Chipotle is a Mexican style eatery that originated in Denver, Colorado by founder Steve Ells back in 1993. The original intention of Steve Ells’ first restaurant was to be that of a fine dining establishment, however, Ells knew nothing about owning a business or running a business so he opened up a small burrito shop, Chipotle, as a low-risk investment that would later give him the capital he needed to open up the fine-dining establishment he had originally set out to open. With a loan of $85,000 that he obtained from his father, Steve opened up his small burrito shop by the University of Denver (Whitten, 2017).
Steve Ells’ idea of Chipotle was based on his experience while living in San Francisco. Though Steve worked at fine-dining restaurants, Ells ate at small burrito shops and taquerias. While San Francisco was filled with taquerias, Denver was not and Steve Ells’ saw this as an opportunity to tap into an untouched market for Denver, which proved to be successful (Whitten, 2017).
After only being open for a couple months, Ells was able to repay his loan and after a year and a half, he was able to open a second location. Ells still had the mindset to open his fine dining restaurant but realized that his venture was so successful that in 1996, he opened up his third location. Steve Ells continued to open up additional locations and in 1998, McDonald’s became an investor and invested over $360 million in the company for growth and expansion. A couple years after McDonald’s original investment, McDonald’s became the majority shareholder and this continued until 2006 when Chipotle decided to go public and McDonald’s divested (Whitten, 2017).
The company continued to grow and expand and by 2017, Chipotle reached nearly 2,300 locations using marketing techniques that reached out to the values of consumers of fueling bodies with whole foods. Chipotle set out with a mission to create food with integrity using organic produce, hormone and antibiotic free meat, and pasture-based dairy (Bose, 2020). In looking at Chipotle, it’s organization’s strategy, and its business model; Chipotle is able to provide the quality of good food while also providing the consumers with convenience of quick service. It is this business model that has gained the company so much success. Middle class Americans make up 50% of the U.S. population and it is this population that Chipotle’s mission, values, and business model speaks to.
Old Vision Statement
“To enhance the way people perceive and partake of fast food.”
Revised Vision Statement
Old Mission Statement
“To provide food with integrity. Quality is a state of mind at Whole Foods market.”
Proposed Mission Statement
“To provide food with quality and integrity, nurturing health and prosperity in customers, employees, and everyone in between.”
External Factor Evaluation Matrix (EFE Matrix, EFEM)
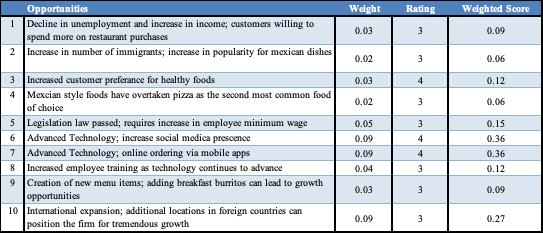
Primary Implication from EFEM (Opportunities)
Technological advancement is an area in which Chipotle may have an advantageous position. Public interest in this topic is increasing, and companies that use unsustainable methods are viewed negatively. However, Chipotle uses a broad range of sustainable practices, including innovative ones such as participation in the development of smart cities. The growing interest in social media and online ordering position Chipotle to benefit considerably from implementing appropriate strategies in these fields.
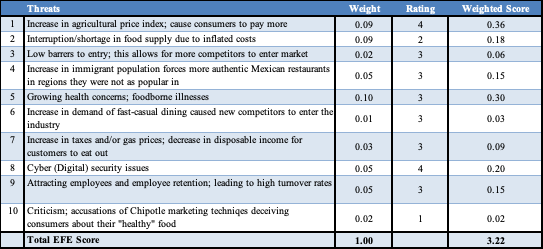
Primary Implications from EFEM (Threats)
The primary external factor affecting Chipotle Mexican Grill is the food costs. This is defined as one of the most critical factors that have to be taken into consideration when discussing a business’s environment. Food shortages cause prices to increase, and even if the company is willing to pay, it cannot necessarily source the products it needs in the necessary quantities. Moreover, to withstand the costs, Chipotle will likely have to increase its prices, which will cause customer dissatisfaction. Both of these factors combined create a substantial threat to the business’ performance
The second crucial external factor would be brand awareness, which is an area the business struggles. Chipotle Mexican Grill (2018) highlights challenges related to past food safety incidents and lack of international reputation. The public may associate the brand with danger, which reduces its popularity and, therefore, revenue. Moreover, Chipotle is not a well-known company outside of the United States, especially when compared to competing businesses such as McDonald’s. This can be proved as a disadvantage, which makes international expansion challenging. In the future, Chipotle will have to restore its reputation and increase its popularity if it plans to continue its expansion plans.
The Competitive
The Competitors
Taco Bell
An American chain of fast food restaurants based in Irvine, California and a subsidiary of Yum! Brands, Inc. This fast food chain serves a variety of Mexican and Tex -Mex foods that include tacos, burritos, quesadillas, and nachos. It was founded by Glen Bell in 1962 in Downey, California. Today, the chain has more than 7,000 locations and over 350 franchisees worldwide.
Qdoba Mexican Eats
Chain of fast causal restaurants in the United States and Canada serving Mexican-style cuisine. The chain first opened in 1995 in Colorado by Anthony Miller and Robert Hauser, using the name Zuma Fresh Mexican Grill. The Denver, Colorado location was an immediate success, with first-year revenues exceeding $1.5 million. The name was changed to Qdoba in 1999 as a result of a lawsuit due to the name being to similar to another company. To date, Qdoba has more than 650 restaurants in 47 states, the district of Columbia, and Canada.
Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM)
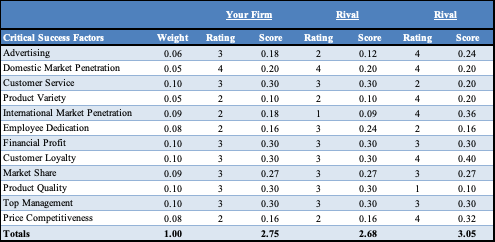
Primary Implications from CPM
Chipotle and its rivals Taco Bell and Qdoba show varying differences on their critical success factors. In reviewing the Competitive Profile Matrix (CPM), you will see that Qdoba indicated in the first rival column below is performing the worst out of the three companies. The areas in which the weight is higher are considered to be the critical factors needed to succeed in the Mexican Restaurant industry. Those are customer service, financial profit, customer loyalty, advertising and product quality. Where Chipotle seems to fall short is product variety, advertising, and employee dedication sections. However, in recent months we have seen that employee turnover rates have declined due to the increase in employee incentives and benefits that have recently been implemented. They are not overly concerned with product variety in recent years due to no significant decline in sales as a result. From an advertising perspective, this is something that could be difficult since Chipotle relies on word of mouth to get new customers. There are options to bring the advertising up so that the other things connected to advertising can grow which would be domestic and international marketing, if the company decided to go around the world with their products. Where Chipotle is exceeding in customer service, financial profit, and customer loyalty despite a history of health concerns.
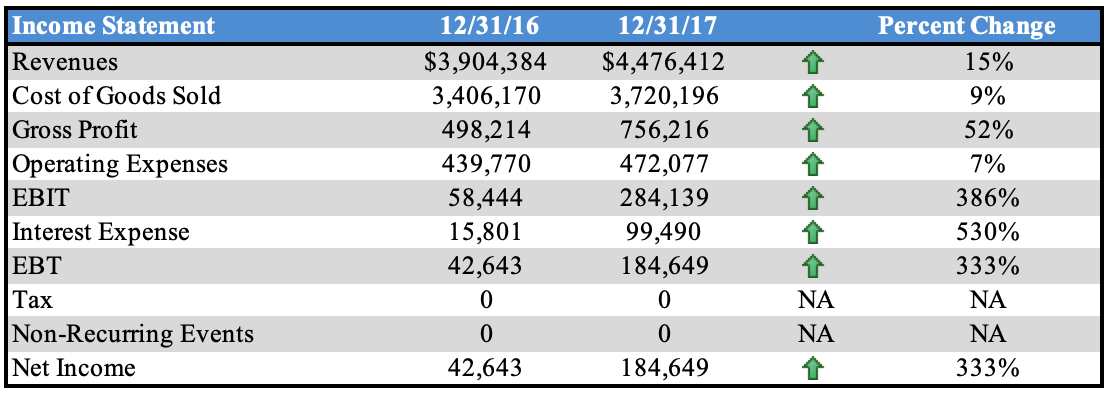
Income Statement Overview
From viewing Chipotle’s income statement, net income increased by $142K from 2016 to 2017. Revenues for the company increased but the cost of goods, operating, interest, and tax expenses went up as well.
Balance Sheet
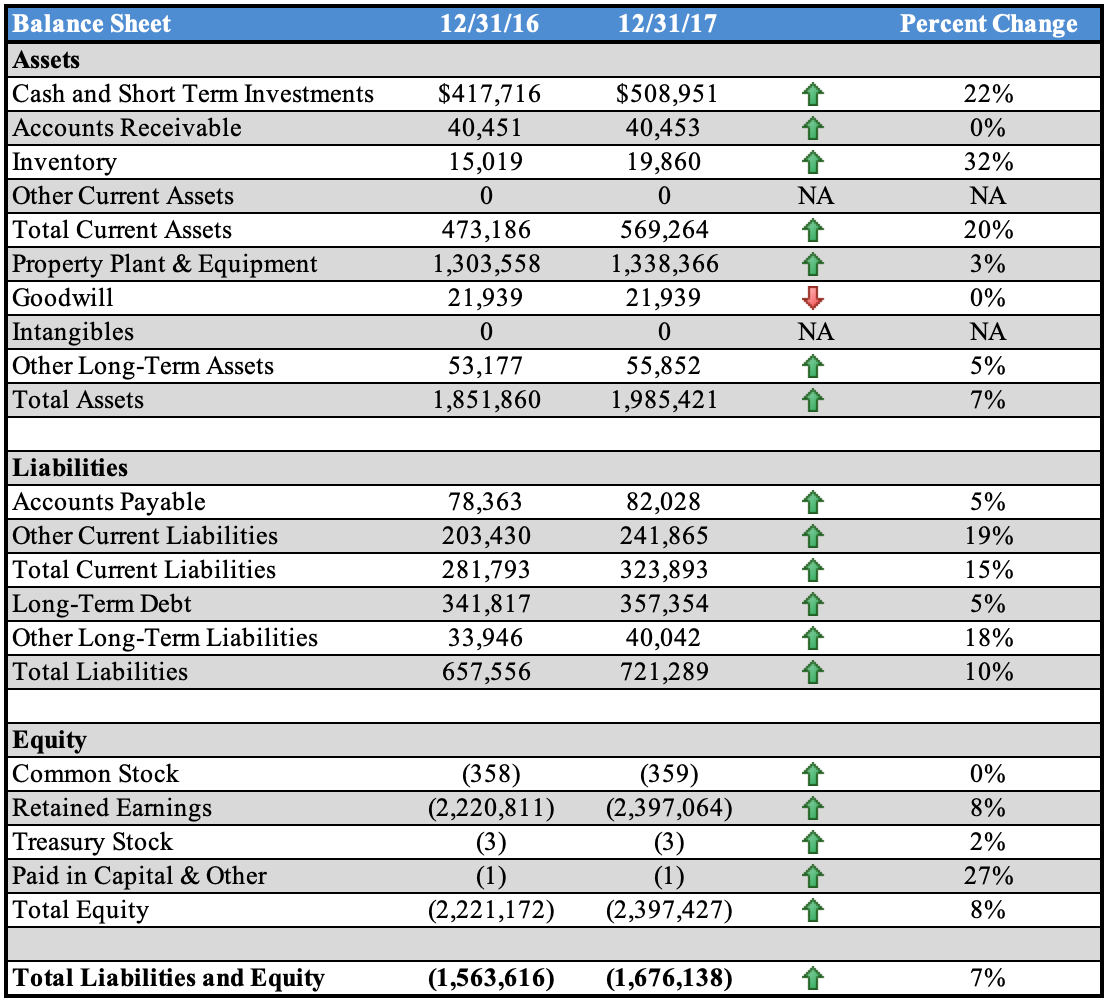
Balance Sheet Overview
Chipotle’s experienced an increase in total assets by over $134K from 2016 to 2017. Each line item under the asset category increased except for the Goodwill assets, which experienced no change from 2016 to 2017. Chipotle’s liabilities experienced a 10% increase, which are due to the current liabilities and long-term debt liabilities.
Historical Ratios
Historical Ratios Overview
In reviewing the historical ratios, there are a few notable strengths and weaknesses to be aware of. For starters, Chipotle was well-positioned in its ability to pay its current and short-term obligations without the need to get additional financing. This is evident when reviewing their quick and current ratios based on the 2016/2017 data. Another positive is their inventory turnover strength. Inventory turnover measures whether an organization holds excessive stocks of inventories or whether they are slowly selling inventories (David et el, 2019). Chipotle’s inventory turnover ratio is high, which implies that they have strong sales. Chipotle did have a drop in this turnover rate from 2016 to 2017, going from 226.79 to 187.32. Please refer to the chart below. A drop in this turnover rate indicates a decrease in sales during that time. This could be attributable to the foodborne illness outbreak Chipotle experienced in 2016. It’s recommended to watch this number over the next year.
An increase in asset turnover has increased from 2016 to 2017 suggesting that the company is capable of effectively using their existing assets to generate sales. However, they are low in comparison to the industry average of 3.3 (“The Complete Toolbox for Investors | finbox.com”, 2020). Although they are performing well from a sales perspective, they are lower than the average suggesting that external factors are continuing to hinder Chipotle reaching the maximum potential.
An area for concern, however, is evidence that suggests the companies’ liabilities were more than its assets between 2016 and 2017. The total debt to equity ratio shows a consistent -0.30 across the board. Total debt to equity ratio measures the total funds provided by creditors versus owners. This representing a negative number could indicate that the company had a negative net worth during this time or that creditor financing is used instead of shareholder financing. Alternatively, the debt to total assets ratio looks good. Debt to total assets measures the percentage of total funds provided by creditors. The higher this ratio, the higher the risk of investing in that company. Having a ratio of 0.36 or 36% does not put the company at risk. Typically, investors like to see this number at 40% or lower.
Lastly, the final area of concern is the return on equity. ROE measures how effectively management is using assets to create profits. Chipotle’s ROE is still in the negative from 2016 to 2017. It has gotten worse from -2% in 2016 and -8% in 2017. A negative ROE suggests that the company is in financial distress. Based on this review, there are several areas to watch and improve from a historical perspective.
Internal Factor Evaluation Matrix (IFE Matrix, IFEM)
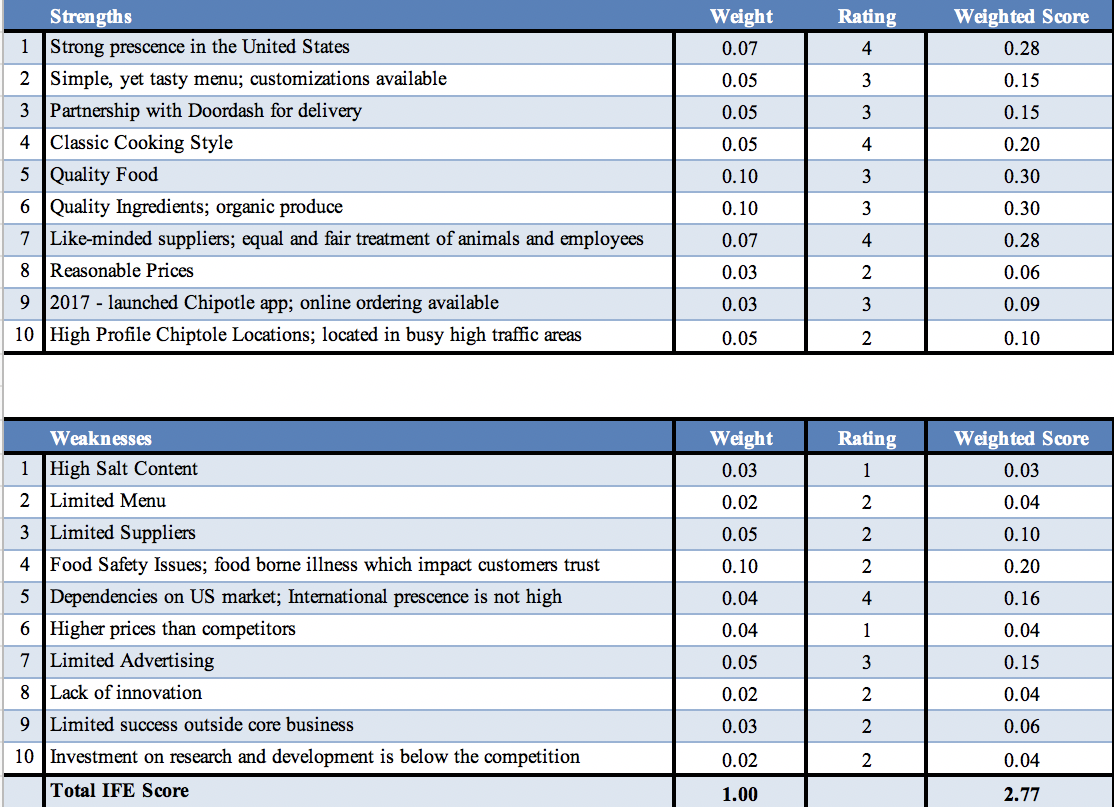
Primary Implications from IFEM (Strengths)
As seen from the first part of the matrix, one of the restaurant’s greatest strengths is its established presence on its domestic market, in the United States. The company has more than 2,400 restaurants in the US, taking up 57% of the share of limited service Mexican restaurants in the country and coming second only to Taco Bell (Lock, 2020). The second biggest strength is the restaurant chain’s integrity when it comes to sourcing raw materials: it has close ties with like-minded suppliers that are environmentally aware. Worth mentioning is Chipotle’s partnership with Doordash for delivery, which is especially relevant today amidst the COVID-19 pandemic. The restaurant owes its success to a simple, yet tasty menu with a customization menu and food made from quality ingredients.
For all its strengths, Chipotle has its own set of challenges, the biggest of which is probably its dependency on the US market and low presence on foreign markets. At the moment, outside the US, Chipotle is only present in the United Kingdom, Canada, Germany, and France, and its overseas growth is quite slow (Show, 2014). As seen from Chipotle’s 2017 annual report, the company has a limited advertising budget and low investment in research and development (Chipotle Mexican Grill, Inc., 2018). Interestingly enough, one of the company’s greatest strengths is also its significant weakness. As reported by Giamonna and Patton (2015), because the chain uses fresh food, it is more prone to spreading E.coli bacteria, which caused outbreaks in the past.
Primary Implications from IFEM (Weaknesses)
As for Chipotle’s weaknesses, they seem to revolve around the company’s disengagement on foreign markets. Since Chipotle is not a recognizable brand outside the United States, other countries might not be aware of its existence. For this reason, entering new markets, offering the same product might be risky. Here Chipotle might have to face its another major weakness: limited menu and prices higher than their competitors. To build a presence on a new market, the restaurant chain might have to localize its production and marketing strategy, which comes at a cost. It is generally challenging to strike the right balance between pandering to foreign customers’ tastes and retaining its unique identity. Aside from that, before making such a step, Chipotle needs to work on its reputation and show the public how it tackles the food safety crisis.
