Introduction
Macroeconomics
This is a branch of economics that deals with the aggregate factors in the economy, it entails factors such as unemployment, inflation, foreign exchange, and investment unlike microeconomics which deals with is mostly involved in setting prices for the scarce resources. Macroeconomics tries to explain the reasons for the current GDP whereas explains the long term GDP
Major macroeconomic indicators
Real GDP
The real GDP of a country is the gross domestic product that has been adjusted for the rate of inflation given the current rate of employment in existence. The gross domestic product of a country is one of the most comprehensive measures of a country’s economic output since it measures all market and non-market goods and services produced within a country.
In our discussion we will consider the UK to analyze the current trends of the performance of the countries economy, for the real GDP levels the graph below was retrieved from the official UK statistic website available at www.statistics.gov.uk
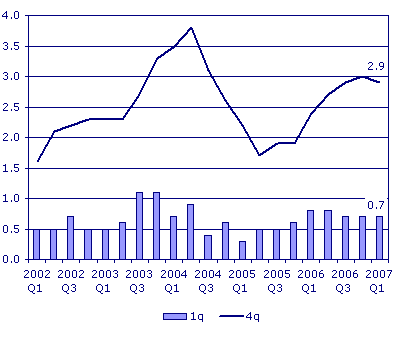
The real GDP of the UK rose by an average of 0.7% in the first three months of 2007; this marked a steady increase in the level of GDP compared to the previous two years although it was less than 2003 and 2004 levels of GDP. The GDP growth rate has been different between different sectors of the economy, for example, the growth rate in the finance and business sector increased relatively higher than the other sectors of the economy.
Since 2002 the GDP rose steadily from 2002 to 2003 where it reached its peak in 2003 before taking a slight decline to mid-2005 where it steadily started to rise against to date, therefore the year 2003 had the highest real GDP growth rate.
Unemployment
Unemployment refers to the extent of the number of people who are jobless in an economy; unemployment is calculated by dividing the number of people who are unemployed by the number of people who are termed as the workforce in a country.
Unemployment can also mean a condition in which an economy has idle resources that are not being utilized, labor is a factor of production and if a country does not utilize this labor to the fullest then we have unemployment of labor which is a factor of production.
Unemployment however can be termed as a state in which an individual is looking for a job but not getting one, however, unemployment does not include students, retired people, or even children.
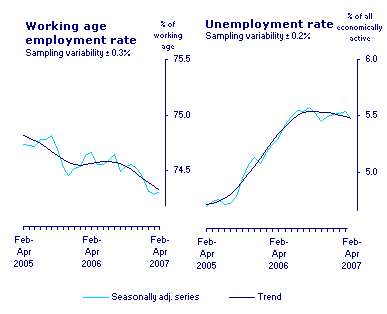
The above diagram represents the rates of unemployment for the UK from the year 2002 to 2007; it also displays the employment rate.
From the above graph, the employment rate has been decreasing while the unemployment rate has been increasing, however, over the last year, the rate of unemployment has been almost constant.
Regardless of the fact that the unemployment has been almost steady we can still claim that some people were self-employed but to the statistics they are unemployed, some people may not claim unemployment benefits and therefore this does not mean that they are employed.
Therefore from our above graph from the UK statistics Website, there has been a decline in the level of employment and also an increase in the level of unemployment.
Current account balances
The current account balance is a section of the balance of payment accounts that gives a net balance of trade, that s exports minus import of goods and services within an economy. It also incorporates factor incomes such as interest or dividends of assets owned abroad or overseas. It also factors in transfer payments such as grants, loans, and foreign aid. A current account surplus increases a nation’s net foreign asset while a current account deficit decreases the net foreign assets.
Over the last decade, UL statistics indicate that the country has experienced current account deficits. There are many explanations as to why this has occurred, but the main reason for the increasing current account deficit is due to an increasing deficit in tradable goods balances, this has been a result of increased imports over exports in almost all sectors of the economy.
Fiscal indicators
The ratio of gross fiscal deficit to GDP:
The ratio of gross fiscal deficit to GDP of the UK economy has increased over the last five years; fiscal deficits have been increasing in relation to GDP as a result of increased public borrowing in the UK, the fiscal debt had increased from 504 billion in 2006 May this year from 499 billion the previous ear the same period of time. Since the year 2001 to date, this ratio was lowest at the end of 2003, but since then, the ratio has been rising leading to an increase in allocation of the public current budget. It’s noted in the UK history that this ratio of gross fiscal deficit was highest in 1997 when it reached 44%, the highest since the 1980s.
Levels of government expenditures to GDP
Ratio of domestic debt to GDP
This ratio indicates the ability of the country to pay what it owes the other countries this is because it compares what a country produces and what it does owe. it helps a country to plan on how it will pay future its debts, otherwise the higher the ratio, the higher the probability of the firm country being unable to pay these debts
The UK levels of government expenditure to GDP has been rising during the last five years, this has been as a result of the Maastricht treaty concerning the deficiencies in the EU.
Monetary indicators
Rate of growth of money supply
The money supply is the amount of quantity of currency held by banks and not by the public. This affects the rate of inflation because it’s directly linked to the money exchange equation. Money in the economy in the UK is termed as either money in the bank of England MO or cash outside banks M4. In the UK the money supply growth is always higher than the rate of growth of real GDP, therefore, resulting to inflation is always
Rate of interest
Interest rate is the return on capital or investment. The real interest rate is calculated as the nominal interest rate minus the inflation rate. Some people use the rule of 78 in the calculation of interest rate however the rate of interest rate must take into account the opportunity cost, inflation, time value of money, and deferred consumption. The interest rate in the UK is classified into three categories with each one having a different rate of return, despite this factor the rate of returns has been oscillating between 2-5 percent between April 2005 to April 2006. This has been caused by changes in the structural private sector
Rate of inflation
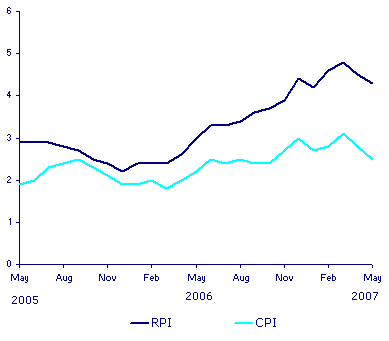
Inflation is the general rise in the price level of all the products in the economy. in a situation where the rate of inflation is high, investors use the real interest rate to charge loans. Inflation in the UK has always been increasing. There was a general decrease in the inflation between December and February in the year 2005 and 2006respectivelythiks this was due to the consumer in the price index of the gas and electric bill, this was accelerated further by the pressure from the food industry and the clothes industries that dropped their prices. The, highest increase in inflation occurred in February in 2007 due to the increase in the cost of air transport. The rate of inflation for the UK is always higher than other EU countries for example in April 2007; the provisional rate for the UK was 2.8%whreas for other EU countries was 2.2%. The figure below shows the rate of inflation.UK between 2005- 2007.
International indicators
Open-ness index
This is defined as imports plus exports as a ratio to GDP; this is a tool to measure the competitiveness of the economy globally which is very important because of the growing level of technology that comes along with opportunities and threats to the UK firm. Statistics have shown that the UK is becoming more competitive in the world and this is because of the huge budget allocation in science and development. The productivity gap between the UK and other developed countries has been declining over the last 5 years and this is indicated by the increased level of innovation, investment, skill competition, and enterprise which are the 5 tools increasing productivity. This ratio has been increasing due to these tools being employed.
Rate of growth of exports
The UK exports growth have been increasing since 2000 with export growth being highest in 2006 reaching 57.9 and has sustained the 50.0 no-change marks for 45 months this being associated with the good economic performance in the Eurozone. This has been coupled with the emergence of the single currency and the sentiments of the consumers
External debt to GDP ratio
External debt shows the total debt of a country owned by another country or firms or corporations. This ratio is determined by dividing the total external debt by the GDP. External debt can be defined in four ways; are loans that are not guaranteed, guaranteed loans, the money of the economy held by the IMF, and the money in the central bank. This ratio shows the burden which a country has, as in the case of the UK, this ratio is increasing due to the fact that there is a decrease in the GDP.
Level of foreign exchange reserves
This is the money in a central bank of a state which is in the form of currencies, gold, and money in foreign accounts owned by a country. A country having a bigger level of foreign exchange reserves has a higher potential to manipulate the money markets, more so, has a higher opportunity cost, a disadvantage to having a big foreign reserve is that it undergoes some fiscal cost hence depreciation.
Importance of crude in the imports or exports athe country
The United Kingdom like any other industrial nation is highly dependent on crude oil in its manufacturing section. Unfortunately, the UK cannot produce the required amount of crude oil in its manufacturing center, this means that it has to import crude oil from the international market at a price that is relatively close to the price set by oil-producing countries. This means that the United Kingdom is highly dependent on the vagaries of the international market in the crude oil sector
The major economic policy changes
Fiscal policies changes
The UK fiscal report prepared in 2006 follows the general structure of other fiscal plans prepared in the previous periods and follows the pre-budget report prepared in the year 2006. it entails a clearly defined framework of the decision made and development which is goal-oriented and sustainable in the UK which is projected both in the short run and long run. The objective of this plan is to ensure that there is a sound economy as it supports the monetary policy whilst guarantying proper usage of the government revenue which must be distributed to all the generations in the economy in the short run, but the long-run goal is to ensure stable economic growth and guarantying that community finances are properly managed and sustainable.
To make sure that there is generational equitability and sustainable fiscal policy, the government put in place two policies; these are a sustainable investment and law golden rules.
The sustainable investments rule is used as a guiding tool to control the public sector debt to the GDP ratio, it was set that the net public debt must always be below 40%of the gross domestic product during a financial year, while the golden law was maintained the United Kingdom Government would only borrow funds to fund for the investment purposes and not to fund the current government expenditure. The sustainable investments rule further stipulates that the current debt should not be exaggerated in a way that it will be pushed to the future generation for sustainability purposes and the golden rule demands that the existing government expenditure should be financed from the taxes collected
Economic prospects
The UK government needs to adopt a more contraction ally monetary policy. By adopting a contraction ally policy, the UK government through the bank of England will lower interest rates to boost investments. These investments should be mainly in the industrial sector and designed for export in order to bring down the current account balance deficit. Once the current account balance has been reduced or transformed to a current account surplus, the sterling p[pound will gain additional value against its major partners like the united states of china and this will help to maintain a moderate money supply within the economy to boost investment activities.
Conclusion
For a country to have a stable economy, it’s important that it maintains a low level of unemployment, low external debts, have high foreign reserves, high export volumes, low ratio of gross fiscal deficit to GDP, and low rate of inflation
References
- Inflation in the UK. Web.
- UK Productivity and Competitiveness Indicators 2006.
- The gross domestic product of UK. Web.
- The public sector of the United Kingdom. Web.
- John Cunningham Wood, Ronald N. Woods, 1989, critical assessment, Routledge publishers UK.
- Olivier Blanchard Jean, Macroeconomics Annual. 1991, mit publishers, UK. Web.
