Executive Summary
Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC, based in the United Kingdom, is a public limited company that trades on the London Stock Exchange. The company operates in the United Kingdom’s retail industry. The company has a market share of 11.3%. The paper carried out financial analysis of Morrison Supermarkets for a period of two years. From the analysis, it can be pointed out that the gearing ratio of the company increased during the period. The company borrowed more money for expansion. There was a reduction of interest cover ratio.
The liquidity of the company remained constant during the two-year period. However, the ratios are quite low and they show that the company has difficulties in paying liabilities that are due within a year. The working capital of the company was negative. This shows that the company had difficulties in generating adequate working capital for the daily operation of the company. There was no significant change in the profitability of the company over the period. Further, the analysis shows that the company reported a slight decline in the level of operating efficiency. There was a decline in the overall financial position of the company as indicated by the shareholder valuation ratios.
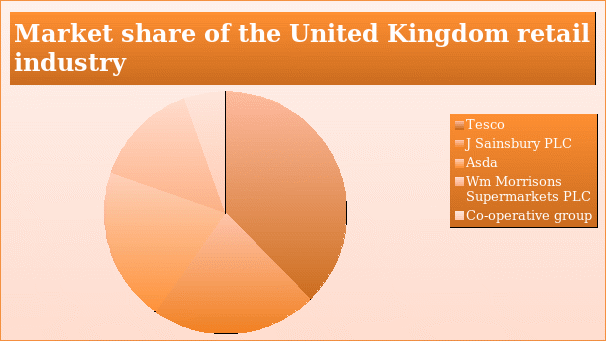
Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC, based in the United Kingdom, is a public limited company that trades on the London Stock Exchange. The company operates in the United Kingdom’s retail industry. Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC ranks fourth among the top five supermarkets in the UK retail industry with a market share of 11.3%. The company has presence in over 600 locations. It engages about 132,000 employees (Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014a). Retail industry in the United Kingdom is quite competitive and the top players engage in aggressive competition so as to increase their market share. The table presented below shows the recent statistics of market share of the United Kingdom’s retail industry.
Source of data – Verdict Consulting 2012.
The information on the market share can be presented in a pie chart as shown below.
The paper seeks to carry out a financial analysis of Morrison Supermarkets for a period of two years.
Comparative analysis
Horizontal analysis of income statement
Under horizontal analysis, the values in the income statement and balance sheet are compared with the previous year’s values. The resulting answers are expressed as a percentage. The table presented below shows horizontal analysis of the income statement for Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC.
Source of data – Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014b.
Horizontal analysis of balance sheet
The table presented below shows horizontal analysis of balance sheet for Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC.
Source of data – Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014b.
Vertical analysis of income statement
Under vertical analysis, the values in the income statement are expressed as a percentage of the total revenue earned. The table presented below shows the vertical analysis of the income statement for the company.
Source of data – Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014b.
Vertical analysis of balance sheet
Under vertical analysis, the values in the balance sheet are expressed as a percentage of the total assets. The table presented below shows the vertical analysis of the balance sheet for the company.
Source of data – Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014b.
Ratio analysis
Ratio analysis breaks down the financial data into various components for better understanding of the financial strengths and weaknesses of the company. These ratios measures different attributes in the financial health of a company. In this section, various ratios will be calculated and analyzed. End of year values will be used in the analysis.
Liquidity and solvency.
Working capital management.
Profitability.
Asset efficiency.
Cash operating cycle.
Shareholder measures.
Source of data – Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014b.
Industry averages
The table presented below shows the industry averages.
Source of data – Verdict Consulting 2012.
Measurement against key performance indicators (KPI)
There are a number of KPIs that the company uses to evaluate the performance of the company. The KPI’s are discussed below.
- Like-for-like sales – The KPI measures the yearly change in sales. There was a decline in the value of sales from the previous year. The company intends to strengthen its brand so as to increase sales.
- UK grocery market share – There was a decline in the value of the market share of the grocery products. The company intends to increase the market share by investing in new stores.
- Sales growth – there was an increase in the value of sales over the years. This can be attributed to the increase in the number of stores.
- Underlying profit – the value of profit declined by £34 million. The company intends to increase profits by improving efficiency.
- Underlying basic earnings per share – the value of basic EPS increased from 25.6p in 2012 to 27.3p in 2013.
- Net debt – the net debt increased from £1,471m in 2012 to £2,181m in 2013. The increase was used for capital expenditure.
- Capital investment – There was an increase in the value of capital investment from £901m in 2012 to £1,016m in 2013. This contributes to growth in total assets.
- Return on capital employed (ROCE) – There was a decline in ROCE from 10.1% in 2012 to 9.6% in 2013. This shows a decline in profitability.
- Colleague engagement – The KPI is measured through surveys and the number of points increased by 6.2% from the previous year.
- Carbon footprint reduction – the company is geared towards reducing carbon emissions during the course of business. However, with the increase in the number of stores, carbon emission increased from 14.6% in 2012 to 19.3% in 2013.
- Waste to landfill reduction – the company has been successful in reducing the amount of direct waste to landfill from 5.6% in 2012 to 1.7% in 2013 by using recyclable materials. The company seeks to reduce waste to 0%.
Evaluation and the uses of KPI in assessing organizational performance
Companies use the KPI to measure organizational performance. These indicators are based on internal and external factors that affect the operation of a business. The KPI gives a fair view of the operations of a business. The KPIs are evaluated and updated on a periodic basis so that they can take into account the changes in the environment and strategic objectives of the company. The KPIs are of different forms. Most companies often prefer to use both financial and non-financial indicators.
Discussion and explanation of results
The gearing ratio of the company increased during the period. The company borrowed more money for expansion. There was a reduction of interest cover ratio. This can be attributed to the increase in the amount of debt. It shows a decline in the ability of the company to pay interest expense. The liquidity of the company remained constant during the two-year period. However, the ratios are quite low and they show that the company has difficulties in paying liabilities that are due within a year.
The working capital of the company was negative. This shows that the company had difficulties in generating adequate working capital for the daily operation of the company. Therefore, it may require external funding. There was no significant change in the profitability of the company over the period. The values were low and constant over the period. The ratios indicate that the company reported a slight decline in the level of operating efficiency because the value of the ratios declined. There was a decline in the values of shareholder valuation ratios over the two year period. This implies that there was a decline in the overall financial position of the company. Also, it can be noted that the performance of the company is lower than the industry average (Holmes, Sugden & Gee 2005).
Advantages and limitations of analysis techniques used
There are a number of advantages of ratio analysis. The first advantage is that it enables an investor to compare the financial performance of a company with other companies. This helps an individual to make a selection of the company to invest in. Secondly, ratios allow analysts to analyze the financial statements of a company. Thirdly, ratio analysis enables users to locate financial and operating efficiency and weaknesses of a company. This information is vital for internal and external users. Finally, ratio analysis aids management and other users in coming up with estimates of future performance of the company (Brigham & Ehrhardt 2009).
There are a number of weaknesses of ratios. First, it is difficult to use a set of industry average ratios when analyzing large companies that have different business segment which fall in different industries. This creates a major challenge when using industry average ratios to compare performance of such companies. The second weakness is that inflation distorts the financial statements of companies. The third weakness of ratios is that it is highly distorted by seasonal factors. For instance a company may report a sporadic increase in sales of a certain product during a one season such as winter. This will distort the ratios calculated. Therefore, an analyst may be required to have prior knowledge of the seasonal factors that affects a business (Collier 2009).
In summary, the analysis above indicates that the company did not report a significant improvement in financial performance.
References
Brigham, E & Ehrhardt, M 2009. Financial management theory and practice, Cengage Learning, USA.
Collier, P 2009. Accounting for managers. John Wiley & Sons Ltd. USA.
Holmes, G, Sugden, A & Gee, P 2005. Interpreting company reports, Prentice Hall, USA.
Verdict Consulting 2012. UK retail 2012 & beyond. Web.
Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014a. About us. Web.
Wm Morrison Supermarkets PLC 2014b. Financial reports. Web.
