Executive Summary
Country Road Limited is an Australian company, which has now limited its operation within the Australian continent. It had a long-lasting reputation to offer high-quality apparel and clothes at a lower price in the Australian continent as well as in the overseas markets. However, various threats and vulnerabilities persuaded the company to exit from the international operation. This text will discuss the accounting, financial and prospective analysis. This part of the accounting analysis expresses the accounting policies of the company. The financial analysis will present the ratio analysis and the cash flow analysis. The prospective analysis will involve forecasting the prospects using the weighted average cost of capital method and valuation using various methods.
Accounting, Financial, & Prospective Analysis
CRL’s accounting, financial and prospective analysis is presenting a true and fair view of all material aspects of financial condition and operational results according to standards of the company. The purpose of these analyses is to focus on financial conditions and requirements of financial instruments in the future.
Accounting Analysis
Accounting analysis provides financial information of any company and its related parties about:
- The manner of doing business by the company;
- The way of business is placed in a current and uncertain situation of the environment.
- The prospects of future business and company (GDSIL, 2005)
In proper accounting analysis of any company, five aspects should fulfill, which are:
It is maintaining these aspects for accounting analysis, which has discussed below in the context of the financial year 2008:
- Profitability: The profit-earning proposition is a long-term vision of the company, by offering outstanding value to customers and improving the market proposition. The net profit of Country Road Limited in 2008 is $9,759,000, which is lower than the profit of 2007 (Country Road, 2008).
- Efficiency: Efficiency has focused on the proper uses of resources, which have been maintained by applicable laws and regulations of financial information. In 2008, the owned equipment of CRL is $33,224,000, with investments of $54,801,000 in sales and other services of the company.
- Liquidity: Country Road is keeping cash and its equivalents in 2008, which is $21,114,000 to be ready for immediate uses of the company.
- Stability: In long-term issues, Country Road has used $11,189,000 in 2008, but it also can repay long-term liabilities it has sufficient cash and other resources.
- Return on Investment: In recent years, it has invested $429,000, to generate more returns on them, which focuses on the revenues of the company.
Accounting Strategy
There are various strategies followed by Country Road, one of the major strategies is the remuneration strategy, which pays for performance by positions in the market and base of pay for labors. The board of directors is also following corporate strategies to make proper decisions on accounting analysis.
Financial Analysis
Liquidity Analysis Ratio
The liquidity ratio shows the relationship of Country Road’s cash and other current assets to its current liabilities (Besely et al, 2007).
Current Ratio
By this, the portion of current liabilities are covered by current assets is considered.

Assumption: By these ratios, it can be found that, in 2008, the ratio stands at 1.44 times, and in 2007, it was 1.51 times. That is, the liabilities have increased.
Quick Ratio
This ratio is indicating the variation of the current ratio, which is, how quickly assets are covered by current liabilities.
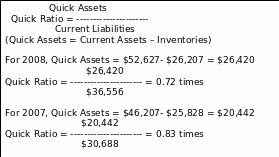
Assumption: The standard of the quick ratio is one time. However, in the current year, the quick ratio is not standing one. Therefore, the quick ratio is not appropriate.
Net Working Capital Ratio
The working capital or assets in the hand of the country road are measured compared with total assets.
Net Working Capital = Current Assets – Current Liabilities
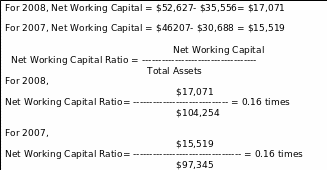
Assumption: Here, Networking capital ratios of both years are under 0.50, but the standard is it. Therefore, the company has to improve the Net Working Capital Ratio.
Profitability Analysis Ratios
These ratios are showing the effect of liquidity, asset management, and debt management on the operating results of the Company.
Return on Assets (ROA)
Return on Assets provides an idea of an overall return on investment earned by the company.
Return on Assets (ROA) = Net Income/Total Assets
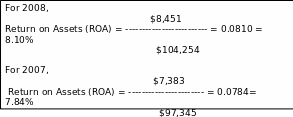
Assumption: As in these two years, ROA in similar states, which indicates that Country Road is using average debt considering assets.
Return on Equity (ROE)
ROE has measured the rate of return on common shareholders’ investments in the Company.
Return on Equity (ROE) = Net Income/Stockholders’ Equity
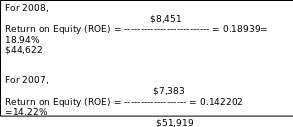
Assumption: The Company is using less debt in these two years, but using net income to the common shareholders’ equity in these moderate ROE is good for the company.
Activity Analysis Ratios
These ratios are measuring the effectiveness of managing assets of the Company.
Assets Turnover Ratio
This ratio has measured the effectiveness of using assets to help generate sales of the Company.
Assets Turnover Ratio = Revenue/ Total Assets

Assumption: The effectiveness of asset turnover is decreasing every period, shown by measuring the ratios of 2008 and 2007.
Inventory Turnover Ratio
By this ratio, the inventory has been measured in terms of stocked or sold out, considering the times of the ratio.
Inventory Turnover Ratio = Operating Expenses/Inventories
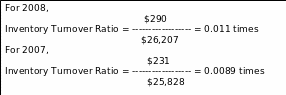
Assumption: By these ratios, it has been estimated that the inventories are larger in number in terms of operating expenses.
Capital Structure Analysis Ratios
These ratios are indicating the capital management of shareholders in terms of liabilities and interests of the Company.
Debt to Equity Ratio
This ratio is indicating the portion of debt can meet up with the help of Shareholders’ equity of the Company.
Debt to Equity Ratio = Total Liabilities/Total Stockholders’ Equity
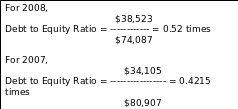
Assumption: To cover the liabilities with shareholders’ equity Country Road must finance from other sources or issue new shares in the current year.
Capital Market Analysis Ratios
These ratios are helping to analyze the market conditions of capital according to the price of a stock, book value of the stock, dividend, and dividend payout by the Company.
Dividend Payout Ratio
The effectiveness of paying the dividend of shareholders with the help of Net Income has been measured by this ratio.
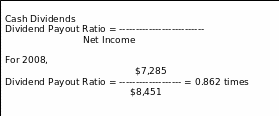
Assumption: In 2008, the dividend payout ratio is constant, but the portions of ratios are not effective to meet the dividend with Net Income. In 2007, the dividend is not paid.
Cash Flow Analysis
Cash flow analysis is the movements of cash inflows and outflows for determining the solvency of any business. In this analysis, the components, which are affecting cash flows, examine for an easy way to identify problems and to improve cash flows (Teegerstrom 2005). It is also prepared for comparing total unpaid purchases and total sales every month. If the sales are lower than unpaid purchases, then it is a potential problem in cash flow analysis. For Country Road Limited, cash flow statements of 2008 & 2007 have shown below: (Country Road. 2008)
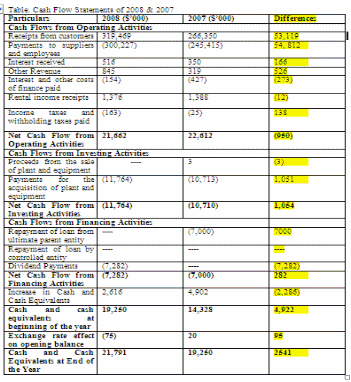
From this table, it is shown that Country Road Limited is used more cash and cash equivalents in operating activities in 2008, which is larger than $53,119,000 in the previous year. This paper has focused that the organization is much efficient to operate the services with existing equipment of operations.
The cash used in investing activities has also increased in the recent period, by $1,054,000 than in 2007. From this, it is shown that the company is concentrating on the uses of its assets rather than investments in new capital or equipment of the organization.
The organization is generating income from financing activities, which was decided by the positivism of the amount in 2008.
At beginning of 2008, cash and its equivalents are $19,250,000, which increase to $21,791,000 at end of the year. It has shown that Country Road can keep cash resources on hand more than $2,541,000 in 2007.
Prospective Analysis
Forecasting
Forecasting is necessary to know about the future estimation of revenues in the organization. Future estimation is justified if the company is calculating revenues compared with the previous period of operations. The forecast of Country Road Limited can be focused with the help of revenue growth and asset growth of the financial year 2008, which has shown below: (Country Road. 2008)
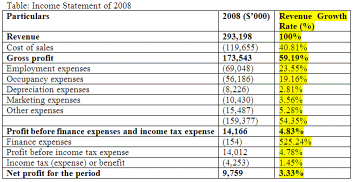
Revenue Growth Rate= (Cost of Sales/ Revenue) × 100
= (119,655/293,198) × 100
= 0.4081
=40.81%
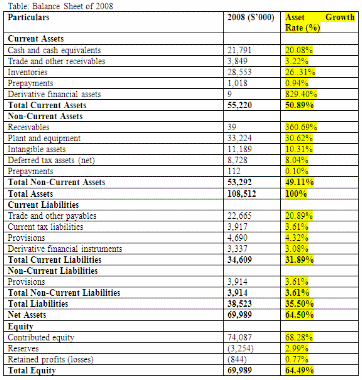
Asset Growth Rate= (Amount of any Particular/ Total Assets) × 100
= (21,791/ 108,512) × 100
= 0.2008
=20.08%
In forecasting analysis, the growth rate is lower in earnings before finance expenses and interest expenses with 4.83%. This growth rate is shown that the profit generation abilities of Country Road are reduced than the 2008 financial year, because of the great recession in the US market and the effects of it on other global markets worldwide.
On the other hand, there are similarities between the total current and total noncurrent assets in 2008, which is the significant potentiality of the company. In addition, net assets, total equity, total current assets, and total assets are increased, which is focusing that, the organization has control over these factors in the 2008 financial year.
WACC
According to Pandey (2007) when all categories of capital of a company is calculated on a weighted basis proportionately, like, common stock, preferred stock, bonds and long term debt is known as WACC (Weighted Average Cost of Capital). The equation will more clarify the definition, which is:
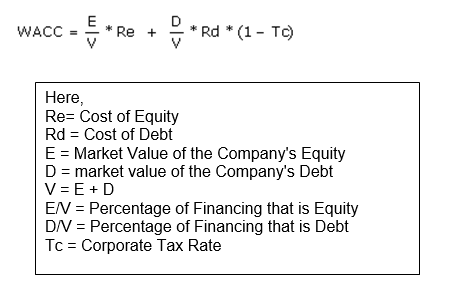
For Country Road, WACC is calculated in below: (Country Road. 2008)
Total Value of Country Road, V= $108,512,000
E = $69,989,000
D = $ 38,523,000
E/V = $69,989,000/ 108,512,000
= 0.6449
=64.49%
D/V = $38,523,000/ 108,512,000
= 0.3550
=35.50%
Re= 0.1422 (ROE)
Rd = 0.22
Tc = 30%
Cost of Debt = Revenue/Total Debt
= $8,451,000/$38,523,000 = 0.2193 (Country Road. 2008)
Therefore, WACC of Country Road is:
= (0.64 × 0.14) + 0.35 × 0.22 (1-0.30)
= 0.0896+ 0.0539
= 0.1435
= 14.35%
WACC represents a straightforward interpretation of the company with an overall return of the company for earning with existing assets to maintain the values of its stock. It also measures the required return for any kind of investments by the company, which are essential risks and operations (Rose et al, 2008).
Valuation
There are main four models, which is the best approach to describe the valuation of CRL, which are:
Discounted Abnormal Earning Model
When the rate of return of book value is equal to costs of equity, then investors are being disappointed in the organization. For this reason, any organization has to pay less in the cost of equity rather than the book value of the rate of return (Globusz 2009). The difference between these two terms has called “Abnormal Earnings”. The way of calculating discounted abnormal earnings model has given below:

Discounted Abnormal Earning Model of Country Road in 2008= 35.41- 14.22 = $21.19
Therefore, from this model, it could see that company has abnormal earnings compared with costs of equity and rate of return. However, it is under control, because, the costs of equity are less than the rate of return.
Dividend Discounted Model
It is a financial model, which is calculating the values of shares at discount rates according to future dividend payments (Anon 2009). The model of dividend discounting is:

However, a real situation is different from it, which is only $25.59 in the financial year of 2008, which means, the market of shares is not attractive to investors.
Discounted Operating Abnormal Earning Model
In the previous part, the abnormal earnings of Country Road have been revealed. However, for forecasting, the final term of the present value of book value will calculate under assumptions of long-term growth is being less than the cost of equity (Brigham & Houseton 2004). Considering the two-period dividend model, the discounted operating abnormal model will calculate: (Country Road. 2008)

Discounted Cash Flow Model
When the valuation of the company is being important, then cash flow analysis is done for making judgments about organizational performances (McClure, 2009). Discounted cash flows are analyzed with current value and estimation of future cash flows.
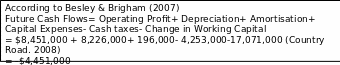
Assuming that, for great recession, market inflation will be 20% in next 10 years in UK market, so, DCF of Country Road is,

Therefore, this discounted cash flow is estimating that Country Road has fewer cash pay abilities in the future forecast, which is removing the opportunity of market potentials in present.
Comparison of Valuation to Market Value
The current market price of the stock of Country Road is $3.24, this valuation model has demonstrated that Country Road will lose its market capital payable abilities, but earnings of shares will increase in the abnormal model by $17.61 (Investment Mart 2009).
Recommendation
By the accounting, financial and prospective analysis, it is focused that, Country Road Limited can use these models and measurements to measure the future to forecast in the odd market situation, like great recession in US market, high competition in apparel industries, etc. So, Country Road should analyze these for seeing future capabilities and lacking the organization in terms of price of stocks, profits, cash flows, and many more.
References List
Anon. 2009. Dividend Discount Model. Web.
Anon. 2009. Discounted Cash Flows- DCF. Web.
Besley, S. & Brigham, F. E., 2007. Essentials of Managerial Finance. 13th ed. Thomson South- Western.
Brigham, E. F., & Houseton, J. F. 2004. Fundamentals of Financial Management. 10th Edition, Singapore: Thomson south-western.
Investment Mart. 2009. Country Road Limited (CTY). Web.
GDSIL, 2005. Book Reviews of Second Edition of Accounting & Analysis-The Indian Experience. Web.
Globusz, 2009. Valuation Based on Discounted Abnormal Earnings: An “Accounting Approach to Valuation”. Web.
Hitchner, R. J. 2002. Financial Valuation: Applications and Models. 2nd ed. John Wiley and Sons.
McClure, B., 2009. Taking Stock of Discounted Cash Flow. Web.
Pandey, I. M. 2007. Financial Management. 9th Edition, Vikas publishing house PVT LTD, New Delhi.
Teegerstrom, T. 2005. Cash Flow Analysis Worksheets. Web.

