Introduction
Turkish airlines are the world’s fourth-largest carrier in the aviation industry. With its headquarters at Ataturk Airport, it has made tremendous progress over the years, transforming how people live and conduct business both in Turkey and internationally. This trend can be attributed to the swiftness of the airplanes that can cover a very long distance within a considerably short time; thus, delivering goods and services to the satisfaction of its customers.
The Porters five forces model gives a complete qualitative analysis of the Turkish airline in aspects such as threats of new entrants, the power of the suppliers, power of the buyers, availability of substitutes, and competitive rivalry. The influence of the buyers, suppliers, and competitors in the airline business plays an important role in the activities of the company. Indeed, the ability of one customer to the firm is deemed to have a significant impact on its sales margins and volumes. This research paper analyses the viability of the Turkish Airline’s business using the Porters Five Forces model.
Companies Involved
Due to the regulation policy introduced in the year 2003, new chartered and privately-owned companies entered the Turkish airline Industry. One of the firms is the Turkish Cargo company, which deals with cargo transportation and warehousing. Another player in the Turkish airline is the Turkish Teknik. This company majorly deals with aircraft maintenance services and repairs besides offering engineering and design services.
The Turkish Ground Services (TGS) company conducts ground handling services while Sun Express majorly undertakes air transportation globally (Alagöz & Ekici, 2014). These companies are distinguished from each other due to their unique brand logos.
The Turkish airline signed an agreement for an alliance with other international companies to enhance its competitiveness (Alagöz & Ekici, 2014). The companies involved include the Pakistan International Airlines Corporate, Royal Brunei Airline Sdn Bhd, and Air Algeria SpA. The firm has also partnered with Japan Airlines to offer services to Osaka and Tokyo.
Services offered by Turkish Airlines
The major service that has made the Turkish Airlines become one of the world’s major carriers is the transportation of passengers. Besides local services, it offers scheduled international transport to destinations in Europe, Africa, the Americas, and Asia. Furthermore, Airline taxi enterprises operate locally; thus, generating income for the country. Turkish Airlines also offers cargo transportation reaching the same destinations as the passenger jets.
Moreover, the carrier provides aircraft repair and maintenance services. It also offers technical and infrastructural assistance related to the airline industry (Alagöz & Ekici, 2014). The airline has an extensive fleet. It puts more emphasis on customer satisfaction; hence, its employees are encouraged to make sure that their passengers feel comfortable and memorable at different points of travel.
The firm has invested in the renewal of the airline corporate identity as well as the implementation of its wide-body and short-haul aircraft. This plan has led to the introduction of new products and services the Turkish airline industry. The products include leather seat covers, seat cover fabrics, leather headrests with embossed logos, and pleated laser cut curtains with tulip styles, class dividers, and carpets.
Porters Five Forces Analysis of the Turkish Airline
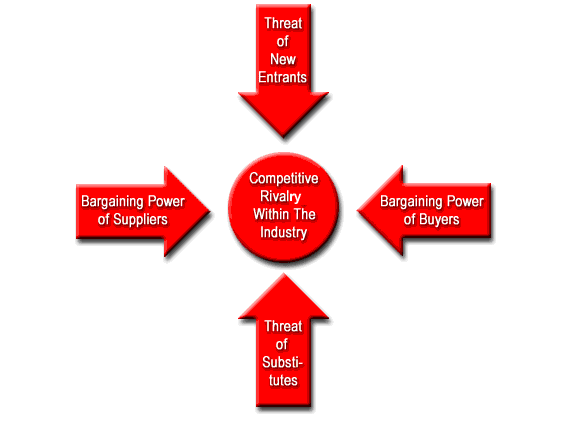
Threat of New Entrants
The new entrants into the industry have posed a big threat to Turkish Airlines. Most of the companies coming to this market receive loans and grants from their governments. As a result, they stand a position to offer better services than their Turkish competitors who are not protected by the government. Some of the new entrants into the airline industry have also been protected by their suppliers who offer them subsidies on materials.
These factors enable competitors to acquire new airplanes (Acar & Karabulak, 2015). Consequently, their cargo traffic liability due to the quality of service by their newly acquired planes has improved significantly. This situation has also led to new companies that have caused saturation in the market. At this rate, the competitors are also offering their services at relatively cheaper prices; thus, compelling consumers to shift their travel preferences. According to most consumers, airline services and destinations are similar. For this reason, they prefer to use the ones that offer subsidized services.
On the other hand, Turkish Airlines has established a strong brand for its various companies by developing unique logos for each one of them. Because of their superior brand, they have managed to be a notch higher than their competitors; hence, attracting more consumers to their camps (Acar & Karabulak, 2015). This standing has enabled them to suppress the threats imposed on them by their competitors. Turkish airline has succeeded in its quest of increasing their brand awareness across the world.
Their mission is to attract attention to their brand among the very many audiences presented before them including anyone with the desire to travel to any destination of choice. Another reason for their establishment of the strong brand is to make traveling the world more accessible by flying to and from many destinations (Ayden, Demirbag, & Tatoglu, 2018). With such a superior strategy in place, the airline has managed to pose a big challenge to the competitors.
Nevertheless, the firm has to find a better way of improving their brands to remain competitive. The Turkish Airline Motto, which states “Globally Yours”, helped in increasing the awareness of their brand. For this reason, the company has succeeded in becoming a key player in the global aviation industry.
Flight Frequencies
Turkish Airlines have taken advantage of their flight frequencies through various routes, a situation that has resulted in the multiplication of their competitive value. The benefits of being at the desired location at a specified time are multiplied by the frequency of the flights. Turkish Airlines has established a Computer Reservation System (CRS). As a result, the more flights they have the more they gain visibility on the CRS screens.
This plan has given them more advantages over their competitors in ticket reservations and sales. Turkish Airlines has also been able to establish alliances with other airlines. Consequently, they have gained higher frequencies that have weakened the position of their competing third alliance airline companies. This realization has enabled them to increase the flexibility of the passengers who are time conscious; thus, making the company more attractive.
The Turkish Airline has a well-ordered departure and arrival time that has led to the development of a taste for their services amongst its customers. Various studies have shown that departure is a leading factor that influences airline preferences particularly amongst passengers who fly short distances, especially for business purposes.
The Network Structure
Turkish Airlines has established a superior network that has enabled them to offer efficient services to its passengers. Due to its strategic location in the main airport, it has effective control of the system. The firm is designed in a H$S network structure, which suggests a system whereby the passengers have to be transported from the spoke airports to a central hub. This situation has led to an increase in demand for their services. It has also enabled them to reduce unit costs.
Their well-established H$S network system resulted in improved protection of their routes against low-cost airlines that have found their way to the industry due to deregulation (Al-Azri, Waleed, & George, 2015). Besides, Turkish Airline uses the system as a barrier to stop new entrants from accessing the market since it has gained significant control at the hub airports.
The carrier competes with other players by flying from one point to another due to their new line network strategy. This system operates differently and uniquely as it is not deployed around a hub airport but rather connects cities in a linear route sequence (Al-Azri et al., 2015). Because of the low-cost carriers and the lack of stopovers, which comes with the system structure, they have been able to go on direct flights. As a result, the firm has significantly reduced the turnaround time thereby increasing the frequencies of the utilization of its aircraft.
Power of Suppliers
The two main suppliers that supply the Turkish Airline are Boeing and Airbus. These companies offer high-quality planes and other services to the Turkish Airline despite the fact that the amenities differ significantly. The planes manufactured by the two companies are similar in quality and competitiveness. In this regard, passengers are assured of high-quality services. This situation has led to the maintenance of loyalty to the supplying companies.
The Turkish Airline signed a long-term contract with both Boeing and Airbus. The two companies have been compelled to continue offering their services according to the agreed standards. This plan has favored the Turkish Airlines as the services offered by the two contracting companies meet the customer needs. The oligopoly situation the companies have created has enabled them to reap maximum income from their services.
In addition, the suppliers offer incentives to the Turkish Airlines. The signing of the contracts has significantly been of great benefit to the Turkish Airline as they have been able to establish more favorable credit terms. Accordingly, the Turkish Airline pays its loans at favorable rates.
The manufacturing companies offer their services to The Turkish Airlines industry at high fixed costs. The planes manufactured by Airbus and Boeing are of high-quality and expensive. The materials needed to manufacture the planes are also costly. Therefore, it has become extremely difficult for a new company to invest in the manufacturing of aircraft of such superiority due to the expertise and amount of capital involved, which goes up to around 200 million US dollars.
For this reason, the Turkish Airline has no option but to continue working with the two companies as there are very few suppliers. The cost of switching suppliers is too expensive for Turkish Airline. The firm has borrowed a lot of loans from the two manufacturing companies. If the Turkish airline has to switch suppliers, it will have to settle their debts and pay for the breach of contract as stated in their agreement. This position leaves it with no option but to stay true to the contract and continue working on its terms.
The government restrictions on legislation have greatly favored the manufacturers in terms of supply. It has put measures in place not to allow the operation of passenger transportation planes older than 15 years starting from the date the plane is registered with the Turkish Civil Aircraft Registry. This law also demands that cargo aircrafts must not operate for a period of more than 25 years. This regulation has made it easy for the Boeing and Airbus manufacturing companies to continue with their production thereby dominating the market (Miller, 2016).
Power of the buyers
The Turkish Airline industry consists of two kinds of buyers; individual passengers such as businesspersons and agencies (Dursun, O’Connell, Lei, & Warnock-Smith, 2014). The former class buys tickets that are aimed at traveling to various destinations. Some of these buyers are tourists who travel for leisure during the holidays. In the course of this period, the Turkish Airline realizes high profits due to the amplified quest for travel.
As a result, the flight charges are temporarily increased to meet the demands. However, the demands by the buyers who travel for leisure is seasonal; thus, the company does not realize high profits during the off pick period. This particular group of buyers is extremely diverse. In addition, there are fliers who travel for important businesses. These kinds of customers are of particular importance to the Turkish Airline because of their frequency. For this reason, they are charged at fair prices because they are regular clients. They also benefit from bonuses and promotions.
The entry of new players to the airline industry has led to the reduction of prices, a situation that has led to an increase in the power of the buyers. This situation has been attributed to the differentiation and focus strategies put in place by the competitors.
The second group of buyers includes travel agencies and online portals. These categories are of great importance to the Turkish Airline because they act as middle persons between the airline and flyers. The fliers normally buy their tickets from the travel agencies. They work with multiple air firms with an aim of giving the customers the best experience possible. Travel agencies and online portals offer a large number of buyers as compared to the existing firms.
The Turkish Airline has managed to get a lot of profit from the buyers because of their low bargaining power. The buyers, especially the flyers, do not have a lot of options due to the high cost involved in switching the planes. The Turkish planes also operate at a level rate. As a result, the services and rates still remain the same. The seats in one airline are similar to those of the other.
The Turkish Airlines have also been able to keep the bargaining power under control because of their influence on the hub at the main airport. The flyers, especially the international travelers, are always served through the hub to ensure efficiency. This approach has enabled the company to establish loyalty among the buyers. The buyers need to know the services which are offered to them during the flights.
Therefore, the firm has a responsibility of ensuring that their services are improved to standards that meet the customer requirements. The buyers also need to know the time of departure and arrival at various destinations. The bargaining power of the buyer has a limited effect on the operations of the Turkish Airlines and cannot lead to the company to making losses.
Availability of Substitutes
The Turkish Airline industry faces a stiff competition from other transport industries such as the train and the bus service industry (Low & Lee, 2014). Turkey has a well-developed standard gauge railway system that is owned by the state. It falls under the remit of the Ministry of Transport and Communications. The train offers long distance and cross-border freight and passenger services. The train is fast and cheap. Because of this many of the travelers who travel locally would not prefer to use the aircrafts, which are considered expensive. Many people especially businesspersons who transport large volumes of cargo locally would also prefer to use the train because of its cost-effectiveness.
The Turkish bus industries are also a substitute for the airplane travel in turkey. The charges for bus travel are cheap and many people can afford, unlike the airplanes. The buses are also more flexible as there are many bus stations where the buses can stop. Being that the buses are many, they can easily be accessed at any convenient time, unlike the airplanes. Because of this, many people opt to use bus services instead of the planes.
Some Turkish citizens who are potential airline travelers also own personal cars. The cars offer them door to door services as one can conveniently drive to his or her working place without necessarily undergoing the procedures of booking flights which are hectic, time-consuming, and highly expensive.
Many Turkish citizens consider traveling by planes as a luxury (Zaim, Bayyurt, Tarim, Zaim, & Guc, 2013). To them, it is not important because of their nature of work and their levels of income. Because the cost of using the other means of transport is cheap and affordable, the Turkish Airline industry has witnessed a stiff competition in the transport industry. However, there is a cost to switching of the services. The other means of transport such as the railway and the bus can extremely very costly at times.
Airplane transport is by so far the fastest means of transport. The airplanes move faster and are therefore able to deliver on time, unlike while using road transport. When we consider the geographical layout of Turkey and the amount of time consumed if one has to travel by road, we can say road transport is not a substitute for the air transport in Turkey. We also have to put it in mind that the Turkish population is mainly composed of high-income earners.
In addition, there is the minimum rate of accidents when it comes to air transportation thus making it safer. This has given the Turkish airline advantage over the other means of transport in the country. Therefore we can say that there are really no substitutes for the services offered by the Turkish airline. This is because people will always go for the services when the need arises (Zaim et al., 2013). This has kept the industry strong and going.
The deregulation policy introduced by the Turkish government led to the entry of many new airlines into the Turkish airline industry. This situation led to increased competition and, consequently, reduction in the transport prices. As a result of low prices, the degree of substitutes was significantly reduced as many people still have the option to fly at affordable rates.
Competitive Rivalry
The Turkish Airline company has experienced an overall increase in the rivalry forces in the Turkish Aviation Market. More entries to the market have led to the decline of the Turkish airline in the general market along with a significant decline in the overall performance of the Turkish domestic market. All this has been contributed by the rivalry created due to the new entrants to the market. The Turkish Airline Industry has always enjoyed a large installed base (Dursun et al., 2014).
This has enhanced the value of their networks hence resulting in more customers associating with the industry. Basing our argument on this advantage, the Turkish airline has been able to move ahead of the competitors thus being able to counter the rivalry. Furthermore, the Turkish Airline has had the privilege of reaping from its opportunity being that it was the earliest entrant into the airline market in the country.
The Turkish Airlines have also been able to counter the power of the rivals by its high quality of in-flight service, brand awareness promotion services and their wellbeing apprehensions associated with entrants (Dursun et al., 2014). This has helped the Airline retain most of its existing customers and be able to continue its price control. In addition, being that they have the biggest domestic network and continuous inflow of international and domestic passengers’ transit capabilities has given the Turkish Airline a competitive benefit over the rivals.
The Turkish airline offers low-cost operational model services and at the same time, they strive to keep the quality of the service constant and on the rise where the need for improvement be. This has enabled the Turkish Airline to maintain the leadership position over its rivals. The low cost led to many of its customers coming back and they were able to lock themselves to the Airlines’ services by using the Turkish Airline Premium Card. This has helped reduce the threats of the rivals to the industry.
The Turkish airline has degenerated its value chain. The relapse of its value chain has helped the company to be operationally competent and a low-cost company. The Turkish airline has degenerated its maintenance services, catering services, ground handling services, and the call center subsidiaries into standalone companies (Acar & Karabulak, 2015). This measure has led to the standalone companies becoming more self-efficient, self-reliant and ultimately highly profitable.
On the same note, the subsidiaries are also able to offer services to other airlines within the country and outside the country, thereby being able to achieve better economic growth and scale and also be able to lower price reflection on their services to the Turkish Airline. Through this, they have been able to counter the rivalry by their competitors making it easy to dominate the market.
The Turkish airline has adopted a strategically unique marketing plan to enable them in marketing the airline. This has enabled them to establish stronger brand recognition all over the world. The company has been able to improve its brand image by redesigning its logo, celebrity endorsements, for example, the endorsement of Lionel Messi, and an intense viral marketing campaign (Acar & Karabulak, 2015). All the efforts have been of economic significance as the quality of their services has become superior over their competitors.
Many of the entrants to the Turkish Airline industry decided to implement a low business course model. This model targets the low and the middle-class population of the Turkish nation. The new entrants have practiced cost-effective leadership and have relied squarely on its hub and spoke network. They also relied on the popular city pairing to ensure high-quality utilization rate and efficiency in their operations. The rival companies have also adopted yield maximization system and were able to adjust their prices in line with the Turkish Airline prices. The rivals have done this considering the fact that the Turkish Airline is the dominant player in the market.
Some of the rivals have also focused on offering better in-flight services to its consumers. Such companies have mainly put their focus on the service tool used to ensure efficiency (Acar & Karabulak, 2015). One of the rival airline industries that have been able to employ such a technique is the Atlas Jet. It has also been able to focus on the look for destinations where the population mainly consists of high-income earners and also focusing on building a strong network system. Through this such rival companies have been able to prove their competitive strength in the market thus posing a big challenge to the Turkish Airlines.
On the other hand, some of the Airline companies such as the Pegasus have been able to enter the market as low carriers. Such company has also been able to focus on its networking system and being able to choose its strategic hub location. Through this, the company has been able to establish a strong competitive rival base in the airline market (Acar & Karabulak, 2015). The company has been able to utilize yield management to establish its pricing. With this kind of acquisition, the company has been able to differentiate its networking and serve the market with different city pairing system.
The Turkish Airlines has been able to respond to the threats of low carriers imposed by the rivals by focusing on lowering the cost of its services while at the same time being able to maintain the quality of its services. For example, the Turkish Airline was able to launch the Anadolu Jet which was a low-cost sub-brand and offered affordable services (Acar & Karabulak, 2015). The Anadolu Jet offered cheap prices with the structural advantages of the Turkish Airline and its geography. The jet was also able to assimilate its networking to Turkish for the domestic passengers who have the advantage of international connections. The jet also offered low prices and efficient city pairing to its passengers. All these measures enabled the Turkish airline to counter the competitive rivalry.
The Turkish Airline has also been able to counter the threats of the new entrants by being able to identify new opportunities in the world and establishing a new network system. For example, the company has been able to identify new opportunities in Africa such as in Algeria. It has also been able to identify opportunities in the Far East. This has enabled them to move a notch higher than their competitors thus establishing a stronger Airline business empire.
Conclusion
Through Porter’s Five Forces analysis model, it is clear that the Turkish Airline remains one of the strongest carriers worldwide. The firm has put in place a number of strategies that enable it to counter the threats of new entrants into the airline industry, the airline company has significantly limited the threats posed by its rivals. AN evaluation of the power of its buyers has indicated that it offers its customers exceptional services with a view to meeting their diverse demands.
The Turkish Airline brings a clear picture that the satisfaction of consumers is directly related to the quality of services offered to them. By mapping and knowing the power of the industries that can offer substitute or alternative services to the consumers, the firm has significantly improved the quality of its services besides creating a good picture in the eyes of its consumers. Most of its clients have been convinced that there is no other carrier that can offer substitute services.
Besides, the firm has strived to counter the threats of its competing rivals by lowering their intensity in the market. Porter’s Five Forces analysis is a clear indication that companies succeed in competitive environments by establishing sound marketing strategies. The Turkish Airline embraces change when new events threatening its business arise in the market. By adopting alternative Introduction
Political scientists believe strongly that security is a subjective term. Traditional concepts of security have propagated specific notions such as poverty reduction, world peace, and national security (Walt 1991, p. 214#). The meaning of security has been broadened to accommodate most of the events experienced in the world such as globalization, terrorism, and changing technology. This paper seeks to support the idea that new technologies present both possibilities and threats to contemporary global security.
New Technology and Contemporary Global Security
What is Contemporary Security?
Baldwin (1997) indicates that security is an important concept used ‘to justify suspending civil liberties, making war, and reallocating resources’ (p. 9**). It is also evident that security is an area that has not received desirable attention within the past few years. The concept of security is now gaining the attention of researchers and experts in global affairs than ever before. Traditional ideas of security have been overridden by modern notions that have led to new conceptualizations. Baldwin (1997, p. 6#) acknowledges that contemporary security should be defined as a country’s capability to maintain its superiority.
The conception empowers nations to think deeply and identify new threats that can inform various policies. This argument shows conclusively that contemporary security has been expanded to capture the impacts of globalization and modern technology on both international security and global relations. The definition reveals the complexity of security and the reason it should be examined from a wide range of perspectives.
Contemporary security, therefore, has emerged as an interdisciplinary field due to the changes experienced in the world today. However, earlier scholars in the field were preoccupied with threatening issues such as nuclear energy. This focus has now shifted to topics such as ‘grand strategy, conventional warfare, and the domestic sources’ (Walt 1991, p. 211**).
Emergence of New Technologies
Historians argue that the upheavals experienced in Europe from 1910 to 1945 catalyzed numerous innovations that changed the way nations interact with each other (Smith 2016). The period was defined by two global wars that led to the death of millions of people. The concept of warfare was transformed using avant-garde technologies. Different nations such as Germany, Russia, and the United States were observed to take charge of various technological developments (Barkawi 2011, p. 5#). Various human aspects such as communication, transport, and surveillance were improved.
These world wars led to the creation of the first atomic bomb. The catastrophic implications of technology continue to affect thousands of Japanese citizens today (Smith 2016, p. 169#). The world also woke up to a new era of improved communication. The Germans were observed to pursue new strategies such as the use of enigma codes. These advancements became predecessors for modern technologies and methods of communication utilized today.
Modern technologies appear to transform almost every aspect of human activity. For instance, the world is discovering new things such as weapons of mass destruction, nuclear bombs, and dangerous chemicals.
Most of these innovations have the potential to kill millions of people. Within the past few years, drones have become common in different parts of the world. Autonomous vehicles are being tested in countries such as Japan and the United States (Smith 2016, p. 175#). Wearable devices are also evident such as sensors and watches. Biological weapons are being developed in different parts of the world. Such deadly chemicals can support a nation’s global agenda.
Social media platforms have transformed the way people communicate and share information. Mobile devices are making it easier for people to collect and share information. Google maps and tracking devices are currently used by different organizations and military agencies (Smith 2016, p. 179#). The internet is arguably one of the biggest intentions of the 20th century. This technology has catalyzed numerous innovations capable of reshaping human life. With these technologies and communication advancements, it becomes quite clear that the world might never be the same again.
Technological Developments and Global Security
The above developments and advancements in technology have become resourceful for nations that want to pursue their aims. Waltz (1991) acknowledges that ‘international politics is sparsely defined by anarchy’ (p. 2**). From this understanding, it becomes clear that different nations and groups capitalize on these developments to achieve their goals. For instance, states can use advanced technologies such as drones to monitor their enemies’ preparedness to wage war. Drones are believed to play a significant role in espionage and clandestine missions (Baron 2013, para. 4#). Technologies such as autonomous vehicles and drones have been applied to save lives after terrorist attacks or natural disasters.
The era of electronic communication has been fuelled by the use of social media, globalization, and the power of the internet. These approaches are being used by nations to pursue their aims. Neorealism has become a guiding principle for countries that want to use different resources to protect their interests. International security is now focusing on the ‘interdependence of nation-states with respect to their security relations’ (Waltz 2004, p. 26**).
Nations are usually uncertain of the intentions of their neighbors or rivals. This situation explains why North Korea is capturing the attention of many countries due to its ambition to produce nuclear weapons (Kristof 2017, para. 4#). The use of new technologies is capable of making other nations feel threatened. Superpowers would not want other nations to develop military capabilities because they might threaten their survival (Baron 2013, para. 1#).
The conflicts experienced in Syria and Yemen have benefited from the utilization of drone technology to survey and monitor different activities. These technological approaches have led to positive outcomes. Drones are also being used in various missions such as monitoring weapons, terrorism, and criminal activities (Smith 2016, p. 189#). This is a clear indication that different technologies can help nations to protect their territories and prepare themselves against potential threats.
The elemental interest of states is ‘to protect their physical, political, and cultural identities against encroachments by other nations’ (Shepherd & Weldes 2008, p. 530**). Nations will continue to study and utilize technologies to improve their military strengths, acquire powerful equipment, and eventually realize their potential. The ultimate goal is for such countries to protect their citizens while at the same time dismantling potential threats.
On the other hand, technological changes have led to numerous threats to contemporary global security. This scenario supports the unique role of neorealism in global and international affairs. Neorealism remains a powerful theory for analyzing the major influences ‘emanating from Greece, Italy, Germany, and America’ (Waltz 2004, p. 6**). Emerging technologies and innovations have, therefore, compelled many scholars to take the concept of neorealism theory seriously. This idea guides nations to understand the implications and issues arising from international relations.
The structural theory reveals that the world is becoming dangerous than ever before. It is evident that modern technologies are pursued by terrorist groups to attack their enemies. Criminals have used biological weapons to wage war against nations (Walt 1991, p. 224#). The emergence of social media makes it possible for terrorist groups to recruit young people. This move has presented a major challenge to many societies due to the problem of terror. Criminal groups use different means of communication to propagate lies in this era of fake news. These changes explain why terrorist attacks and wars have become common.
Globalization and the use of new inventions have made it possible for terrorists to pursue their missions using superior weapons (Sanger, Sang-Hun & Rich 2017, para. 4#). Propaganda has become a new threat to international relations. Different groups and nations are also capitalizing on modern technologies to spread fake news. These processes have fueled animosities in different parts of the world. Cyber-crime is a social evil arising from the power of technology. More nations should brace themselves for tough times thanks to every innovation emerging from technological advancements.
Conclusion
This discussion has revealed that the notion of neorealism should be taken seriously than ever before. The emerging complexity should guide nations to develop adequate internal policies and deal with foreign threats (Shepherd & Weldes 2008, p. 533#).
It is agreeable that modern technologies present both opportunities and threats that can undermine the survival of different nations. The benefits and threats appear to be double-edged. Terrorists and sovereignties can use these developments to their own advantage. A threat to a nation can be viewed as an opportunity for a criminal or terrorist. In conclusion, modern developments in communication and technology pose greater opportunities and challenges to international relations.
Strategies the company anticipates a bright future in the air transport industry and will most likely continue to be a good example to upcoming carriers.
Reference List
Acar, A. Z., & Karabulak, S. (2015). Competition between full-service network carriers and low-cost carriers in Turkish airline market. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 207(1), 642-651.
Alagöz, S. B., & Ekici, N. (2014). Experiential marketing and vacation experience: The sample of Turkish airlines. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 150(1), 500-510.
Al-Azri, A., Waleed, R., & George, S. (2015). Same strategies different performances: A comparative analysis of business models & business strategies adopted by Turkish Airlines and Cathay Pacific Airways. International Journal of Multidisciplinary Management Studies, 5(6), 164-186.
Ayden, Y., Demirbag, M., & Tatoglu, E. (2018). Market entry strategies of Turkish MNEs. London: Palgrave Macmillan.
Dursun, M. E., O’Connell, J. F., Lei, Z., & Warnock-Smith, D. (2014). The transformation of a legacy carrier–A case study of Turkish Airlines. Journal of air transport management, 40(1), 106-118.
Low, J. M., & Lee, B. K. (2014). Effects of internal resources on airline competitiveness. Journal of Air Transport Management, 36, 23-32.
Zaim, S., Bayyurt, N., Tarim, M., Zaim, H., & Guc, Y. (2013). System dynamics modeling of a knowledge management process: A case study in Turkish Airlines. Procedia-Social and Behavioral Sciences, 99(1), 545-552.

