Organizational leadership has become a topic for vocal discussion in recent years. It is currently outlined as one of the most crucial constituents of successful internal and external management. Effective leadership helps implement various innovations, strategies, and considerably influences the communication within the organization. Professional development highly depends on the execution of specific adjustments inside the company, for which the leaders are primarily responsible. Therefore, this paper aims to explore the role of leadership and its effect on organizational changes based on the example of The Society of Human Resource Management (SHRM).
Organizational Leadership Development Report
Leadership Traits Exhibited by Leaders in Effecting Change
A shift to online education requires many resources and a well-organized timeline plan. For this reason, leaders responsible for the project implementation must possess several vital traits that can ensure the success of the plan. Firstly, the ability to manage finances is critical for leaders. Sufficient budgeting for implementation is as essential as human management (Alsher, 2012). Project establishment and management is the most crucial part of the undertaking, as it outlines every step of the process.
Budgeting and planning is the primary step for innovation realization that outlines the process as a whole, giving each member the directions. Leaders must compose a realistic timeline and funds, tracking the performance, securing a smooth implementation of change (National Center for Healthcare Leadership, 2006). Such a trait is fundamental for each administration as it is the first step to successful project execution. If one phase is incorrectly outlined, the further process may become out of order.
The second crucial trait that is frequently mentioned to be vital for leaders is assertiveness. Multiple leadership theories suggest that such an attribute is essential for each manager to effectively control change implementation (Zakeer et al., 2016). Willpower allows controlling and commanding of the team, and if used wisely, ensures a sufficient project installation. Such managers are more likely to achieve the results than others (APQC, 2014). Therefore, such a characteristic is crucial in the implementation of changing practices and ensuring coherent teamwork.
Evaluation of Leadership Traits and Factors that Contribute to High Performing Teams
All leaders possess a particular set of traits that ensure their effectiveness in managing teams within the organization. Even though the researchers have been trying to distinguish a specific list of leaders’ qualities, they significantly vary across different organizations and groups (Özbağ, 2016). Nevertheless, possession of distinct personality features increase the chances of building and maintaining a high performing team. Personal traits of a leader may raise the effectiveness of the workspace, improve the relationship between staff, and better the company’s performance. The first group allocates only personal characteristics, whereas the second point out the manager’s ability to influence ethical conduct and performance (Özbağ, 2016). Effective leadership is impossible without balancing these groups, contributing to the company’s moral and performance-based changes.
Team-leaders are highly responsible for the results of their units, which is confirmed by multiple types of research. High-performing teams usually possess similar features that guarantee their success (Borkowski, 2016). SHRM is an example of a purpose-driven workplace, which reflects on the satisfied employees and clients. A clearly stated mission of contributing to the enhancement of workplace conditions drives its employees to increase performance.
The second factor that contributes to team accomplishment is engagement practices. The ability to encourage indicates a leader who can carry on its vision by involving the employees (Aarons et al., 2015). SHRM is known to advocate for its workers and share their engagement practices as one of the largest HR associations. The website states that the encouragement of diversity allows the organization to implement innovative solutions and keep on track with the recent developments (SHRM, 2020). Therefore, the positive influence of employee commitment is confirmed in the example of SHRM.
Evaluation of Leadership Traits and Factors That Promote a Culture for Creativity and Innovation
Most industries’ highly competitive environment requires organizations to continually adapt innovation and practices to stay relevant to the employees. Leaders are one of the responsible figures for the company’s staff satisfaction. Managers must be open-minded and approachable, establishing such a corporate culture, where employees are free to share their ideas (Borkowski, 2016).
Firms must deviate from the concept that only top-management has the power to generate novel approaches. Organizing a congenial working environment is proved to increase the team’s creative behavior, subsequently enhancing professional development (Ali Taha et al., 2016). SHRM is one example of how the encouragement of innovative ideas among employees reflects the company’s success.
The organization values diversity and self-development, including the creative one. The website confirms this concept stating that SHRM fosters respectful and empowering conditions for each employee (SHRM, 2020). Such an approach to corporate culture inspires staff to develop innovative ideas on how to grow the company further. An essential trait of the leader is the ability to recognize potential. Effective managers know when employees are capable of more by engaging them in out of the box activities and providing an opportunity to grow inside the company (Borkowski, 2016). Such trait benefits the company by delivering talented employees, which SHRM conveys by providing career growth ability with the help of educational assistance.
Strategies the Leadership Could Apply for Working Successfully With Teams and Effecting Change
Change is hard for each company, as it requires transforming the habitual conduct of work. Classical leadership style has not been effective in the modern workspace (Al Rahbi et al., 2017). A strict management approach does not give space or motivation for growth, therefore causing the company’s stagnation and irrelevance. On the contrary, open-minded, engaging leaders who manage to create a healthy environment ensure its success and growth.
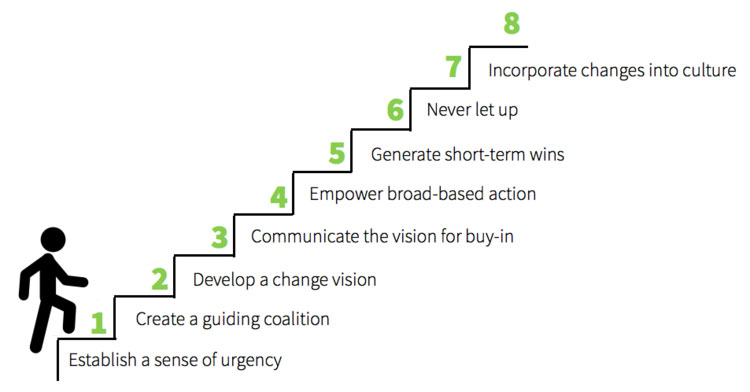
At the time of rapid technological advancement, companies must adapt to the environment. Moreover, creativity is a factor of company differentiation, making them stand out among the competitors (Landry, 2018). For that reason, leaders must implement various strategies to ensure successful change implementation and Kotter’s 8-step change model is one of the most effective. Based on the observation of a hundred organizations, the systematic guide provides a detailed plan for implementing change (Kotter, n.d.). The strategy proves the necessity of transformation in business and an effective leader able to execute it.
Change Management Proposal
Organization Overview
Many existing organizations promote change and innovation; however, a few manage to implement it onto the workspace properly. SHRM is the largest association in the HR field, founded in 1948 that actively promotes and supports professional development and qualification advancement (The Society of Human Resource Management, 2019).
With headquarters based in Alexandria, Virginia, however, SHRM provides various educational materials for personal growth, represented across the world, holding accountable for over 300,000 members in 165 countries. Their mission is stated as follows: “to empower people and workplaces by advancing HR practices and by maximizing human potential” (The Society of Human Resource Management, 2019, para 4). Associate members have constant access to learning materials, conferences, and training that enhance their professional skills, which SHRM is best-known for.
Outline of the Change Implemented by SHRM
Online learning has become widely popular over the last decade, providing for easy access to education. SHRM is implementing innovative eLearning courses for the partners to provide more access to their materials. The coronavirus pandemic caused many businesses to adapt to the new reality, which became a crucial factor in the effectiveness of an organization (Brisson‐Banks, 2010). SHRM decided to fully emerge in online learning by opening access to various information resources. Therefore, such a notion of professional development has become extremely convenient for all members.
Organizing a transition process from one system to another is a considerable leadership challenge due to the amount of work needed to be conducted. Arranging an effective team headed by an excellent manager is the most crucial part of the initiative’s success or failure. Moreover, the mobile app for eLearning from SHRM was the most recent change. Its database contains hundreds of text and video learning materials from the best professionals in the human resources industry organized in a simple and easily accessible way.
Change Drivers
The coronavirus pandemic set new trends in business, therefore, the organization had to adapt to the novel strategies quickly in order to survive. Being one of the largest HR-educational platforms, SHRM had to start shifting from offline courses and print books as their only way to study for the certifications. Therefore, to stay relevant to the customers, SHRM has been continuously updating their online education base.
As the world is rapidly shifting to online platforms, the HR industry largely depends on this transformation. Education is vital for any HR worker, and as education is shifting to a mobile on-demand platform, SHRM, had to react to such innovations quickly as one of the most top organizations of HR industry. E-learning provided by this organization can now be used to educate workers collectively at the workplace, which increases employee engagement and subsequently raises the reputation of SHRM (Rimon, 2017). Therefore, the main driver is growing digitalization, which provides the opportunity to expand its influence.
Resistance to an Organizational Change
It is common for employees to resist change because it means altering their habits and routine. A transfer to online learning may become a significant challenge for some members of SHRM. It is a company that includes all age groups, therefore adapting more online courses may cause resistance from the older audience. The reason for the oppression is due to their lack of technical skills and habits of using paper materials. Being used to print materials and offline learning, senior associates feel more productive than at times of online education. Nevertheless, the constant shift in generations and advanced technology require each worker to be familiar with the technology, especially in HR.
Despite such resistance, the prevalence of younger employees is more significant, which makes innovation more crucial for each organization. All SHRM staff members should be educated on the usage and benefits of eLearning to convey the corporate mission among employees and members of the association. If needed, the executives may initiate specific training and give an overall presentation of the portal and the mobile app to the staff. However, if this group of people resisting technology is ignored, it would reflect on the organization’s productivity and marginalize the employees.
Application of Kotter’s 8-step Change Model
Kotter’s change model is one of the most detailed and effective strategies for innovation implementation. It consists of eight steps on successfully realizing a change management project, aiming at the strategic level of the change management process (Tang, 2019). Therefore, this approach was chosen for the application to the eLearning portal of SHRM. The first step outlined by Kotter is establishing a sense of urgency. The scholar explains that urgency motivates the employees and sets a specific deadline concerning work effectiveness (Tang, 2019). Moreover, the leader needs to establish a healthy environment inside the workplace to ensure successful outcomes. The second phase is to form a powerful guiding coalition. Top management must be of positive influence on the organizational work, encouraging and uniting the employees.
Creating a vision for change is the third step of the change model. Kotter emphasizes that establishing a clear idea will define innovation and become a roadmap to change effort (as cited in Tang, 2019). In the fourth stage, the leaders must communicate the concept. Once the vision is set, it must be frequently repeated to embed it in everyday work to remind the team of the process’s primary purpose.
The fifth part of implementing a change initiative is the encouragement of workers to adhere their behavior according to the corporate vision. Kotter explains it as eliminating change obstacles and focusing on the implementation’s future, where risk-taking is encouraged (as cited in Tang, 2019). The sixth stage is focused on planning and creating short-term wins. Achievement of more manageable goals will give the team a sense of accomplishment in the beginning stages of the process and motivate them to do more. The last two stages of the model are among the most crucial ones. On the 7th step, Kotter suggests consolidating the improvements and building on it (as cited in Tang, 2019). Change does not end on short-term wins, which is essential to comprehend.
This part is focused on establishing policies and hiring highly competent people for the implementation. The final constituent in Kotter’s model is the institutionalization of new approaches, which makes an immense effort to build the change into the corporate culture. By outlining Kotter’s change model, evident that it is applicable to the change implementation executed in SHRM. The plan is suitable for organizations with many employees and provides a detailed outline of every step.
Application of System Thinking to Address Organizational Challenges While Executing Organizational Change
System’s thinking has been gaining increasing attention as a novel comprehensive approach to change management. System thinking allows understanding design through multiple tests and connections to fully comprehend it. Such an approach has been increasingly used in the development models as one of the most efficient methods to achieve innovations. It is also one of the most effective strategies for managing and overcoming challenges during transformation, as its initial purpose is to tackle the difficulties. Systems thinking evaluates the challenges to identify the valid leverage point, subsequently enhancing the strategy to create a profitable outcome.
In SHRM implementation of eLearning portals, systems thinking would be feasible in identifying the primary challenges. Leaders with such an ability see the change as an opportunity to enhance team collaboration and shift the workers’ mindset to the new concepts, which is what SHRM needs (Westover, 2020). This approach will be highly effective in converting pessimistic resistant employees to active learners of the new digital platform.
Systems thinking provides many benefits to the organization apart from outlining the primary challenges and enforcing change strategies. It may help identify unconventional issues not related to the project. Systems thinking is a useful tool that quickly resolves issues without any time delays (Zurcher et al., 2018). Lastly, an essential financial aspect of the company can also be managed by systems thinking, where this approach aids in resolving them from the collaborative and shared understanding perspective.
Analysis of Strategies, Innovation, and Techniques for Effecting Change
Strategies and Innovations to Effect Organizational Change
Effecting change is always challenging, requiring thorough planning and strategizing. The first effective strategy that can also apply to the chosen organization is based on making people the ambassadors of change. Employees do not usually favor forceful advancement; instead, leaders should be able to infuse change so that workers feel they did it. Scientifically, when a person independently solves an issue, the brain releases a rush of neurotransmitters, positively associated with the change experience (Goman, 2016). Therefore, giving employees the power to create change will ensure more effective implementation of it.
The second strategy is based on transparency, as it is critical to establish an open environment that translates frank messages about the flow of the change campaign. It is scientifically proved that the brain is constantly alert for danger signals, and when the leaders are overly optimistic about clearly unsuccessful change, our body switches to high warning looking for signs of deception, which cause the primitive mind to respond with heightened anxiety (Goman, 2016). Therefore, it is on the psychological level that transparency in the company initiates the change implementation’s success. One of the best examples is Google, whose primary mantra is full transparency with the employees, leading to worldwide success.
Innovative models of organizational structures may significantly change the conduct of the organization. One of the most recent innovations is eliminating the business hierarchy, allowing all employees to take part in organizational management. McDonald’s implemented such a design, where it is open to ideas from suppliers to cashiers. Besides, a test-kitchen may be implemented as an activity to share all the ideas among employees of every level. Such innovation will help discover a new perspective of a company and propose new ideas for the development of an organization
The Role of Communication in a Change Management Plan
Communication is the key to successful change management, which may be the primary driver of the project. Scholars have ranked change management interaction among the top three prioritized issues among the leaders (Neill, 2018). Communication strategies may be the principal constituents enabling growth. The plan developed with the purpose of change must contain contact approaches, as these are what keeps the teams united, connected to the top management. Reportedly, 70% of innovative programs fail due to ineffective communicational patterns (Neill, 2018). Such statistics allow theorizing that failure to establish healthy communication between within the organization and the teams’ relationships increases the chances of the innovation management unsuccessful outcomes.
Strategies for Motivating Stakeholders to Accept Organizational Change
Convincing the stakeholders to implement the organizational change may be a challenge for many companies; however, scholars provide various strategies to persuade stakeholders to rethink their beliefs. The first strategy may seem basic and straightforward; nevertheless, it is among the most effective ones – monetary rewarding. Bonuses and rewards such as recognition encourage internal stakeholders to become more proactive in the organizational change while simultaneously focusing on the consumers and their needs, which subsequently benefits all parties (Chebbi et al., 2019). The rewarding system can cause partners’ active participation in the innovation and further genuine interest in it.
Another strategy that will allow the shareholders to invest in the organizational change is setting administrative boundaries that benefit them. Stakeholders may become the drivers of innovation implementation by emphasizing their role as facilitators and critical contributors to the company (Chebbi et al., 2019). Such a psychologically-based strategy will ensure associates’ favorability, resulting in employee training activities and innovational culture establishment.
The last strategy is somewhat experimental but may be feasible in certain organizations. Chebbi (2019) explains that the “stakeholder theory is conceptualized as firm theory, referring to an explanation or foundation of the firm’s existence” (p. 3) The plan is based on the idea that the stakeholder’s interest should not be limited to financial benefits but deliver more distinct advantages. The theory focuses more on employee satisfaction, provided by the partners as the primary driver of change.
Training and Support Required for the Successful Implementation of an Organizational Change
Training is one of the most efficient resources for increasing employee productivity. The introduction of change may require previous workers’ education, and scholars suggest a hypothesis for sales education. The training is related to the commerce process, where organizational growth is fueled by market changes (Gil et al., 2015). Demonstrating the novel trends in a similar market through the interactive practice of economics models can become a powerful innovation instrument. It is always more effective to show new models and innovation in practical use rather than theoretical. Such an approach can significantly increase staff’s attitude to the product and the productivity of its use in the future.
Correct staff administration and strategies to successfully realize the innovation can be gained through respective training. Academic writing agrees with such a suggestion, stating that each change for leaders involves training and improvement of their skills in the first place (Gil et al., 2015). Therefore, to start implementing change, managers must prepare for it themselves through relevant training. Such a strategy will significantly affect the conduct of the work, its environment and most likely boost the company’s productivity. Leaders are responsible for various factors in corporations; thus, their training is an essential part of investing in the firm’s prosperity.
Strategies for Sustaining an Organizational Change
The change process in an organization is not limited to its implementation; at times, sustaining it may be more challenging. A strategy based on being open to shifting paradigms is a useful tool for maintaining a company’s innovations. Scholars’ statement of 70% failure outcome among organizational change project sustainability hypothesizes that some constituents may have been modified with time (Voehl et al., 2015). It is vital to comprehend that some parts of the plan may have a better implementation outcome with acquired changes on the market or within customer’s behavior, therefore, needing to be modified. Being open to altering the current mindset, preparing employees for it, and planning to change is a feasible plan for sustaining transformation in the company.
Another strategy that will help predict sustainable innovaton is investing in planning for achieving sustainable results. Ability to see future outcomes will significantly decrease the possibility of unsuccessful change implementation. Scholars agree that sustainable planning investment creates additional capacities that become a practical resource and further part of the corporate culture (Voehl et al., 2015). As simple as it sounds, many companies fail to see concrete results and plan upon them. Therefore, the management must subjectively define the environment and invest in sufficient planning, which in such manner would significantly increase the chances of successful results.
How Stakeholders are Involved in and Held Accountable for Organizational Change
Stakeholders are one of the most crucial people that can enable organizational change. Various associates are interested in the company; therefore, they must be assured of corporate change campaigns’ achievements. One approach of involving partners is implementing an inclusive strategy, where only selected ones can affect the decisions. Such a model gives shareholders a voice in shaping strategies from mutual diagnosis to action planning and implementation (Weatherston, n.d.). Another way of connecting the stakeholders is by motivating them through the employee success. Ensuring the associates of benefits available for the employees may influence their decisions and subsequently encourage staff to adopt and sustain new behaviors required for change, knowing the top-management full support.
The accountability of the stakeholders is a crucial part of organizational change implementation. A strategy that will ensure accountability among the stakeholders is based on the notion of balance. Global governance is defined by the businesses that manage to establish liability, which is key to a balanced relationship. Creating an environment in which the interests of the powerful top-management do not dominate the views of people affected by a company is an effective strategy of accountability (Blagescu et al., n.d.). In such a way, the capacity to create a balance between the managers, stakeholders, and the organization to voice the opinions allows the partners to be accountable for each organizational change.
Engagement in the change processes may be one of the most effective strategies for holding the associates accountable for their innovations. Involvement is the best path to determine the partners’ interests, including participation in decision-making process (Blagescu et al., n.d). Shareholders’ ability to input their ideas into the organizational change process will remain them accountable for each step of the implementation. It is vital to understand that stakeholders’ engagement goes beyond asking for approval or making the decision between determined matters; they must feel the ability to have a voice in making organizational decisions.
Ways to Measure Success of Organizational Change
The process of organizational change is not completed at the stage of its implementation. It is crucial to measure the effectiveness of the innovations to receive an adequate picture of the process for future reflection. The first strategy of measuring success is to evaluate the implementation. Tracking the effectiveness of the design through the plan adherence is a useful strategy of seeing the progress of implemented organizational change (SHRM, 2019). Companies must look back on implementing change and determine which parts were the most and least efficient.
Another strategy for evaluating the success of change is to measure the alteration in behavior. Advances in perceiving the company are a natural outcome for innovation implementation, consequently increasing company performance (SHRM, 2019). Evaluating the way employees and clients adopt and reject the novel updates is an essential matter to track to obtain a comprehensive picture of change management efforts. Such a strategy helps in measuring the innovation influence on a human factor, which is crucial as companies depend on their people.
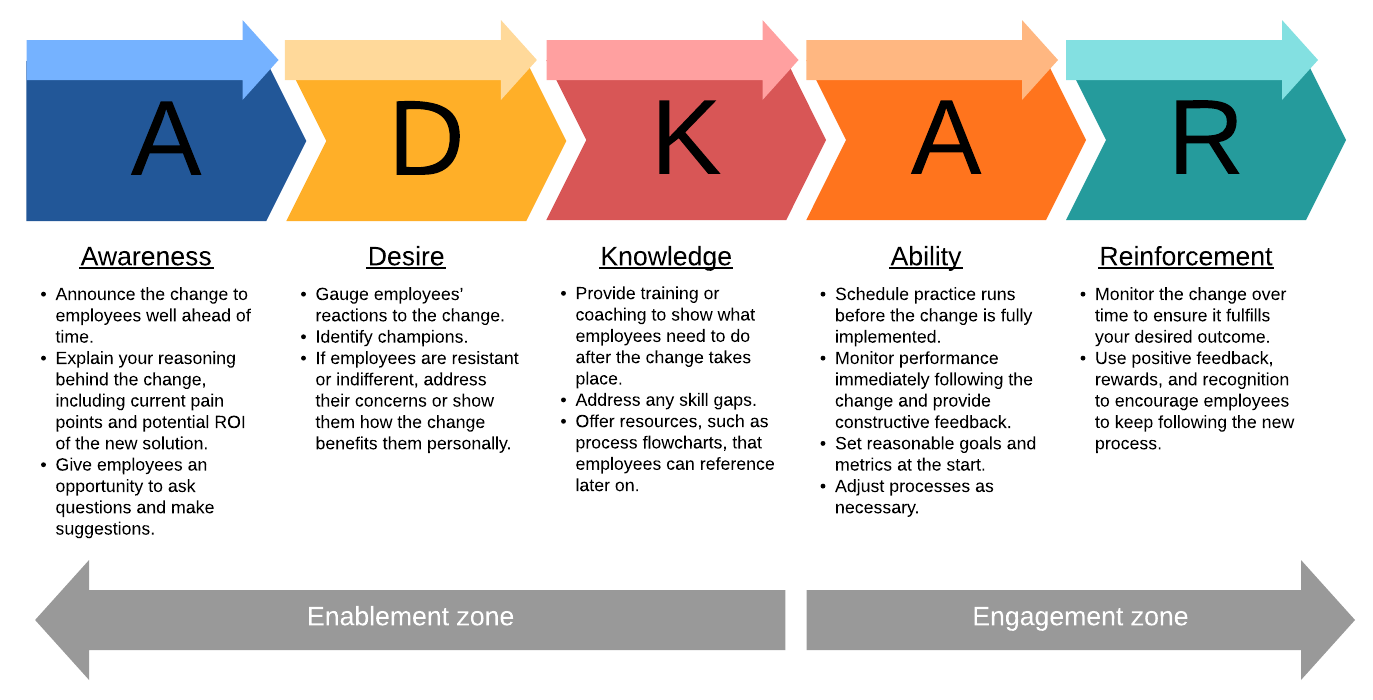
Lastly, measuring individual progress using the ADKAR model is a powerful tool for evaluating the adoption and utilization of change. The framework consists of five constituents of awareness of the needed change, desire to participate and support growth, knowledge on how to change, ability to implement required skills and behavior, and reinforcement to sustain change (The People Side of Change, 2020). These blocks effectively determine whether the implemented change was a success or not based on individual transitions, identifying barriers for transformation.
Conclusion
Effective leadership consists of various crucial constituents that require thorough training to sufficiently lead the organization to success. Organizational change is an inevitable part of corporate development, as the market is continually altering, demanding the implementation of innovations. Various change models are available for the managers to effectively incorporate the transformation among the employees. Moreover, the participation of the stakeholders is another vital factor that ensures the success of the initiatives. Incorporating organizational change into the company is challenging at most times; however, with the knowledge of managers’ availability and application of effective strategies, each organization can achieve its goals.
References
Aarons, G. A., Ehrhart, M. G., Farahnak, L. R., & Hurlburt, M. S. (2015). Leadership and organizational change for implementation (LOCI): A randomized mixed method pilot study of a leadership and organization development intervention for evidence-based practice implementation. Implementation Science, 10(1). Web.
ADKAR Model. (2020). Cloudfront. Web.
Al Rahbi, D., Khalid, K., & Khan, M. (2017). The effects of leadership styles on team motivation. Academy of Strategic Management Journal, 16(2).
Ali Taha, V., Sirkova, M., & Ferencova, M. (2016). The impact of organizational culture on creativity and innovation. Polish Journal of Management Studies, 14(1), 7–17. Web.
Alsher, P. (2012). How do you measure transformational change success? Imaworldwide. Web.
APQC. (2014). APQC research identifies communication, accountability as best practices to achieve transformational change. APQC. Web.
Blagescu, M., De, L., Casas, L., & Lloyd, R. (n.d.). Pathways to accountability: A short guide to the gap framework. 2020, Web.
Borkowski, N. (2016). Organizational behavior in health care. Jones & Bartlett Learning.
Brisson‐Banks, C. V. (2010). Managing change and transitions: A comparison of different models and their commonalities. Library Management, 31(4/5), 241–252. Web.
Chebbi, H., Yahiaoui, D., Sellami, M., Papasolomou, I., & Melanthiou, Y. (2019). Focusing on internal stakeholders to enable the implementation of organizational change towards corporate entrepreneurship: A case study from France. Journal of Business Research. Web.
Gil, A. J., Garcia-Alcaraz, J. L., & Mataveli, M. (2015). The training demand in organizational changes processes in the Spanish wine sector. European Journal of Training and Development, 39(4), 315–331. Web.
Goman, C. K. (2016). 10 change-management strategies that are backed by science. Forbes. Web.
Kotter, J. (n.d.). The 8-step process for leading change – Kotter. Kotter. Web.
Kotter’s 8-step Change Model. (n.d.). In Edinburgh Napier University. Web.
Landry, L. (2018). The importance of creativity in business. Northeastern University Graduate Programs. Web.
National Center for Healthcare Leadership. (2006). Healthcare leadership competency model. Web.
Neill, M. S. (2018). Change management communication: Barriers, strategies & messaging. Public Relations Journal, 12(1).
Özbağ, G. K. (2016). The role of personality in leadership: five factor personality traits and ethical leadership. Procedia – Social and Behavioral Sciences, 235, 235–242. Web.
Rimon, G. (2017). Six surprising truths about how digital transformation will change HR. Strategic HR Review, 16(2), 102–104. Web.
SHRM. (2019). The formula for assessing organization change success. HRPS Blog. Web.
SHRM. (2020). Careers. SHRM. Web.
Tang, K. N. (2019). Leadership and change management. In Leadership and Change Management (pp. 47–55). Springer Singapore.
The People Side of Change. (2020). What is ADKAR – the people side of change. Tpsoc.
The Society of Human Resource Management. (2019). About SHRM. Society of Human Resource Management. Web.
Voehl, F., Harrington, H. J., & Voehl, C. F. (2015). Model for sustainable change. PMI White Papers. Web.
Weatherston, A. (n.d.). Engaging all stakeholders in strategies for organizational change. Hni. Web.
Westover, J. H. (2020). Council post: The role of systems thinking in organizational change and development. Forbes. Web.
Zakeer, A., Khan, A., & Nawaz, I. (2016). Leadership theories and styles: A literature review. ISSN. An International Peer-Reviewed Journal, 16. Web.
Zurcher, K. A., Jensen, J., & Mansfield, A. (2018). Using a systems approach to achieve impact and sustain results. Health Promotion Practice, 19, 15S-23S. Web.

