly known as the wealthiest economy in the entire world a fact that gives its member countries significant clout in the global economy.
In the recent years leading up to 2010, the growth of the European economy has been near stagnant but recent statistics suggest a growth of 2.6% for the year 2010. Most of the economies within this region were hit very hard by the global economic downturn. Economies such as Finland and Ireland that were until very recently booming and experiencing a high rate of growth have gone into recession. Some of the larger more prosperous economies have been stagnant or are experiencing negative growth due to a high inflation rate. This has given way to a very gloomy mood throughout the region. The rate of unemployment post the global economic downturn within Europe is still quite high, with the problem being complicated by migration from poor to wealthy countries. Also, Europe suffers from inefficient and bureaucratic regulation that has served to worsen the effects of the recession on most countries (Blanchard, 24). In response, a wide-ranging reform effort has been initiated targeting the financial, product, and labor markets. To reduce government debt and budget deficits, social reforms targeting the welfare state have also been launched. This has resulted in political tensions with bitter confrontations between the general public and government officials.
Pacific Rim
Pacific Rim refers to countries that border the Pacific Ocean from Asia, Oceania, and North and South America. These countries include Australia, New Zealand, Japan, Singapore, Philippines, South Korea, Taiwan, Costa Rica, Honduras, Colombia, Mexico, and the United States. Most of these countries have experienced rapid significant economic growth and change with cross-country trade and investments leading to an integrated economic region being formed in the process.
The Pacific Rim has continued to gain strength globally from an economic point of view. Within this region four countries Taiwan, South Korea, Hong Kong, and Singapore are referred to as economic tigers due to the aggressive nature of the growth of their economies (Phillips, 123). These countries have grown from poverty in the 1960s to first-world status. Through economies that are based on manufacturing, high-tech production, and growth of services. The citizens of these countries now enjoy high GDP income per capita almost equal to that of western economies with very low rates of unemployment and inflation. The recent recession did not have a very negative impact on most of these countries due to the different models of growth that they use and the strength of cross-border trade that was able to sustain exports and growth.
In 1989, 18 Pacific Rim countries formed an organization known as Asia Pacific Economic Cooperation to promote integration and free trade among the member countries. As barriers of trade among the member countries are loosened the clout and economic significance of the region keeps growing and with time, it is likely to be one of the important economic regions globally.
Conclusion
With most countries emerging from the recent recession the world could most likely be prepared for another period of growth as is characteristic of economic cycles. Only this time economists, public officials, financial institutions, and the general public will be more cautious in their approach towards spending. While in the past a booming economy was the sign of goods times and hence unregulated spending, this time around such a phase might be viewed as the time to save for a rainy day.
Governments have reacted to the recession and its effects by cutting on spending especially on social welfare as is the case in Europe, also reforms have been initiated specifically targeting the financial sector. The aim of this is to avoid a repeat of the situation that was witnessed in the recent past.
While China might have faced a setback due to the decrease in the market for its products in Europe and the United States, its new commitment to “look inwards” in trying to increase the domestic market for its products is likely to pay off. The success of this initiative will mean that China is likely to grow economically with a faster rate of growth in employment and domestic incomes. Also, its strategy to diversify its markets with a focus on Africa, the Middle East, and South America is likely to lead to an increase in exports further consolidating this growth.
Most of Europe except for a few countries such as the economic powerhouse Germany is still undergoing a tough economic situation. Most recently countries such as Greece, Spain, and Denmark have slipped into recession. Others such as Britain are on the brink. The result of this has been painful reforms that will have to be carried out effectively if Europe is to regain its competitive edge. But even with the reforms tough times still lay ahead as the rate of unemployment is going up in most countries. The strength of the Euro also means that European products are expensive in the global market a fact that is likely to result in sluggish sales and a worsening economic environment. Optimism for the future of the European economy can only be guarded at best.
Saudi Arabia is likely to keep its impressive growth rate as the prices for oil have risen again. Government efforts to reform the economy are likely to pay good dividends shortly. The Pacific Rim as a region is likely to face mixed fortunes as the countries are too diverse to place in one category. The Asian tigers with their high-tech innovative economies face a future of growth but at a slower rate than before. The resource-rich countries such as Australia might also enjoy sustained economic growth due to demand for the products as the world economy recovers.
In the United States, recent economic growth has been received with caution as the economy is not completely out of the woods. For a more solid growth to enable the economy to move out of its current situation a lot of cuts in public spending will have to be initiated. Also, the Government will have to adopt measures that will enable the country’s firms to regain their edge over global competitors who are catching up quite fast in terms of technology and markets.
Overall the outlook of the world economy is positive, with growth likely to be experienced in most regions shortly. Focus is likely to shift from the traditional economic powerhouses of Japan, Western Europe, and North America to the emerging economies of developing countries like China, Brazil, Russia, and India. These emerging economies are increasingly able to compete and match developed economies in terms of exports, technology, and quality of products. The main advantage they possess is access to cheap resources and a young, educated, and skilled labor force which enables them to sell the products at more competitive prices. Thus the economic growth that will be witnessed in the future is likely to be more balanced and spread out across different regions in the world.
Works Cited
Blanchard, Olivier. The Journal of Economic Perspectives, Volume 2004. pp. 3-26.
Huw, McKay & Ligang Song. China as a Global Manufacturing Powerhouse: Strategic Considerations and Structural Adjustment. China & World Economy, Volume 18, Issue 1. Web.
Knoop, Todd. Recessions and Depressions: Understanding Business Cycles, Praeger Publishers, 2004. pp. 166–71.
Phillips, Douglas and Steven C. Lewis. The Pacific Rim Region: Emerging Giant. Hillside, NJ: Enslow Publishers, 1988. pp 123-127.
